Chapter 6: Roman Art
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Art History
AP Art History
Legendary founding of Rome by Romulus and Remus
Roman Republic
Roman Empire
Roman Architecture
House of Vettii
Flavian Amphitheater
The Colosseum
Content Area for Petra: West and Central Asia
Petra, Jordan
Great Temple of Petra
Treasury of Petra
Apollodorus of Damascus
Forum of Trajan
Basilica of Ulpia
Trajan Markets
Pantheon
Roman Painting
Pentheus Room
Roman Sculpture
Head of a Roman patrician
Augustus of Prima Porta
Column of Trajan
Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus
12th
Last updated 8:07 AM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
Romulus and Remus
According to legend, ____, abandoned twins, were suckled by a she-wolf, and later established the city of Rome on its fabled seven hills.
2
New cards
Augustus Caesar
Civil war in the late Republic caused a power vacuum that was filled by Octavian, later called ____, who became emperor in 27 B.C.E.
3
New cards
Ashlar Masonry
A technique used where building are built without mortar.
4
New cards
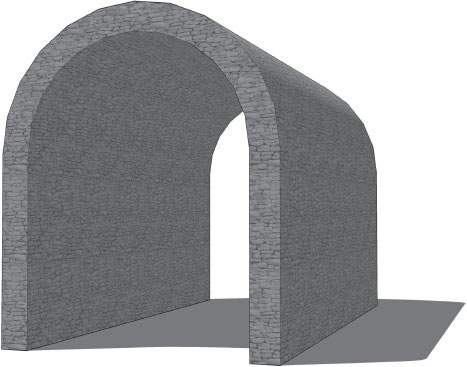
barrel vault
Roman architects understood that arches could be extended in space and form a continuous tunnel-like construction called a \___.
5
New cards
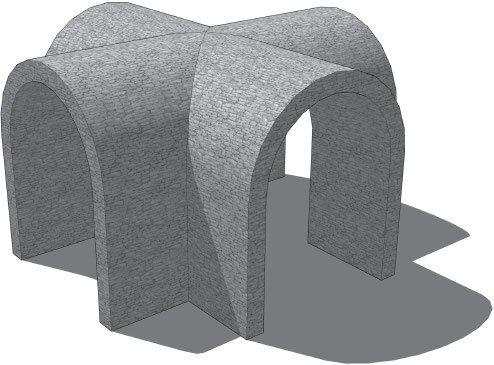
groin vault
A larger more open space, formed when two barrel vaults intersect.
6
New cards
corner piers
The latter is particularly important because the groin vault could be supported with only four \____, rather than requiring a continuous wall space that a barrel vault needed.
7
New cards
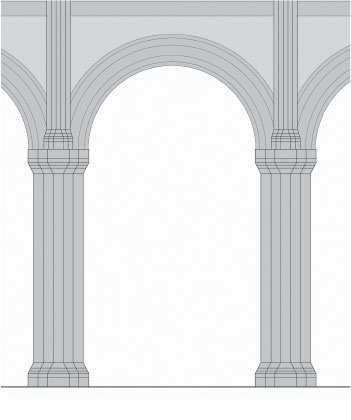
Piers
a vertical support that holds up an arch or a vault
8
New cards
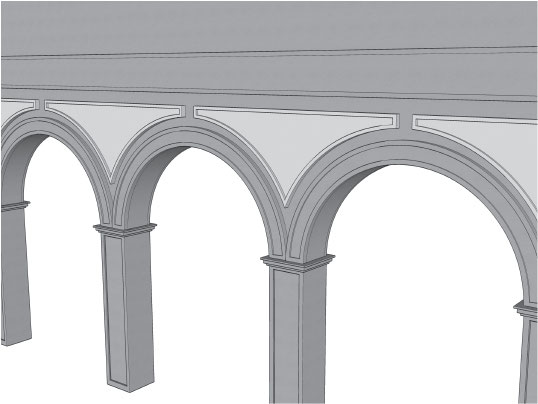

Spandrels
The spaces between the arches on the piers.
9
New cards
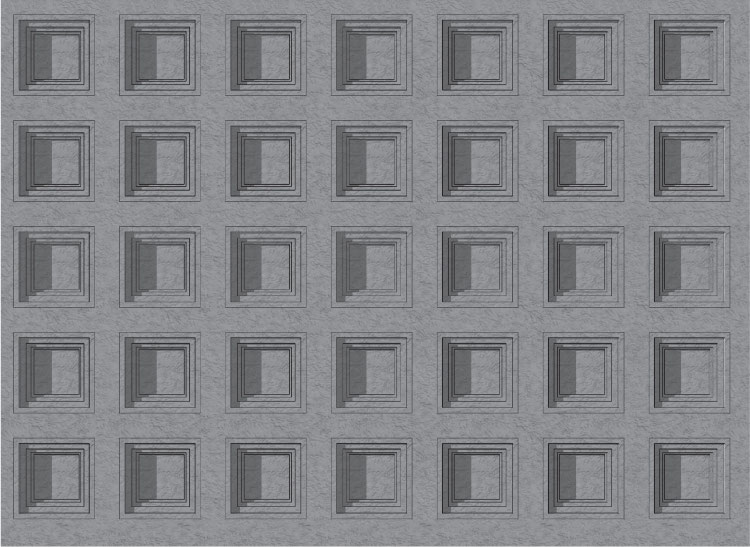
Coffer
in architecture, a sunken panel in a ceiling
10
New cards
concrete
The Romans used \____ in constructing many of their oversized buildings.
11
New cards
Impluvium
a rectangular basin in a Roman house that is placed in the open-air atrium in order to collect rainwater
12
New cards
Cubiculum
a Roman bedroom flanking an atrium; in Early Christian art, a mortuary chapel in a catacomb
13
New cards
Atrium
a courtyard in a Roman house or before a Christian church
14
New cards
peristyle
The Romans placed their intimate rooms deeper into the house. Eventually another atrium, perhaps held up by columns called a \_____, provided access to a garden flanked by more cubicula.
15
New cards
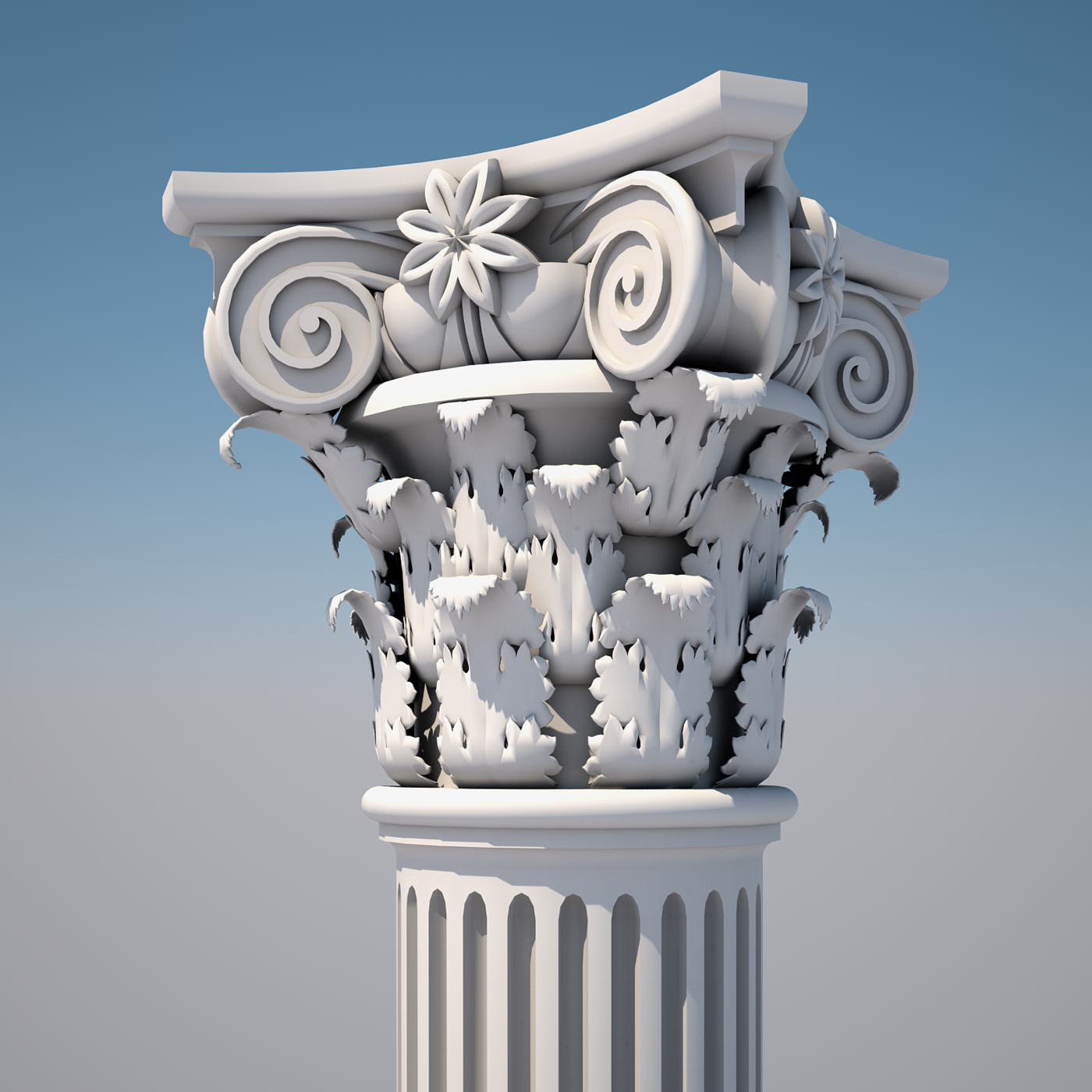

Composite column
one that contains a combination of volutes from the Ionic order and acanthus leaves from the Corinthian order
16
New cards
Keystone
the center stone of an arch that holds the others in place
17
New cards
Flagstaffs
These staffs are the anchors for a retractable canvas roof, called a velarium.
18
New cards
Velarium
A retractable canvas roof used to protect the crowd on hot days.
19
New cards
Hypogeum
The subterranean part of an ancient building.
20
New cards
Basilica
in Roman architecture, a large axially planned building with a nave, side aisles, and apses
21
New cards
Cupola
a small dome rising over the roof of a building; in architecture, a cupola is achieved by rotating an arch on its axis
22
New cards
Oculus
a circular window in a church, or a round opening at the top of a dome
23
New cards
Fresco
a painting technique that involves applying water-based paint onto a freshly plastered wall. The paint forms a bond with the plaster that is durable and long-lasting
24
New cards
Encaustic
an ancient method of painting that uses colored waxes burned into a wooden surface
