Topic 2B 3 the structure of DNA and RNA
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are nucleotides made of ?
5-carbón pentose sugar
A nitrogen containing base group
A phosphate group
The difference between the pentose sugar in DNA and RNA ?
The pentose sugar in RNA is ribose and the pentose sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, it has one less oxygen than ribose.
What are the differences between a purine base and a pyramiding base ?
A purine base has two nitrogen containing rings
A pyramiding base has only one nitrogen containing rings
What are the common purine bases ?
Adenine (A)
Guanaine (G)
What should we note about the phosphate group of nucleotides ?
-PO3- 4
The inorganic phosphate ions are present in the cytoplasm of every cell.
The readily releasable H ions mean that the phosphate group is acidic and carries a -ve charge.
In what reaction are the 3 components of a nucleotide bind ?
In a condensation reaction, in the process 2H2O molecules are released forming a mononucleotide .
What are polynucleotides ?
Polymers made of mononucleotides.
Where is the DNA stored in a eurokayotic cell ?
In the nucleus .
Where is the DNA stored in a prokaryotic cell ?
Floating freely in the cytoplasm.
How does a polynucleotide form ?
Nucleic acids bond to the phosphate backbone of another neucleotide via a condensation reaction
Forming phosphodiester bonds between the sugar on one neucleotide and the phosphate group on the other.
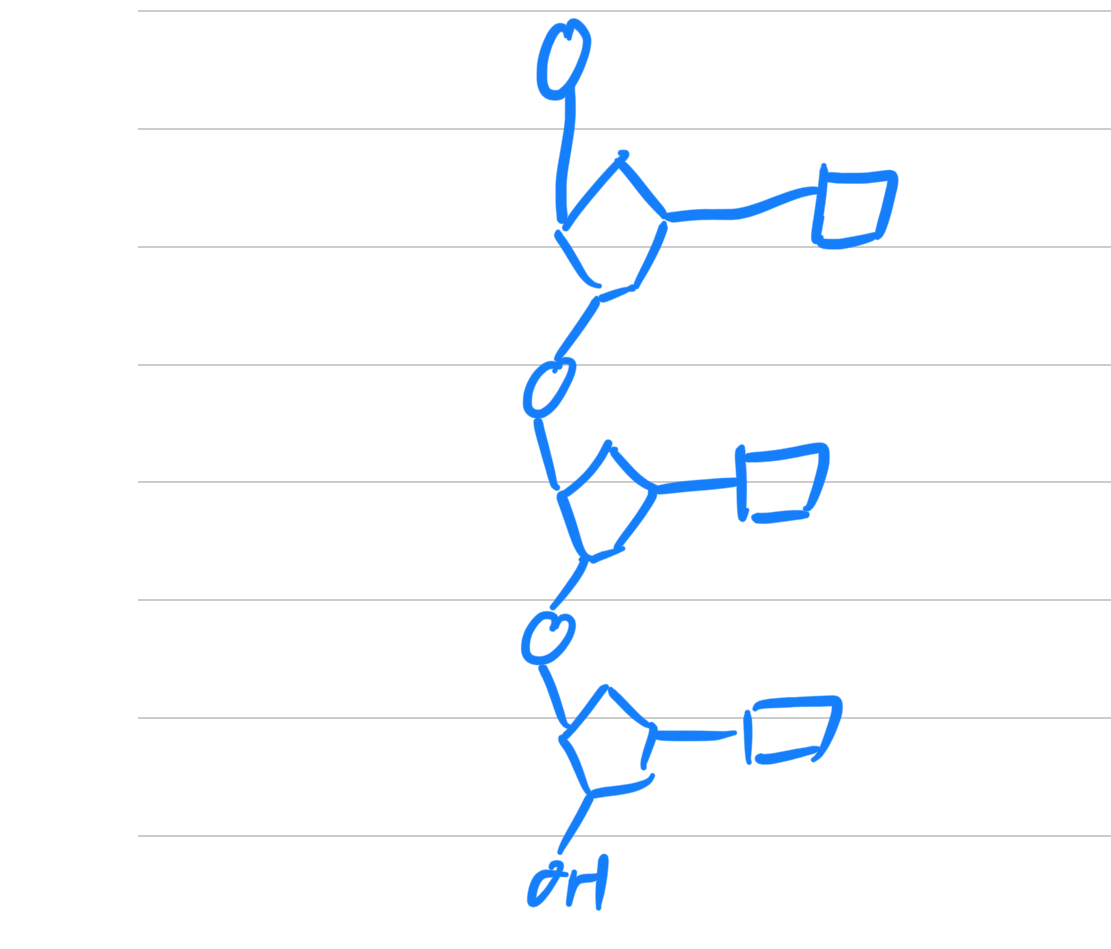
What should we note about polynucleotides ?
They always have a phosphate group on one side and a hydroxyl group on the other.
Bases for DNA ?
Cystosine (C)
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T)
Guanine (G)
Bases for RNA ?
Cystosine (C)
Adenine (A)
Uracil (U)
Guanine (G)
What shape can an RNA take ?
Either remain as a long chain or fold up into complex shapes via hydrogen bonds.
What structure does DNA have ?
DNA is a double helix structure .
Two polynucleotide strands twist around each other.
The sugar phosphate molecules form the backbones.
The bases point inward and are linked up in a complimentary way.
How are two DNA strands held together ?
They are held together by hydrogen bonds between the complimentary base pairs.
These hydrogen bonds are formed between the amino acid and the carbonyl groups of purine and pyrimidine bases on the opposite strands.
2 hydrogen bonds between A and T, 3 hydrogen bonds between C and G.
10 base pairs for a complete twist of the helix.
Why do base pairs always involve one purine and one pyramiding base ?
The size combination of the two molecules is crucial.
A purine and a pyrimidine base fit between the two sugar/phosphate backbones of the two strands of the DNA molecule.
Pyrimidine bases are too small for hydrogen bonds to form between them, they would be far apart.
Purine bases are too large to pair up together, they would overlap.