biology: topic 8
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
1
New cards
function of a sensory neurone
carry impulses from receptors to the central nervous system
2
New cards
function of a motor neurone
conducts impulses from the central nervous system to the effectors
3
New cards
function of a relay neurone
transmit impulses from sensory neurones to motor neurones
located within the central nervous system
located within the central nervous system
4
New cards
draw a sensory neurone
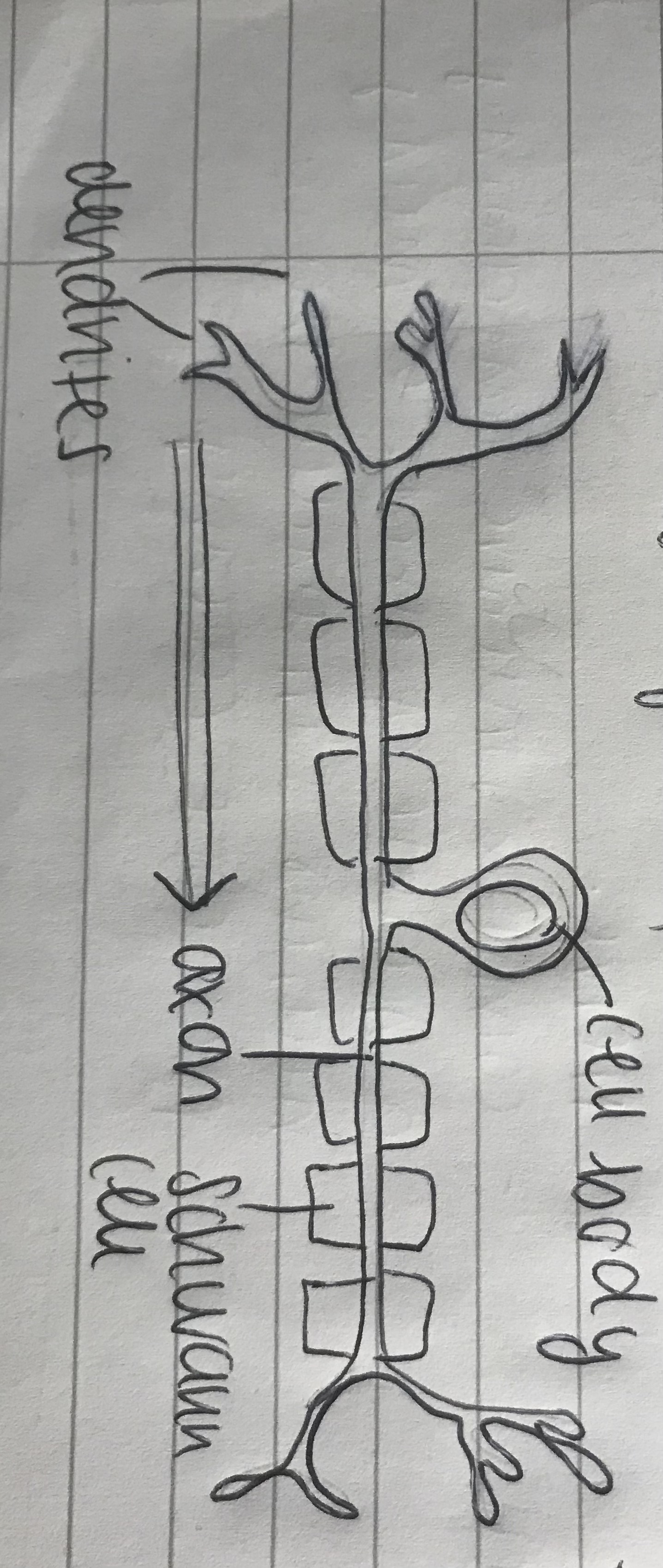
5
New cards
draw a motor neurone

6
New cards
draw a relay neurone
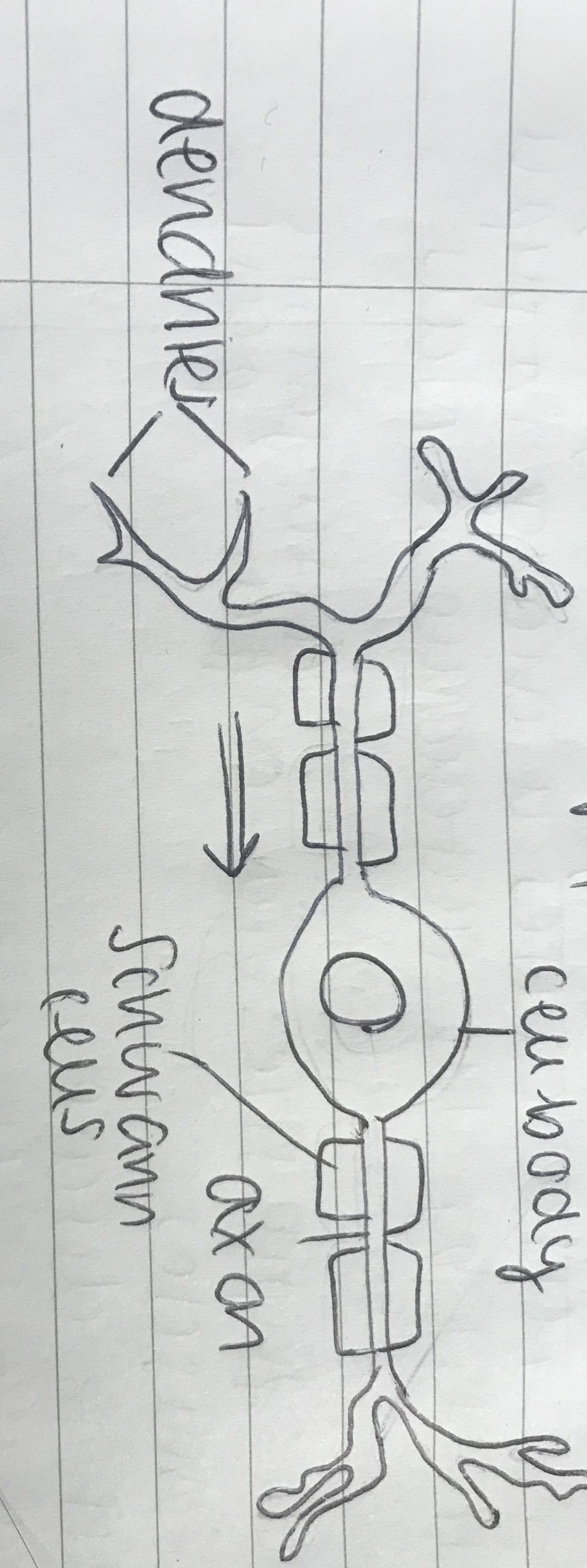
7
New cards
cell body
contains nucleus and cell organelles within cytoplasm
8
New cards
very fine dendrites
conduct impulses toward the cell body, collected from other neurones
9
New cards
axon
transmit impulse away from the cell body
10
New cards
fatty insulated layer
aka myelin sheath
made up of schwann cels wrapped around the axon
made up of schwann cels wrapped around the axon
11
New cards
stimulus
the change in environment
12
New cards
receptor
detects the stimulus
eg photoreceptors, thermoreceptors, chemoreceptors
eg photoreceptors, thermoreceptors, chemoreceptors
13
New cards
effector
muscles or glands that carry out the response
14
New cards
response
what happens in response to the stimuli
15
New cards
co-ordinated response
stimulus → receptor → sensory neurone → spine → brain → spine → motor neurone → effector → response
16
New cards
reflex arc
skips the spine and brain, instead goes through the relay neurone
17
New cards
which part of the nervous system controls the pupil reflex?
autonomic nervous system
18
New cards
antagonistic muscles in the iris
* radial muscles
contract to dilate
sympathetic reflex
* circular muscles
contract to contract pupil
parasympathetic reflex
contract to dilate
sympathetic reflex
* circular muscles
contract to contract pupil
parasympathetic reflex
19
New cards
pupil reflex in high light levels
* high light levels hit the photoreceptors in the retina
* causes nerve impulses to pass along the optic nerve
* sends an impulse to nerve sites within the CNS (including coordinating cells in the midbrain)
* impulses sent along parasympathetic motor neurones to the circular muscles
* radial muscles relax to constrict the pupil and reduce the light entering the eye
* causes nerve impulses to pass along the optic nerve
* sends an impulse to nerve sites within the CNS (including coordinating cells in the midbrain)
* impulses sent along parasympathetic motor neurones to the circular muscles
* radial muscles relax to constrict the pupil and reduce the light entering the eye
20
New cards
pupil reflex in low light levels
* low light levels detected by photoreceptors in the retina
* impulses sent down sensory neurone in the optic nerve in the midbrain
* impulses sent along sympathetic motor neurones to radial muscles
* contract to widen the pupil
* impulses sent down sensory neurone in the optic nerve in the midbrain
* impulses sent along sympathetic motor neurones to radial muscles
* contract to widen the pupil
21
New cards
resting potential of an axon
\-70mV
due to the ion distribution
more X- ions inside, X+ outside
due to the ion distribution
more X- ions inside, X+ outside
22
New cards
what causes an uneven distribution of ions?
sodium-potassium pumps
K+ → cell
cell → Na+
work against the concentration gradient, requiring energy from ATP
chlorine ions move out of the cell to balance the charge, though not actively BY the cell
K+ → cell
cell → Na+
work against the concentration gradient, requiring energy from ATP
chlorine ions move out of the cell to balance the charge, though not actively BY the cell
23
New cards
how is resting potential generated?
1. Na+/K+ pump creates concentration gradients across the membrane
2. K+ diffuse outside of the cell down the K+ concentration gradient, making the outside of the membrane positive and inside negative to create a potential difference
3. the potential difference will pull K+ back into the cell
4. at -70mV, the two gradients counteract each other and there’s no net movement of K+
24
New cards
how is an action potential produced
1. as it becomes less negative, voltage gates Na+ channels open and Na+ flows into the axon to depolarise the membrane
2. at +40mV, voltage-dependent Na+ channels close, voltage-dependent K+ channels open
3. K+ leave the axon, repolarising the membrane of the neurone and charge the outside
4. the membrane becomes hyperpolarised as it takes time for the channels to shut (-90mV)
5. K+ diffuse back until resting potential is restored
25
New cards
passing impulses across a neuron
1. part of the membrane becomes depolarised at the site of the action potential
2. local electrical current is created as Na+ flow between the depolarised part of the membrane and adjacent region
3. depolarisation spreads to the adjacent region
4. nearby Na+ gates open to trigger another action potential
5. repeated along the membrane to cause a wave of depolarisation
26
New cards
what is the refractory period and why does it occur?
due to hyperpolarisation at the end of an action potential, there is a refractory period
a new action potential cannot be generated as there’s too great a difference in charge (-90mV instead of -70mV
this ensures an impulse only travels in one direction
a new action potential cannot be generated as there’s too great a difference in charge (-90mV instead of -70mV
this ensures an impulse only travels in one direction
27
New cards
what happens at the presynaptic neurone?
1. depolarised by an action potential
2. channel membranes open, increase membrane permeability to Ca2+
3. Ca2+ concentration is greater outside, so diffuses across the membrane into the cytoplasm
4. increased Ca2+ concentration causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with presynaptic membrane
5. neurotransmitter is released into the sunaptic cleft by exocytosis
28
New cards
what happens at the postsynaptic neurone?
1. neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and reaches the postsynaptic membrane
2. binds to complementary shaped receptor
3. receptor changes shape to open cation channels, making the membrane permeable to Na+
4. this flow causes depolarisation, the extent of which depends on the amount of neurotransmitter reaching the membrane and number of receptors on it
29
New cards
what happens to the neurotransmitters after synaptic transmission?
* some neurotransmitters are actively taken up and reused by the presynaptic membrane
* others rapidly diffuse away from the synaptic cleft
* some are taken up by other cells or broken down by enzymes so can no longer bind to receptors
* others rapidly diffuse away from the synaptic cleft
* some are taken up by other cells or broken down by enzymes so can no longer bind to receptors
30
New cards
impact of axon diameter on speed of conduction
the wider the diameter, the faster the impulse travels
31
New cards
saltatory conduction
* due to myelination with schwann cells, there are gaps along the axon called nodes of ranvier
* depolarisation can only occur at these places
* the impulse jumps from one node to the next
* this is much quicker than depolarising along the whole membrane
* depolarisation can only occur at these places
* the impulse jumps from one node to the next
* this is much quicker than depolarising along the whole membrane
32
New cards
does impulse strength vary by the strength of the stimulus?
no
the stimulus must be at or above the threshold level to generate an action potential
* as long as it is at or above, the size of impulse generated is the exact same regardless of stimulus size
the stimulus must be at or above the threshold level to generate an action potential
* as long as it is at or above, the size of impulse generated is the exact same regardless of stimulus size
33
New cards
what does the size of the stimulus affect?
* frequency of impulses
* number of neurones in a nerve conducting impulse
eg strong stimulus → high frequency and many neurones
* number of neurones in a nerve conducting impulse
eg strong stimulus → high frequency and many neurones
34
New cards
roles of synapses
* control of nerve pathways, allowing flexibility of response
* integration of information from different neurones to allow a coordinated response
* integration of information from different neurones to allow a coordinated response
35
New cards
factors impacting the chance of depolarisation:
* type of synapse
* number of impulses received
* number of impulses received
36
New cards
types of synapse
* excitatory synapse
help stimulate an action potential
* inhibitory synapse
make it less likely for a postsynaptic membrane to depolarise
\
a postsynaptic cell can have both types of synapse, generation depends on the balance of the synapses at any one time.
help stimulate an action potential
* inhibitory synapse
make it less likely for a postsynaptic membrane to depolarise
\
a postsynaptic cell can have both types of synapse, generation depends on the balance of the synapses at any one time.
37
New cards
excitatory synapses
* make the membrane more permeable to Na+
* a single synapse does not depolarise the membrane enough for an action potential
* several impulses arriving within a short amount of time will do, however
* this happens either through spatial summation (many from diff. neurones) or temporal summation (lots from the same neurone)
* a single synapse does not depolarise the membrane enough for an action potential
* several impulses arriving within a short amount of time will do, however
* this happens either through spatial summation (many from diff. neurones) or temporal summation (lots from the same neurone)
38
New cards
inhibitory synapses
open Cl- and K+ ion channels, allowing the ions to move down their concentration gradients
* produces hyperpolarisation of -90mV
* action potential is NOT generated as it can’t in a hyperpolarised area
* produces hyperpolarisation of -90mV
* action potential is NOT generated as it can’t in a hyperpolarised area
39
New cards
problems with synapses and the blood brain barrier
endothelial cells of capillaries are more tightly packed together
* forms blood brain barrier
* aimed to protect it from changes in ionic composition and toxic molecules
* problems occur with an imbalance in chemicalc crossing the barrier
* forms blood brain barrier
* aimed to protect it from changes in ionic composition and toxic molecules
* problems occur with an imbalance in chemicalc crossing the barrier
40
New cards
dopamine release
* dopamine released by neurones in the midbrain and is involved in movement
* these neurones’ axons extend to the spinal cord, brainstem and frontal cortex
\
* these neurones’ axons extend to the spinal cord, brainstem and frontal cortex
\
41
New cards
dopamine and parkinson’s
the dopamine-releasing neurones die, so little dopamine is released into the motor cortex
* resulting in a loss of motor control
* and symptoms such as:
* muscle stiffness and tremors
* slowness of movement
* poor balance and walking problems
* resulting in a loss of motor control
* and symptoms such as:
* muscle stiffness and tremors
* slowness of movement
* poor balance and walking problems
42
New cards
treatments for parkinsons
* slow the loss of dopamine by protecting dopamine secreting neurones
* treat symptoms with L-DOPA drugs
* dopamine agonists (trigger the same neural pathway)
* gene therapy (does not always accept or retain the new gene)
* deep brain stimluation
* electrodes placed into the brain and connected to a battery pack in the chest that applies a voltage to trigger the neural pathway
* treat symptoms with L-DOPA drugs
* dopamine agonists (trigger the same neural pathway)
* gene therapy (does not always accept or retain the new gene)
* deep brain stimluation
* electrodes placed into the brain and connected to a battery pack in the chest that applies a voltage to trigger the neural pathway
43
New cards
condition associated with excess dopamine
schizophrenia
* hallucinations, delusions
* hallucinations, delusions
44
