AP Psychology Unit 2 Cognition
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocab from unit 2 of AP Psychology, Cognition. Taken mostly directly from Mr. Stevens notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Perception
Process of selecting, organizing, interpreting sensory information, to give meaning to what we are sensing.
Inattentional Blindness
The inability to see an object or a person in our midst.
Change Blindness
A form of inattentional blindness; two-thirds of individuals don’t a change right in front of them. It occurs when attention is diverted away from the area where the change is happening
Perceptual Set
Is what we “expect” to see, which influences what we DO see. It is top-down processing.
Perceptual Context Effects
Experiences, beliefs, motivation, and context affect what we see.
Visual Capture
When vision competes with our other senses, vision usually wins.
Gestalt Psychology
This posits that the human mind perceives the world as a unified whole rather than individual, isolated parts, emphasizing patterns and configurations.
Ground-Figure Form Perception
Organization of the visual field into patterns of objects that stand out
Retinal Disparity
Images from the two eyes differ.
Convergence
Eyes can follow objects traveling toward and away from them.
Influences on Perception
This can bias our interpretation of neutral stimuli.
Motivation: Ex. a mountain seems steeper when carrying a heavy backpack and tired.
Emotion: Ex. hearing cheerful music makes an experience seem more fun.
Texture Gradient
Indistinct (fine) texture signals an increasing distance.
Algorithms
This is one method of problem solving. They are time consuming and exhaust all possibilities before arriving at a solution.
Heuristics
This is a method of problem solving that includes simple thinking strategies, gut instincts. They can be less time consuming, but more error prone than algorithms.
There are two types:
Representative: stereotypes
Availability: most recent memory
Insight
A sudden realization of a solution to a problem.
Confirmation BIas
We search for information that confirms our personal bias.
Fixation
An inability to see a problem from a fresh persepctive.
Mental Set
We approach a problem in a particular way, especially if that way was successful in the past.
Functional Fixedness
We think only of the familiar functions of an object. Ex. coat hanger to unlock car door.
Representative Heuristics
(stereotype) This is judging the likelihood of objects in terms of how well they seem to represent a prototype.
Prototype: a mental image or the best, most typical example of a category, used to categorize new information and make quick decisions.
Availability Heuristic
What comes to mind quickly is deemed significant - sometimes incorrectly.
Childrens Visual Schemas
These are patterns of repeated actions that children use to explore the world and learn about concepts through play, often involving movement and objects.
Schemas: concepts that organize and interpret unfamiliar information. “brain files”
Perceptual Shape Constancy
Perceiving objects as unchanging even as angle of retinal images change.
Perceptual Interpretation
John Locke (1632-1704) argued that we learn to perceive the world through our experiences. Then we assign meaning to the selected information.
Perceptual Color Constancy
Perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color even when illumination changes.
Perceptual Adaptation
The brain’s relatively quick ability to adjust to changes in sensory input over time.
Phi Phenomenon
When lights flash at a certain speed they tend to present illusions of motion.
Stroboscopic Movement
illusion of continuous movement; like a movie or flip book.
Autokinetic Effect
Illusion of movement of a spot of light in a dark room.
Anterograde Amnesia
This is when you remember the past but can’t make new memories.
Retrograde Amnesia
This is when you can’t remember events or information from before an injury, but you can still form new memories.
Encoding Failure
This is when information isn't properly stored in memory in the first place
Retrieval Failure
This is when stored information is not recalled due to a lack of retrieval cues or other factors
Proactive Interference
This occurs when prior learning disrupts your recall of new information. If you buy a new combination lock, your well-rehearsed old combination may interfere with your retrieval of the new one.
Retroactive Interference
This occurs when new learning disrupts your recall of old information. If someone sings new lyrics to an old song’s tune, you may have trouble remembering the original words.
Reconsolidation
When we “replay” a memory, we often replace the original with a slightly modified version, rather like what happens in the telephone game.
Misinformation Effect
After exposure to subtly misleading information, we may confidently misremember what we’ve seen or heard.
Suggestibility
In memory this refers to the tendency to incorporate misleading information or suggestions into one's recollection of an event, leading to distorted or inaccurate memories
Source Amnesia
Forgetting where you learned something, can lead to false memories because the context and source of a memory are lost, making it difficult to distinguish between real and imagined event.
Ex. when you dream about something and then are later unsure if it actually happened or not .
Recall
Retrieving info that is not currently in your awareness. ex. fill in the blank quiz.
Recognition
Identifying items already learned. ex. multiple choice
Relearning
Learning things more quickly when you learn it a second time.
“The more we rehearse info, the quicker we relearn it” - Hermann Ebbinghaus
Memory Stages
1st step - Encoding: get the info into our brain.
