Virology 12-Prions
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is a prion?
A misfolded, pathogenic isoform of a normal host protein (PrPc) that becomes PrPsc and is infectious despite containing no nucleic acid.
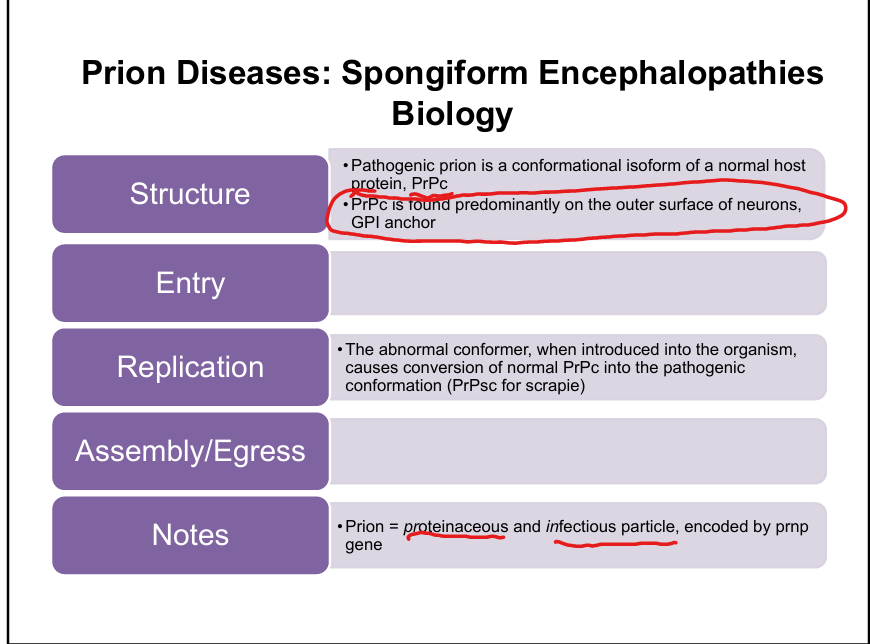

Where is normal PrPc found?
On the outer surface of neurons, attached via a GPI anchor.
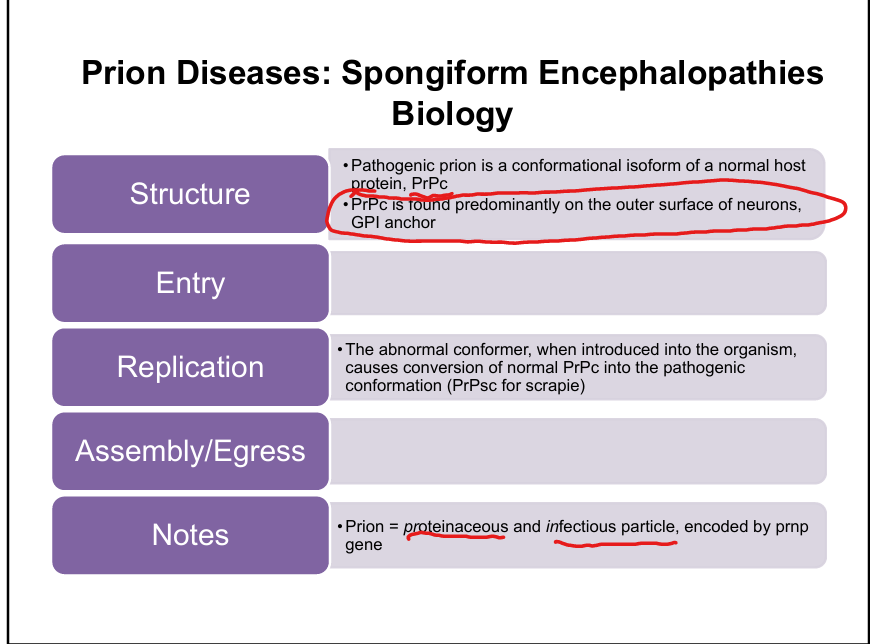

What is the key pathogenic mechanism of prion disease?
PrPsc induces conformational change of normal PrPc → autocatalytic cascade → accumulation of misfolded protein.


