GI E1- Disorders of the Large Intestine
1/58
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What are the functions of the large intestine?
compact intestinal contents & form feces, store feces prior to defecation, absorb water, elytes, & vitamins produced by bacteria
The large intestine is _______ than the small intestine
shorter & wider
What is the blind pouch inferior to the ileocecal sphincter?
cecum
where is the appendix attached?
medial posterior portion of cecum
What is anterior to the sacrum and coccyx and expandable to accommodate feces?
rectum
What is the terminal portion of the rectum?
anal canal
What refers to the presence of diverticula in an asymptomatic individual?
diverticulosis
What refers to the presence of diverticula associated with symptoms?
diverticulitis
what is the most common structural abnormality of the colon and the MCC of a lower GI bleed (95% in sigmoid colon)?
Diverticulosis
What is diverticulosis?
acquired saccular outpouchings of the colon from mucosa/submucosa herniating through weak areas of muscular propia (usually near where vasa recta penetrates)
What studies are done to diagnose diverticulosis?
plain abd films, contrast (barium) enema, abd CT, flex sig or colonoscopy
often discovered incidentally
What is diverticulitis?
inflammation of one or more diverticula; due to fecalith or infx from high intraluminal pressure & rupture
what develops in 5-10% of pts w/ diverticulosis?
diverticular hemorrhage (typically massive but self limiting)
Diverticular bleed/hemorrhage is the MCC of ______
massive lower GI bleed
What condition presents with the following symptoms?
acute LLQ persistent abd pain/tenderness (MC)
loose bowel movements or constipation
N, V, cramping, leukocytosis, +/- fever
possible urinary sx from irritation of bladder from sigmoid colon
diverticulitis
What is relatively contraindicated in diverticulitis due to risk of perforation?
colonoscopy
Diverticulitis patients should undergo a colonoscopy after they are healed due to ________
increased risk of colon cancer
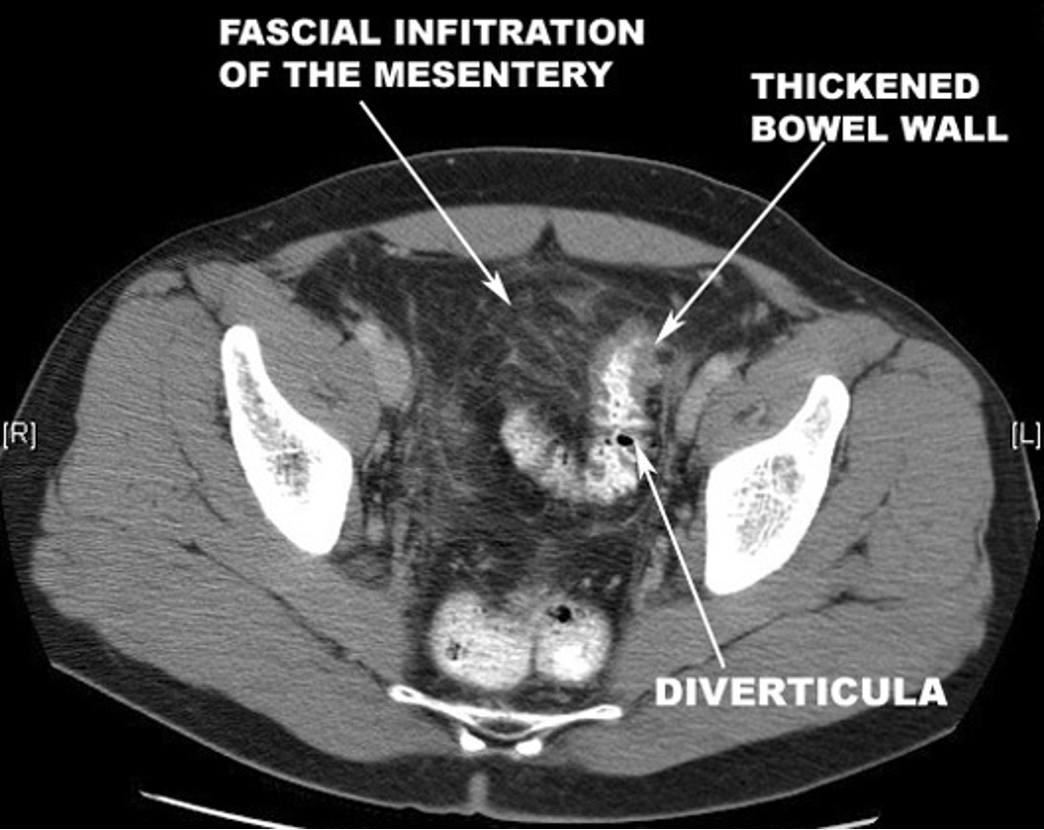
How would diverticulitis appear on an abdominal CT?
stranding, fatty infiltration, streaking, “dirty fat”, phlegmon, “mural thickening of the colon w/ pericolic fat stranding”
What is the treatment for diverticulitis?
abx: cipro & falgyl or augmentin
clear liquid diet (bowel rest)
surgical resection
what are the 3 main branches of the abdominal aorta?
celiac artery, superior mesenteric artery (SMA), inferior mesenteric artery (IMA)
What condition?
inadequate delivery of O2 & nutrients due to occlusion, vasospasm, or hypoperfusion
medical & surgical emergency
injury ranges from reversible to transmural bowel necrosis
reperfusion can aggravate injury
intestinal ischemia
Why must intestinal ischemia be corrected quickly?