25
New cards
Perspective
depth and recession in a painting or a relief sculpture.
26
New cards
Orthogonals
\_______ recede to multiple vanishing points in the distance.
27
New cards
Foreshortening
a visual effect in which an object is shortened and turned deeper into the picture plane to give the effect of receding in space
28
New cards
**First Pompeian Style**
Characterized by painted rectangular squares meant to resemble marble facing.
29
New cards
**Second Pompeian Style**
had large mythological scenes and/or landscapes dominating the wall surface. Painted stucco decoration of the First Style appears beneath in horizontal bands.
30
New cards
**Third Pompeian Style**
characterized by small scenes set in a field of color and framed by delicate columns of tracery.
31
New cards
Triclinium
a dining room in a Roman house.
32
New cards
Veristic
sculptures from the Roman Republic characterized by extreme realism of facial features
33
New cards
Bust
a sculpture depicting the head, neck, and upper chest of a figure
34
New cards
Contrapposto
a graceful arrangement of the body based on tilted shoulders and hips and bent knees
35
New cards
Continuous narrative
a work of art that contains several scenes of the same story painted or sculpted in continuous succession
36
New cards
Horror vacui
(Latin for a “fear of empty spaces”) a type of artwork in which the entire surface is filled with objects, people, designs, and ornaments in a crowded, sometimes congested way
37
New cards

House of Vettii
* Private citizen’s home in Pompeii
* Originally built during the Republic with early imperial additions.
* Two brothers owned the house; both were freedmen who made their money as merchants.
* Originally built during the Republic with early imperial additions.
* Two brothers owned the house; both were freedmen who made their money as merchants.
