ap chem unit 3
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
UV or visible light
causes electrons to transition to different energy levels
infrared radiation
causes molecules to vibrate
microwave ratiation
causes molecules to rotate
c=λν
speed of light = wavelength*frequency
E=hν
energy of a single photon = Planck’s constant*frequency
Beer-Lambert Law
A = εbc (Absorbance = molar absorptivity * path length * concentration of the solution
outlier that’s too high on a concentration v. absorbance graph
contamination from a solution of higher concentration
outlier that’s too low on a concentration v. absorbance graph
contamination from water or a solution of lower concentration
more electrons = more polarizable =
stronger LDF
hydrogen bonds
molecules with O-H, N-H, or F-H bonds only
stronger attraction =
higher boiling and melting point
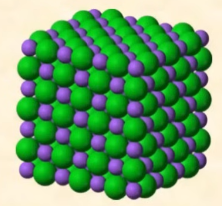
ionic solids
high melting point, brittle, conduct electricity when dissolved in water
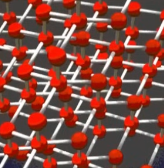
covalent network solids
highest melting point, extremely high hardness, strongest covalent forces
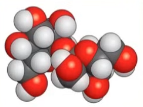
molecular solids
low melting point, weak intermolecular forces
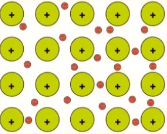
metallic solids
sea of electrons, excellent conductivity, malleable and ductile
true solids
crystalline structure, vibrational motion
amorphous solids
noncrystalline, vibrational motion
temperature
average kinetic energy of molecules in a sample
ideal gas
no intermolecular attractions, molecules don’t take up space
gases close to ideal gases
very small molecules, He, H2, Ne; high temperature and low pressure
distillation
different components of a mixture boil at different temperatures
vapor pressure
