CHEM 1C EXAM 2
1/26
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Alkane
find longest carbon chain (may not be straight)
"end with ‘ane’, in between branches end in “yl” and halogens end with ‘o” with the corresponding carbon #
saturated hydrocarbon
- no multiple(double/ triple)bonds
- holds max amount of hydrogens
unsaturated hydrocarbon
-has multiple bonds
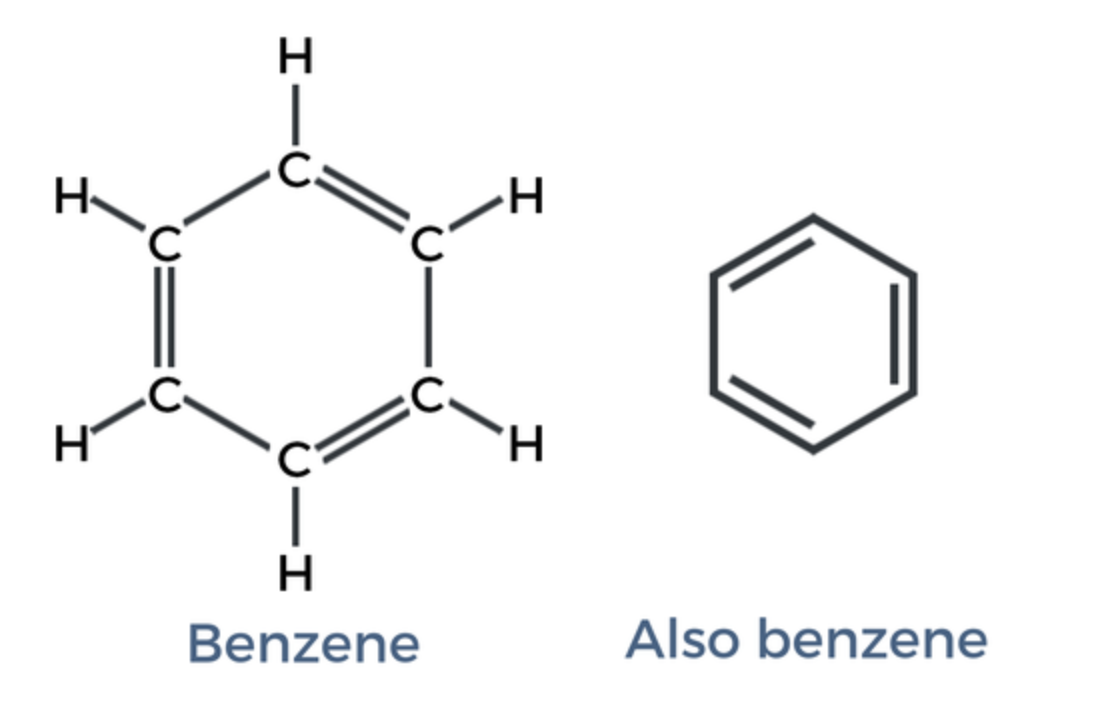
Benzene Ring
aromatic compounds
delocalized pi bonding
contains alternating double bond
name halogen branches alphabetically
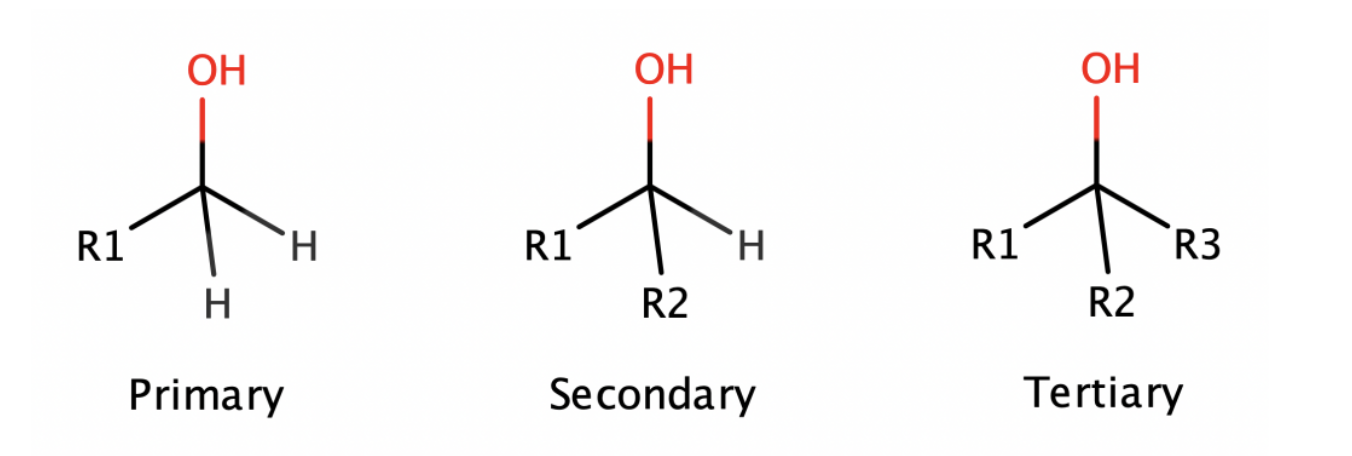
Alcohol
bent shaped
sp2 hybridized
IMFS: LDF, D/D, H-Bond
polar, soluble in H2O
can lose OH- or H+ (amphoteric)
remove suffix “-e” from the parent alkane chain name and add the suffix “-ol”
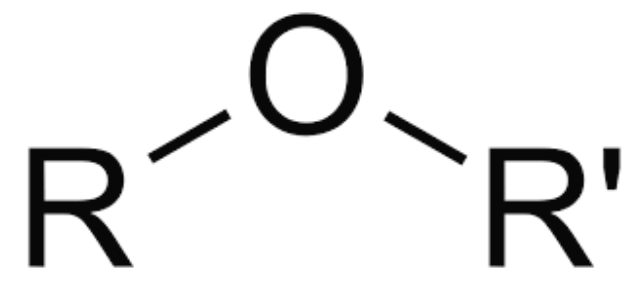
Ether
bent («109.5°)
small ethers are polar
name shorter part, branch with oxygen, end in “oxy”
longest carbon branch ends in “ane”
Aldehyde
drop “-e “ from alkane name and add ending “-al”
small aldehydes are polar
IMF: LDF, D/D
sp2, trig planar
120°
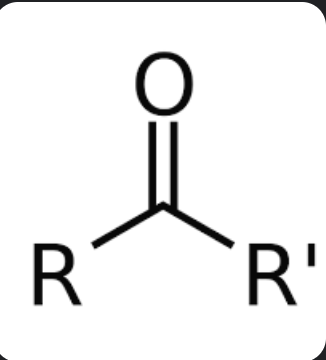
ketone
drop “-e “ from alkane name and replace end with “-one”
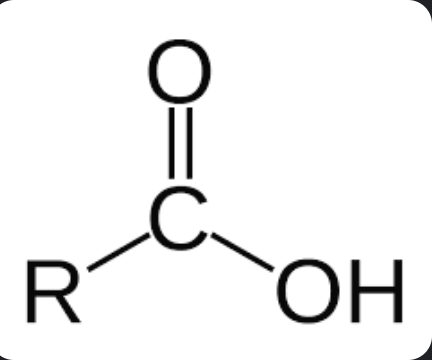
Carboxylic Acid
amphoteric
soluble in H2O
higher BP
The suffix of this carbon chain is then replaced, as carboxylic acids always end in "-oic acid."
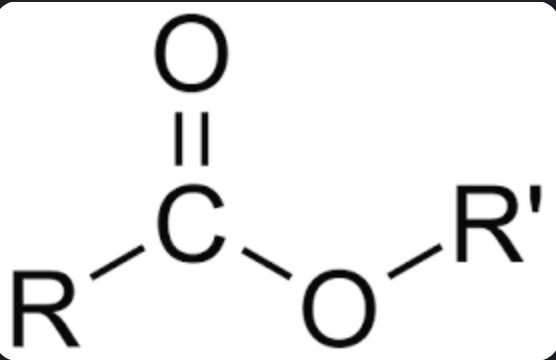
Ester
first count carbon chain in R’, end in ”-yl”
second count carbons in R, end in “-oate”
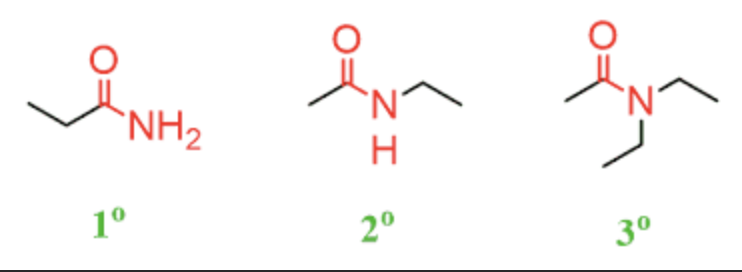
Amides
contain N and carbon chain
primary, secondary and tertiary
Alkyne
triple bonded alkane
name where triple bonds are located
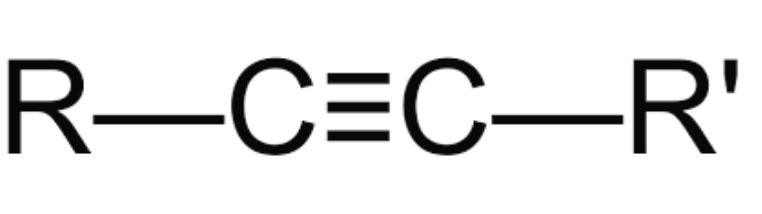
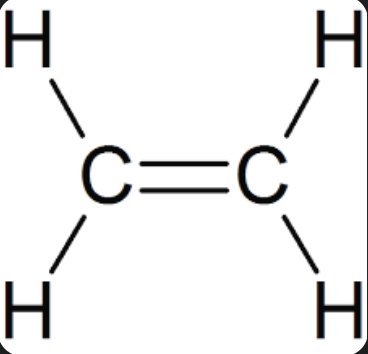
Alkene
double bonded alkane
name where double bonds are located
Other Alkane Groups
“iso” represents Y shaped branching
other examples: sec-butyl, tert-butyl
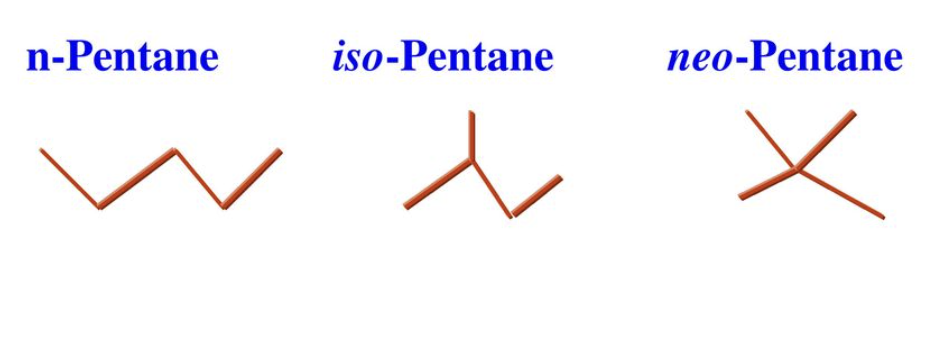
How to count carbons?
start counting from the end of the chain closest to the nearest components (‘yl’ groups)
Multiple “‘yl’ groups” are named individually and placed in alphabetical order at the front of the name.
Multiple of the same branches while naming alkane?
add “di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta…” prefix
Halohydrocarbon
contains halogens
multiple halogens are named in alphabetical order
Isomers
same # and type of atom
different bonds
different formula
different name
Stereoisomers
same bonds, different orientations
same formula
different names
ex: cis/trans, optical isomers
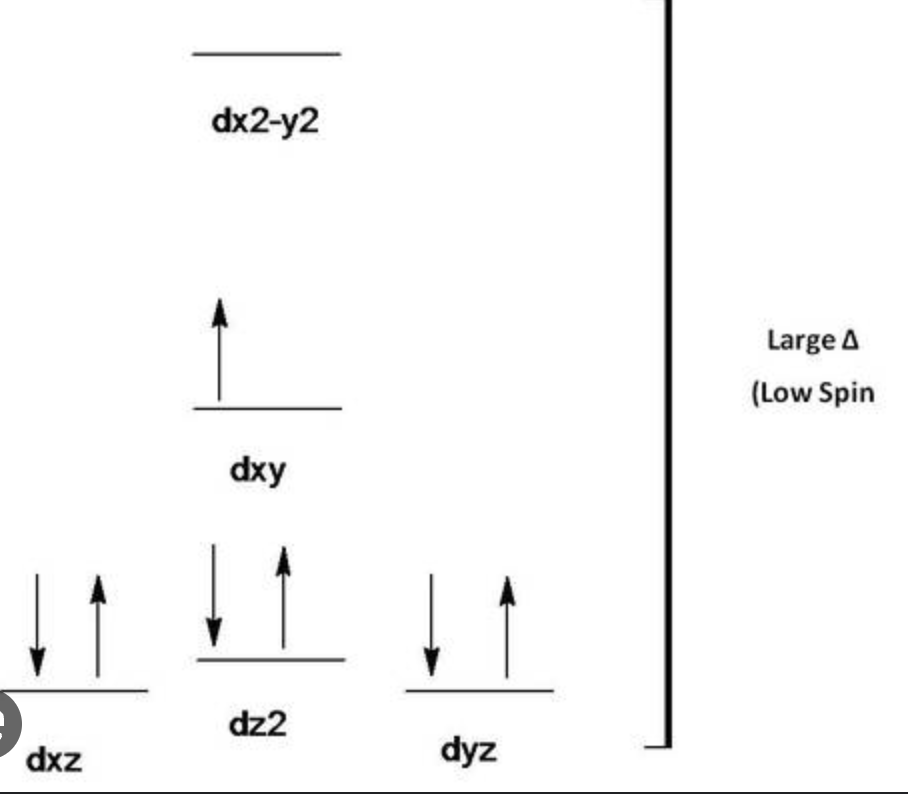
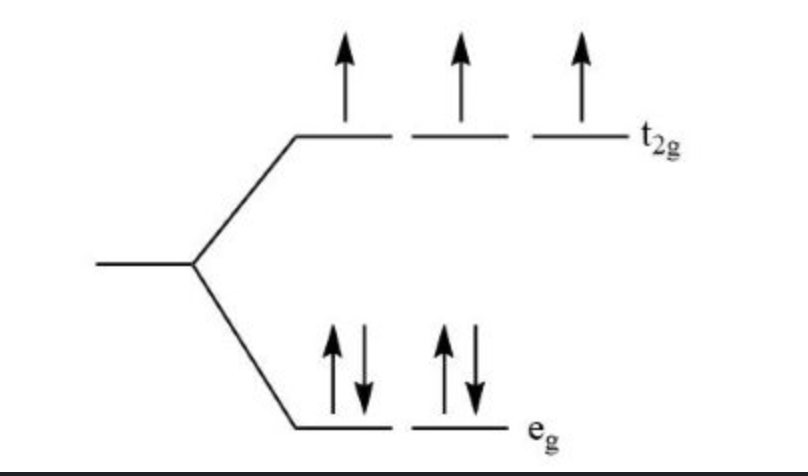
Crystal Field Theory
deals with d-orbital orientations and covalent bonds to transition metals
eg on axis (electron density)
t2g between axes
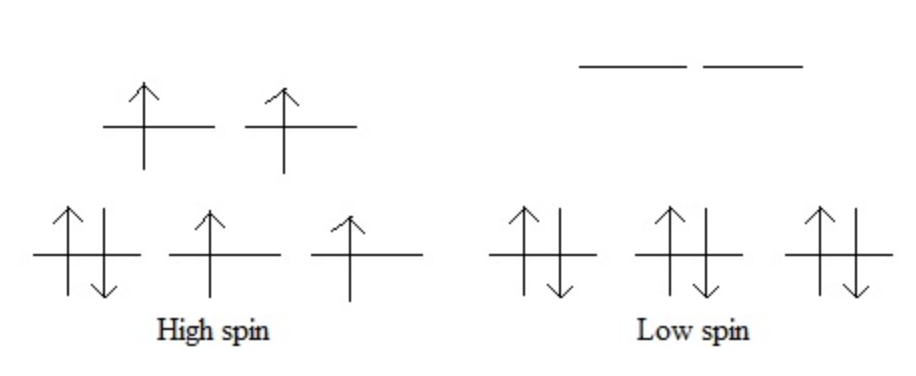
Splitting Energy
computing 2 different affects
energy from pairing
energy from promotion
when Δ = small, e⁻ would rather be promoted *high spin
when Δ = large, e⁻ would rather be paired *low spin
Spectrochemical Series
ligands tell us if octahedral is strong or weak field if not specified
given to us :)
How do we see color?
result in e⁻ transition between eg —> t2g
e⁻ can absorb photon for promotion
-absorbed light depends on splitting energy, we see reflected light, which are opposite sides of color wheel
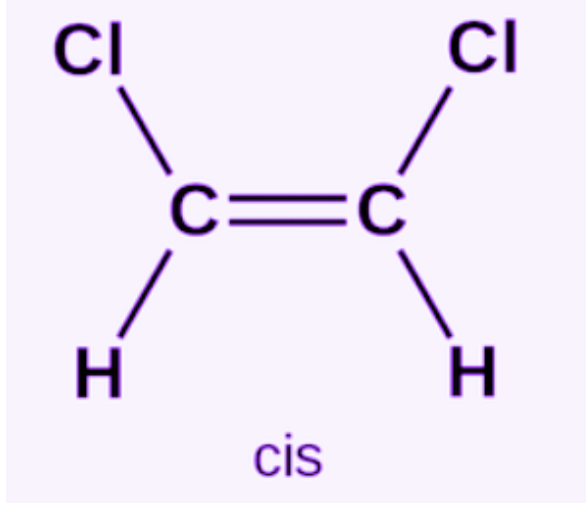
Cis Isomers
same elements are next to each other
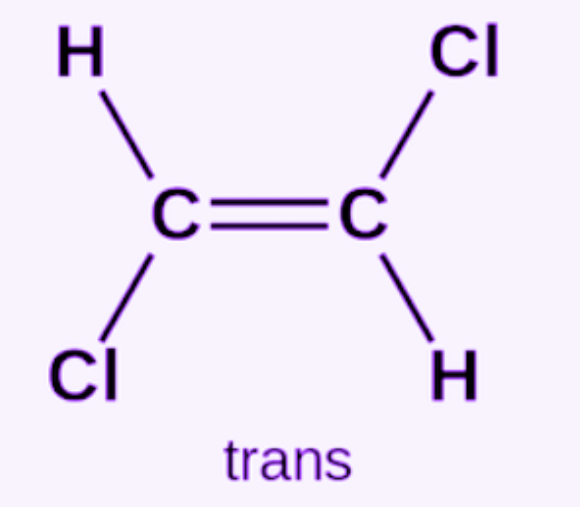
Trans Isomers
same elements are across from each other
Optical Isomers
one molecule is mirror image
cannot superimpose (wont fit together)
ex: tetrahedral

octahedral d-orbital diagram
look at spectrochemical series. Series goes from weakest field to strongest field.
tetrahedral d-orbital diagram
Δ=small, weak field so e⁻ would rather be promoted
square planar d-orbital diagram
Δ=large, strong field so e⁻ would rather be paired