persistent vasoconstriction will cause progression of injury despite it’s initial relief measures
what condition?
medical & surgical emergency in small bowel
risk: afib, recent MI, valvular heart dz, recent cardiac or vascular cath
sudden onset abd pain out of proportion, N/V/D, bloody stools, guarding, rebound tenderness
acute mesenteric ischemia
what is the most prevalent GI complication from CV surgery?
ischemic colitis
What is the gold standard for acute mesenteric ischemia?
mesenteric angiography
what is the workup for acute mesenteric ischemia?
mesenteric angiography, xray, CT, colonoscopy if ischemic colitis suspected, laporotomy in emergent situations
What is the treatment for acute mesenteric ischemia?
aggressive fluid resuscitation
anticoagulants & broad spectrum abx
surgery - embolectomy, laparotomy, resection
vasodilator to relieve vasoconstriction asap (papvarine)
What should you think of with an elderly patient presenting with an acute abdomen OR if abdominal pain is disproportionate to PE findings?
mesenteric ischemia
What condition?
chronic (> 3 mos) functional disorder
late teens - 20s; F > M
chronic abd pain or discomfort associated with altered bowel habits; sx NOT explained by structural or biochemical abnormalities (idiopathic)
episodic or constant
discomfort frequently relieved by defecation
irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
What are the 4 categories of IBS?
IBS-D: diarrhea; > 3 daily episodes of loose water stool; urgency or fecal incontinence
IBS-C: constipation; < 3 weekly episodes of hard or lumpy stools; straining
IBS-M: mixed diarrhea & constipation
IBS-A: alternating diarrhea & constipation
what condition?
intermittent, crampy lower abd pain that usually does NOT occur at night or wake pt up
abnormal stool passage: straining, urgency, feeling of incomplete evacuation, mucous
bloating or distension
> 3 mos duration (continuous or intermittent) w/ atleast 1 episode per wk
+/-: dyspepsia, fatigue, depression, anxiety
normal PE besides mild tenderness
IBS
What are the alarm symptoms that suggest a diagnosis other than IBS?
> 50 y/o
progressive abd pain
severe constipation or diarrhea; nocturnal diarrhea
hematochezia
unintentional weight loss
fever
fhx cancer, IBD, celiac dz
What is the Rome IV criteria that allows a diagnosis of IBS?
recurrent abd pain atleast once a week for the last 3 mos assoc w/ 2 or more of the following
related to defecation
change in stool frequency
change in stool form or appearance
What is the manning criteria for the diagnosis of IBS?
pain relieved w/ defecation, more frequent stools at onset of pain, looser stools at onset of pain, visible abd distension, passage of mucus, sensation of incomplete evacuation
What does IBS treatment focus on?
coping with symptoms (no cure)
What is the non-pharm management for IBS?
diet therapy, r/o lactose intolerance, low - fodmap diet, CBT, psych eval
What are pharmacological treatment options for IBS?
anticholinergic (antispasmodic) agents- levin, bentyl
probiotics- bifidobacterium infantis
xifaxan (rifaximin)
antidiarrheal agents- loperamide, cholestyramine
constipation- osmotic laxatives, lubiprostone
psychotropic agents- TCAs, SSRIs
Which osmotic laxatives should to be used for IBS due to increased flatus and distention?
lactulose or sorbitol
Does abx-associated diarrhea require a lab eval or rx?
no (resolves spontaneously after discontinuation)
What drugs are common causes of abx associated diarrhea?
ampicillin, clindamycin, 3rd gen cephalosporins, FQs
what is a spore forming, toxin producing, gram positive bacteria that is one of the most common health care associated infections?
c diff
what are risk factors for abx associated colitis?
hospilitzation, nursing home, abx use, advanced age, gastric acid suppression
what are sx of abx associated colitis?
profuse watery foul smelling diarrhea → can progress to fulminant colitis and lead to toxic megacolon
what is the tx for abx associated colitis?
PO vanco or fidaxomicin
alt: falgyl
how can abx associated diarrhea be prevented?
probiotics: lactobacillus, bifidobacterium, streptococcus thermophiles, saccharomyces
How long do probiotics last in the GI tract?
no longer than 2 weeks (regular consumption is necessary)
What is the 3rd MC diagnosed cancer in males and 2nd MC in females worldwide?
colorectal cancer
how long does the transition from adenoma to cancer take?
~10 years
Which can progress to cancer, hyperplastic polyps or flat polyps?
flat polyps
what are risk factors for CRC?
genetics & environment
IBD
abd radiation
> 50
smoking / alcohol
African American; M > F
FAP, Lynch syndrome, obesity, red meat, etc
what is the most common symptom of CRC?
change in bowel habits + blood in stool
Change in bowel habits is more likely to be seen in which tumor location of CRC?
left sided CRC
Rectal cancer can lead to ____
blood in stool and pencil like stools
What is more likely associated with right sided colon caner?
IDA
what is the best test for colon cancer?
colonoscopy
How is CRC staged?
TNM
When should colonoscopy screening for colon cancer begin?
average risk: start at 45
Fhx: start at 40 or 10 yrs prior to relative’s age at dx
repeat every 10 years
What is the treatment for CRC?
localized → surgical resection
poor prognosis with metastasized
What are the MC metastatic sites of CRC?
liver, lung, lymph nodes, peritoneum