CAT scans, gamma cameras and PET scans
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
why are CAT scans better than x-rays?
CAT scans create 3D images but x-rays only do 2D ones, so CAT scans give a better idea of size, shape and position of tumour so easier to treat
CAT scans can also see cross-sections of tumour
CAT scans can differentiate between materials of similar densities and attenuation coefficicents but x-rays can’t
why are CAT scans not better than X-rays?
CAT scans are longer so patient receives more ionising radiation and will be more uncomfortable
CAT could damage their cells more because they receive several years of background radiation
patient has to stay still for a long period of time in CAT scans
what does CAT stand for?
computerised axial tomography
it records a large number of 2D x-ray images from different angles and assembles them into a 3D image using software or something
the computer controls the scanning process and analysis of electrical signals
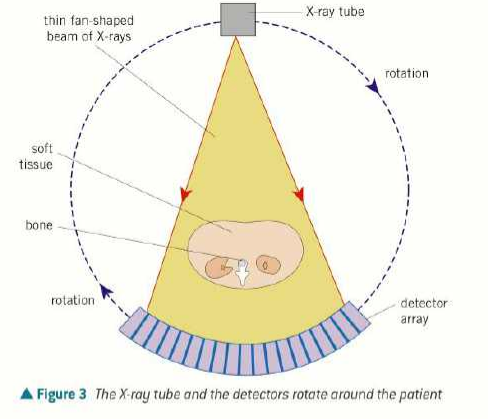
how does a CAT scan work?
patient lies on back in a horizontal table that can slide in/out of gantry
gantry has x-ray tube on one side and an array of electronic x-ray detectors on opposite side (both rotate)
the x-ray tube produces a fan-shaped beam of x-rays 1-10mm thick
the detectors record the intensity of the transmitted x-rays and send electrical signals to a computer
every time 360 rotation, a two-d image or slice is acquired and the table moves 1cm through the ring, then the beam irradiates the next slice of the patients body
radiographer can view each 2D slice and make a 3D image
what is the purpose of a gamma camera?
detects gamma radiation (high energy photons) emitted by tracers and turns it into an image
shows the function and processes of the body instead of just anatomy
can scan brain/lungs/liver etc
can also kill tumour cells when it is emitted from multiple sources and concentrated on a target
minimises damage to healthy cells and max damage to tumour
what factors are taken into account when choosing a tracer?
whether the tracer is going to travel through the digestive system or circulate in blood
can be drunk/eaten/breathed in
if a certain tissue needs to be targeted, radioisotopes can be combined with other elements to achieve specificity
should have a short half life to minimise the amount of radiation that the patient receives
must be gamma emitter because gamma is weakly ionising and can travel through bones to the detectors
facts about fluorine-18 or something
is used in PET scans
has a short half life and has to be produced on site in hospital using particle accelerator
110 min half life
beta plus decay
decays into oxygen-18 nucleus, positron, neutrino and gamma photon
can be made by high-speed protons colliding with oxygen-18 nuclei
who or what is technetium-99m?
the m means metastable apparently (it stays in a high energy state for a long period)
has a 6 hour half life
instead of storing technetium, hospitals store molybdenum-99 because it decays into technetium
beta minus decay
its photons have 140keV
can be combined with Na and O2 to make NaTcO4 which can target braincells
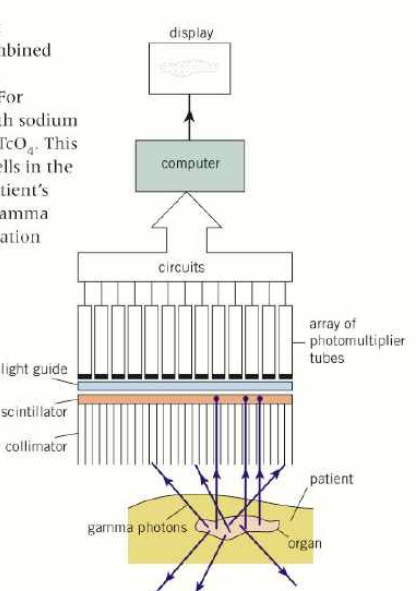
how does the gamma camera turn gamma photons into images?
photons travel towards collinator (honeycomb of long thin lead tubes)
collinator only lets gamma photons through along the axis of the tubes
the photons then reach the scintillator crystal (NaI)
when one gamma photon strikes the scintillator thousands of visible light photons are produced
10% of photon energy converted to light energy
visible light photons travel into photomultiplier tubes, in hexagonal pattern
for each light photon that hits the cathode, electron is released through photoelectric effect
electron is accelerated repeatedly towards anodes, releasing 2-4 electrons each time
repeats until electrical pulse formed, representing 1 pixel
software is used to process electrical signals and determine where the tracer decayed or something which produces a high quality image showing concentrations
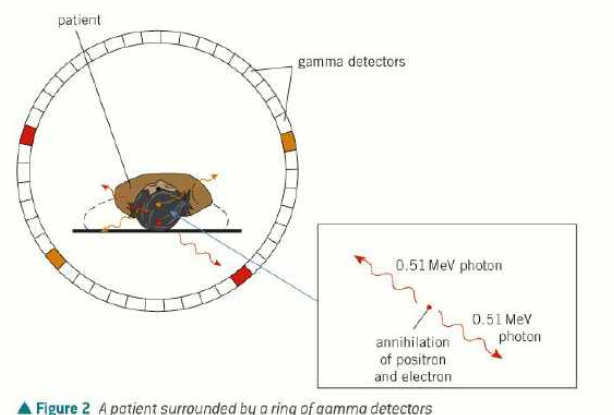
what happens in a PET scan?
tracer injected into patient
the patient lies on a table inside a ring of gamma detectors
the tracer decays and emits beta plus positrons
inside the patient, each positron collides with and annihilates a nearby electron
this causes two gamma photons to be emitted in opposite directions to conserve momentum
detectors on opposite sides of the ring detect the gamma photons
the computer identifies the precise point of the origin of decay by calculating the time difference between the detections of the 2 gamma photons
repeated many times to make 2D slices
software is used to construct a 3D image of the tracer’s location
tracer density can be determined from rate of gamma photons emitted in each region
what tracers are used in PET scans?
fluorodeoxyglucose
(it’s like glucose but it has a fluorine-18 atom in it somewhere instead of oxygen)
accumulates in tissues with a high rate of respiration because the body treats it like glucose
carbon monoxide
made from carbon-11
emits positron and has half life of 20 minutes
good at clinging to haemoglobin in RBCs so can be transported through the blood
what are the advantages of PET scans?
non-invasive
diagnoses cancer
observes organ function
produces 3D image of processes in body
assess effects of new meds
what are the disadvantages of PET scans?
very expensive because producing radioactive tracers on site is hard
only found in larger hospitals
only used for patients with complex health problems