Allery Chem 6.1.1 Aromatic Compounds rev
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/66
Earn XP
Last updated 7:20 PM on 8/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
1
New cards
Benzene is a
cyclic, planar molecule w the formula C6H6
2
New cards
Carbon has 4
valent electrons
3
New cards
Each carbon is bonded to
2 other carbons and 1 hydrogen atom
4
New cards
the final lone electron is in a
p-orbital which sticks out above and below the planar ring
5
New cards
due to the delocalised electron structure
all the C-C bonds in the molecule are the same (same bond length 139pm)
6
New cards
the lone electrons in the p-orbitals combine to form
a delocalised ring of electrons
7
New cards
C-C single bond length
154pm
8
New cards
C=C double bond length
134pm
9
New cards
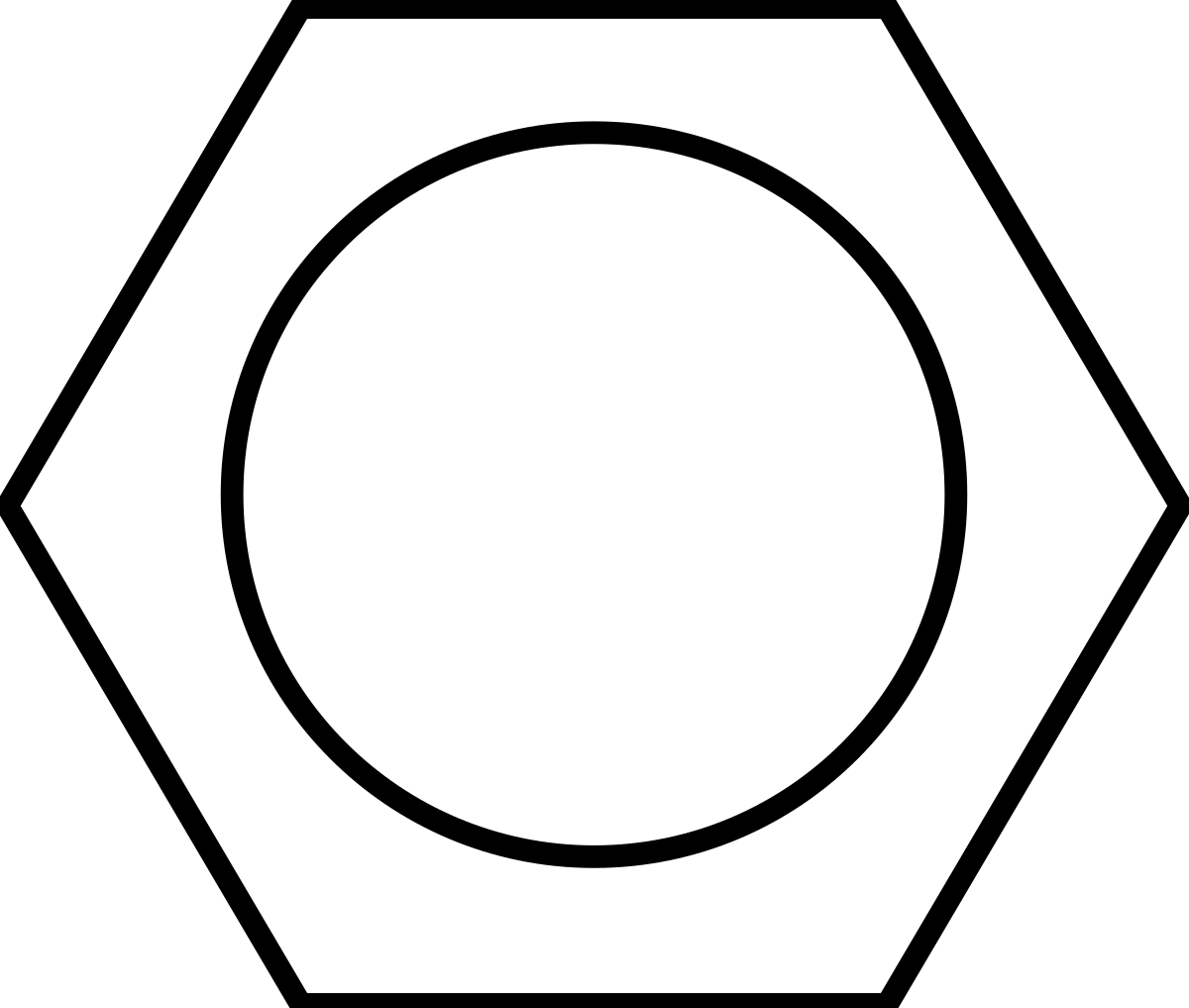
\
this structure shows benzene’s delocalised electrons
10
New cards
Benzene is more stable than Kekule’s structure
cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene
11
New cards
measure stability of benzene
by comparing the enthalpy change of hydrogenation in benzene & cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene
12
New cards
If we hydrogenate cyclohexene it has an enthalpy change
of -120KJmol-1 (cyclohexene has 1 double bond)
13
New cards
If benzene has 3 double bonds we would expect an enthalpy change of hydrogenation of
\-360KJmol-1
14
New cards
actual enthalpy change of hydrogenation of benzene it is -208KJmol-1 (experimental value)
15
New cards
energy required to
break bonds
16
New cards
energy released to
form bonds
17
New cards
more energy required to break bonds in
benzene than cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene
18
New cards
more energy required to break bonds in benzene than cyclo-1,3,5-triene which suggests
benzene is more stable than theoretical cyclo-1,3,5-triene with 3 double bonds. This stability is due to delocalised electron structure
19
New cards
aromatic compounds are molecules that
contain a benzene ring, they are known as arenes. They are named 2 different ways
20
New cards
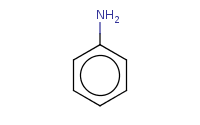
phenylamine
21
New cards
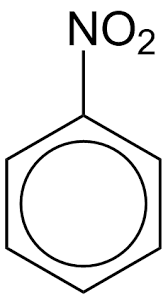
nitrobenzene
22
New cards
alkenes have a double bond and undergo
electrophilic addition
23
New cards
adding bromine water to an alkene
causes a colour change from brown/orange to colourless
24
New cards
bromine (brown/orange) is the electrophile and adds to the alkene forming
a dibromoalkane (colourless)
25
New cards
Br2 is polarised because
the electrons in the double bond repels electrons in Br2
26
New cards
an electron pair in the double bond is attracted to delta+ bromine and forms
a bond which breaks the Br-Br bond
27
New cards
a carboncation intermediate is formed and
Br- is attracted to C+
28
New cards
whens arenes react they undergo
electrophilic substitution reactions
29
New cards
Why does benzene have a high electron density?
It has a delocalised ring of electrons
30
New cards
Benzene’s high electron density attracts
electrophiles
31
New cards
Benzene is stable unlike
traditionally alkenes so don’t undergo electrophilic addition reactions (like the bromination of alkene) as this would distrupt the stable ring of electrons
32
New cards
Instead, arenes undergo electrophilic substitution reactions where
a hydrogen or functional group on the benzene ring is substituted for the electrophile
33
New cards
2 mechanisms you need to know
Friedal-Crafts Acylation and Nitration reaction
34
New cards
Benzene is widely used in
pharmaceuticals & dye stuffs however its stability makes it hard for it to react. Friedal-Crafts acylation can help solve this problem
35
New cards
In order to add onto benzene ring the electrophile must have
a very strong postive charge - acyl groups have a postive charge but not postive enough
36
New cards
We can use a halogen carrier to act as a catalyst (eg AlCl3) which will produce
a much stronger electrophile with a stronger positive charge
37
New cards
In the Friedel-Crafts Acylation we have to react
an acyl chloride with the halogen carrier (AlCl3) to create a strongly positive electrophile
38
New cards
Now we have made the electrophile we need to react it with benzene to make
a less stable phenylketone under reflux and a dry ether solvent
39
New cards
carbocation
an ion with a positively-charged carbon atom
40
New cards
The delocalised electrons are attracted to the carbocation, 2 electrons move to form a bond which
breaks the ring and a positive charge develops
41
New cards
The negative AlCl4- is then attracted to the positively charged ring and one of the chlorine atoms
breaks away to form a bond with the hydrogen
42
New cards
The electrons in the C-H bond move to
neutralise the positive charge and re-form the ring
43
New cards
Why is nitrating benzene useful?
it allows us to make dyes for clothing & explosives
44
New cards
If we heat benzene with concentrated nitric acid (HNO3) and sulfuric accid (H2SO4) we form
nitrobenzene (need to make an electrophile first)
45
New cards
first step make electrophile first
sulphuric acid with nitric acid
46
New cards
the H2NO3+ decomposes to form
the electrophile (nitronium ion NO2+)
47
New cards
use the nitronium ion (NO2+) and react with
benzene to produce nitrobenzene
48
New cards
the nitronium ion is attacked by the benzene ring forming
an unstable, positively charged ring
49
New cards
the electrons in the C-H bond move to reform
the delocalised electron ring
50
New cards
nitrobenzene formed and a H+ is formed which reacts
with the HSO4 formed to make H2SO4 again (catalyst regeneration)
51
New cards

salicylic acid
52
New cards
Why are phenols more reactive than benzene?
The electron density in the ring is higher
53
New cards
Why are electrophilic substitution reactions are more likely to occur with phenol than with benzene?
It’s due to the -OH group and orbital overlap
54
New cards
What can the position of functional groups on a benzene ring affect?
reactivity with electrophiles
55
New cards
Benzene has the same reactivity for each carbon because?
benzene has carbons that have the same electron density
56
New cards
Substituted benzene rings distort the electron density in the ring which affects
the reactivity of carbon atoms in the ring
57
New cards
electron withdrawing groups affect
substitution reactions on carbon 3 and 5
58
New cards
electronegtive groups such as NO2 withdraws
electron density from the ring and specifically from carbon 2,4 and 6
59
New cards
Because electron density is withdrawn from the ring (especially 2, 4 and 6)
this means electrophiles are more likely to attack carbons 3 and 5 so substitution is more likely to happen at these positions
60
New cards
We know phenols are weak aids because?
they partially dissociate
61
New cards
phenols dissociate weakly to form a
phenoxide ion and H+ ion
62
New cards
phenols react with alkalis to form
a salt and water
63
New cards
What is made when phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide?
sodium phenoxide
64
New cards
phenols react with bromine water because
phenols are more reactive than benzene
65
New cards
2,4,6-tribromophenol smells of
antiseptic and is insoluble in water
66
New cards
We need concentrated nitric acid and
concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst
67
New cards
As OH is an electron donating group substitution occurs at
carbon 2 and 4