2nd step - Storage: retain the info
3rd step - Retrieval: get the info back out.
Sensory Memory
The information is called “iconic” it it’s visual. It only lasts about ½ a second.
The information is called “echoic” it it’s auditory (lasts 3-4 seconds)
What remains is passed to the short-term memory.
Short-term / Working Memory
This can hold info for 2 seconds to 2 minutes
The “Magic Seven” - on average, humans can only remember 7 things at the same time (+ or - 2)
“Maintenance rehearsal” - is repeating the info over and over.
“Elaborative rehearsal” - give meaning to the info.
Both “elaborative” and “maintenance’ rehearsal are called “effortful processing”
A component called the Central Executive coordinates:
Phonological loop: - briefly holds auditory info (hearing new song lyrics)
Visuo Sketchpad: - briefly holds visual info (remember where you parked in the lot)
Phonological Loop
- briefly holds auditory info (hearing new song lyrics)
Visuo Sketchpad
briefly holds visual info (remember where you parked in the lot)
Long-Term Memory
As far as we know, it is limitless
Long-term potentiation (LTP) - increases memory
Somatically: remember the meaning of the word
Episodic: we remember events in our life
Procedural: memories of skills
Declarative (explicit) Memory: remember specific facts
Nondeclarative (implicit) Memory: unintentional memories that we might not even realize we have (procedural memories)
This type of memory also includes the following, which have individual flashcards:
Context-dependent memory
State-dependent memory
Flashbulb memory
Source Confusion
Context-Dependent Memory
info is more likely to be remembered if recall is the same context
as when it was learned.
State-Dependent Memory
Info is best recalled if your physical/mental state is the same as when you learned the info.
Flashbulb Memory
a deep, vivid memory. Like a photograph of the event.
Source Confusion
We attribute the memory to a different source than it really was.
Cocktail Party Effect
This refers to the ability to focus on one specific auditory stimulus while filtering out other sounds in a noisy environment
Yes, I thought it was a trick question.
Automatic Memory Processing
the effortless and unconscious encoding of information, like remembering the sequence of events in a day,
Effortful Memory Processing
the conscious and deliberate encoding of information, requiring attention and effort, as opposed to automatic processing
Mnemonics
This is a memory aid or technique that uses specific strategies to enhance learning and recall, often by associating new information with something already known or easily remembered, like acronyms, rhymes, or visual imagery
Method of Loci
This is a specific mnemonic that uses imagined physical locations to remember information in sequence.
Link Method
Making a story out of vocab to create chain associations between items on a list, aiding recall.
Priming
Making connections to related characteristics.
Example: “firetruck.” It’s red, sirens, ladder, hoses, etc.
Chunking
Organize info into meaningful, smaller units.
The Spacing Effect
Study/practice smaller chunks of info every day, rather than cramming.
Testing Effect
IT has been proven that retrieving, rather than rereading, enhances memory.
Dual Processing
Information is often processed in two separate unconscious tracks: System 1 (sloppy, quick decisions, Heuristics), and System 2: (conscious, intentional and calculated, algorithms).
Shallow Processing
Encoding on a basic level, based on the structure or appearance of words.
Deep Processing
Encoding “semantically” based on the meaning of the words.
Atkinson-Shiffrin Model
This three-stage memory model proposes that memory is processed through three distinct stages: sensory memory, short-term memory (STM), and long-term memory (LTM).
Long-Term Potentiation
This is the strengthening of synaptic connections between neurons, believed to be a cellular basis for learning and memory. Kandel and Schwartz found that when learning occurs, more of the neurotransmitter serotonin is released into synapses.
Blocking
refers to the temporary inability to retrieve a stored memory, even though it's known to be present. This is often described as a "tip-of-the-tongue" phenomenon, where a memory is readily available but feels just out of reach. Blocking is one of the "sins of memory" identified by Daniel Schacter, which also include transience, absent-mindedness, misattribution, suggestion, bias, and persistence.