What is the hallmark pathology of prion diseases?
Spongiform change: vacuolation of neurons and glial cells, neuronal loss, astrocytosis, amyloid plaques.


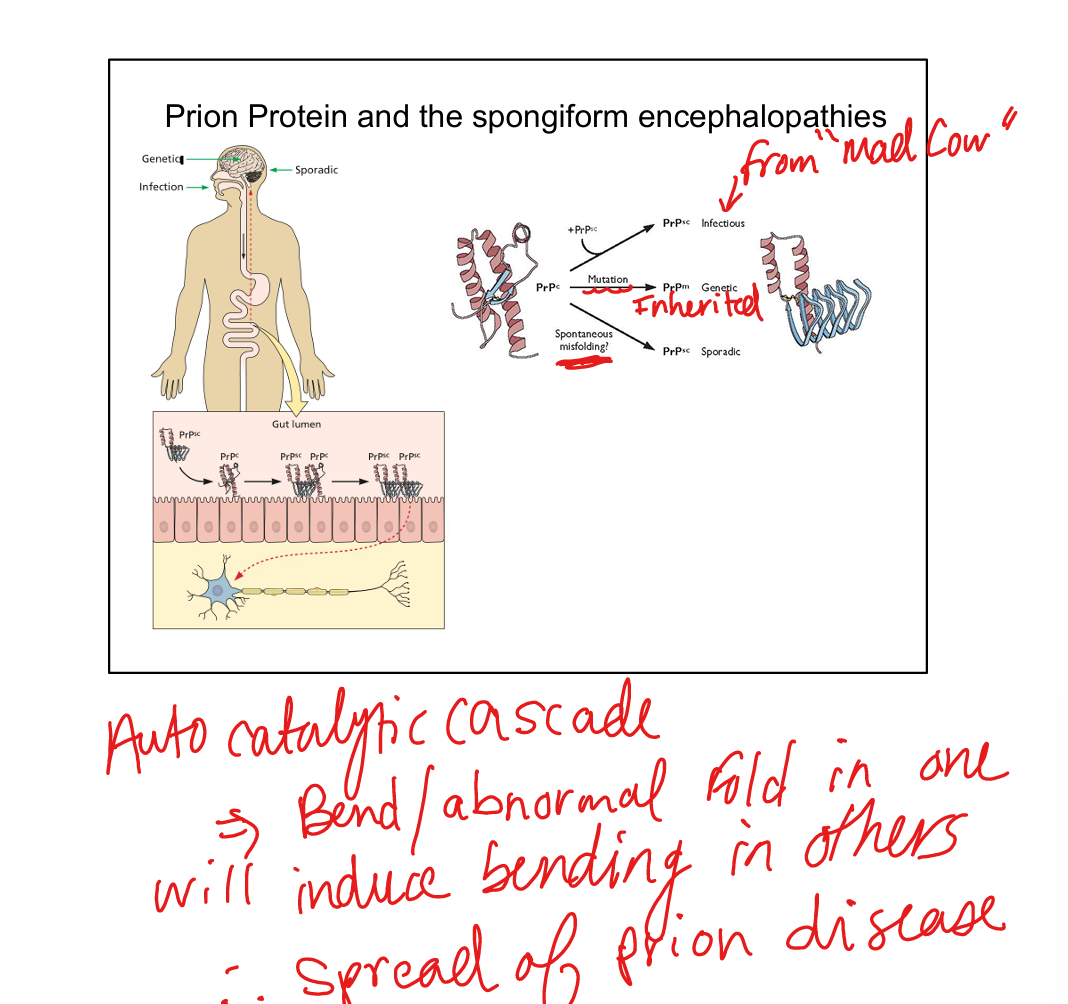
What are the three major categories of prion diseases?
Infectious (transmitted), familial (genetic prnp mutation), sporadic (spontaneous misfolding).

