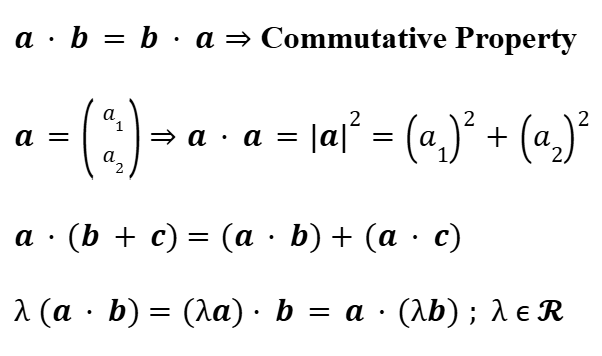UNIT 3: Geometry and Trigonometry
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Formulae (SL & HL)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Distance Formula (2D)
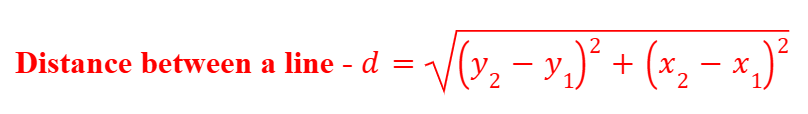
Coordinates of Midpoints (2D)

Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
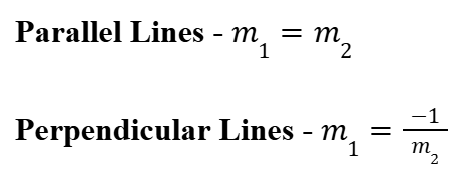
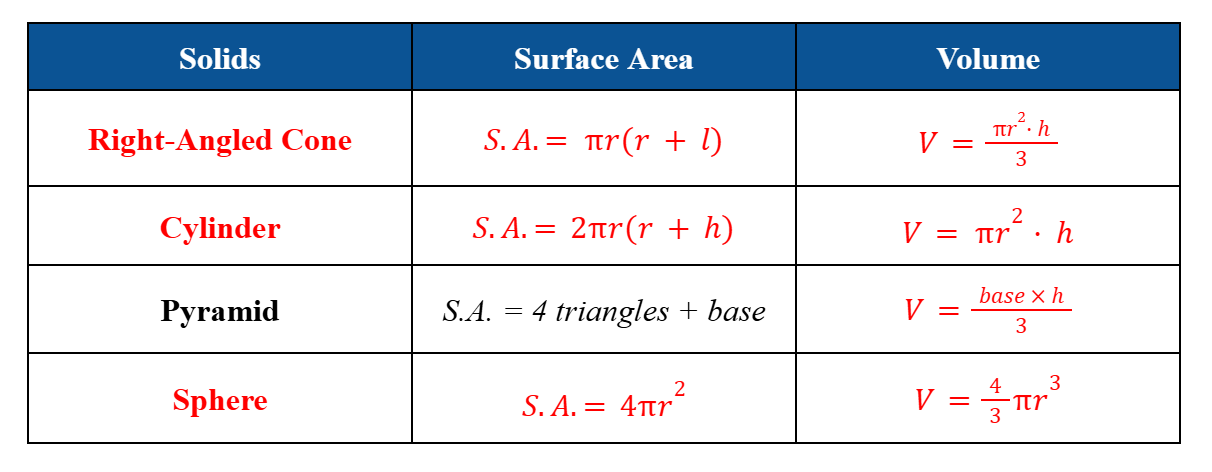
Surface Area and Volumes of Common Solids
Distance Formula (3D)
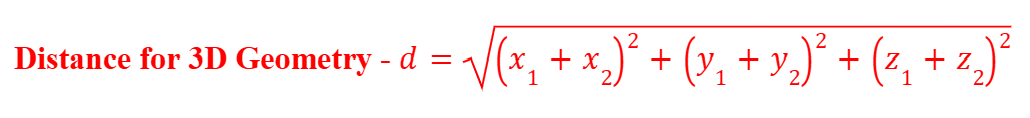
Coordinates of Midpoints (3D)
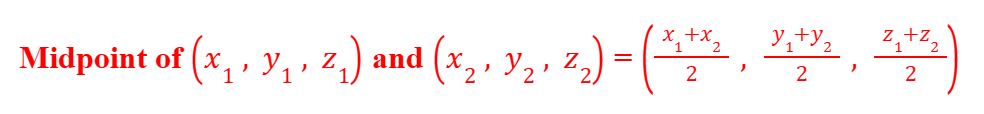
Radians
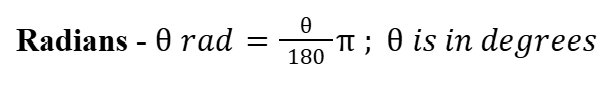
Common Angles in Radians
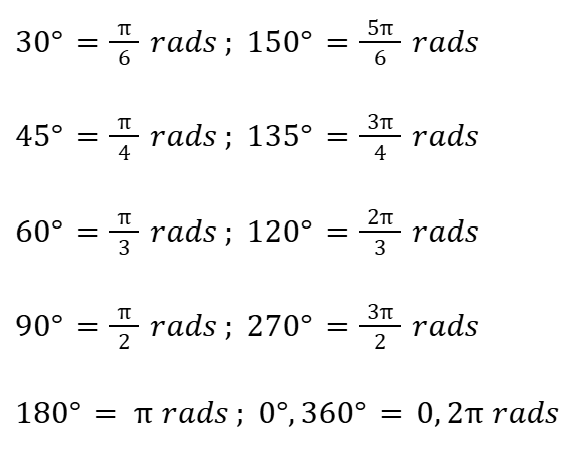
Sine and Cosine in the Unit Circle
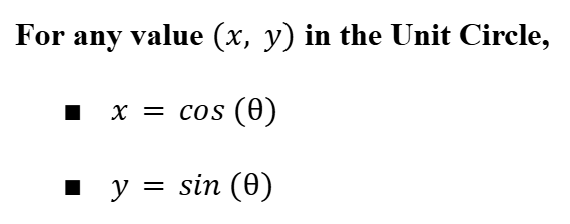
Unit Circle
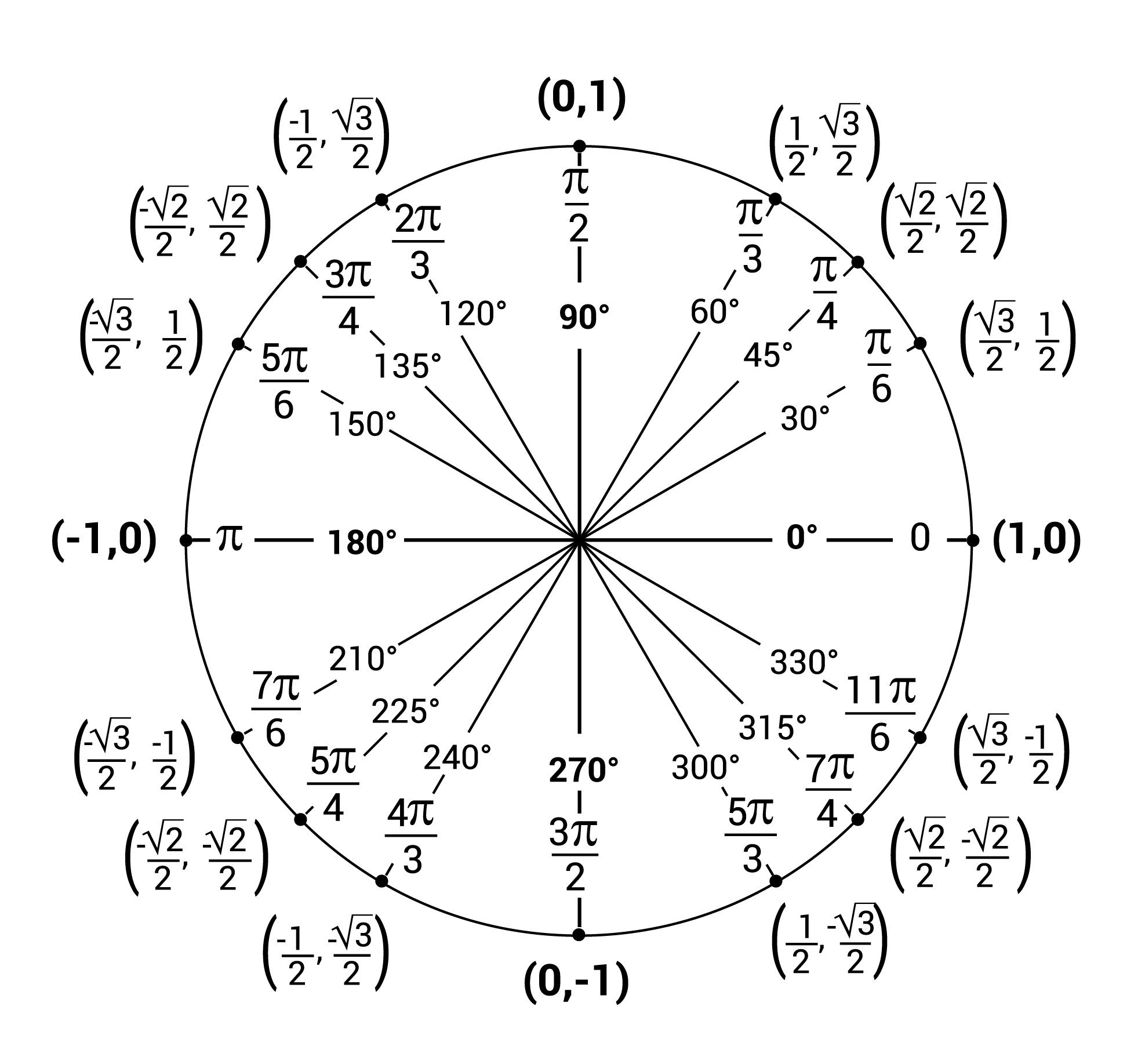
Arc Length
Area of a Sector

Sine Rule
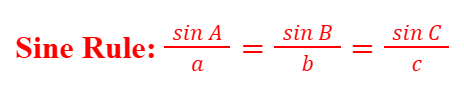
Cosine Rule
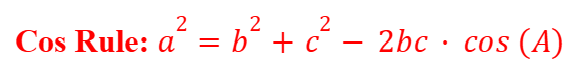
Area of any Triangle

tan (θ)
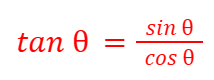
cosec (θ)
