Cognitive Psych Exam 1
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
William Wundt
Focused on introspection; criticized for being too subjective.
Herman Ebbinghaus
Tested people on memorizing nonsense words like 'G5B'.
Mary Whiton Calkins
Studied the recency effect; first female president of the APA.
William James
Known for the 'tip-of-the-tongue' phenomenon and principles of psychology.
The Gestalt Approach
Emphasizes that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts; involves principles like closure, proximity, continuity, and similarity.
Gestalt
an overall quality that transcends the individual elements
Gestalt Psych
emphasizes we have basic tendencies to organize things and that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts
Behaviorism
Led by John B. Watson; focuses on observable reactions to stimuli rather than introspection.
Operational Definition
A precise definition specifying how a concept is to be measured.
Why did the Cognitive Revolution start…
people were disappointed with the behaviorist approach
Well known Cognitive Psychologists…
Jean Piaget with his focus on children’s thought processes & Noam Chomsky with linguistics and the concept of universal grammar
The birth of modern Cognitive Psych began in…
1956
Cognitive Psych in Present Times…
Enormous influence on the discipline of psych; issues with ecological validity; study of real life issues.
Cognitive Science:
an interdisciplinary field whose principal concern is answering questions about the mind and how it functions
Cognitive Psych Interdisciplinary Fields
cognitive psych, neuroscience, computer science, philosophy, linguistics (in some cases), sociology, anthropology, and economics
Cognitive Psychology
Synonym for cognition and refers to the cognitive approach in psychology
Cognition
Refers to mental activity, involving acquisition, storage, transformation, and use of knowledge. Related to knowledge processes.
Attention
concentration of mental activity
Top-down processing
Mental focus directed by objectives; attending to specific stimuli.
Bottom-up processing
Attention captured by stimuli from the environment.
Recency Effect
observation that our recall is especially accurate for the final items in a series of stimuli
Ebbinghaus’ Forgetting Curve
A graphical representation of how information is lost over time when there is no attempt to retain it.
Saccadic Eye Movement
series of little jumps of the eye bring the center of the retina (Fovea) over the words being read
Fixation
period between two saccadic movements where your visual system pauses briefly in order to acquire information that is useful for comprehending the written text
Working Memory
Brief immediate memory for the limited amount of material that you are currently processing
Working-Memory Approach
Our immediate memory is a multipart system that temporarily holds and manipulates information while we perform cognitive tasks
Long-term Memory
Memory system that retains information accumulated throughout one's lifetime.
Chunking
Grouping information into larger units to enhance memory + strongly associated components
Cognitive Neuroscience
Combines research from cognitive psychology with brain structure and function assessments.
Phonological Loop
Component of working memory that processes auditory information for a short period of time.
What impairs visual search tasks…
The isolated-feature/combined feature effect & the feature present/feature-absent effect
The isolated-feature/combined feature effect
the target differed from the irrelevant items in display w/ respect to a simple feature such as color, observers could quickly detect target
The feature present/feature-absent effect
people can typically locate a feature that is present more quickly than a feature that is absent.
Cerebral Cortex
Outer layer of the brain crucial for cognitive processes.
Social Cognitive Neuroscience
Exploration of cognitive processes in social interactions using neuroscience techniques.
Brain Lesions
destruction of the brain in an area most often by strokes, tumors, or blows to the head and other accidents
Mind Wandering
Shift of thoughts from external environment to internal processing.
Mindless Reading
Your eyes may move but you’re reading without processing the meaning of the text.
Thought Suppression
the attempt to eliminate thoughts, ideas, and images related to an undesirable stimulus
Ironic Effects of Mental Control
a term used by Wegner to describe how our efforts can backfire when we attempt to control the contents of our consciousness
Empirical Evidence
scientific evidence obtained through careful observation and experimentation
Introspection
Carefully trained observers analyzing their own sensation and report them
AI (Artificial Intelligence)
branch of computer science that seeks to explore human cognitive processes with computer models that show “intelligent behavior” and can accomplish the same tasks that humans do.
Pure AI
an approach which designs a program to accomplish a cognitive task as efficiently as possible
Computer Modeling
Attempts to take human limitations into account and thus create a program that performs a cognitive task in an analogous way to how humans would solve the problem.
The Computer Metaphor of the Mind and Information Processing
a metaphor for human cognitive processes that describes them like a computer. Receiving input, storing memory, performing operations on it and producing an output.
The Connectionist Approach
argues that cognitive process can be best understood in terms of linked networks
Spreading Activation Theory
an analogous model for the association of ideas, memories, and the like, based on the notion that activation of one item stored in memory travels through associated links to activate another item.
