PCOL3022 Lecture 7: Transporters
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1
New cards
Difference between receptors, ion channels, and transporters
Receptors - Ligand interacts with the extracellular domain and does not enter the cell
Ion channels - Allows ions to passively diffuse into the cell (with electrochemical gradient)
Transporters - Moves substrates/everything into the cell against an electrochemical gradient
Ion channels - Allows ions to passively diffuse into the cell (with electrochemical gradient)
Transporters - Moves substrates/everything into the cell against an electrochemical gradient
2
New cards
Difference between passive and active transport
Passive - Facilitated diffusion / The movement of molecules across the cell membrane via the aid of a membrane protein
(e.g. Na+-independent glucose transporter)
Active - Requires energy, moves substrate against a concentration gradient
(a) Primary - Energy comes from light/ Direct hydrolysis of ATP
(e.g. Na+K+ ATPase)
(b) Secondary - Uses pre-existing ion gradients / Indirectly coupling transport with another molecule that is moving along its gradient
(e.g. plasma membrane glutamate transporter)
(e.g. Na+-independent glucose transporter)
Active - Requires energy, moves substrate against a concentration gradient
(a) Primary - Energy comes from light/ Direct hydrolysis of ATP
(e.g. Na+K+ ATPase)
(b) Secondary - Uses pre-existing ion gradients / Indirectly coupling transport with another molecule that is moving along its gradient
(e.g. plasma membrane glutamate transporter)
3
New cards
Passive transport example
- Na+ independent glucose transporters
4
New cards
Primary active transporters examples
- Pumps
- Na/K ATPase
- Na/K ATPase
5
New cards
Secondary active transporters example
- Plasma membrane glutamate transporter
- Uses pre-existing ion gradients
- Uses pre-existing ion gradients
6
New cards
Neurotransmitter Transporters location
- Post- and pre-synaptic neurons
- Glial cells
- Glial cells
7
New cards
Neurotransmitter Transporters Function
- To clear neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft
8
New cards
Neurotransmitter transporter type of transport
Secondary active
9
New cards
What is the role of glutamate and NSS family transporters?
- Glutamate family transporters regulate extracellular glutamate concentrations to maintain dynamic synaptic signaling processes
- NSS family transporters regulate termination of neurotransmission by rapid removal of neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft
- NSS family transporters regulate termination of neurotransmission by rapid removal of neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft
10
New cards
Glutamate transporter family responsibility
- Only responsible for glutamate and aspartate
11
New cards
What are glutamate transporters called?
- VLGUTs (not studied)
- EAATs (excitatory amino acid transporters)
- EAATs (excitatory amino acid transporters)
12
New cards
Glutamate transporters co-transports...
1 glu-
3 Na+
1 H+
Counter transport of 1 K+
- Can maintain a 10^6 fold gradient across the membrane
3 Na+
1 H+
Counter transport of 1 K+
- Can maintain a 10^6 fold gradient across the membrane
13
New cards
How many subtypes of glutamate transporters are there?
- EAATs have 5 subtypes, with 50-60% amino acid identity
- EAATs are ~1% of total brain membrane proteins
- EAATs are ~1% of total brain membrane proteins
14
New cards
EAAT Subtype 1
- Cell type: Glia
- Found in astrocytes
- CNS Location: Widely expressed
- Found in astrocytes
- CNS Location: Widely expressed
15
New cards
EAAT Subtype 2
- Cell type: Glia
- Found in astrocytes
- CNS Location: Widely expressed
- Found in astrocytes
- CNS Location: Widely expressed
16
New cards
EAAT Subtype 3
- Cell type: Neuron
- Found on post-synaptic neurons
- CNS Location: Widely expressed, kidneys
- Found on post-synaptic neurons
- CNS Location: Widely expressed, kidneys
17
New cards
EAAT Subtype 4
- Cell type: Neuron
- Found on post-synaptic neurons
- CNS Location: Cerebellum
- Found on post-synaptic neurons
- CNS Location: Cerebellum
18
New cards
EAAT Subtype 5
- Cell type: Neuron
- CNS Location: Retina *can be on presynaptic neuron
- CNS Location: Retina *can be on presynaptic neuron
19
New cards
Where can you find EAAT Subtypes 1 and 2?
Astrocytes
20
New cards
Where can you find EAAT Subtypes 3 and 4?
- Post-synaptic neurons
- To "mop up" excess glutamate
- To "mop up" excess glutamate
21
New cards
What do EAATs transport?
- Coupled to Na+, H+ with K+ counterion
- IN: Glu-, 3x Na+, H+
- OUT: K+
- Net transfer of 2+
- Can maintain a million-fold gradient across the membrane
- IN: Glu-, 3x Na+, H+
- OUT: K+
- Net transfer of 2+
- Can maintain a million-fold gradient across the membrane
22
New cards
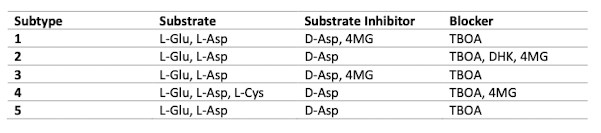
EAAT common substrates, substrate inhibitors, and blockers
- Substrate = L-glutamate/L-aspartate
- Substrate inhibitors = D-aspartate
- Blocker = TBOA
- Substrate inhibitors = D-aspartate
- Blocker = TBOA
23
New cards
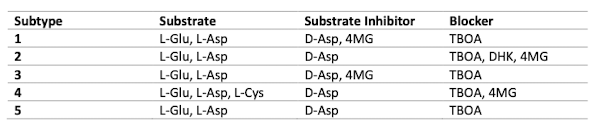
What is the substrate inhibitor for EAATs 1 and 3, but blocker for EAATs 2 and 4?
4-MG
24
New cards
What is the Na+-dependent aspartate transporter from archaea?
Glt(Ph)
25
New cards
What is the competitive inhibitor (vs L-Asp) of Glt(Ph)? Benzene ring opened the ring
TBOA
26
New cards
What does TBOA's benzene ring prevent?
- Prevent HP2 from closing
- Thus preventing necessary conformational change
- Thus preventing necessary conformational change
27
New cards
Structure of Glt(Ph)
- From Pyrococcus horikoshii (archaea -- easier to crystallise, stable under lab conditions)
- Trimer of 3 identical subunits, each capable of transport
- 37% identity to human EAAT 2
- Trimer of 3 identical subunits, each capable of transport
- 37% identity to human EAAT 2
28
New cards
EAAT Excitotoxicity Process
- Ischaemia (lack of oxygen in the brain)
- Depletion of glucose
- Reduction of ATP
- Causes failure of Na+/K+ ATPase
- Causes rundown of membrane potential, uncoordinated action potential generation
- Causes excessive Glu release + Glutamate Transporter failure
- Cause excessive stimulation of Glutamate Receptors
- Causes excessive Ca2+ influx
- Causes activation of protease, lipases, NO synthase, endonucleases
- Causes cell death (necrosis/apoptosis)
- Depletion of glucose
- Reduction of ATP
- Causes failure of Na+/K+ ATPase
- Causes rundown of membrane potential, uncoordinated action potential generation
- Causes excessive Glu release + Glutamate Transporter failure
- Cause excessive stimulation of Glutamate Receptors
- Causes excessive Ca2+ influx
- Causes activation of protease, lipases, NO synthase, endonucleases
- Causes cell death (necrosis/apoptosis)
29
New cards
Glutamate Transporters as Drug Targets
- For neurodegenerative conditions: Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Motor neurone disease
30
New cards
NSS Family
Neurotransmitter sodium symporter
31
New cards
What NTs are the transporters for in NSS Family?
- Gly, DA, GABA, NA, 5HT
32
New cards
NSS Family coupled to...
- Co-transport of Na+ and Cl-
33
New cards
What are transporter/s for Neurotransmitter Gly? Function? Therapeutics?
- GlyT1 and GlyT2
- Function: Transport glycine
- Therapeutics: Pain, antipsychotics
- Function: Transport glycine
- Therapeutics: Pain, antipsychotics
34
New cards
Gly T1
- 2x Na+, Cl-
- Slightly less effective
- Found in excitatory neurones where some low level of Gly is required as a co-agonist of NMDA-Rs
- Slightly less effective
- Found in excitatory neurones where some low level of Gly is required as a co-agonist of NMDA-Rs
35
New cards
Gly T2
- 3x Na+, Cl-
- More effective
- Found in inhibitory neurones where no Gly is required as an agonist
- More effective
- Found in inhibitory neurones where no Gly is required as an agonist
36
New cards
Pharmacological relevance of Gly T1
- Gly T1 inhibitors: sarcosine, NFPS
- Elevates [Gly] at excitatory synapses to increase NMDA-R stimulation
- Treats schizophrenia (thought to be linked to reduced NMDA-R activity)
- Elevates [Gly] at excitatory synapses to increase NMDA-R stimulation
- Treats schizophrenia (thought to be linked to reduced NMDA-R activity)
37
New cards
Pharmacological relevance of Gly T2
- Enhance glycinergic inhibition in spinal cord
- Reduces excitatory transmissions of pain signals to brain
- Reduces perception of pain
- Could be useful in sp
- Reduces excitatory transmissions of pain signals to brain
- Reduces perception of pain
- Could be useful in sp
38
New cards
What are transporter/s for Neurotransmitter GABA? Function? Therapeutics?
- GAT 1-4
- Function: Transport ABA
- In neurons/glial cells throughout CNS
- Therapeutics: Anticonvulsants drugs
- Function: Transport ABA
- In neurons/glial cells throughout CNS
- Therapeutics: Anticonvulsants drugs
39
New cards
GATs
- Found in neurons and glial cells in CNS
- Coupled to 2x Na+, Cl-
- Transporter inhibition increases inhibitory GABA transmission
- Used as a anticonvulsant
- E.g. tigabine, nipecotic acid (GAT1 selective)
- Coupled to 2x Na+, Cl-
- Transporter inhibition increases inhibitory GABA transmission
- Used as a anticonvulsant
- E.g. tigabine, nipecotic acid (GAT1 selective)
40
New cards
Catecho
- DAT (DA): 2x Na+, Cl-
- Drugs of abuse: Amphertamine, meth, cocaine, MTPT
- NET (NA): Na+, Cl-
- Drugs of abuse: Cocaine, meth, amphetamines
- SERT (5HT): Na+, Cl- (potentially K+ as counterion)
- Drugs of abuse: MDMA, cocaine
- Drugs of abuse: Amphertamine, meth, cocaine, MTPT
- NET (NA): Na+, Cl-
- Drugs of abuse: Cocaine, meth, amphetamines
- SERT (5HT): Na+, Cl- (potentially K+ as counterion)
- Drugs of abuse: MDMA, cocaine
41
New cards
Methamphetamine effects
- Meth has more exaggerated effects and higher addiction risk
- Effects: Alertness, euphoria, agitation, energy, increased libido, nausea, irritability (more intense than amphetamine)
- Effects: Alertness, euphoria, agitation, energy, increased libido, nausea, irritability (more intense than amphetamine)
42
New cards
Metham
- Cravings, withdrawal-depression, weight loss, psychosis, meth mouth
43
New cards
Methamphetamine overdose
- Brain damage, paranoia, delusions, hallucinations, death by stroke, heart failure, cardiac arrest
44
New cards
Amphetamine mechanism of action (AMP MOP)
- AMP is a false substrate of DAT
- AMP reduces DA uptake AND causes reverse transport of DA
- Competes with DAT/NET AMP accumulates in the cytoplasm, DA is elevated in synapse
- Depletes cystolic DA - reverse transport
- AMP inhibits MAO to prevent NT breakdown
- Competes with VMAT to deplete DA storage in vesicle
- AMP reduces DA uptake AND causes reverse transport of DA
- Competes with DAT/NET AMP accumulates in the cytoplasm, DA is elevated in synapse
- Depletes cystolic DA - reverse transport
- AMP inhibits MAO to prevent NT breakdown
- Competes with VMAT to deplete DA storage in vesicle
45
New cards
Cocaine Pharmacology
- Stimulant and appetite suppressant
- Na+ channel blocker (Used as a topical anaesthetic)
- Inhibits DAT, SERT, and NET
(Competitive blocker of NT transport -- molecule is too large to pass through transporter)
- Na+ channel blocker (Used as a topical anaesthetic)
- Inhibits DAT, SERT, and NET
(Competitive blocker of NT transport -- molecule is too large to pass through transporter)
46
New cards
dDAT
- Drosophila dopamine transporter
- 12 x TMD, "shot glass" shape
- Substrate buried within
- Co-transport of 2 x Na+, Cl-
- Substrate and Na+ binding sites are similar to all of the NSS family
- 12 x TMD, "shot glass" shape
- Substrate buried within
- Co-transport of 2 x Na+, Cl-
- Substrate and Na+ binding sites are similar to all of the NSS family