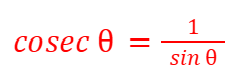
sec (θ)
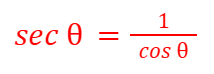
cot (θ)
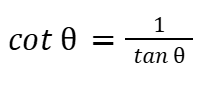
Pythagorean Identity (Trigonometry)
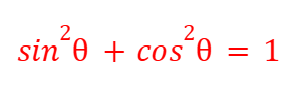
sin(2θ) - Double Angles
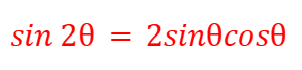
cos(2θ) - Double Angles
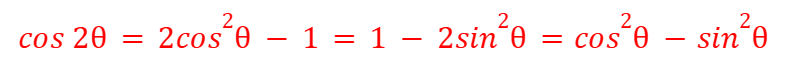
tan(2θ) - Double Angles
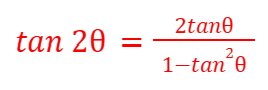
sec2(θ)
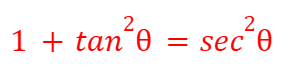
cosec2(θ)
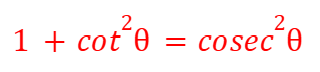
sin (A±B) - Compound Angles
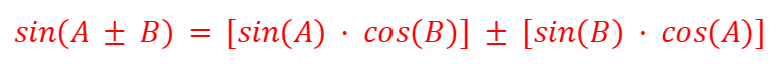
cos (A±B) - Compound Angles
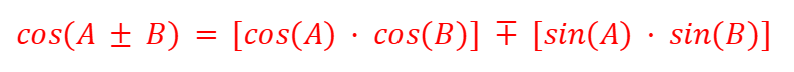
tan (A±B) - Compound Angles
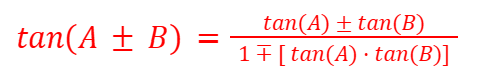
Transformations (Trigonometry)
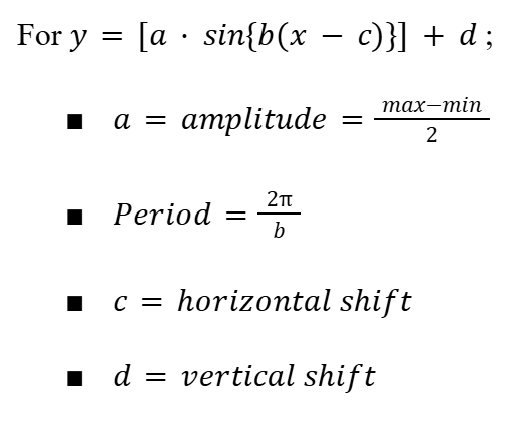
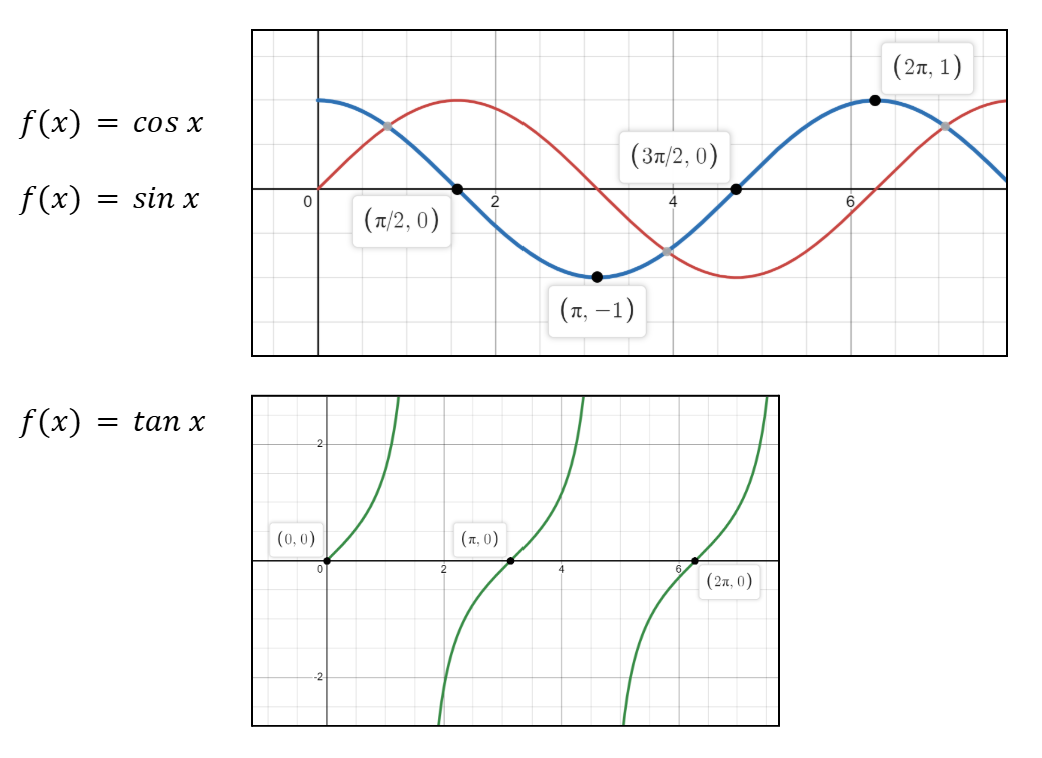
Graphs of sin(x), cos(x) and tan(x)
Periodicity of Angles in Radians
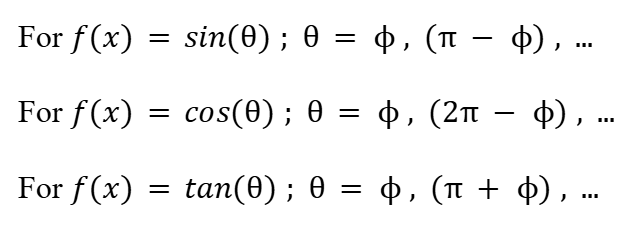
Directed Line Segment

Vectors

Properties of Vectors
Collinearity - Two points are colinear if they lie on the same line.
Coplanarity - Two points or lines are coplanar if they lie in the same plane.
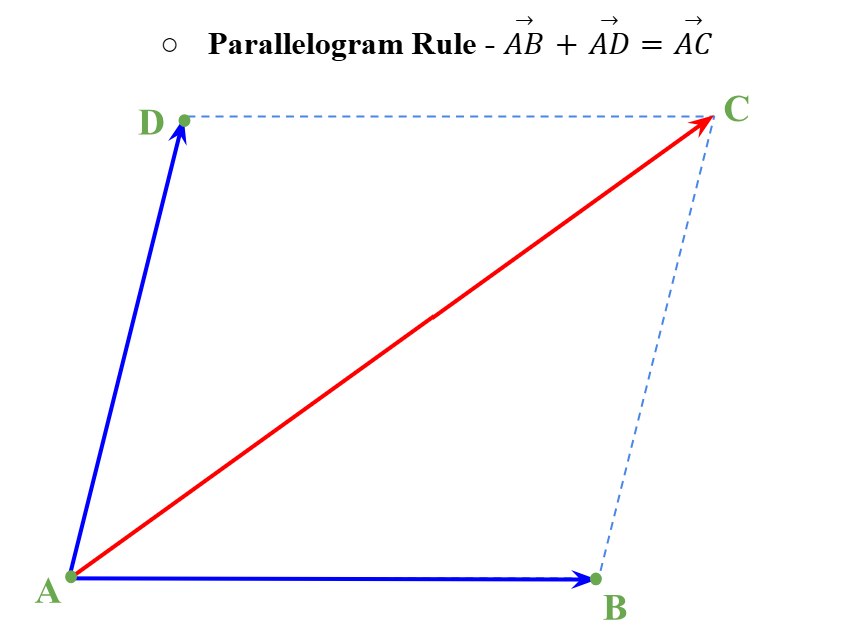
Parallelogram Rule (Vectors)
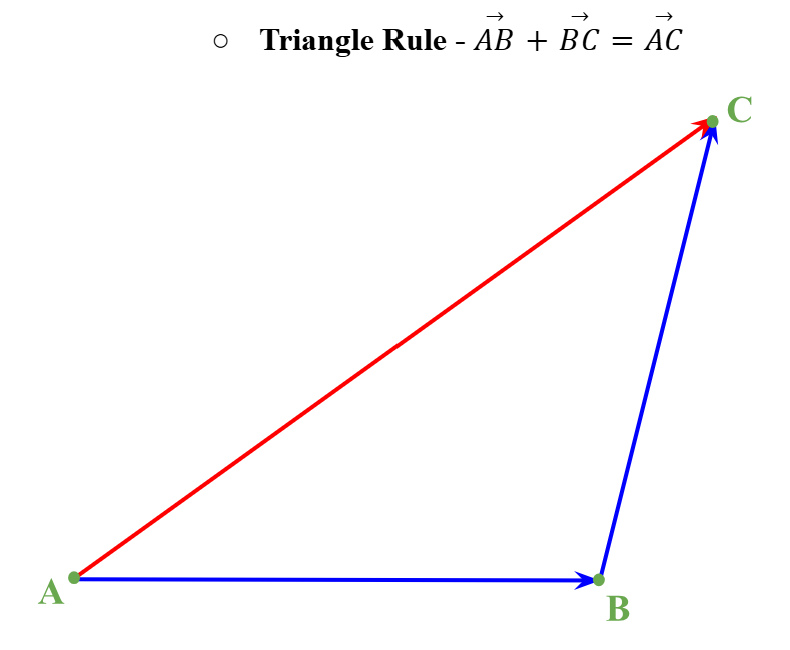
Triangle Rule (Vectors)
Zero Vector
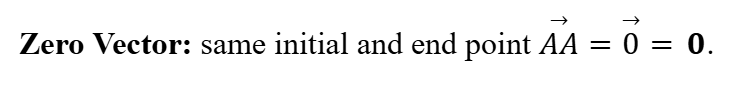
Multiplication by a Scalar (Vectors)

Linear Combination of Vectors
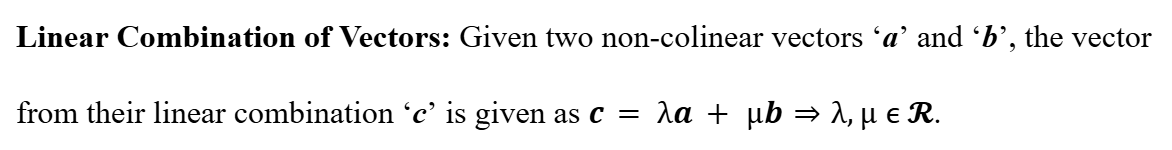
Subtraction of Vectors
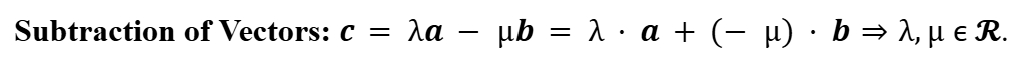
Coplanarity of Vectors (in 3D Space)
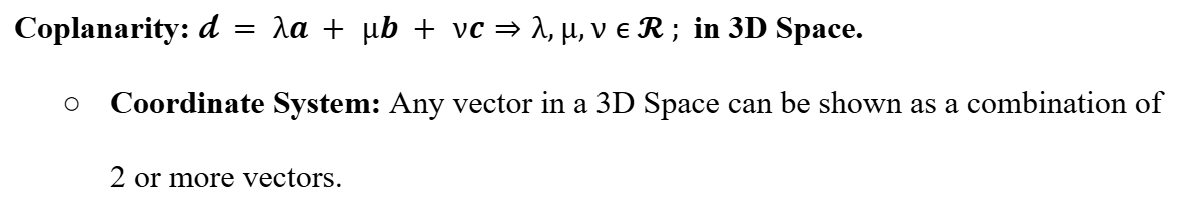
Vectors in Geometry
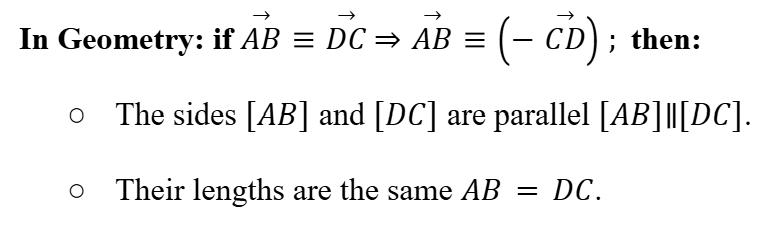
Base Vectors
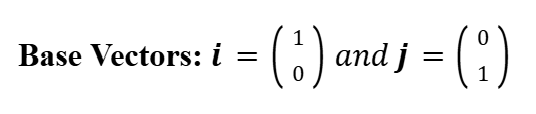
Position Vectors
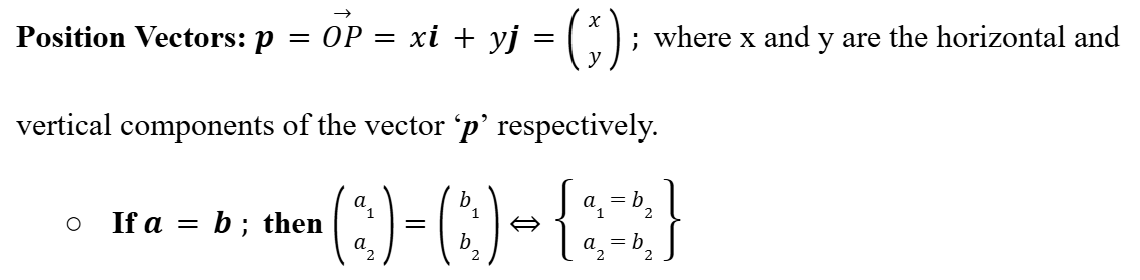
Vector Addition
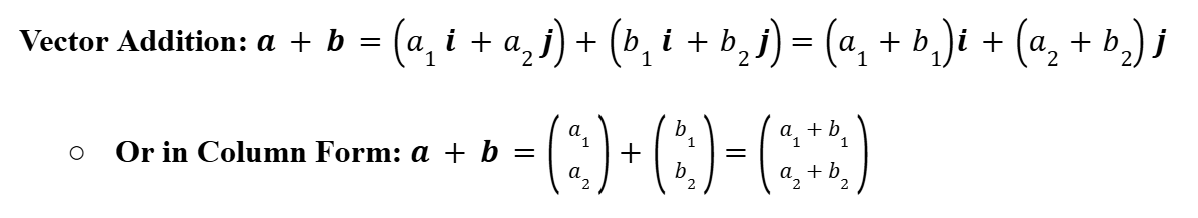
Multiplication by a Scalar (Vector Algebra)
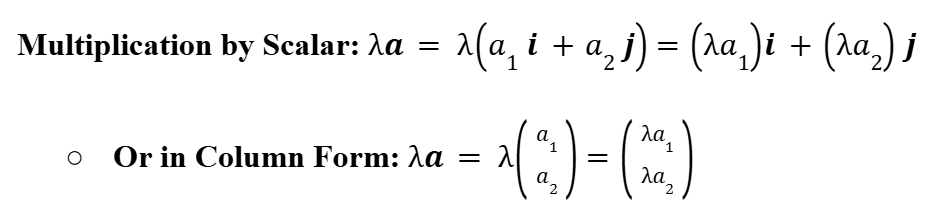
Linear Combination (Vector Algebra)
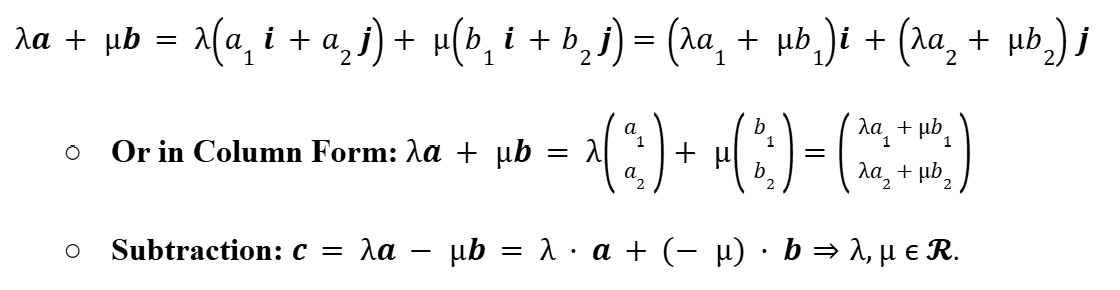
Finding Position Vectors from Coordinate Points
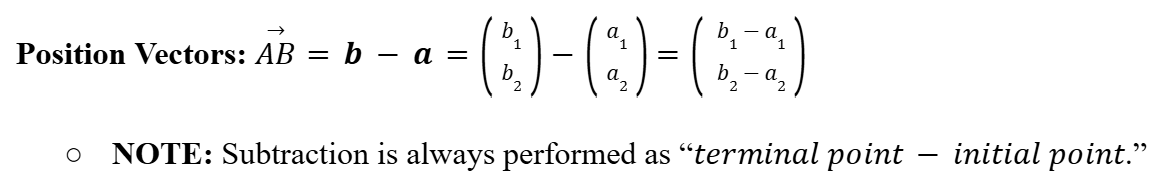
3D Algebra (Vectors)
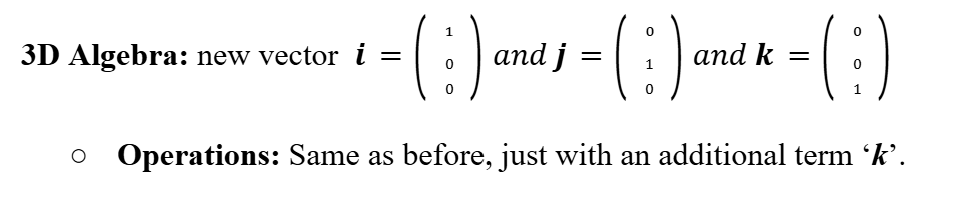
Magnitude of a Vector
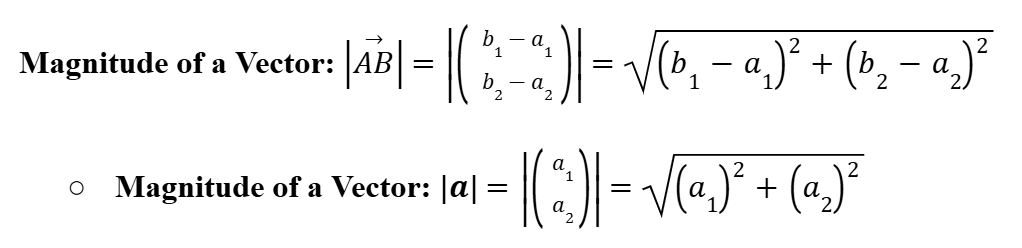
Unit Vectors
Unit vectors are vectors with a magnitude of 1 in any direction, any vector can now be represented as its parallel unit vector.
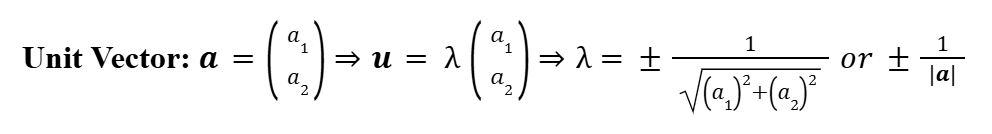
Scalar/Dot Product
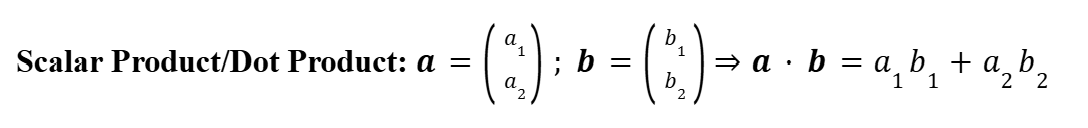
Geometric Definition (Scalar/Dot Product)
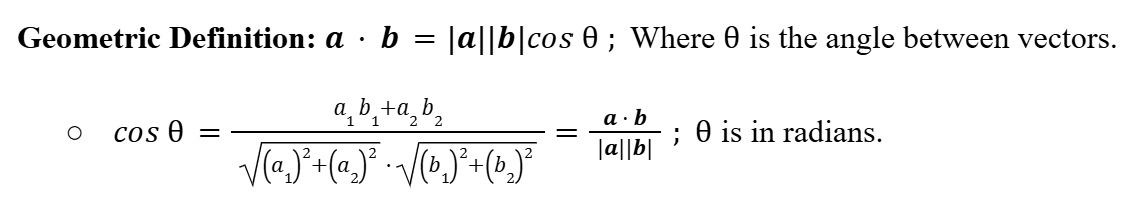
Zero Dot Product (Vectors)
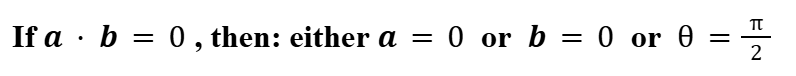
Properties of Scalar/Dot Product (Vectors)