ANAT 200 Final Review
1/603
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
604 Terms
Ingestion
Food and liquid intake (oral cavity)
Mechanical processing
Swirling, mixing, churning, propulsive motions in GI tract (entire tube)
Compaction
Dehydration of undigested material and waste into feces (colon to anus)
Digestion
Chemical and enzymatic breakdown of sugars, lipids, and proteins into small molecules (mostly in stomach, small intestine)
Secretion
Acids, enzymes, and buffers by accessory organs
Absorption
Movement of molecules, electrolytes, vitamins, and water into interstitial fluid
- blood vessels -> liver -> heart -> rest of body
Excretion
Elimination of undigested residue and waste products
Main components of GI system
- Oral cavity
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Anus
Accessory organs of GI system
- Salivary glands
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas
Components of small intestine
- Duodenum
- Jejunum
- Ileum
Components of large intestine
- Cecum
- Ascending colon
- Transverse colon
- Descending colon
- Sigmoid colon
- Rectum
Layers of GI tube
- Mucosa
- Submucosa
- Muscularis externa
- Serosa
Components of mucosa
- Epithelium (stratified or squamous depending on location)
- Lamina propria (connective tissue containing glands and immune cells)
- Muscularis mucosa (propels contents of glands in lumen)
Components of submucosa
Conduit for vasculature, nerves, and lymphatics; connective tissue
- Immune cells
- Some exocrine glands
- Submucosal nerve plexus
Components of muscularis externa
- Inner circular smooth muscle
- Outer longitudinal smooth muscle
- Myenteric plexus (controls GI motility)
- Skeletal muscle and beginning and end of tube
- Oblique smooth muscle in stomach
Components of serosa
Wrapping of the tube layer(s)
- Serous membrane (simple squamous epithelium + areolar CT)
- Continually produces watery fluid for lubrication
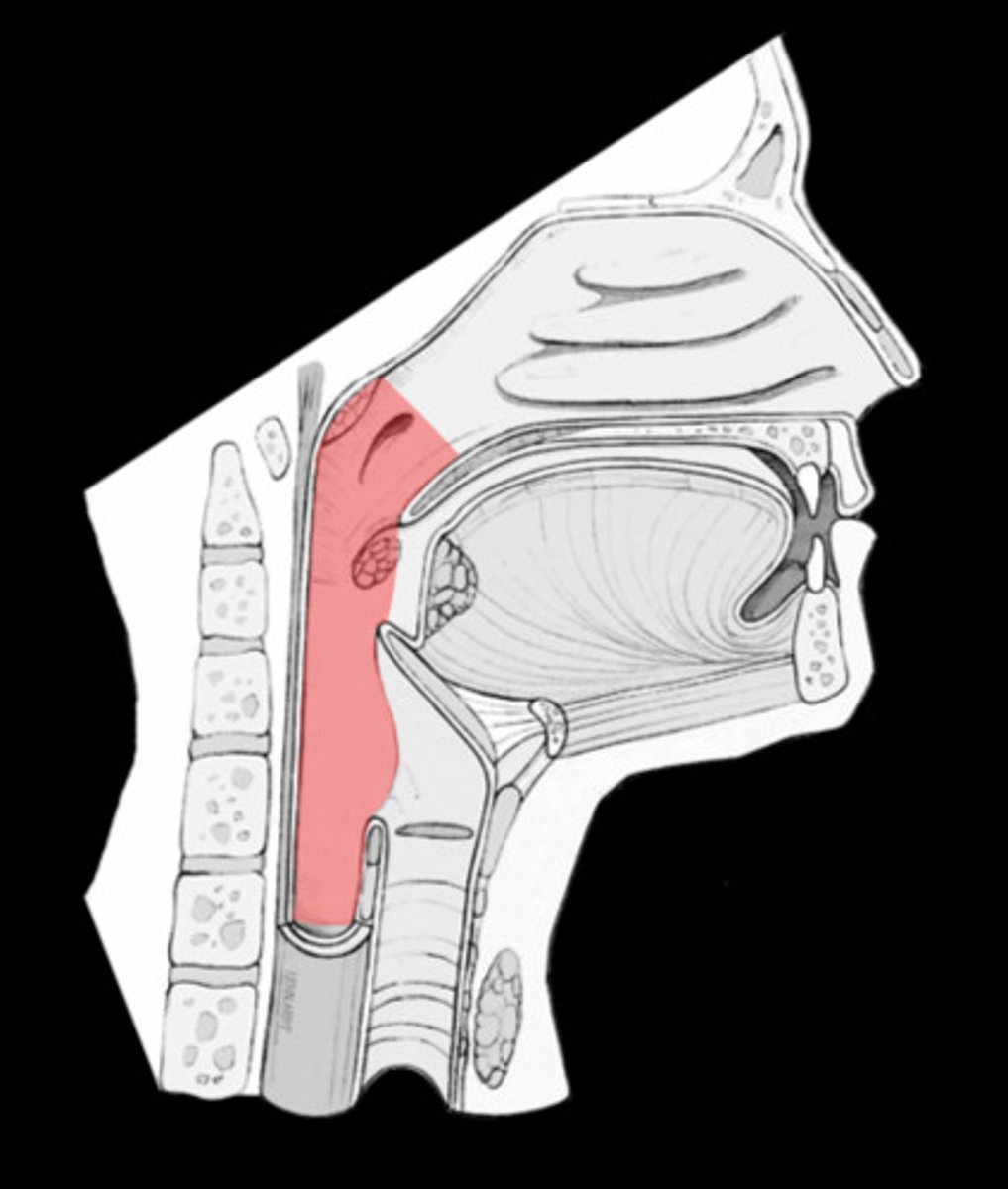
Location of pharynx
Behind nose, mouth, throat
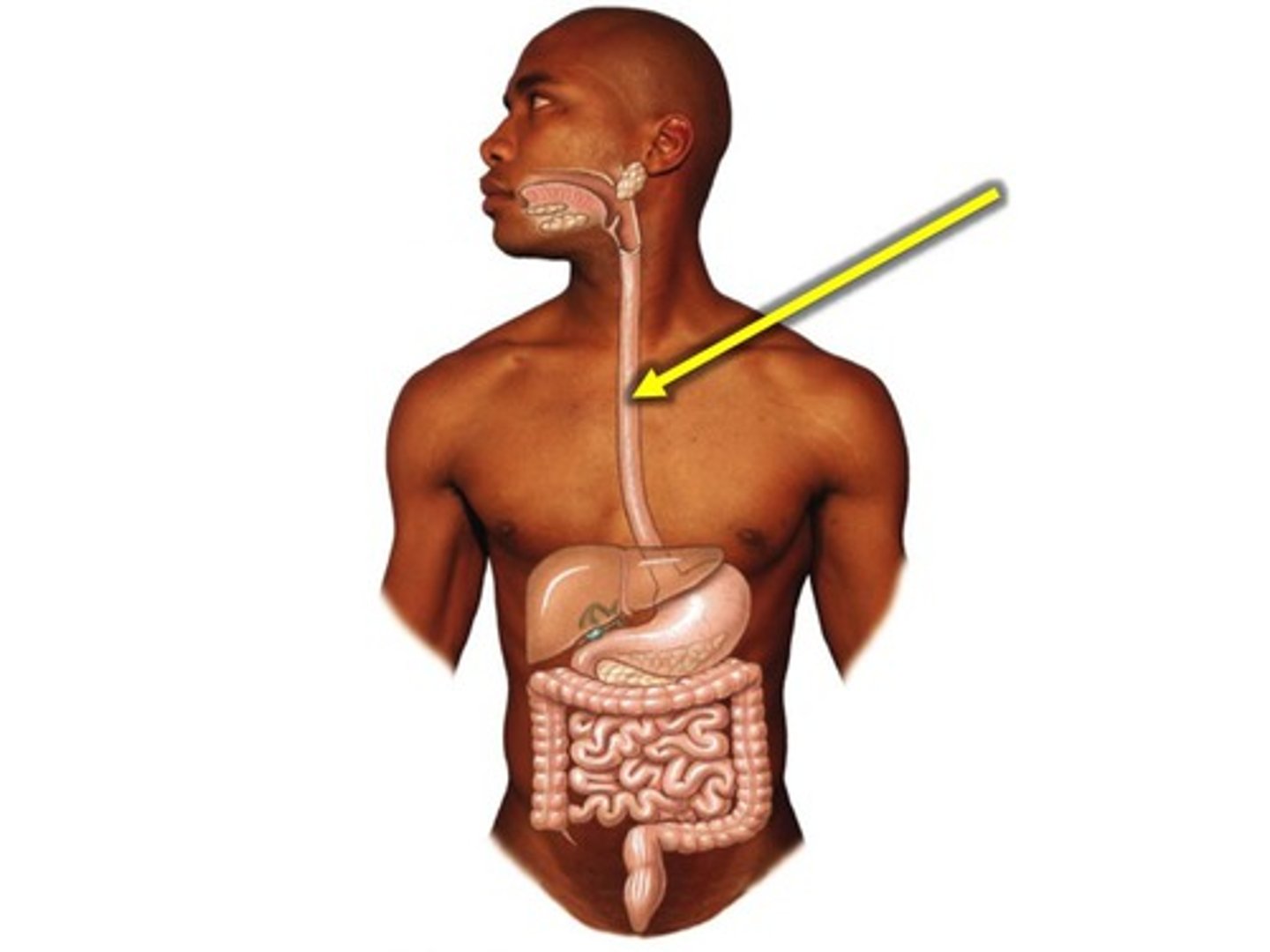
Location of esophagus
Sits behind respiratory system and disphragm
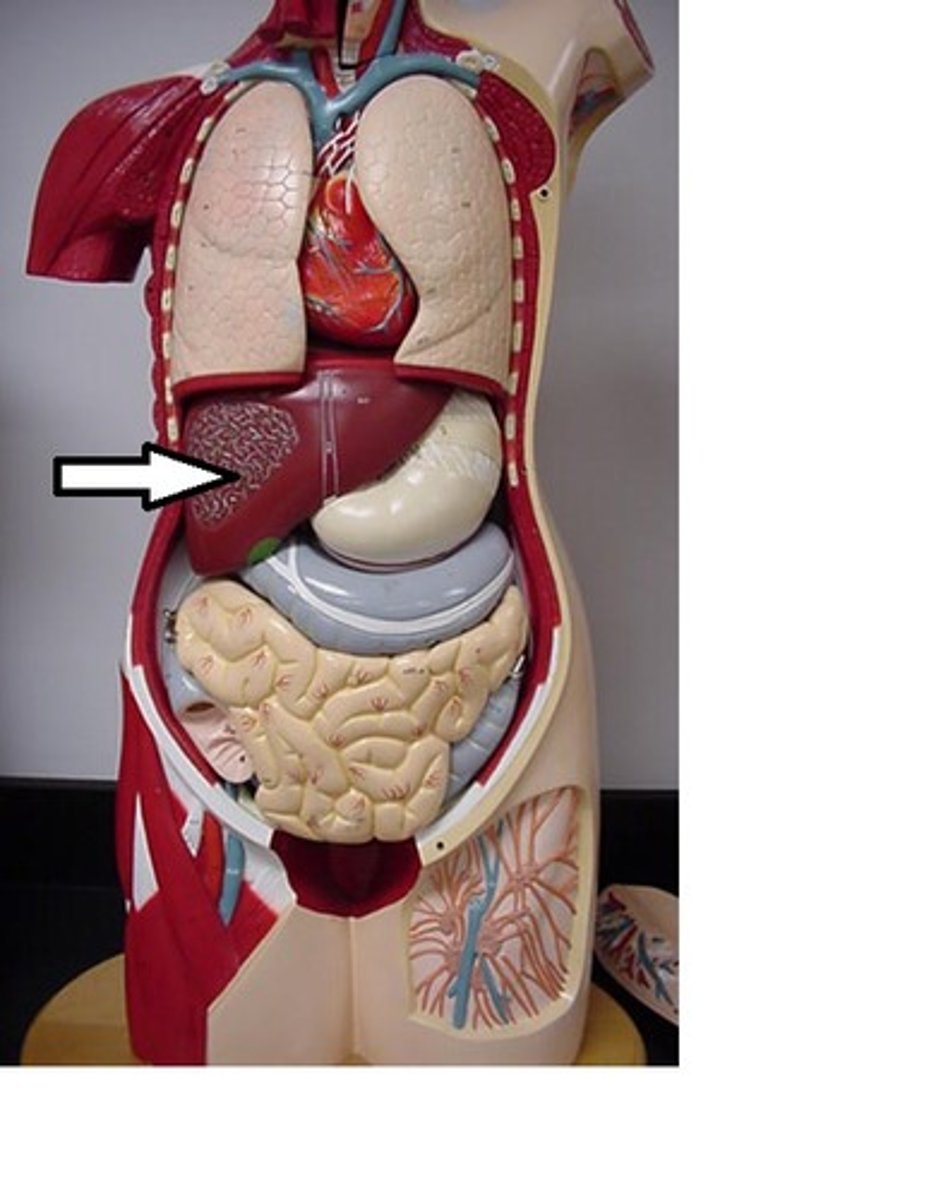
Location of liver and gallbladder
Location of stomach
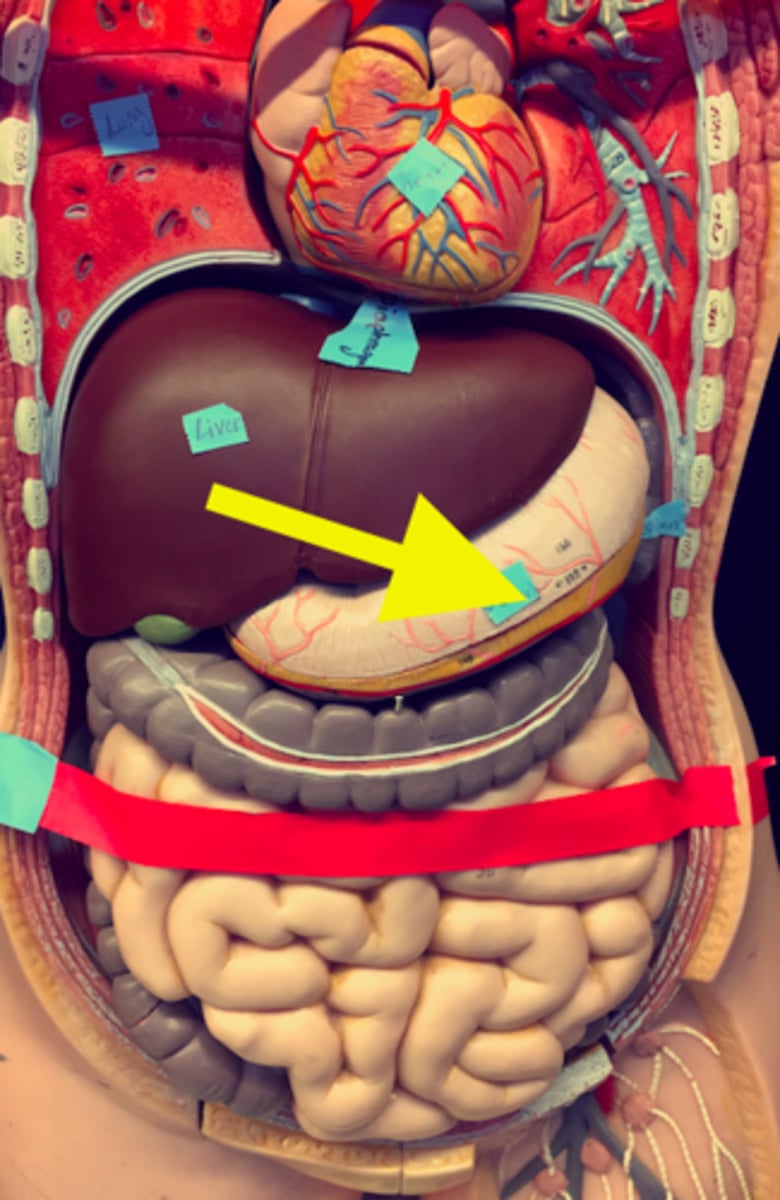
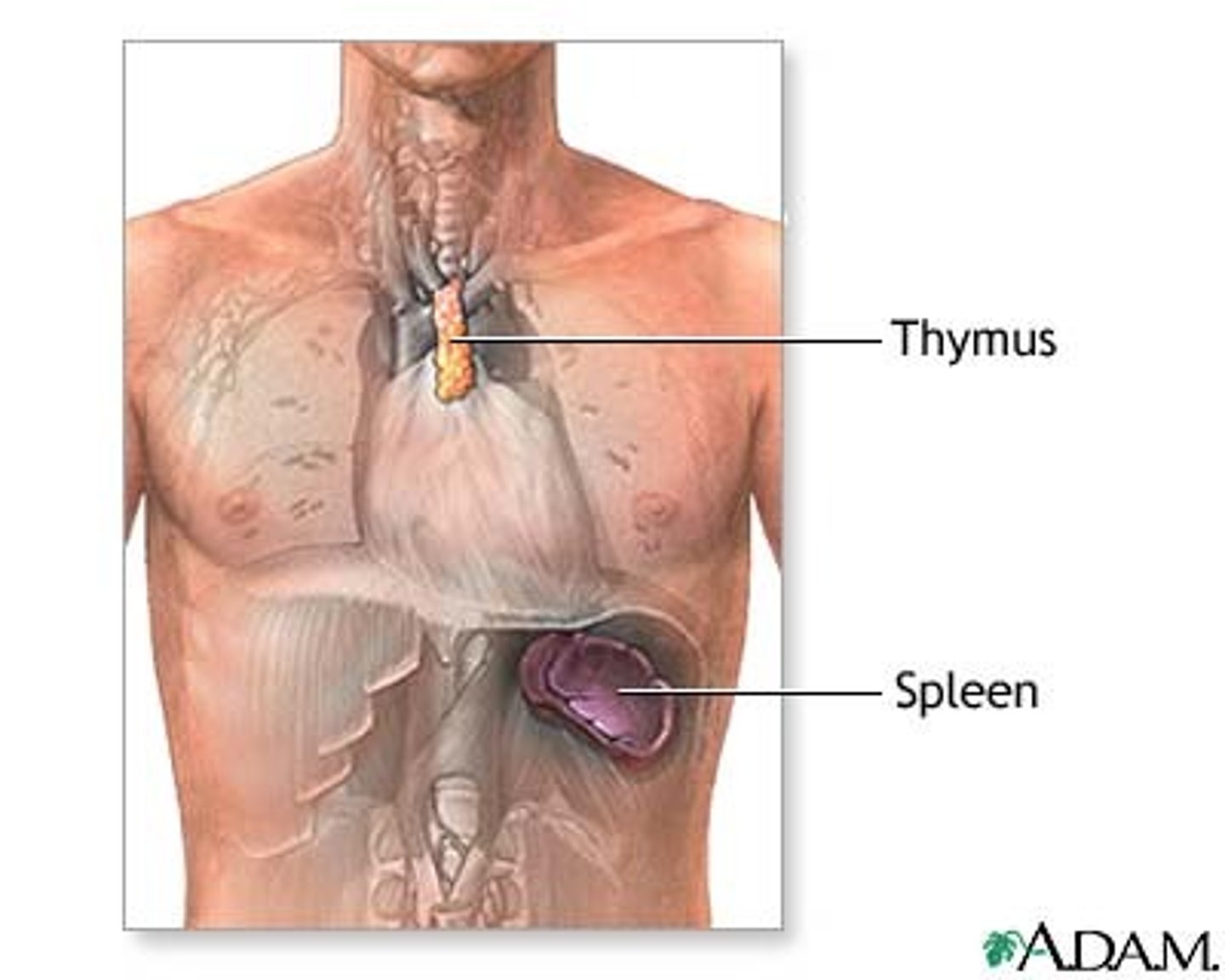
Location of spleen
Behind the stomach and left side of heart
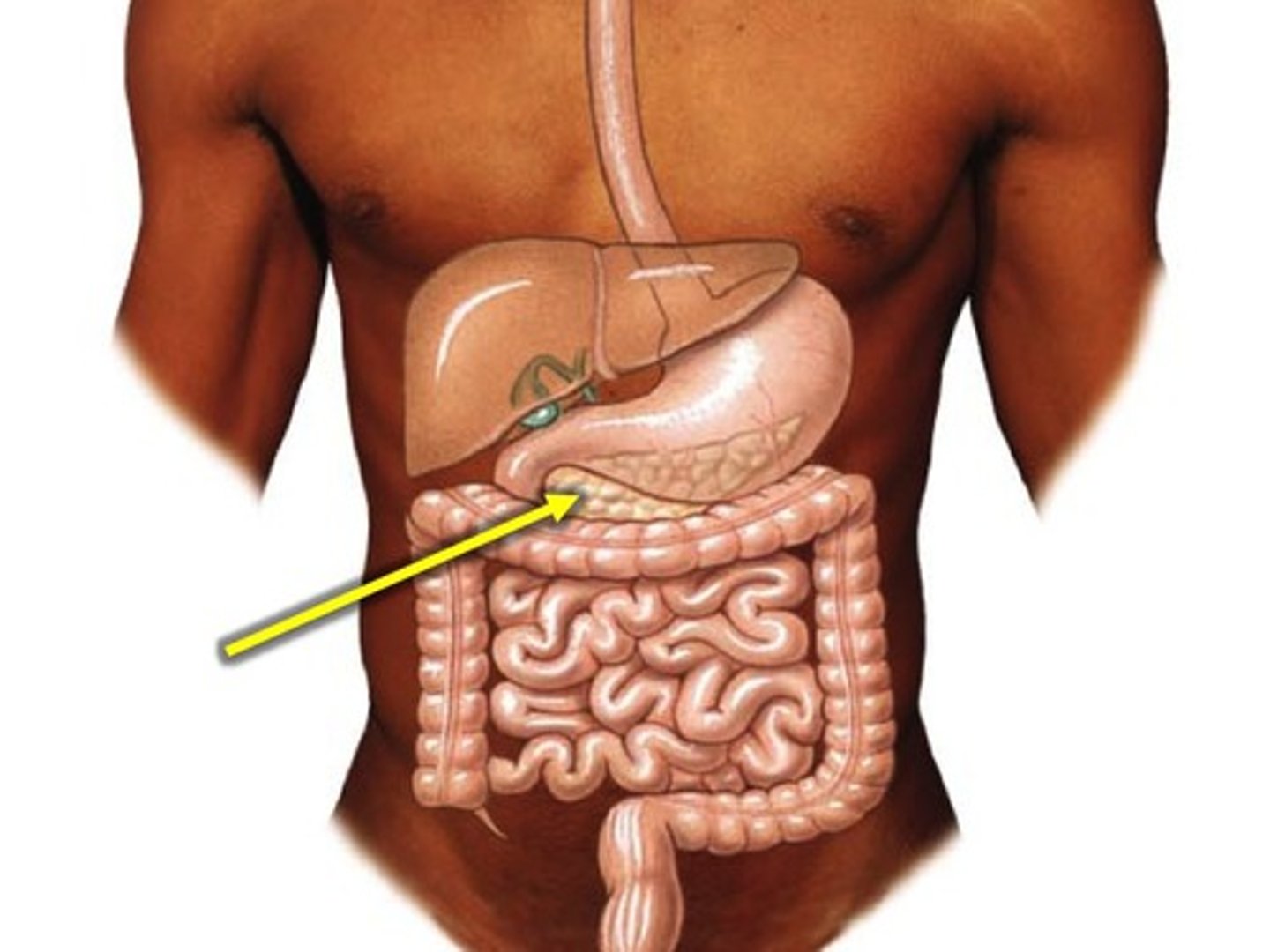
Location of pancreas
Behind stomach
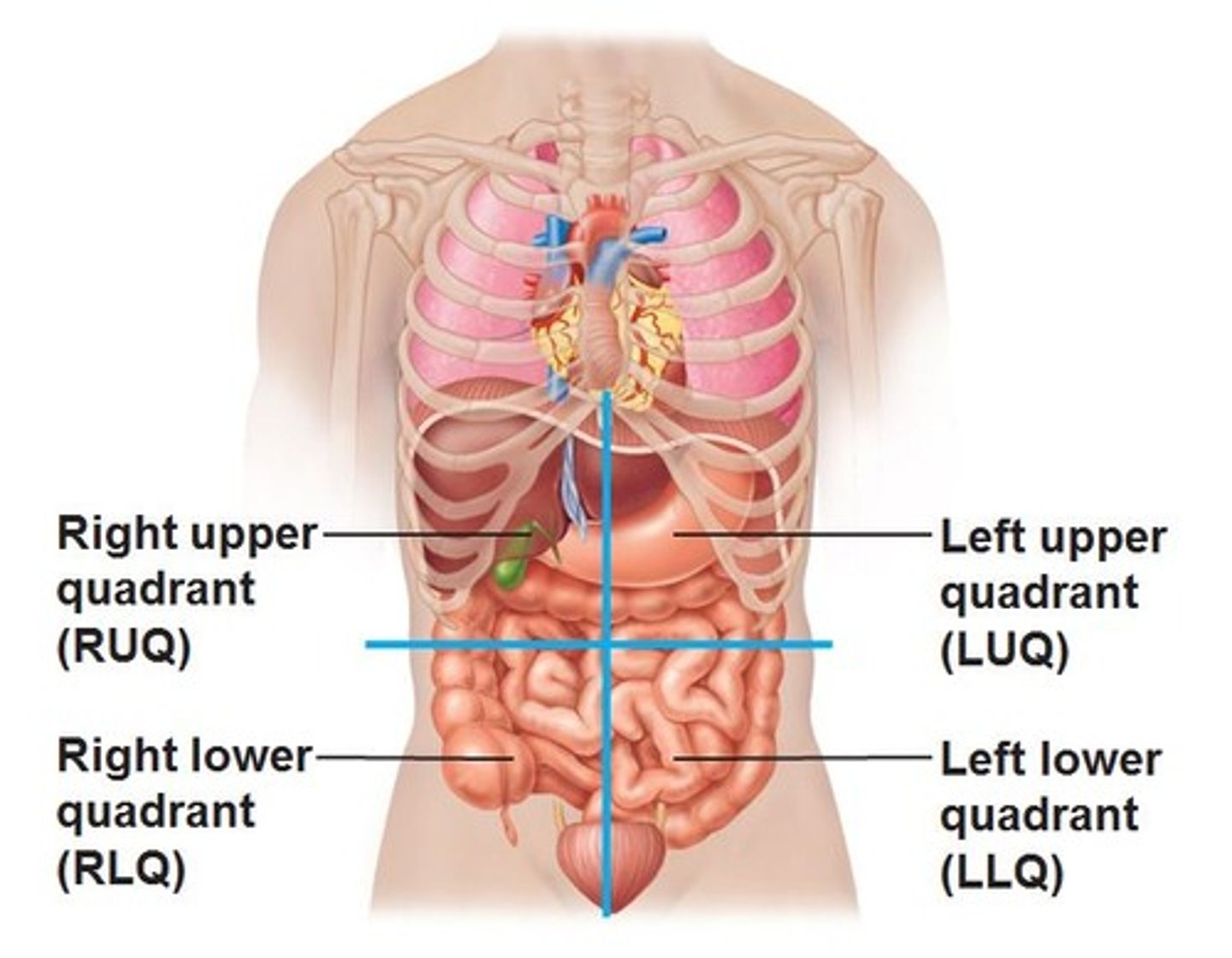