New cards
treatment for schizophrenia
antagonist drugs that block dopamine binding sites on postsynaptic receptors, NOT stimulating them
* can cause side effects of symptoms of parkinson’s
* NOT parkinson’s itself as the neural cells are still alive
* can cause side effects of symptoms of parkinson’s
* NOT parkinson’s itself as the neural cells are still alive
45
New cards
seratonin
neurotransmitter that plays a role in determining mood
the neurones that secrete it are found in the brain stem
* axons extend into the cortex, spinal cord and cerebellum
the neurones that secrete it are found in the brain stem
* axons extend into the cortex, spinal cord and cerebellum
46
New cards
low seratonin and depression
linked to depression, along with noradrenaline
fewer nerve impulses than normal are transmitted around the brain, so lower levels of neurotransmitter released
* molecules needed for seratonin synthesis are present in only low concentrations
* seratonin binding sites are more numerous to compensate for the low levels of the molecules
fewer nerve impulses than normal are transmitted around the brain, so lower levels of neurotransmitter released
* molecules needed for seratonin synthesis are present in only low concentrations
* seratonin binding sites are more numerous to compensate for the low levels of the molecules
47
New cards
treatments for depression
* monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
enzymes that break down neurotransmitters are inhibited, maintaining seratonin levels
(rarely used now)
* selective seratonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
inhibits reuptake of seratonin from synaptic clefts
maintain higher levels of seratonin, increasing the rate of nerve impulses
enzymes that break down neurotransmitters are inhibited, maintaining seratonin levels
(rarely used now)
* selective seratonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
inhibits reuptake of seratonin from synaptic clefts
maintain higher levels of seratonin, increasing the rate of nerve impulses
48
New cards
genes and depression
there may be a gene known to increase susceptibility that may be triggered by environmental factors
→ twin studies
→ epigenetic causes
→ twin studies
→ epigenetic causes
49
New cards
how do drugs interact with synapses?
chemicals with similar molecular structure to a particular neurotransmitter is likely to bind to the same receptor site
* from this it could stimulate the postsynaptic neurone
* the chemicals may also prevent the release of a neurotransmitter, block or open ion channels or inhibit the breakdown of enzymes
* from this it could stimulate the postsynaptic neurone
* the chemicals may also prevent the release of a neurotransmitter, block or open ion channels or inhibit the breakdown of enzymes
50
New cards
ecstasy and seratonin
MDMA impacts thinking, mood and memory
* increases seratonin concentration in the synaptic cleft by binding to the molecules in the presynaptic membrane
* prevents the reuptake of seratonin into the membrane
* increases seratonin concentration in the synaptic cleft by binding to the molecules in the presynaptic membrane
* prevents the reuptake of seratonin into the membrane
51
New cards
effects of MDMA
* euphoria and enhanced senses
* clouded thinking and agitation
* sweating
* fatigue
* rapid heart rate
* insomnia and depression
* as cells cannot meet the seratonin demand that MDMA increases
* clouded thinking and agitation
* sweating
* fatigue
* rapid heart rate
* insomnia and depression
* as cells cannot meet the seratonin demand that MDMA increases
52
New cards
what is acetylcholine
neurotransmitter that binds to postsynaptic neurone to change their shape, allowing sodium ions so diffuse in via the newly opened sodium ion channel
53
New cards
auxins
eg IAA
responsible for phototropisms, geotropisms and growth responses
produce in low concenrations, then transported to produce the response
* root tip → inhibits elongation
* shoot tip → promotes elongation
responsible for phototropisms, geotropisms and growth responses
produce in low concenrations, then transported to produce the response
* root tip → inhibits elongation
* shoot tip → promotes elongation
54
New cards
auxin effect on shoot in term of light
moves towards shaded side
promoted elongation of cells on shaded side
curves towards the light
positively phototropic
promoted elongation of cells on shaded side
curves towards the light
positively phototropic
55
New cards
auxin effect on shoot in terms of gravity
promotes elongation of cells
auxin moves down with the pull of gravity
promotes elongation of cells downward
negatively geotropic
auxin moves down with the pull of gravity
promotes elongation of cells downward
negatively geotropic
56
New cards
auxin effect on root in terms of light
auxin moved to the shaded side
inhibits elongation
root moves away from the light
negatively phototropic
inhibits elongation
root moves away from the light
negatively phototropic
57
New cards
auxin effect on root in terms of gravity
auxin moves away from the gravitational pull
inhibiting elongation
root grows down
positively geotropic
inhibiting elongation
root grows down
positively geotropic
58
New cards
phytochromes
absorb red and far-red light
consists of a protein component, bonded to a non protein light absorbing pigment molecule
consists of a protein component, bonded to a non protein light absorbing pigment molecule
59
New cards
Pr
phytochrome red (660nm)
Pr + red light → Pfr
Pr + red light → Pfr
60
New cards
Pfr
phytochrome far red (730nm)
Pfr + far red light → Pr
Pfr + far red light → Pr
61
New cards
which pigment dominates in sunlight?
Pfr
hence overnight it reverts to Pr
hence overnight it reverts to Pr
62
New cards
what plant responses do phytochromes regulate
* seed germination
* stem elongation
* leaf expansion
* chlorophyll formation
* flowering
* stem elongation
* leaf expansion
* chlorophyll formation
* flowering
63
New cards
germination and phytochromes
when exposed to far red light, Pfr converts to Pr and germination is inhibited
red light triggers germination
if flashed with f.r light, germination is inhibited
if flashed again, germination is re-triggered, proving that the effects are reversible
red light triggers germination
if flashed with f.r light, germination is inhibited
if flashed again, germination is re-triggered, proving that the effects are reversible
64
New cards
photoperiods
relative day/night length and environmental cue determining time of flowering
* the Pr:Pfr ratio in plant allows it to internally determine the length of days and nights
* short days give enough time for Pfr → Pr
* the Pr:Pfr ratio in plant allows it to internally determine the length of days and nights
* short days give enough time for Pfr → Pr
65
New cards
long day plants
eg strawberries
associated with the summer
when there is darkness less than 12 hours
reqiure Pfr to flower, therefore not enough time for it to convert to Pr
associated with the summer
when there is darkness less than 12 hours
reqiure Pfr to flower, therefore not enough time for it to convert to Pr
66
New cards
short day plants
eg poinsettias
requires uninterrupted darkness greater than 12 hours to give enough time for all Pfr → Pr
Pfr inhibits flowering
\
requires uninterrupted darkness greater than 12 hours to give enough time for all Pfr → Pr
Pfr inhibits flowering
\
67
New cards
greening
* shoots undergo greening once the shoot breaks through the soil into sunlight
* once in the light, phytochromes promote development of primary leaves and pigment
* need Pfr for chlorophyll production
* once in the light, phytochromes promote development of primary leaves and pigment
* need Pfr for chlorophyll production
68
New cards
phytochromes and switching on and off
each activated phytochrome interacts with other proteins, causing either binding to the protein or disrupting binding of a protein complex
69
New cards
what does Pfr inhibit?
short day plants
no flowering
no flowering
70
New cards
what does Pfr enable?
germination
long day plants
chlorophyll formation
it is a signal protein that acts as a transcription factors to enable the usual transciption pathway
long day plants
chlorophyll formation
it is a signal protein that acts as a transcription factors to enable the usual transciption pathway
71
New cards
grey matter
neurone cell bodies
72
New cards
white matter
neurone fibres
73
New cards
cerebral hemispheres
* controls higher functions
* thinking, feeling, seeing and learning
* mainly grey matter
* folded cortex to give a large surface area
* divided into lobes
* thinking, feeling, seeing and learning
* mainly grey matter
* folded cortex to give a large surface area
* divided into lobes
74
New cards
how to the left and right cerebral hemispheres communicate
joined at the centre with a band of axons called the corpus callosum
\
\
75
New cards
frontal lobe
* emotional response, planning ahead, reasoning and decision making
* the ‘conscious’ area of the brain
* last to be fully developed
* primary motor cortex, controlling body movements via motor neurones passing through the hindbrain and spinal cord
* the ‘conscious’ area of the brain
* last to be fully developed
* primary motor cortex, controlling body movements via motor neurones passing through the hindbrain and spinal cord
76
New cards
temporal lobes
* auditory information
* near to the ears
* near to the ears
77
New cards
occipital lobe
* visual information
* input from the eyes to deal with vision, shape recognition, colour and perspective
* at the back of the brain
* input from the eyes to deal with vision, shape recognition, colour and perspective
* at the back of the brain
78
New cards
parietal lobe
* memory recognition
* ability to calculate
* sense of movement and orientation
* ability to calculate
* sense of movement and orientation
79
New cards
hypothalamus
* controls the autonomic nervous system
* thermoregulation
* right in the centre of the brain
* monitors:
* blood chemistry
* hormone secretions of the pituitary gland
* basic drives → thirst, hunger, aggression and reproductive behaviour
* thermoregulation
* right in the centre of the brain
* monitors:
* blood chemistry
* hormone secretions of the pituitary gland
* basic drives → thirst, hunger, aggression and reproductive behaviour
80
New cards
thalamus
* larger structure attached to hypothalamus
* routes all incoming sensory information to the correct parts of the brain
* routes all incoming sensory information to the correct parts of the brain
81
New cards
hippocampus
* lays down long term memory
* underneath the hypothalamus
* underneath the hypothalamus
82
New cards
cerebellum
* coordinates smooth motor movements
* uses info from muscles and ears for posture and balance
* uses info from muscles and ears for posture and balance
83
New cards
medulla oblongata
* the most primitive part of the brain
* controls reflex centres:
* heart rate
* blood pressure
* sneezing
* digestive muscles
* maintains basic life responses even where major areas of the brain are damaged
* bottom of the skull, down the back of the neck
* will not be considered ‘dead’ until the medulla is no longer functioning
* controls reflex centres:
* heart rate
* blood pressure
* sneezing
* digestive muscles
* maintains basic life responses even where major areas of the brain are damaged
* bottom of the skull, down the back of the neck
* will not be considered ‘dead’ until the medulla is no longer functioning
84
New cards
what is a CAT/CT scan used for?
* producing frozen pictures of the brain to identify structures to detect brain disease
* monitor tissues over the course of an illness
* monitor tissues over the course of an illness
85
New cards
how does a CAT/CT scan work?
1. narrow beam X-rays rotate around the patient
2. the strength of the beam varies depending on the density of the tissue it is passing through
3. X-rays are detected to produce an image
86
New cards
what are MRIs used for?
* diagnosis of tumors, brain injuries, strokes and infections
* MRIs have better resolutions than CT scans so more detailed images of the brain can be produced
* MRIs have better resolutions than CT scans so more detailed images of the brain can be produced
87
New cards
how do MRIs work?
1. magnetic fields and radio waves detect soft tissue
2. in a magnetic field, nuclei of atoms line up with the direction of the magnetic field
3. H atoms are monitored due to the high water content in the tissues and they line up with the magnetic field
4. energy absorbed by the H ions is detected and analysed by the computer to produce an image
88
New cards
what is a functional MRI used for?
* makes it possible to study human activities
* can also be used to follow the sequence of events over a short period of time
* can also be used to follow the sequence of events over a short period of time
89
New cards
how does a functional MRI work?
1. increased neural activity results in an increase in O2 absorption from the blood, reducing the signal received by the computer
2. the less signal absorbed, the higher activity in that area
3. different ares of the brain light up on the image when they are active
90
New cards
what is a PET scan used for?
* evaluate the structures and functions of tissues and organs
* diagnosis of cancers, heart disease, brain disorders
* monitors spread of cancers and observe the effect of treatment
* diagnosis of cancers, heart disease, brain disorders
* monitors spread of cancers and observe the effect of treatment
91
New cards
how does a PET scan work?
1. patient injected with a radiotracer (short half life isotopes incorporated into glucose or water that will bind to receptors)
2. as it decays it emits positrons
3. when a particular area is active, there is increased blood flow, so more radiotracers are present in that area
4. release of gamma rays as they collide with positrons that are converted into an image on the computer