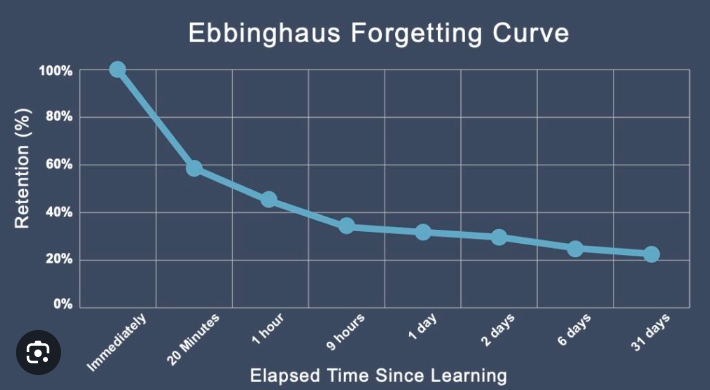
Ebbinghaus’ Forgetting Curve
a graphical representation that shows how quickly info is forgotten over time.
Gradual Decay
After the initial drop, the rate of forgetting slows down over time
Cognitive Psych in Present Times:
Enormous influence on the discipline of psych; issues with ecological validity; study of real life issues.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) / rTMS
Uses magnets to introduce activity in a certain region of the Brian. Likened to a “temporary brain lesion.” Only works on outer brain regions
Event-Related Potential Technique (ERP)
Uses electrodes on the outside of a person’s skull…even through hair.
Positron Emissions Tomography (PET scan)
Similar to an MRI
Uses radioactive tracer chemicals to allow the study of blood flow
Allows us to see areas using lots of blood.
Higher Spatial Resolution Data
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
Uses oxygen to track brain activity
Using high blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast
More precise that PET & no need for radioactive tracer
Divided-Attention Task
trying to pay attention to 2 or more simultaneous stimuli
Multitasking
trying to accomplish two or more tasks at the same time
Task Switching Delays
It takes us time to change tasks, causing us to work more slowly and make more errors during the transitions
Selective Attention
paying attention to certain kinds of info, while ignoring other ongoing info
Cocktail Party Effect
Even if you are paying close attention to one conversation, you may notice if your name is mentioned in a nearby conversation
Working Memory Capacity
the brief, immediate memory for material that we are currently processing
Phobic Disorder
an excessive fear of a specific object or situation
Attention Bias
situation/phenomenon in which people pay extra attention to some stimuli or some features
Cognitive-Behavioral Approach
psychological problems arise from inappropriate thinking (cognitive factors) and inappropriate learning (behavioral factors)
Fixation
period between two saccadic movements where your visual system pauses briefly in order to acquire information that is useful for comprehending the written text
Perceptual Span
the number of letters and spaces that we perceive during a fixation
Parafoveal Preview
the fact that readers can access information about upcoming words even though they are currently fixated on a word to the left (in English) of those words
Regressions
moving your eyes backward to earlier material in the sentence or passage. Rereading
Parietal Lobe
an area of the brain which processes your sense of touch and assembles input from your other senses into a form you can use
Unilateral Spatial Neglect
A condition in which a person ignores part of his or her visual field often as result to damage to the Parietal lobe
The Orienting Attention
a network of brain regions responsible for the kind of attention required for visual search, in which you must shift your attention around to various spatial locations
The Executive Attention Network
a network of brain regions responsible for the kind of attention we use when a task focuses on conflict (inhibition)
Split-phrase Switching
in dichotic listening task If you were told to attend to the right ear, you should just repeat that message with no problems, even though it is a confusing sentence. INSTEAD, almost all participants inadvertently switched to shadoring the other ear because that message “finished”
Consciousness
the awareness people have about the outside world and about their perceptions, images, thoughts, memories, and feelings
Dichotic Listening Task
1 message presented to left ear & a different message is presented to the right
The Stroop Task
Online questionnaire related to female body image (shape, weight, & eating + neutral words)
Women took longer to read words related to shape v.s. to control words
They were especially likely to have high scores on the Eating Attitudes Test (risk for developing eating disorders)
Visual Search Task
Find a target in a visual display w/ numerous distractors
More accurate @ identifying targets if it appears frequently
Variables influencing visual search
Illusory Conjunction
wrong combo of features; occurs during attention overload or distraction. Features are processed independently. Role of top-down processing
Blindsight
Vision w/o awareness; damage to the visual cortex.
People can still identify some visual attributes of stimulus reported a “not seen,” perception of stimulus (w/o conscious awareness) may be possible
Small portion of the info from the retina travels to other locations on the cerebral cortex, outside the visual cortex.
Research on consciousness demonstrate that “how things seem” is not necessarily “how things are”
Visual stimulus may be identified by info registered in other cortical locations
Damage to the visual cortex. Has no vision but still possesses the ability to move in ways that mimic those with sight. (not bumping into objects) Typically seen in cases with people who’ve gone blind later in life
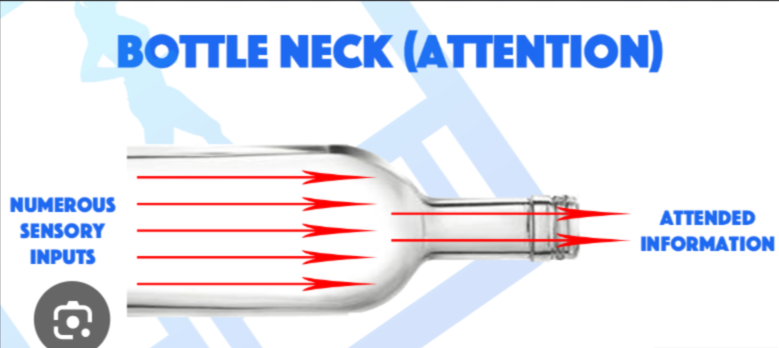
Bottleneck Theory’s:
Models: 1.Broadbent’s, 2. Treisman’s, 3. Split-phrase Switching, 4. Deutsch & Deutsch
Narrow passageways
Info either passes through bottleneck or is lost
Too simple; underestimate flexibility
Info not lost @ just one phase of the attention process
Broadbent’s Model
Series of info-processing channels
Sensory buffer processes physical characteristics
Limit processing to a single stream
Everything else is blocked out
Treisman’s Model
Similar to Broadbent, but the filter is different
Other info isn’t completely blocked
Value analogy: other info gets less attention unless you reach a threshold
Still can’t focus on everything
Split-phrase Switching Model
Recieving different info in each ear
Deutsch & Deutsch Model
Late selection model
We can process all stimuli for meaning
No filter
We can only respond to a limited subset of stimuli
Allows for subliminal messaging
Short-term Memory
the memory system responsible for holding on to a small amount of information that has been recently taken from the environment
Rehearsal
repeating the items to remember silently
Serial Position Effect
The U shape relationship between a words position in a list and its probability of accurate recall.
Primacy Effect
Better recall for items at the beginning of the list
Semantics
the meaning of words and sentence
Proactive Interference (PI)
When people have trouble learning new material because previous material interferes with new learning
Sensory Memory
a storage system that records information from each of the senses
Control Processes
intentional strategies, such as rehearsal, that people may use to improve their memory
Acoustic Confusions
when people confuse similar sounding stimuli
Visuospatial Sketchpad
processes both visual and spatial information
Episodic Buffer
temporary storehouse that can hold and combine information from the phonological loop, the visuospatial sketchpad, and long-term memory
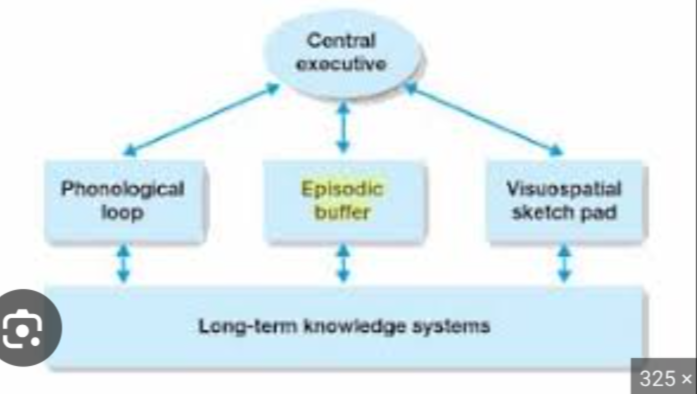
Central Executive
integrates information from the phonological loop, the visuospatial sketchpad, the episodic buffer, and long-term memory
Atkinson and Shiffrin's Model of Information Processing
Info processing approach
mental processes are similar to the operations of computer
Info progresses through a series of stages, one step @ a time
Baddeledy’s Model of Working Memory
people performed quickly & quickly and accurately on both these 2 simultaneous tasks
Dr. Oberauer’s Model
Maintianing structural representations by dynamic bindings
Manipulating structural representations
Flexible configurations
Partial decoupling from long-term memory
Controlled retrieval from long-term memory
Encoding of new structures into long-term memory
Brown/Peterson & Peterson Technique
present some items to be remembered; count backwards by 3 then attempt recall. Material held in short term is frequently forgotten in a minute.