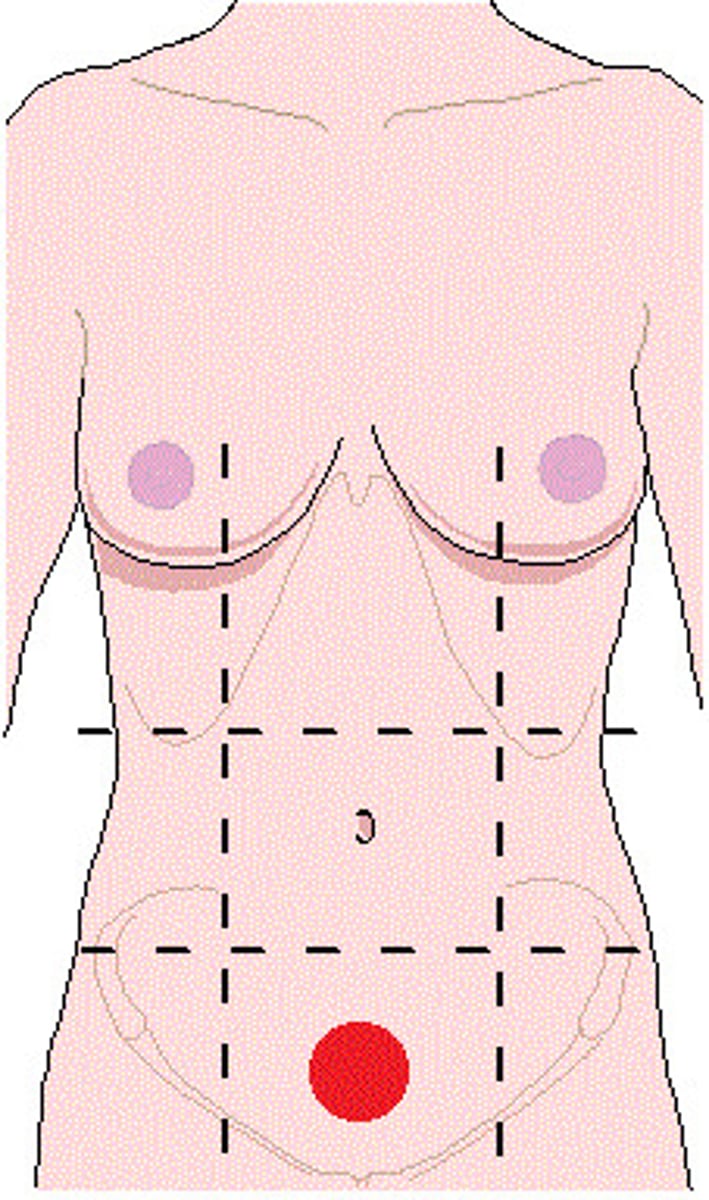
Organs in left upper quadrant
- Stomach
- Spleen
- Body and tail of pancreas
- Jejunum
- Transverse colon
- Left kidney
Organs in right upper quadrant
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Duodenum
- Head of pancreas
- Transverse colon
- Right kidney
Organs in left lower quadrant
- Ileum
- Descending and sigmoid colon
Organs in right lower quadrant
- Ileum
- Cecum
- Appendix
- Ascending colon
Location of rectum and anus
In pelvis; inferior to abdominal quadrants
Abdominal quadrants
Vertical and horizontal planes intersecting at the unbilicus
Midclavicular plane
Sagittal plane through the middle of clavicles
Subcostal plane
Transverse plane below the ribs (L1)
Intertubercular plane
Transverse plane through the tubercles of iliac crests (L5)
Epigastric region
Region of the abdomen between the midclavicular planes and superior to the subcostal plane
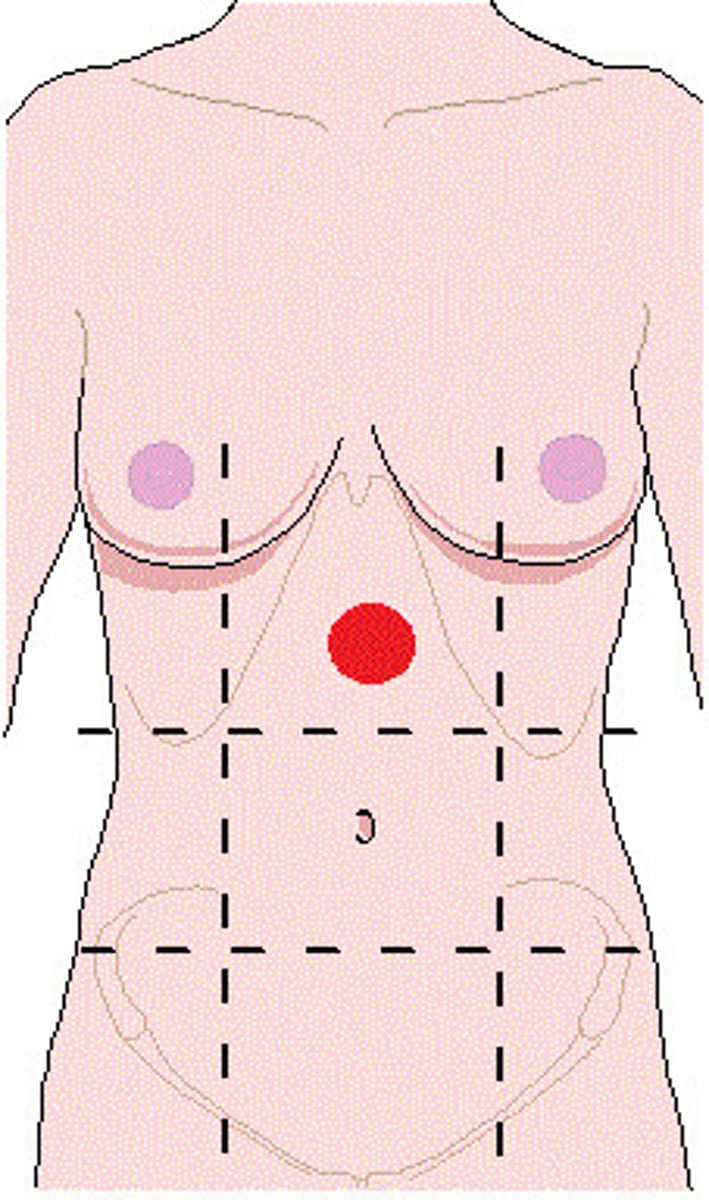
Umbilical region
Region of the abdomen between the midclavicular planes and the subcostal and intertubercular planes
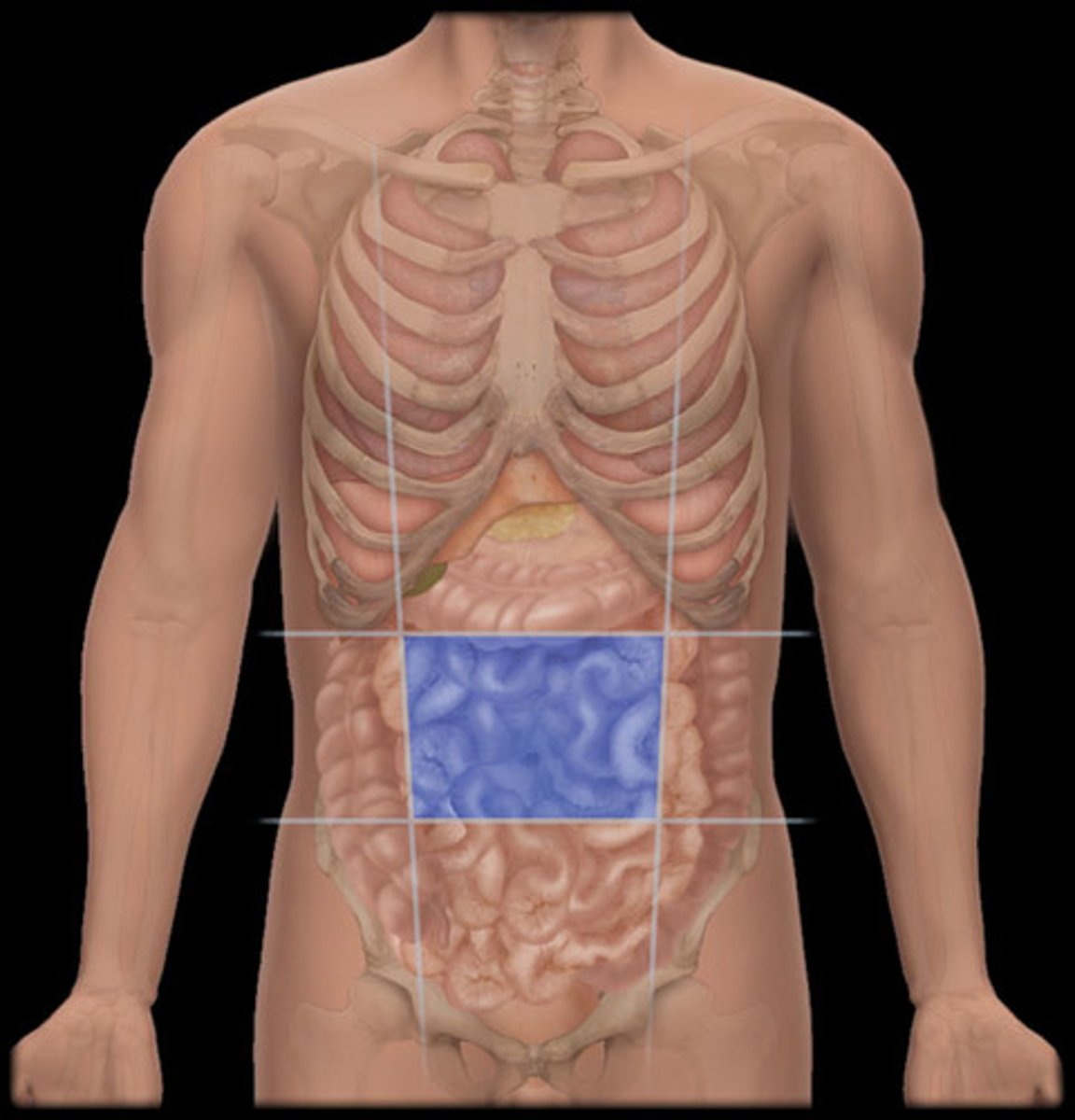
Hypogastric region
Region of the abdomen between the midclavicular planes and inferior to the intertubercular plane