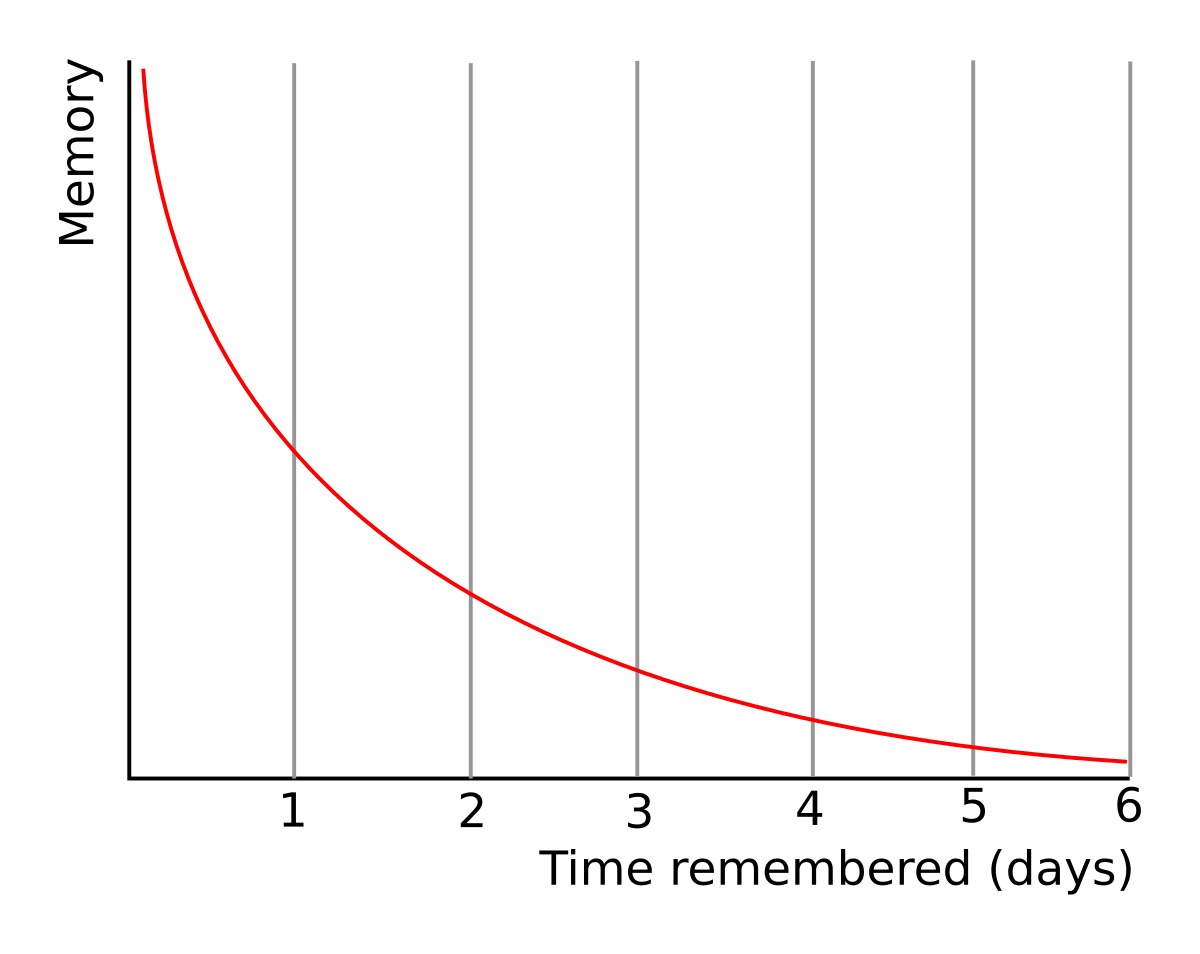
Forgetting Curve
Designed by Hermann Ebbinghaus, this describes the natural decline in memory retention over time, described by a rapid initial decline in retention becoming stable thereafter.
General Intelligence
This was proposed by Charles Spearman. He used factor analysis (statistical data) to identify clusters of related items.
Reification
Erroneously treating something immaterial (like happiness, evil, or evolution), as a material thing.
Gardner vs Sternberg
Howard Gardner proposed 8 different intelligences. He said “Savant Syndrome” is proof.
Robert Sternberg reduced the number from 8 to 3: analytical, creative, and practical.
Emotional Intelligence
Your ability to:
perceive emotion
understand emotion
manage emotion
use emotion
Alfred Binet
He developed questions that would predict children’s future progress in the Paris school system.
Lewis Terman
From Stanford University, he believed intelligence is inherited. He “Americanized” Binet’s test. He developed an “Intelligence Quotient” (IQ)
IQ = Mental age (test score) / chronological age x 100
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
David Wechsler created a new test for adults and children. It is now the most widely used intelligence test. It is more hands on and taken one-on-one with a proctor.
Aptitude Tests
These predict your ability to learn (SAT)
Achievement Tests
These reflect what you have already learned.
Normal Curve
Standardized tests establish a normal distribution of scores in a bell-shaped pattern.
Standardization
A randomly selected group takes the test as a baseline first.
Reliability
Consistent scores.
Validity
Tests what its supposed to.
Aging vs Intelligence
Intelligence scores become stable after about 7 years of age.
Fluid intelligence decreases with age, our ability to process info and reason quickly gets worse.
Crystallized Intelligence increases with age. This is our accumulated knowledge of facts.
Stereotype Threat
A belief that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype.