div 1 lab practical 2
1/215
Earn XP
Description and Tags
suny esf
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
216 Terms
Juniperus Genus is within the family
Cupressaceae with dimoprhic foliage and flower-like cones that remain on the branches
Larix Genus is within the family
Pinaceae with deciduous foliage
Pinus Genus within the family
Pinaceae with needles in groups of 2,3 or 5.
cones with an apophysis
Picea Genus within the family
Pinaceae with individual needles on sterigmata
Abies Genus within the family
Pinaceae with individual flattened, aromatic needles
cones with excreted bracts
What is the name given to the groups of needles
Fasicles
The two genera within the family Cupressaceae with deciduous foliage
Taxodium and Metasequoia
Arborvitae, whitecedar, redcedar
Thuja
You saw a single species baldcypress
Taxodium
Cypress, false cypress
Chamaecyparis
There is a single species, dawn redwood
Metasequoia
Douglas- fir
Pseudotsuga
Fir
Abies
Hemlock
Tsuga
Juniper
Juniperus
Larch
Larix
Pine
Pinus
Spruce
Picea
Cupressaceae OR Pinaceae: Metasequoia
Cupressaceae
Cupressaceae OR Pinaceae: Taxodium
Cupressaceae
Cupressaceae OR Pinaceae: Thuga
Cupressaceae
Cupressaceae OR Pinaceae: Chamaecyparis
Cupressaceae
Cupressaceae OR Pinaceae: Juniperus
Cupressaceae
Cupressaceae OR Pinaceae: Abies
Pinaceae
Cupressaceae OR Pinaceae: Larix
Pinaceae
Cupressaceae OR Pinaceae: Picea
Pinaceae
Cupressaceae OR Pinaceae: Pinus
Pinaceae
Cupressaceae OR Pinaceae: Pseutosuga
Pinaceae
Cupressaceae OR Pinaceae: Tsuga
Pinaceae
Foliage — occurs singly, leaves circular leaf scar, aromatic
Fruit — cone with deciduous scales
Abies
Foliage — flattened sprays, finer texture
Fruit — peltate cone (exploding soccer ball), persistent
Chamaecyparis
Foliage - dimorphic
Fruit — berry-like
Juniperus
Foliage — produced on terminal shoots and spur shoots
Fruit — upright persistent cone
Larix
Foliage — occurs singly on sterigmata
Fruit — cone without apophysis or umbo
Picea
Foliage — occurs in fascicles of 2,3 or 5
Pinus
Foliage — occurs singly, elevated slightly off twig, buds sharp
Fruit — cone with exserted bracts
Pseuotsuga
Foliage — flattened sprays, evergreen
Fruit — upright, flower-like cone, persistent
Thuja
Sporophyte Dominant
is a defining character of Lycopodiophyta
Possession of microphylls
is a defining character of Lycopodiophyta
Sporangia-bearing sporophylls clustered into strobili
is a defining character of Lycopodiophyta
Club Mosses are most
conspicuous in winter
Club mosses remain green in the winter
in stark contrast to surrounding plants or snow.
Microphylls thickly cover stems that may or may not branch
in club mosses
In club mosses Mains tems may be
erect, prostrate or creeping.
club mosses develop roots
along a horizontal stem
in club mosses the horizontal stem is called a
rhizome
All club mosses are
dichotomously branched (forked)
In club mosses, strobili occur
at the end of an upright stem
Club mosses produce how many types of spores?
