Anti's and their Biotas
1/107
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
False
Antibiotic works for Bacterial fungal and viral infections (True or False)
Bacteriostatic
Type of drug that inhibits the growth of the bacteria by suppressing the multiplication and production if bacteria.
Bactericidal
Type of drug that eliminates / kills the bacteria
NAM
Structure in the peptidoglycan that serves as the terminal of tetrapeptides
Cross linking
Process to make the peptidoglycan structure stable
transpeptidase
Enzyme that connects two tetrapeptides together to make two peptidoglycan structures stable
Transglycosylase
Enzyme that connects polysaccharides together to make two peptidoglycan structures stable.
L - Alanine
the first amino acid that is attached at the terminal of NAM
Beta-lactams
Penicillin, cepahlosporins, penems, cephems, carbapenems, Monobactams are under what category of Antibiotic,
Cell wall synthesis
What part of the bacteria does beta-lactams inhibits.
penicillin binding proteins
Described as bifunctional transpeptidase
penicillin binding proteins
Enzyme that mediate peptidoglycan cross linking
Transpeptidase
Beta lactams prevent cell wall synthesis by binding to what specific enzyme.
Beta-lactamase
Bacteria defense mechanism against penicillin
Glycopeptides
Antibiotic that prevents cell wall synthesis by binding to the substrate of PBP, the D-ala part of the tetra peptides of NAM
Glycopeptides
vancomycin, Dalbavancin, teicoplanin, Oritavancin, Telavancin are part of family of drugs called.
D - Alanine
Penicillin binding protein of N. gonorrhea
False
Vancomycin is effective against gram negative bacteria, true or false.
Cell wall synthesis
Beta lactams and glycopeptides Inhibtis what part of the bacteria.
Inhibition of Cell membrane function
Lipopeptides, Polymixins
Gram negative
Polymixins work best on what type of bacteria.
Lipopeptides
Under what family of drug is Daptomycin
Polymixins
Polymixin B and E are what part of family of drugs.
Aminoglycosides
Type of drug that inhibits the docking of Aminoacyl Trna synthetase.
Gram positive
Daptomycin under lipopeptides is effective on what type of bacteria
Polymixins
Type of drug that disrupts the cell membrane / targets the phospholipids in the cell membrane of the bacteria.
Lipopeptides
Binds and disrupts cell membrane of gram positive bacteria
Aminoglycosides
Inhibits the Docking of Aminoacyl Trna synthetase causing mistranslation of proteins
Aminoglycosides
Gentamycin, Amikacin, Tobramycin, neomycin, streptomycin, and Kanamycin are under what family of drugs.
Aminopeptidase
Enzyme responsible for the elongation of proteins in the ribosome.
30s inhibition
Aminoglycosides, tetracycline, and Glycyl cycline inhibits what function of the bacteria.
Aminoacyl Trna synthetase
Enzyme in the 30s responsible for attaching the right amino acid to the TRNA.
Tetracyclines
Antibiotic that inhibits transfer of amino acids from A to P site
Tetracycline
Doxycline, and minocyclineare under what family of drugs
Glcylcyclines
Antibiotic used in exchange for tetracycline, used for tetracycline resistant bacteria
Glycylcyclines
Tigecycline are under what family of Antibiotics
50s inhibition
What is the function of the antibiotics, MLS, Oxazolidone, Chlorampenicol
MLS
Family of antibiotic where it inhibits 50s inhibition by inhibiting elongation by blocking the exit tunnel
MLS
Erythromycin, clarithromycin and azithromycin are under what family of antibiotics
Oxazolidone
Linezolid and tedizolid are under what family of antibiotics.
Oxazolidone
Antibiotic that blocks initiation steps needed for translation process in the protein synthesis of the bacteria.
Chloramphenicol
prevents aminopeptidase inhibiting elongation of the amino acids.
DNA/RNA synthesis
Fluoroquinolones, metronidazole, Rifampin inhibits what system of the bacteria.
Fluoroquinolones
Ciproflaxin, Nalidixic acid, Levofloxacin, Gemifloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Norfloxacin are under what family of antibiotics.
Topoisomerase / DNA gyrase
Fluoroquinolones attacks what enzyme for prevention of DNA synthesis
Metronidazole
Antibiotic that breaks the DNA strands
anaerobic
What is the air requirement for metronidazole
Rifampin
this antibiotic inhibits RNA polymerase that interferes with RNA synthesis
Folic acid synthesis
Sulfonamides, trimethoprim, and Nitrofuratonin inhibits what system in the bacteria
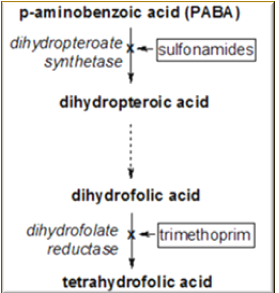
Sulfonamides
Inhibits Dihydropteroate reductase
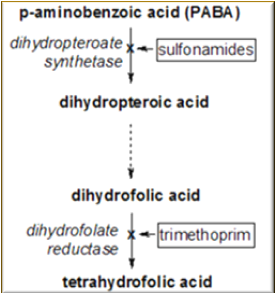
Trimethoprim
Inhibits Dihydrofolate reductase
Nitrofuratonin
An antibiotic that inhibits folic acid synthetase and is also used for the treatment of UTI
pH of 7.2 - 7.4
What is the normal pH range for the growth of bacteria
aerobic atmosphere
Environment needed for Aminoglycosides
false resistance against tetracycline
Less than 7.2 pH can cause what effect in bacterial resistance.
False resistance against EAC
More than 7.4 pH can cause what effect in bacterial resistance.
12.5 mg/L
Required cation concentration of Magnesium
95 mg/L
Required cation concentration of calcium
False resistance of Pseudomonas vs Aminoglycosides
Increase in cation concentration results in what phenomenon in bacterial resistance
False resistance of all organisms vs tetracycline
Lower concentration of cations results in what phenomenon in bacterial resistance
Low to none
Thymidines required concentration for bacterial growth
Increase resistance of enterococcus to Sulfonamides and trimethroprim.
Increase of concentration of thymidine can result in what phenomenon in bacterial resistance.
Intrinsic resistance
Bacterial resistance that the bacteria has since it’s birth.
Acquired resistance
bacterial resistance that the bacteria gains through genetic recombination and exchanges of plasmids.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
Test done to a bacteria that involves a set of antibiotics.
Conventional susceptibility test
Broth dilution, agar dilution, and disc dilution are what type of susceptibility testing
Commercial susceptibility test
Agar dilution, Diffusion in agar derivations, Automated test system are under what types of susceptibility testing
Antimicrobial resistance detection
Agar or disc screen, and D test are what type of susceptibility testing.
Broth dilution
5 × 10^5 is the standardized inoculum for what type of dilution.
Agar dilution
1 × 10^4 is the standardized inoculum for what type of dilution.
Disc diffusion
1.5 × 10^8 is the standardized inoculum for what type of dilution.
Cartilage damage
Why is Fluoroquinolones bad for children
Damage to developing teeth
Why is tetracycline bad for children
Suppresses bone marrow causing anemia
Why does chloramphenicol needed to be regulated.
16 - 20 hours
Duration of test for Enterobacteriaceae in Broth dilution.
24 hours
Duration of test for N. meningitis for broth dilution test.
Resistant
In breakpoint cut off what is the result when both tubes are turbid
Intermediate susceptibility
In breakpoint cutoff what is the result when the tube with the lowest concentration is turbid but the highest concentration is clear.
Susceptible
In breakpoint cutoff what is the result when both tubes are not turbid.
False resistance
Too thick of a agar plate (>5mm) can cause what in bacterial resistance.
False susceptibility
Too thick of a agar plate (<3mm) can cause what in bacterial resistance.
15 - 20 ml
Volume of agar media required for standardization
25 mg/L
Calcium requirement for standardization of agar
12.5 g/ml magnesium
Magnesium requirement for standardization of magnesium
Oxacillin agar screen
Detects resistance of penicillin against staphylococcus
Vancomycin vs enterococcus
Vancomycin agar screen is for what test.
Gentamycin vs enterococcus
Aminoglycoside screens is the test for what.
Penicillin vs strep
Oxacillin disk screen is a test for what
Erythromycin and clindamycin
D test (macrolide resistance) is a test to differentiate resistance of what antibiotics.
D zone
what is the positive test for the D test
ERM gene
What gene is present in the bacteria when is is positive for the D test
Penicillin
Oxacilin, methicilin, Nafcicillin and Dichoxacillin is under what family of antibiotics.
Mec A gene
What gene is in MRSA that makes them resistant to methicillin.

Chromogenic cephalosporin Nitrocefin test
What test is needed to test for beta lactamase presence in bacteria.
Acidimetric method and Iodometric method
test for the presence of penicillinase presence in bacteria
Penicilloic acid
acidic component of penicillin

Iodometric test
test for beta lactamase which gives a purple color for negative indication.

Time kill studies
Time between the loss of 1000 bacteria to the baseline in 24 hours
Serum bactericidal test
Test that measure the capacity of the antimicrobial agents alongside the other serum factors
5 x 5^2 CFU/mL
CFU of serumstatic titre