What is the most common form of human prion disease?
Sporadic Creutzfeldt‑Jakob disease (CJD), accounting for ~65% of cases.
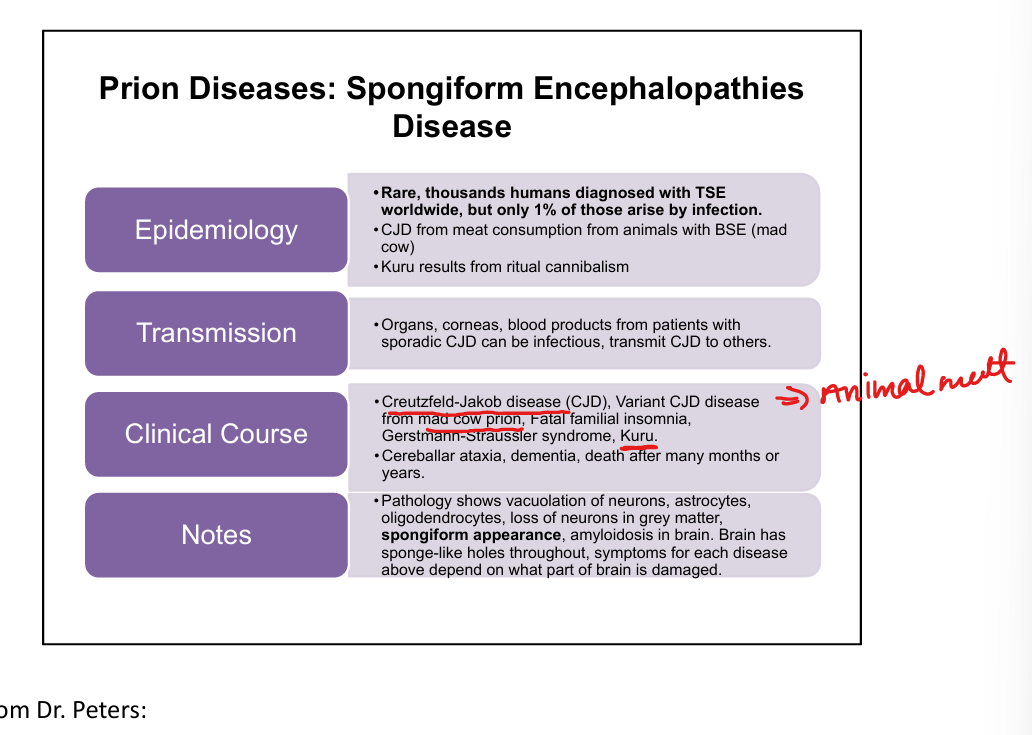

How can prion diseases be transmitted?
Contaminated organs, corneas, blood products; ingestion of infected tissue (e.g., BSE beef); ritual cannibalism (Kuru).
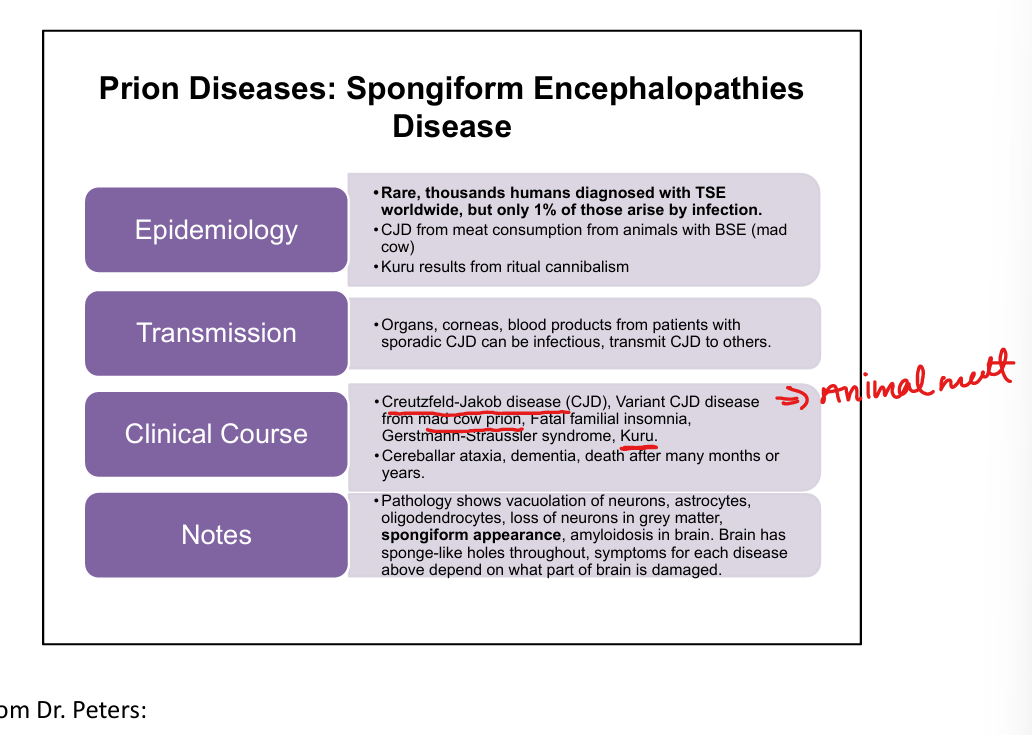

What are the major human prion diseases?
CJD-Creutzfield-Jakob Disease, variant CJD from Mad Cow Disease, Kuru(eating brain of person with CJD), Fatal Familial Insomnia, Gerstmann‑Sträussler‑Scheinker syndrome.
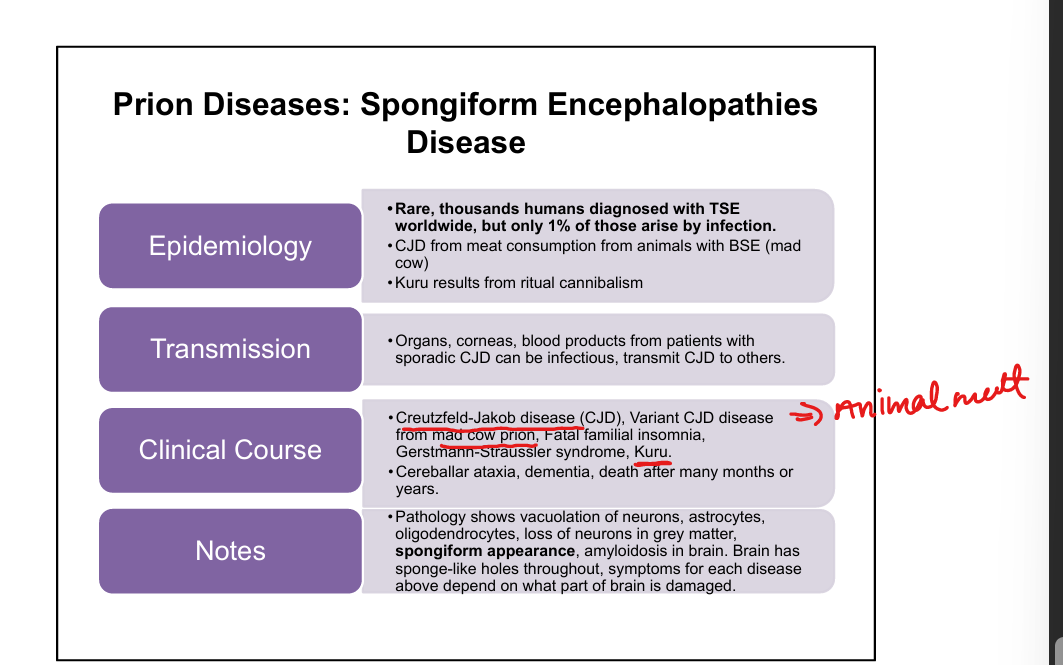

What is the classic triad of CJD?
Rapidly progressive dementia, myoclonus, ataxia.
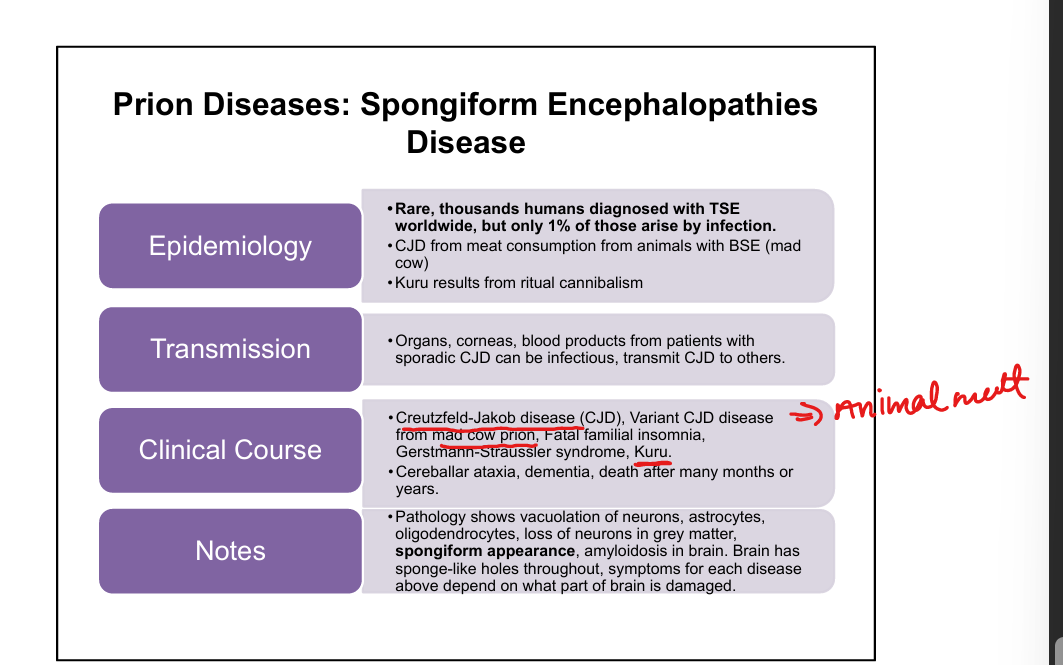

What distinguishes variant CJD from classic CJD?
Younger patients, psychiatric symptoms early, longer course, linked to BSE (“mad cow”).
What is Kuru associated with?
Ritual cannibalism; presents with cerebellar ataxia, tremors, emotional lability (“laughing sickness”).
What is Fatal Familial Insomnia?
Autosomal dominant prnp mutation causing progressive insomnia, autonomic dysfunction, hallucinations, and death.
What is Gerstmann‑Sträussler‑Scheinker syndrome?
Genetic prion disease with cerebellar ataxia, dysarthria, and slower progression than CJD.
What neurological findings are common across prion diseases?
Ataxia, myoclonus, rapidly progressive dementia, behavioral changes, pyramidal/extrapyramidal signs.
How is variant CJD acquired?
Consumption of beef contaminated with BSE prions (“mad cow disease”).
What animal prion diseases pose potential human risk?
Chronic wasting disease (CWD) in deer/elk/moose; BSE in cattle.


What percentage of prion diseases are infectious?
Only ~1%; most are sporadic or genetic.
What is the treatment for prion diseases?
None; universally fatal.
What precautions should hunters take regarding chronic wasting disease?
Avoid sick animals; wear gloves; avoid brain/spinal tissue; bone out meat; wash hands thoroughly.