Kin 312 Augmented Feedback
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:41 AM on 9/22/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
Feedback Definition
a generic term that describes information a person receives about the performance of a skill during or after the performance
2
New cards
2 Categories of Feedback
1. Task Intrinsic Feedback (sensory)
2. Augmented Feedback (task-extrinsic)
2. Augmented Feedback (task-extrinsic)
3
New cards
Task Intrinsic Feedback
-performance related sensory information that is naturally available to the performer
o visual
o tactile
o auditory
o proprioceptive (naturally available)
o visual
o tactile
o auditory
o proprioceptive (naturally available)
4
New cards
Augmented Feedback: Definition
-information the person receives about a performance from sources external to themself
-the information adds to or enhances the task-intrinsic information
-the information adds to or enhances the task-intrinsic information
5
New cards
2 Types of Augmented Feedback
1. Knowledge of Results (KR): performance related information about the outcome of the performance
2. Knowledge of Performance (KP): performance related information about the movement characteristics that led to the outcome of the performance
2. Knowledge of Performance (KP): performance related information about the movement characteristics that led to the outcome of the performance
6
New cards
How essential is augmented feedback for skill learning?
1) It can be essential for skill learning
2) It can hinder/slow skill learning
2) It can hinder/slow skill learning
7
New cards
3 Situations Where Augmented Feedback Can be Essential for Skill Learning
1) Critical task-intrinsic feedback is not available (obstructed view)
ex: big team, no individual attention
2) Person is not capable of detecting the critical task-intrinsic feedback
ex: injury
3) Person is not capable of interpreting the critical task-intrinsic feedback
ex: lack of experience
ex: big team, no individual attention
2) Person is not capable of detecting the critical task-intrinsic feedback
ex: injury
3) Person is not capable of interpreting the critical task-intrinsic feedback
ex: lack of experience
8
New cards
3 Situations Where Augmented Feedback Can Hinder/Slow Skill Learning
1) Erroneous (incorrect) KR or KP
2) Concurrent presentation of KP
3) KR or KP presented too frequently
2) Concurrent presentation of KP
3) KR or KP presented too frequently
9
New cards
2 Issues with Content of Augmented Feedback
1) Errors v. correct aspects of performance
2) KR v. KP
2) KR v. KP
10
New cards
Errors vs Correct Aspects of Performance
-Which type of information do we give the learner?
o Error-related information: action goal achievement role
o "Correct" : motivation role
o Combine both for needs of the learner
o Error-related information: action goal achievement role
o "Correct" : motivation role
o Combine both for needs of the learner
11
New cards
KR vs. KP
-both can provide valuable information
1.KR is especially beneficial to:
-confirm subjective assessment of task-intrinsic feedback
-determine performance outcome when task-intrinsic feedback is not available
-motivate the person to continue (ex: provide times for sprints; gives athlete a time they want to beat & therefore continue sprinting)
-establish a "discovery learning" practice strategy
2. KP is especially beneficial to:
-learn skills with specified movements--the outcome is assessed by movement characteristics (ex: gymnastics, diving)
-improve specific movements or correct specific movement errors
-learn to activate specific muscles
-facilitate learning when KR is redundant with task-intrinsic feedback (ex: "you missed the free throw" , "yeah no shit")
1.KR is especially beneficial to:
-confirm subjective assessment of task-intrinsic feedback
-determine performance outcome when task-intrinsic feedback is not available
-motivate the person to continue (ex: provide times for sprints; gives athlete a time they want to beat & therefore continue sprinting)
-establish a "discovery learning" practice strategy
2. KP is especially beneficial to:
-learn skills with specified movements--the outcome is assessed by movement characteristics (ex: gymnastics, diving)
-improve specific movements or correct specific movement errors
-learn to activate specific muscles
-facilitate learning when KR is redundant with task-intrinsic feedback (ex: "you missed the free throw" , "yeah no shit")
12
New cards
Types of KP
1) Descriptive KP: KP describes error
2) Prescriptive KP: KP describes error and prescribes how to correct it
-which one is better to facilitate skill learning?
o depends on the learner's stage of learning
-- initial stage of learning: prescriptive preferred
-- later stages of learning: descriptive preferred
2) Prescriptive KP: KP describes error and prescribes how to correct it
-which one is better to facilitate skill learning?
o depends on the learner's stage of learning
-- initial stage of learning: prescriptive preferred
-- later stages of learning: descriptive preferred
13
New cards
Video Replay
the use of videotape replay should relate to the stage of learning
-initial stage: provide attention-directing or error-correction cues
-later stages: some assistance may be needed, but attention-directing cues may help
-initial stage: provide attention-directing or error-correction cues
-later stages: some assistance may be needed, but attention-directing cues may help
14
New cards
The Timing of Augmented Feedback: Three Issues
1. Concurrent and terminal augmented feedback
2. Time intervals related to terminal augmented feedback
3. Frequency concerns
2. Time intervals related to terminal augmented feedback
3. Frequency concerns
15
New cards
Concurrent Augmented Feedback: Definition
augmented feedback available during the performance of a skill
16
New cards
Terminal Augmented Feedback: Definition
augmented feedback available after the performance of a skill
17
New cards
Research Based Conclusions: Concurrent Augmented Feedback
Concurrent augmented feedback can:
-facilitate the learning of skills in which critical task-intrinsic feedback is difficult to interpret
ex) learning to activate specific muscles
learning to produce a specific movement force
-Hinder or slow the learning of skills by leading to a dependency on the feedback
ex) performance poorer without the feedback than with it
-facilitate the learning of skills in which critical task-intrinsic feedback is difficult to interpret
ex) learning to activate specific muscles
learning to produce a specific movement force
-Hinder or slow the learning of skills by leading to a dependency on the feedback
ex) performance poorer without the feedback than with it
18
New cards
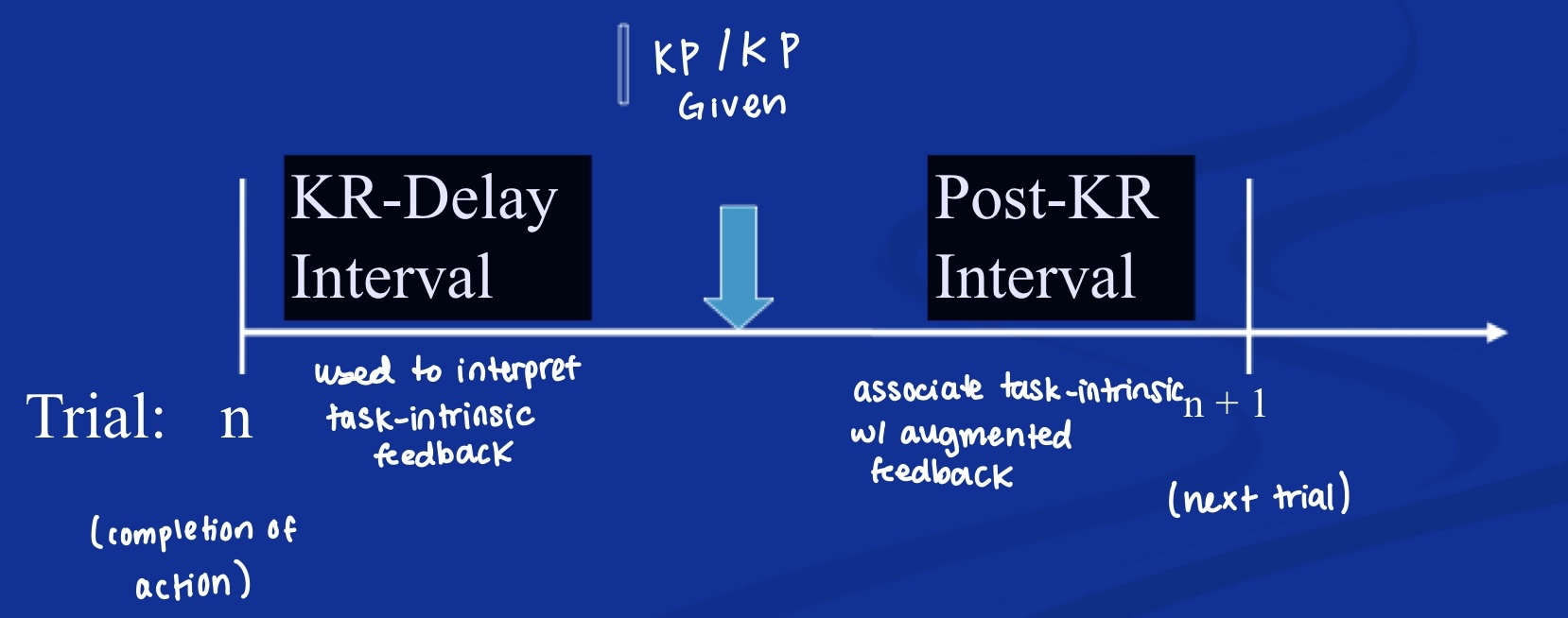
Time Intervals Related to Terminal Augmented Feedback
-KR-Delay Interval: used to interpret task-intrinsic feedback
-Post-KR Interval: associate task-intrinsic with augmented feedback
-Post-KR Interval: associate task-intrinsic with augmented feedback
19
New cards
Research Based Conclusions for the KR-Delay Interval and the Post-KR Interval
Interval Length: minimum length needed for augmented feedback to be effective; no evidence for maximum length
Activity during the interval:
\-most have no effect
\-some hinder learning (ex: similar learning processes required for both)
\-some beneficial for learning (KR-Delay Ex: subjective error estimation; Post-KR Ex: Problem solving activity)
Activity during the interval:
\-most have no effect
\-some hinder learning (ex: similar learning processes required for both)
\-some beneficial for learning (KR-Delay Ex: subjective error estimation; Post-KR Ex: Problem solving activity)
20
New cards
Frequency of Presenting Augmented Feedback
-Traditional view: augmented feedback for every trial (100% frequency) is best for learning
-Current view: less than 100% frequency is best for learning
*based on research that has investigated several types of techniques that reduce augmented feedback frequency
-Current view: less than 100% frequency is best for learning
*based on research that has investigated several types of techniques that reduce augmented feedback frequency
21
New cards
2 Reasons Less Than 100% Frequency of Augmented Feedback is Better for Learning
1. Increases problem solving activity:
\-less frequency allows person to actively use their own problem solving strategies
\-100% frequency directs problem solving activity from the instructor's point of view
\
2. Guidance Hypothesis:
\-beneficial performance effects of receiving augmented feedback on every practice trial become negative learning effects
\-Why? : augmented feedback becomes a "crutch" on which the learner depends to perform the skill
22
New cards
4 Techniques that Reduce Augmented Feedback Frequency
1) Fading Technique
2) Performance Bandwidth Technique
3) Learner Requested Feedback Technique
4) Summary Technique
2) Performance Bandwidth Technique
3) Learner Requested Feedback Technique
4) Summary Technique
23
New cards
Fading Technique
-first described in experiment by Winstein & Schmidt (1990)
-systematically reduced KR frequency from every trial to 2/8 trials
-"fading" technique led to better learning than receiving KR every trial
-systematically reduced KR frequency from every trial to 2/8 trials
-"fading" technique led to better learning than receiving KR every trial
24
New cards
Performance Bandwidth Technique
-leads to a less than 100% frequency
-results in better learning than KR/KP every trial
-results in better learning than KR/KP every trial
25
New cards
Learner Requested Feedback Technique
-KR/KP only given when learner requests it
-leads to a less than 100% frequency
-results in better learning than KR/KP every trial
-leads to a less than 100% frequency
-results in better learning than KR/KP every trial
26
New cards
Summary Technique
-KR/KP given for a set of trials (ex: every 5 trials)
-amount of KR/KP is same as 100% frequency, but given less frequently during a practice session
-results in better learning than KR/KP every trial
-amount of KR/KP is same as 100% frequency, but given less frequently during a practice session
-results in better learning than KR/KP every trial