1
Club mosses are
homosporous
Spike mosses produce ____ types spores
2
spike mosses are
heterosporous
In spike mosses, megaspores are produced in a
megasporangium on a megasporophyll
megasporangium on a megasporophyll give rise to
female gametophytes
in spike mosses microspores produced in a microsporangium
on a macrosporophyll
microspores produced in a microsporangium on a macrosporophyll
give rise to male gametophytes
in spike mosses, both types of spores are produced in the same
strobilus
in spike mosses, both types of spores are produced in different
sporangia
A defining characteristic of Equisetidae is Jointed
stems and rough texture
A defining characteristic of Equisetidae is Leaves
whorled at the nodes
A defining characteristic of Equisetidae is Internodes are
ribbed and the ribs are strengthened with siliceous deposits
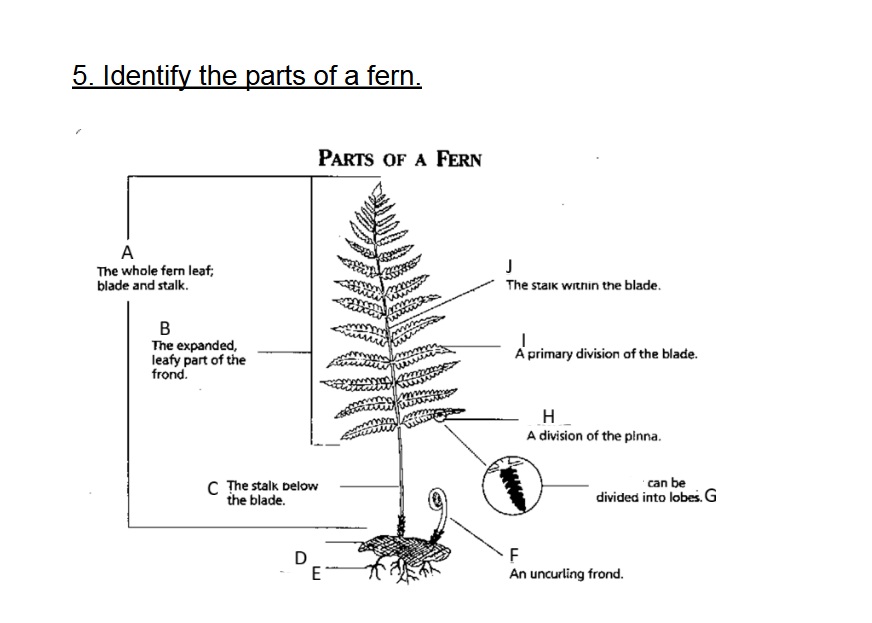
Identify A
Frond
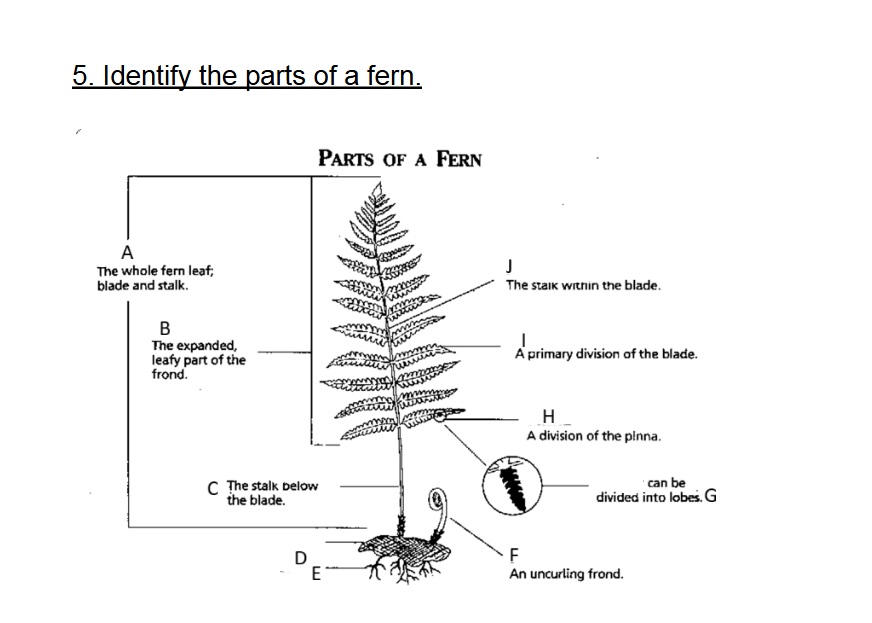
Identify B
Blade
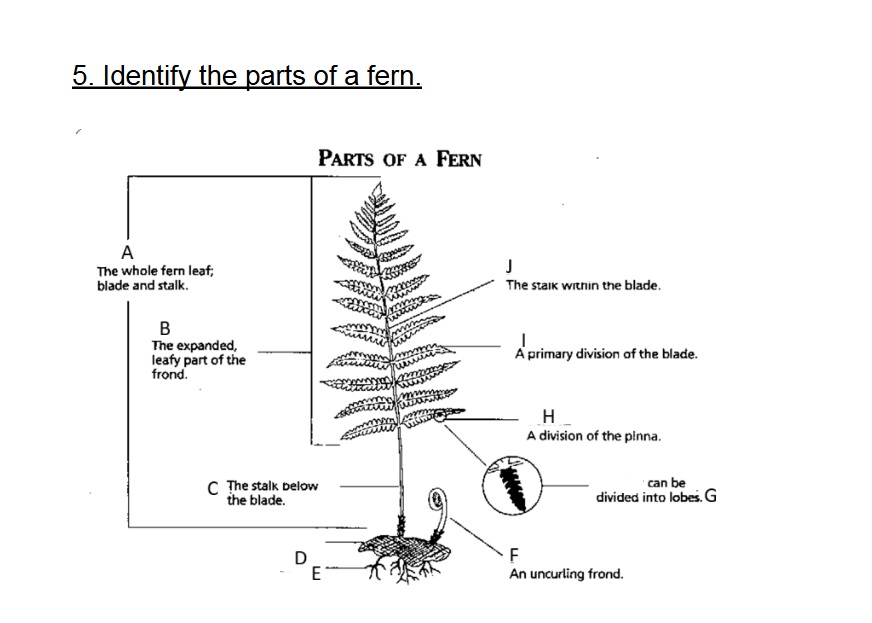
Identify C
Stalk/Stipe
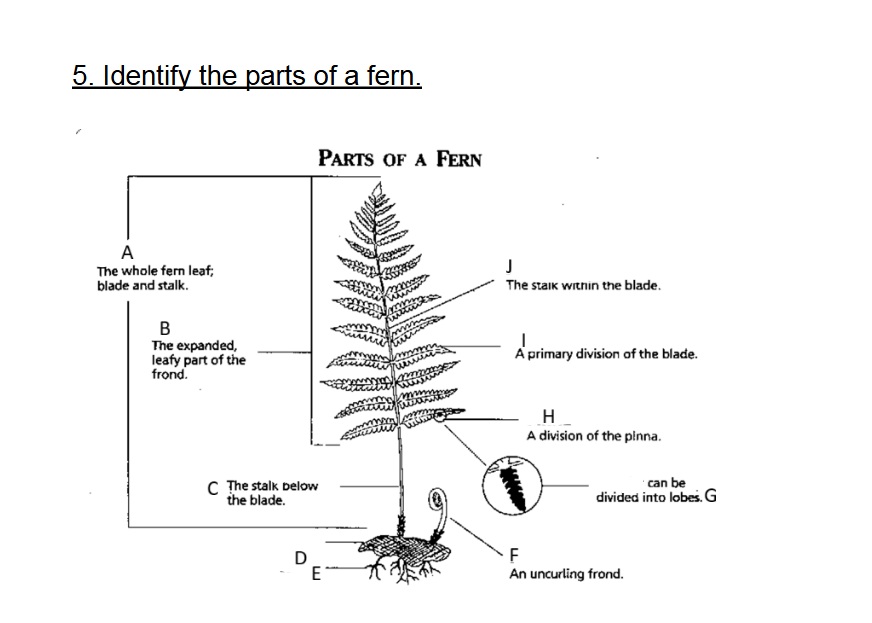
Identify D
Rhizome
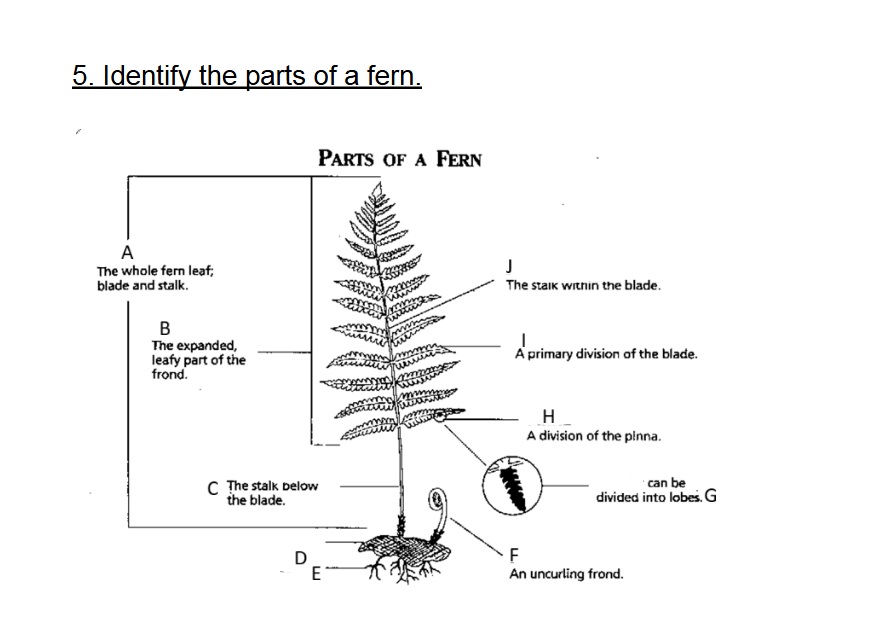
Identify E
Root
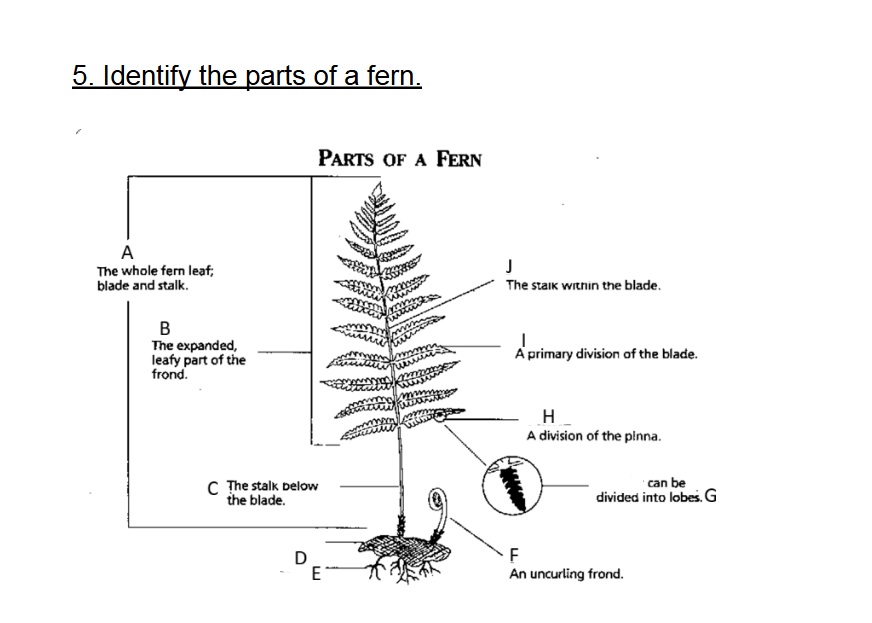
Identify F
Fiddlehead(Crosler)
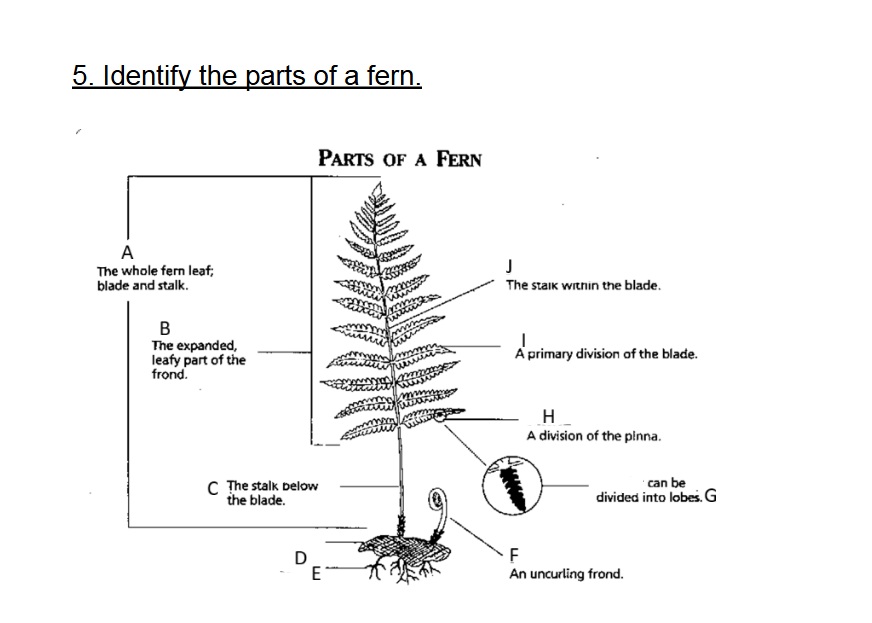
Identify G
Pinnule
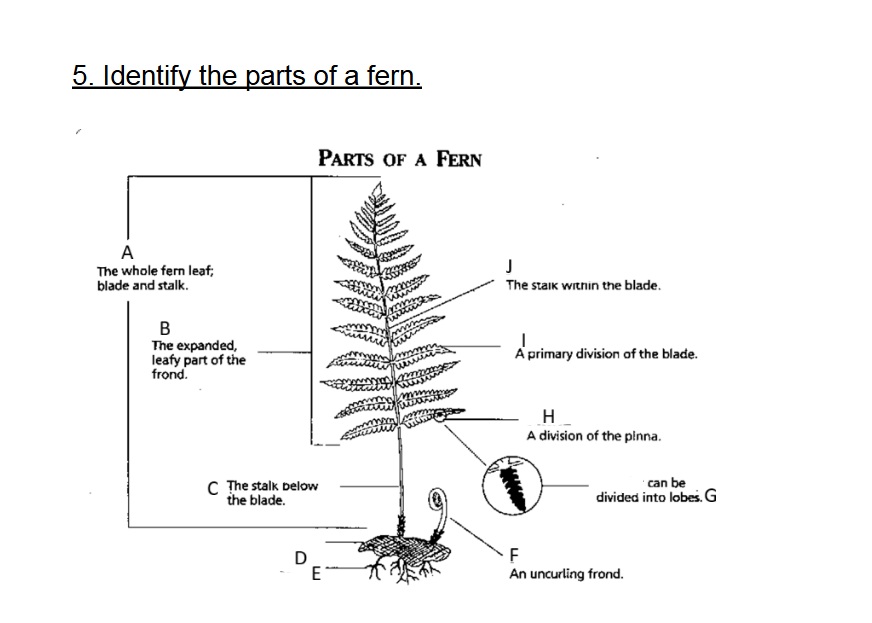
G on this chart can be divided into
lobes
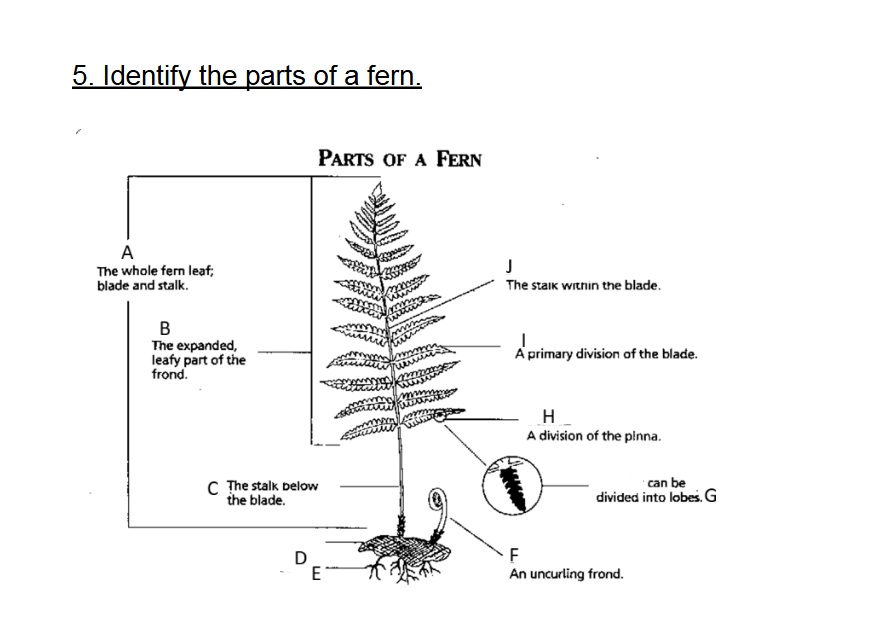
Identify H
Pinna
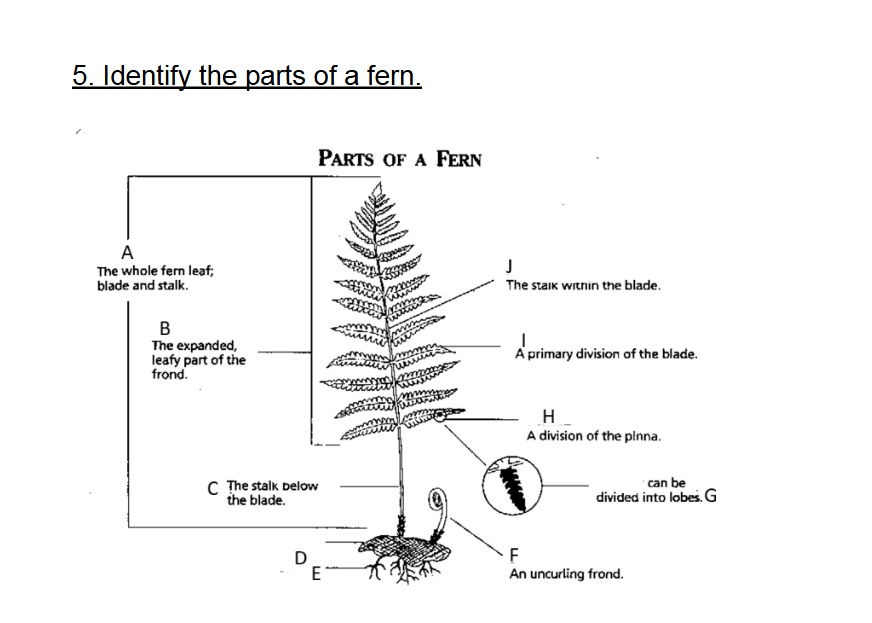
Identify I
Axis (Rachis)
The seedless vascular plants and gymnosperms covered are all
sporophyte-dominant.
The seedless vascular plants and gymnosperms are
Inconspicuous
short lived gametophytes
develope when spores germinate
short lived gametophytes develope when spores germinate
but the male and female gametes they produce untie to form a zygote
that zygote grows into the more
conspicuous often perennial sporophyte
Height, shape or outline of the frond CHARACTER STATES
slides no say ☹
growth form CHARACTER STATES
individual or in spiral like clumps
Blade dissection CHARACTER STATES
fronds can emerge individually, along a creeping rhizome or fronds can emerge in circular or clumped patterns.
Stipe color CHARACTER STATES
ferns can either be generally the came color or have color gradation
stipe texture, stipe grooving CHARACTER
grooved or not grooved
pinnae shape,
lobing, teeth, vein, patterning, position, sessile vs stalked
presence of reproductive parts on specialized fronds or structures that differ from sterile ones
sori arrangement and position
sori can be circular or linear, on the margin or away from the margin, or visible or non visible
presence and shape of induism
habitat
evolution: protection
seeds can have a thicker and harder coat than spores
evolution: nutrition
seeds can have a higher internal volume than spores, allowing for the storage of oils, nutrients and starch to start the embryos development
evolution: often a means of dispersal
seeds allow for new dispersal mechanisms such as passing through the digestive system of animals such as deer, being cached by animals such as squirrels and being easily collected and planted by humans.
Cycadophyta
was one of the 3 gymnosperms discussed in lab
Ginkgophyta
was one of the 3 gymnosperms discussed in lab
Gnetophyta
was one of the 3 gymnosperms discussed in lab
What are five synapomorphies of flowering plants?
Flowers.
Closed carpels.
Stamens with 2 pairs of pollen sacs.
Double fertilization.
Phloem with sieve tubes and companion cells.
What characterizes primitive angiosperms?
Many stamens with undifferentiated anther and filament; many whorled tepals (non-differentiated petals and sepals).
What are key features of monocots?
1 cotyledon.
Floral parts in 3s.
Parallel venation.
What are key features of eudicots?
2 cotyledons.
Floral parts in 4s or 5s.
Net venation.
What adaptation helps spring ephemerals disperse seeds?
Seeds have an elaiosome (tasty coating for ants).
Why can spring ephemerals survive in cold or variable conditions?
They have underground storage tissues.
What specialized tissue helps aquatic and wetland plants with gas exchange?
Aerenchyma.
What are key adaptations of aquatic species?
Broad, flat leaves; no internal support; flexible structure.