Foregut
From abdominal esophagus to descending part of duodenum
- Vasculature: celiac trunk
- Innervation: celiac ganglia T7-T9
Midgut
From descending part of duodenum to left colic flexure of transverse colon
- Vasculature: superior mesenteric artery
- Innervation: SMA ganglia T9-T11
Hindgut
From left colic flexure of transverse colon to rectum
- Vasculature: inferior mesenteric artery
- Innervation: IMA ganglia T11-L1
Parasympathetic innervation of abdominal organs
Vagus nerve (CN X)
Superior mesenteric artery location
Organs supplied by superior mesenteric artery
- Pancreas (1/2)
- Duodenum (1/2)
- Jejunum
- Ileum
- Cecum and appendix
- Ascending colon
- Transverse colon
Descending aorta location and function
Supplies thoracic esophagus
Celiac trunk location
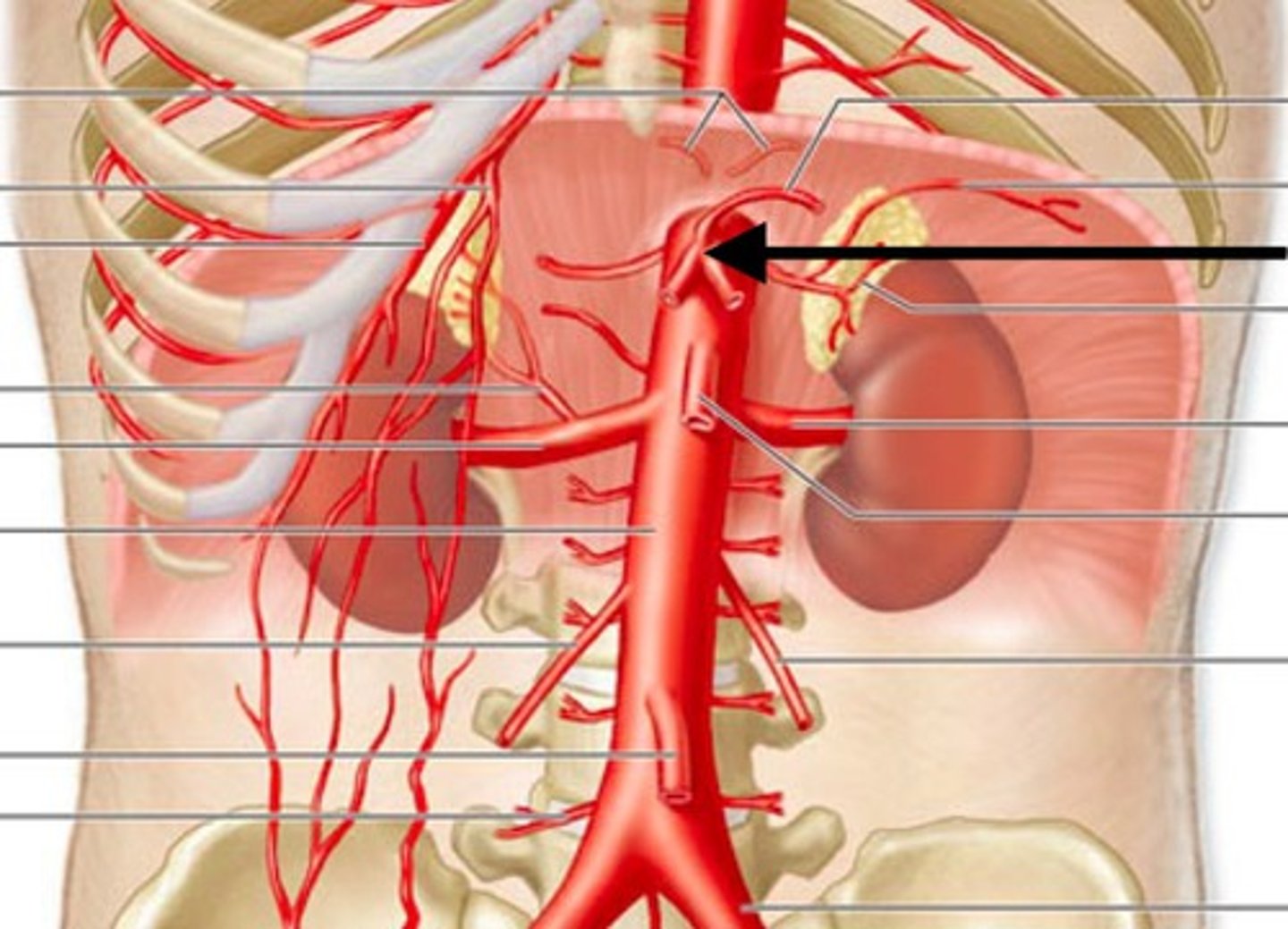
Organs supplied by celiac trunk
- Abdominal esophagus
- Stomach
- Spleen
- Liver
- Gallbladder
- Pancreas (1/2)
- Duodenum (1/2)
Inferior mesenteric artery location
Organs supplied by inferior mesenteric artery
- Descending colon
- Sigmoid colon
- Rectum
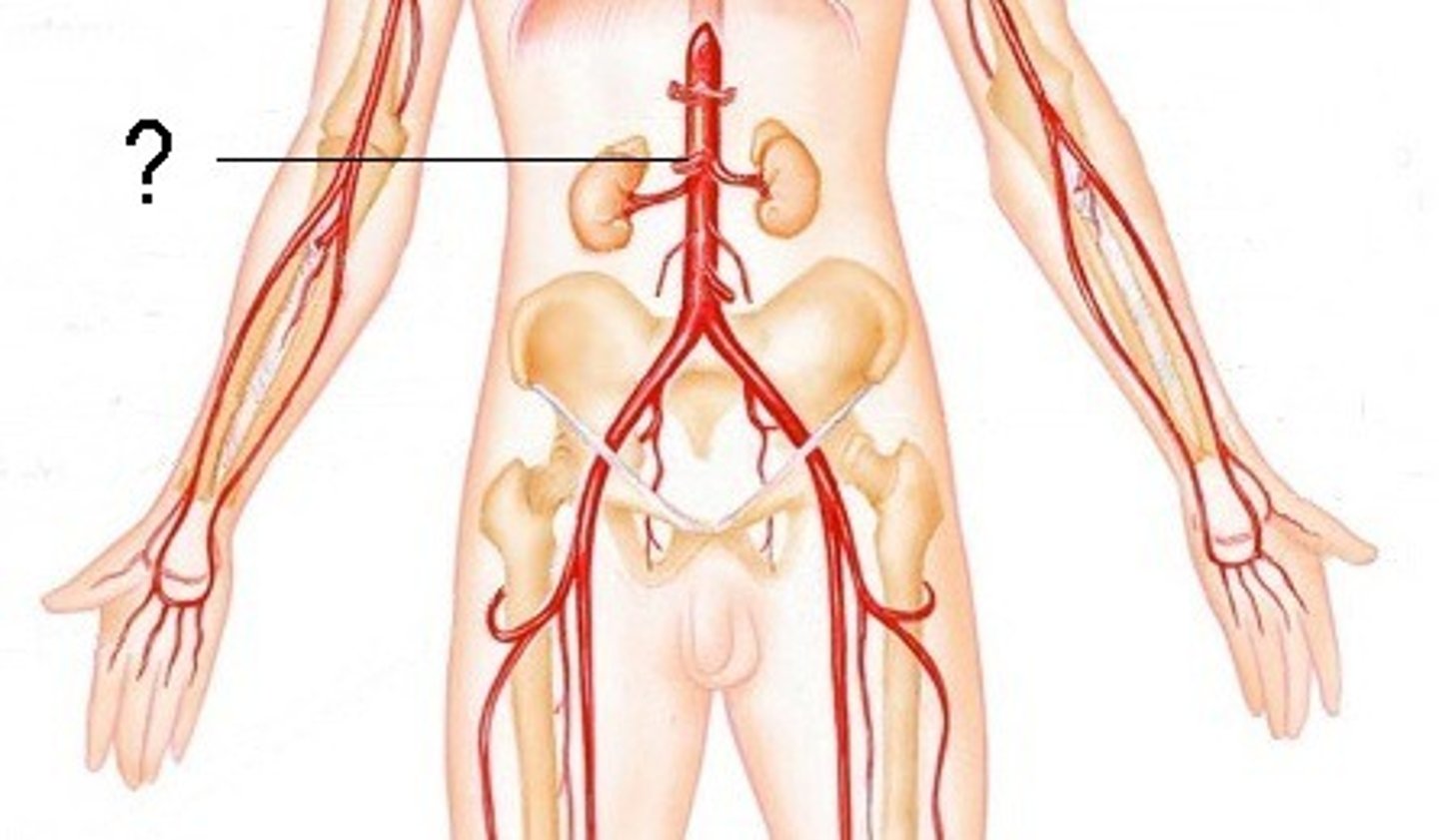
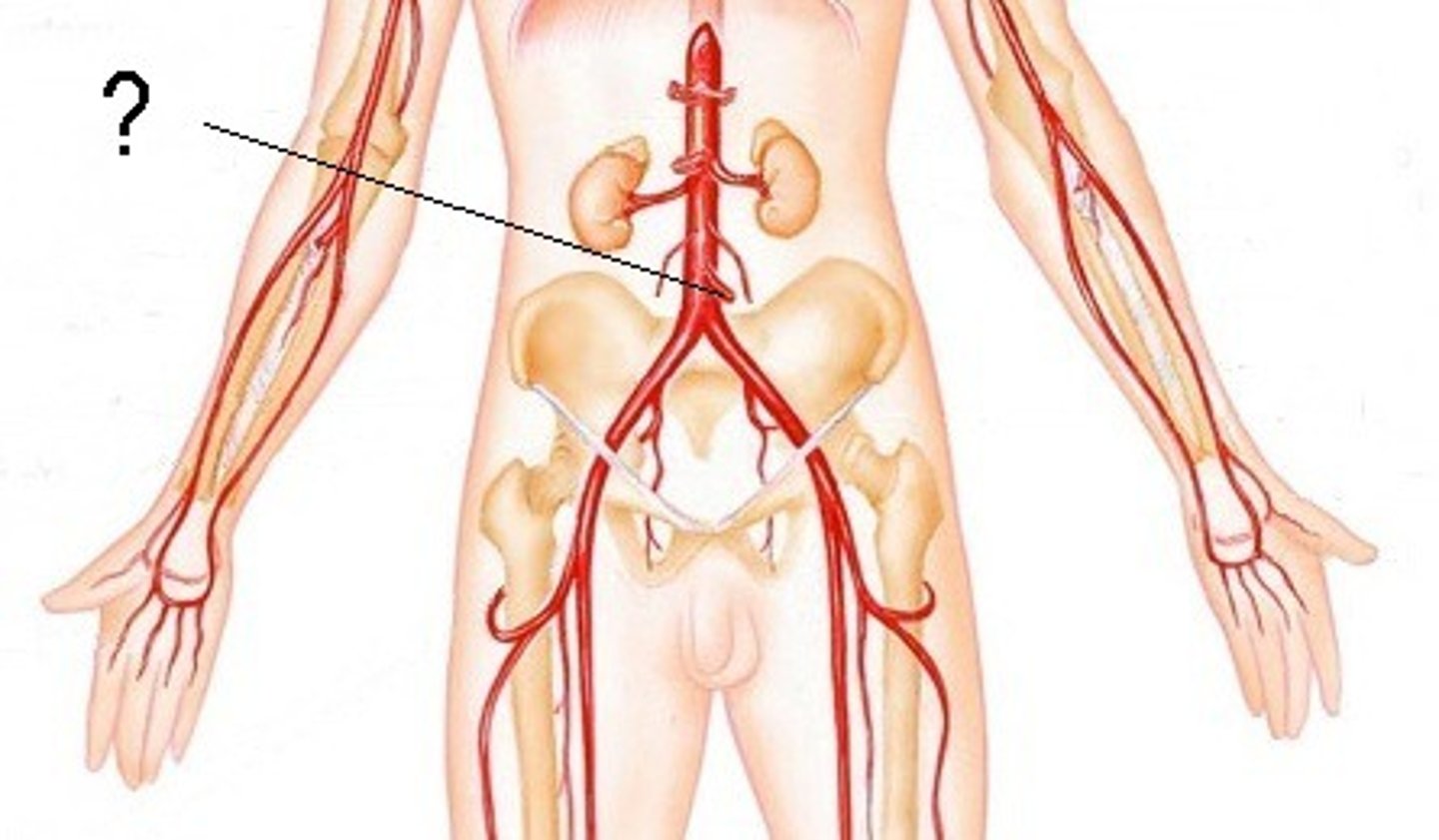
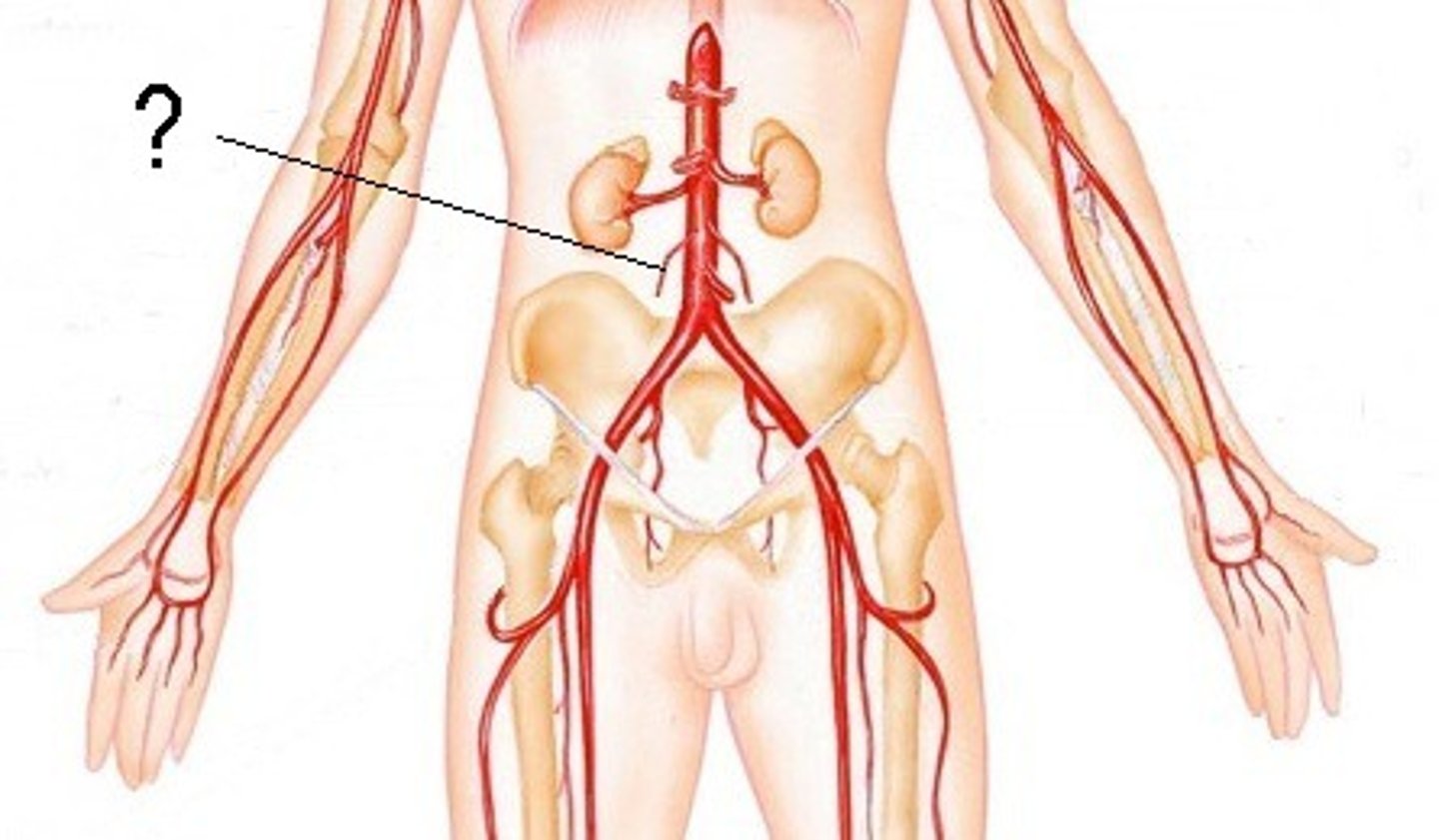
Gonadal artery location and function
Supplies ovaries/testes
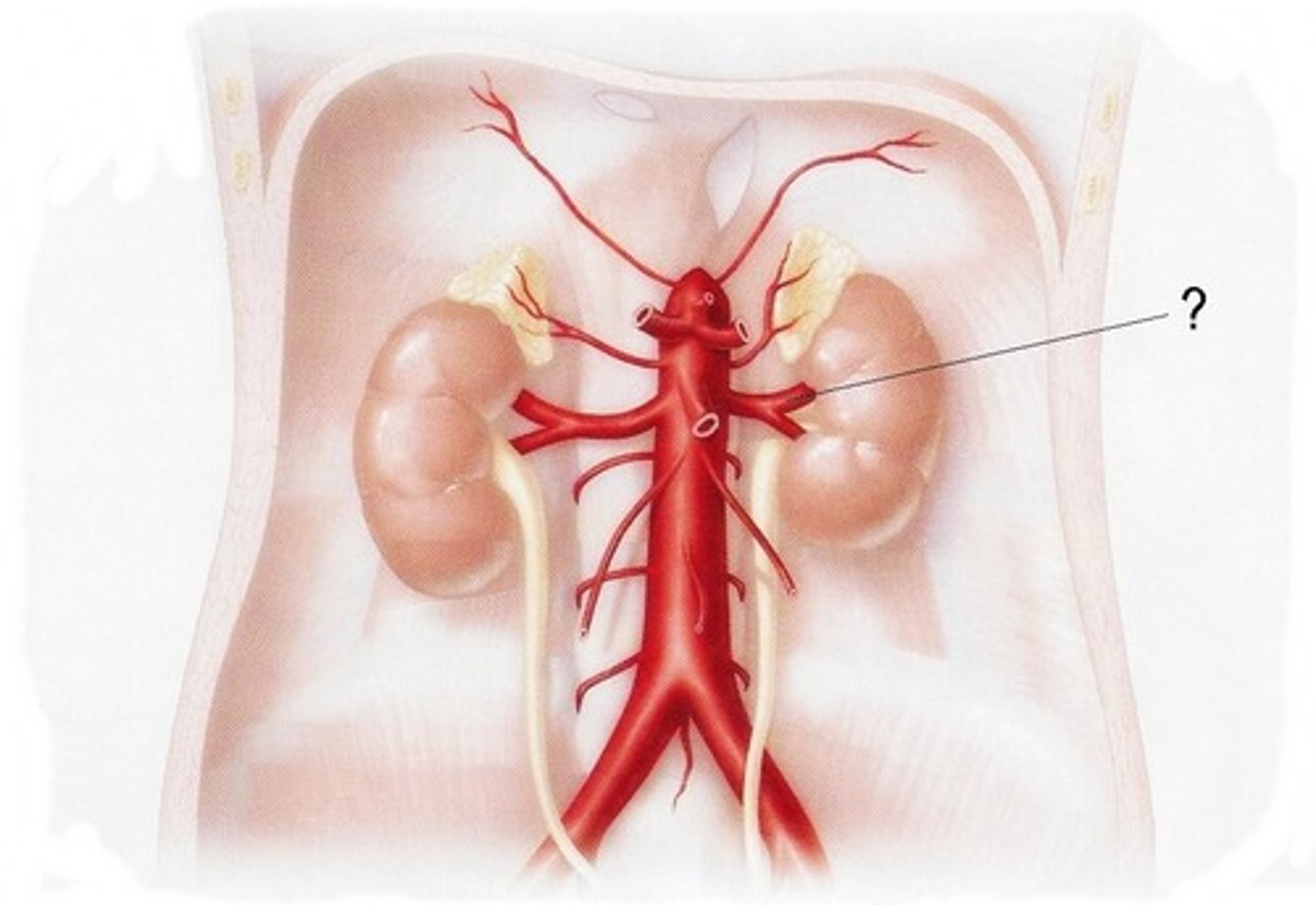
Renal artery location and function
Supplies kidneys and adrenal glands
Splenic vein
Veinous equivalent of celiac trunk
Veins from body wall
Drain directly into inferior vena cava
Veins from GI tube
Go to liver for filtration via hepatic portal vein
Peritoneum
Serous membrane lining the peritoneal body wall and organs
Parietal peritoneum
Lines the peritoneal cavity; body wall - somatic innervation
Visceral peritoneum
Lines the peritoneal organs; viscera - autonomic innervation
Mesentary
Sandwich of peritoneum; 2 layers of peritoneum serves as a conduit for vessels, nerves, and lymphatics
Greater omentum
Large pouch of mesentery from greater curvature of stomach to transverse colon that forms an apron; contains blood, nerves, lymphoid tissue; lipid deposition for temperature control; immune function
Intraperitoneal
Within the peritoneal cavity
Retroperitoneal
Posterior to the peritoneum; anchored in place
Retroperitoneal organs
- Adrenal glands
- Kidneys and ureters
- Abdominal aorta
- Inferior vena cava
- Abdominal esophagus
- Most of duodenum
- Pancreas
- Ascending/descending colon
- Rectum
- Bladder
- Prostate
- Uterus
Oral mucosa
Stratified squamous epithelium that protects from abrasion and stress
Functions of oral cavity
- Sensory analysis of ingested material
- Mechanical digestion
- Lubrication by mixing ingested material with saliva (bolus)
- Start of enzymatic digestion (amylase)
Oral vestibule
Space between lips, cheeks, and teeth
Tonsils in the oral cavity
- Pharyngeal
- Palatine
- Lingual
Components of the pharynx
- Nasopharynx
- Oropharynx
- Laryngopharynx
Cheeks
Buccal fat pads + oral mucosa
Hard palate
Maxillae and palatine bones
Enamel
Hard, outermost layer of a tooth
Dentin
Alive component of a tooth covered by enamel and supplied by pulp
Pulp cavity
Cavity within a tooth that contains blood vessels and nerves
Gingiva
Gums (mucosa)
Bone surrounding teeth
Maxilla or mandible
Cement
Connective tissue that anchors tooth to periodontal ligament
Periodontal ligament
Forms gomphosis joint
Root canals
Neurovascular bundles that enter tooth from bone
Crown of tooth
Portion of tooth above mucosa
Neck of tooth
Portion of tooth in the gingiva
Root of tooth
Portion of tooth in bone
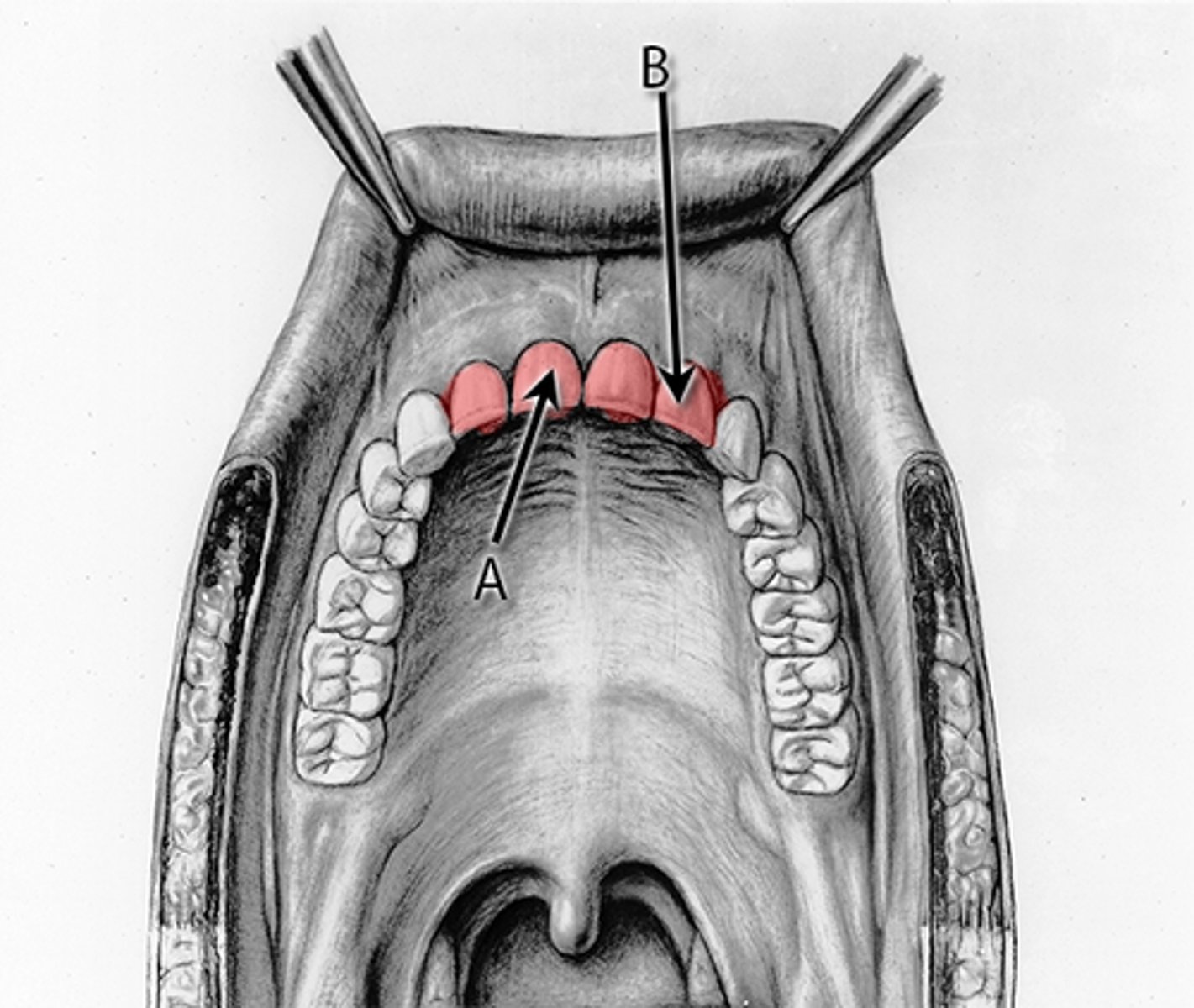
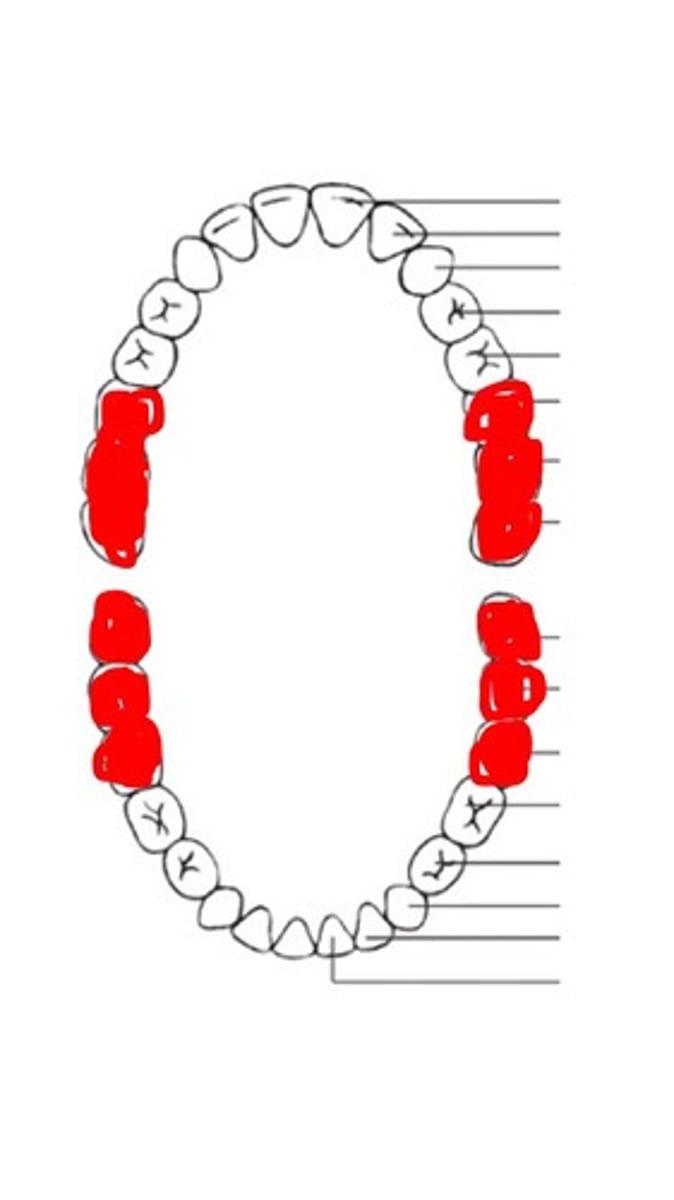
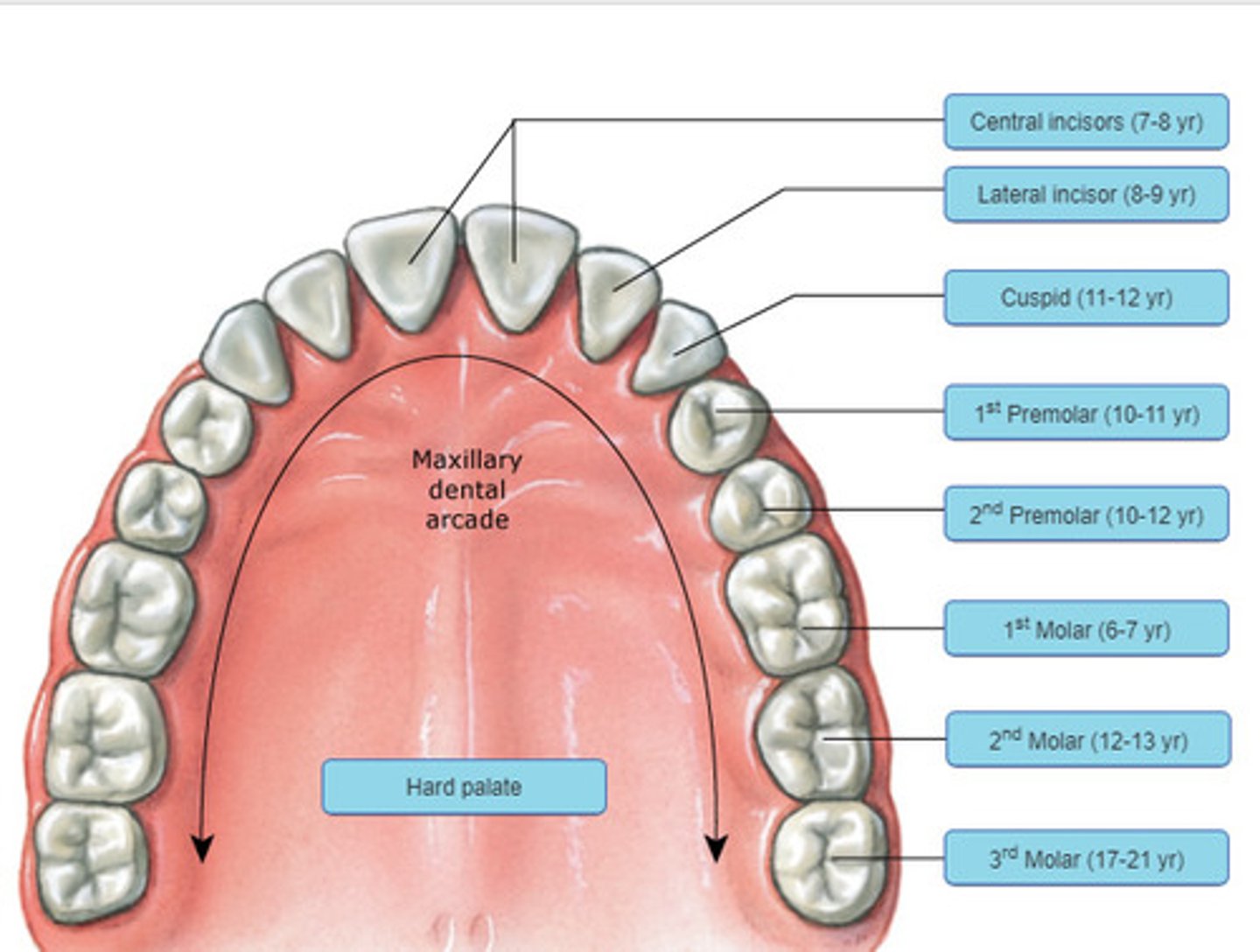
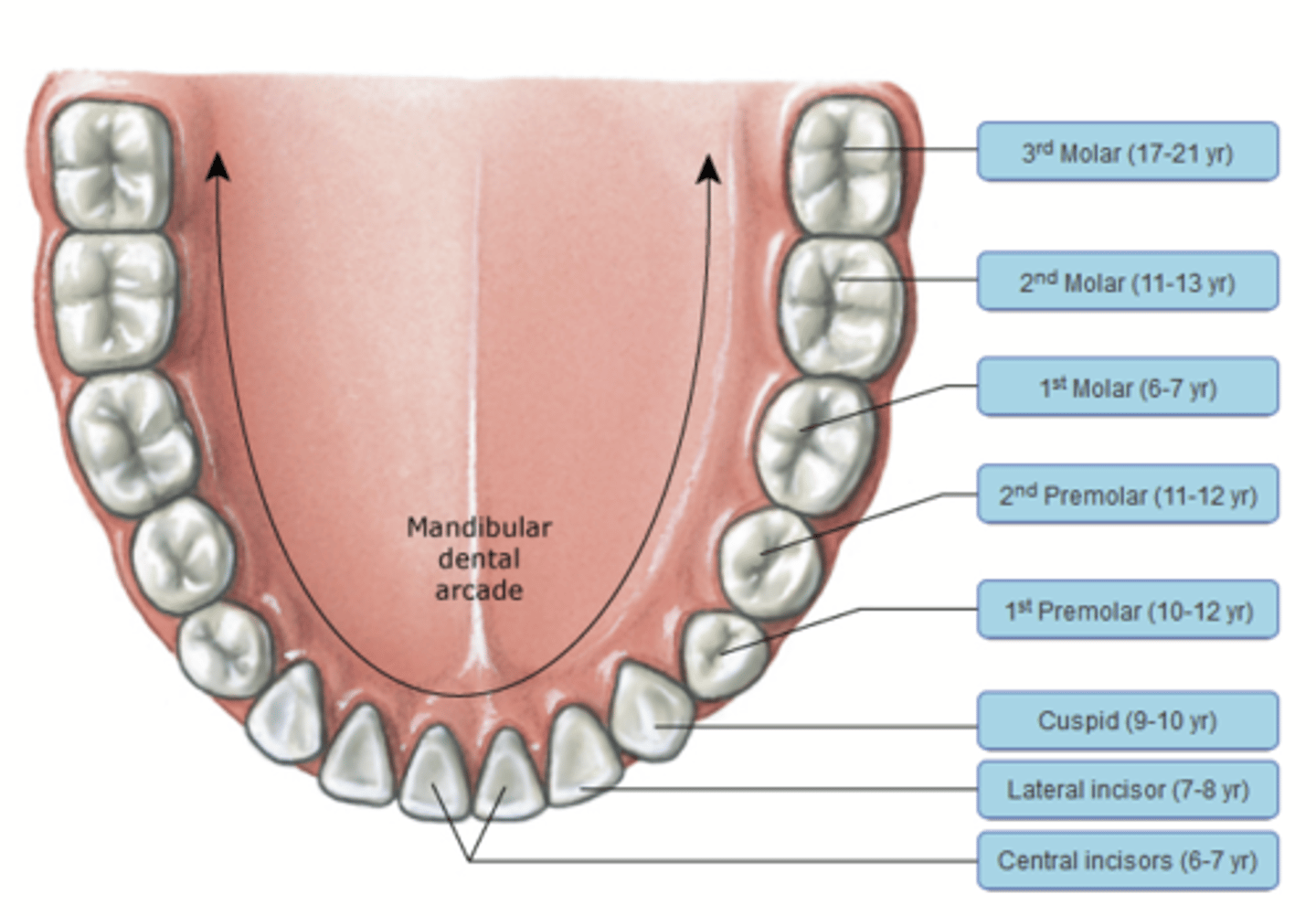
Incisors
Blade-like teeth that clip/cut food
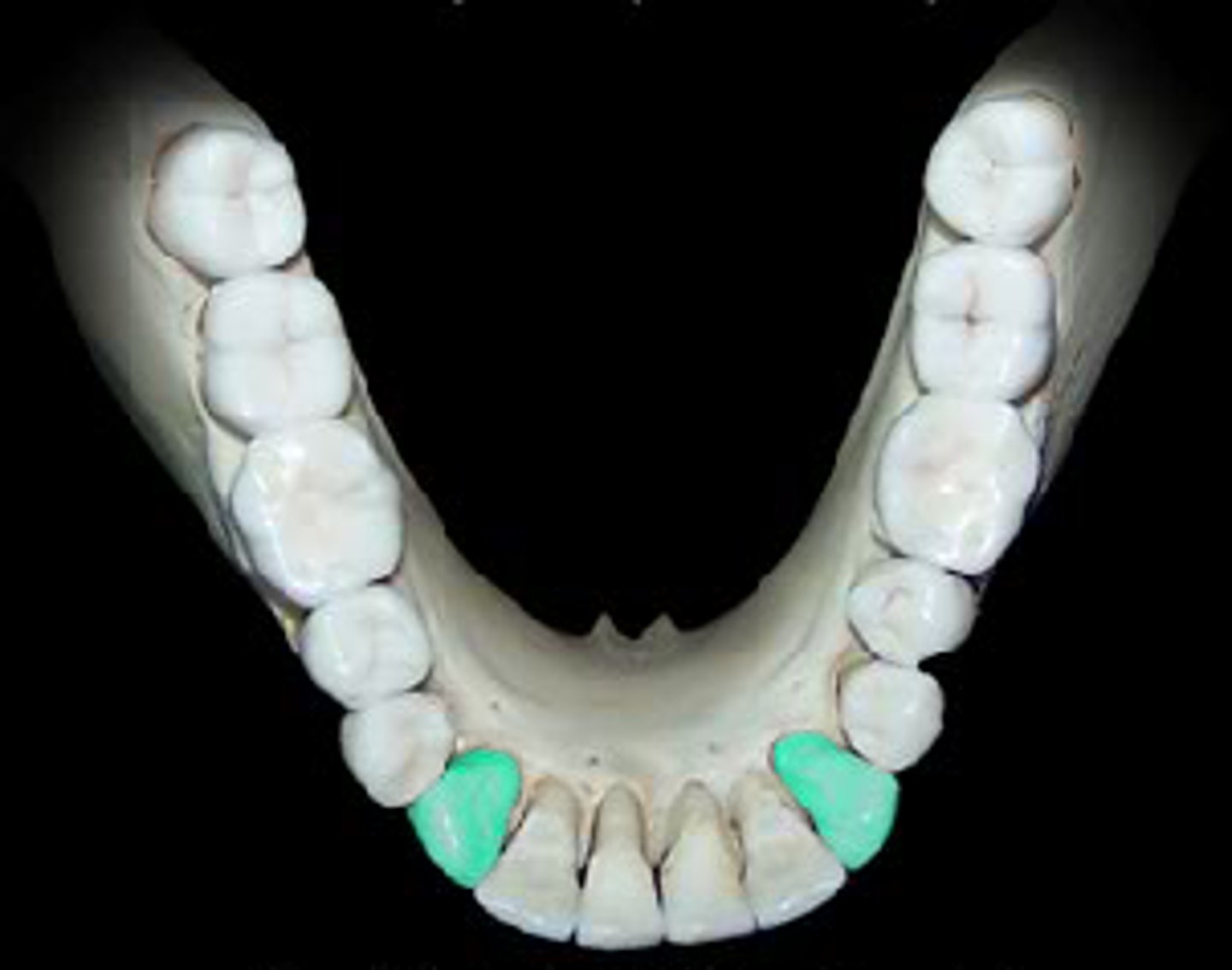
Canines
Pointed teeth that tear/slash food
Premolars
Bicuspid teeth that crush/mash/grind food
Molars
Multi-cuspid teeth that crush/grind food
Upper dentition innervation
CN V2; superior alveolar nerve
Lower dentition innervation
CN V3; inferior alveolar nerve
Maxillary dental arcade
Mandibular dental arcade
Permanent teeth
32 teeth in adults; eruption from 6-18 years
- 2 (central and lateral) incisors
- 1 canine
- 2 premolars
- 3 molars
Deciduous teeth
20 teeth in children; eruption from 6-24 months and shed 6-12 years
- 2 incisors
- 1 canine
- 2 molars
- no premolars
Tongue muscle innervation
CN XII
Intrinsic muscles of tongue
Control shape of tongue
- superior longitudinal
- vertical
- transverse
- inferior longitudinal
Extrinsic muscles of the tongue
Function in swallowing
- palatoglossus
- styloglossus
- hyoglossus
- genioglossus
Anterior 2/3 of tongue
Anterior to terminal sulcus; innervated by CN V3 and CN IX
Posterior 1/3 of tongue
Posterior to terminal sulcus; innervated by CN VII via chorda tympani and CN IX
Taste receptors
Sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami; throughout all papillae of tongue
Salivary glands
Exocrine glands with ducts into the oral cavity; serous moistens food and mucus lubricates passage of food
Functions of saliva
- Amylase initiates carbohydrate digestion
- Buffers regulate oral pH
- Antibodies provide immune surveillance
- Dissolves chemicals that stimulate taste buds
Autonomic innervation of salivary glands
- Sympathetic: inhibits secretion
- Parasympathetic: stimulates secretion
Pharynx
- Common passageway for food, liquid, and air
- Ends at the proximal esophagus and trachea
- Innervated by CN X
- Glands secrete serous and mucus substances
- Stratified squamous epithelium
Muscles involved in swallowing
- Tensor and levator palatini elevate soft palate
- Pharyngeal constrictors and suprahyoid muscles help elevate the larynx and push the bolus towards esophagus
Movement of bolus
1. Contraction of circular muscles behind bolus
2. Contraction of longitudinal muscles in front of bolus
3. Contraction in circular muscle layer forces bolus forward
Segmentation
- Mainly circular muscle contraction
- Churns and mixes contents
- No movement in any direction
- Mechanical digestion
Peristalsis
Propels bolus along the length of the tube via coordination of circular and longitudinal muscles