38
New cards
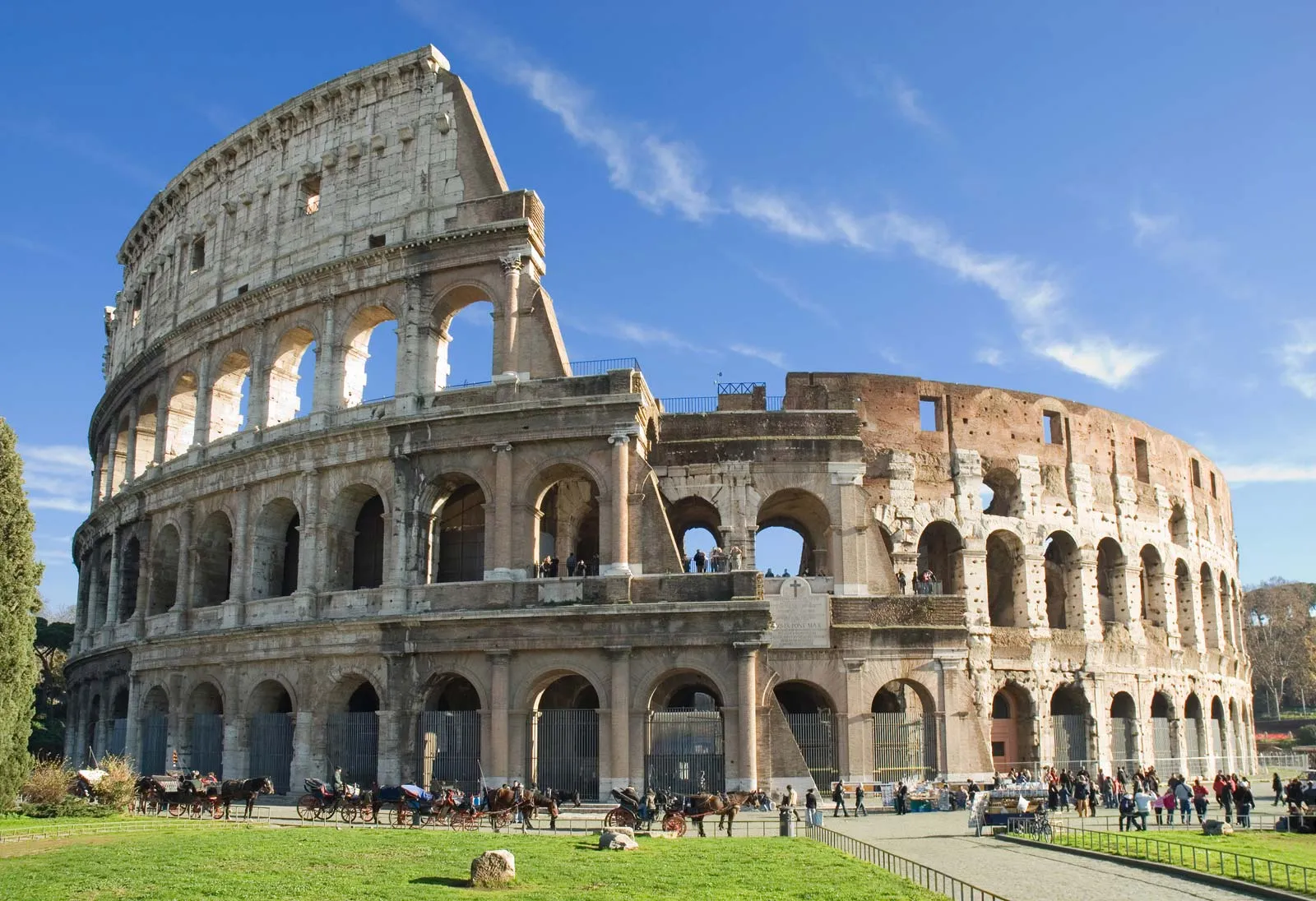

The Colosseum
* meant for wild and dangerous spectacles—gladiator combat, animal hunts, naval battles.
* Accommodated 50,000 spectators.
* 76 entrances and exits circle the façade.
* the name comes from a colossal statue of Nero that used to be adjacent.
* Accommodated 50,000 spectators.
* 76 entrances and exits circle the façade.
* the name comes from a colossal statue of Nero that used to be adjacent.
39
New cards
Petra
was a central city of the Nabataeans, a nomadic people, until Roman occupation in 106 C.E.
40
New cards
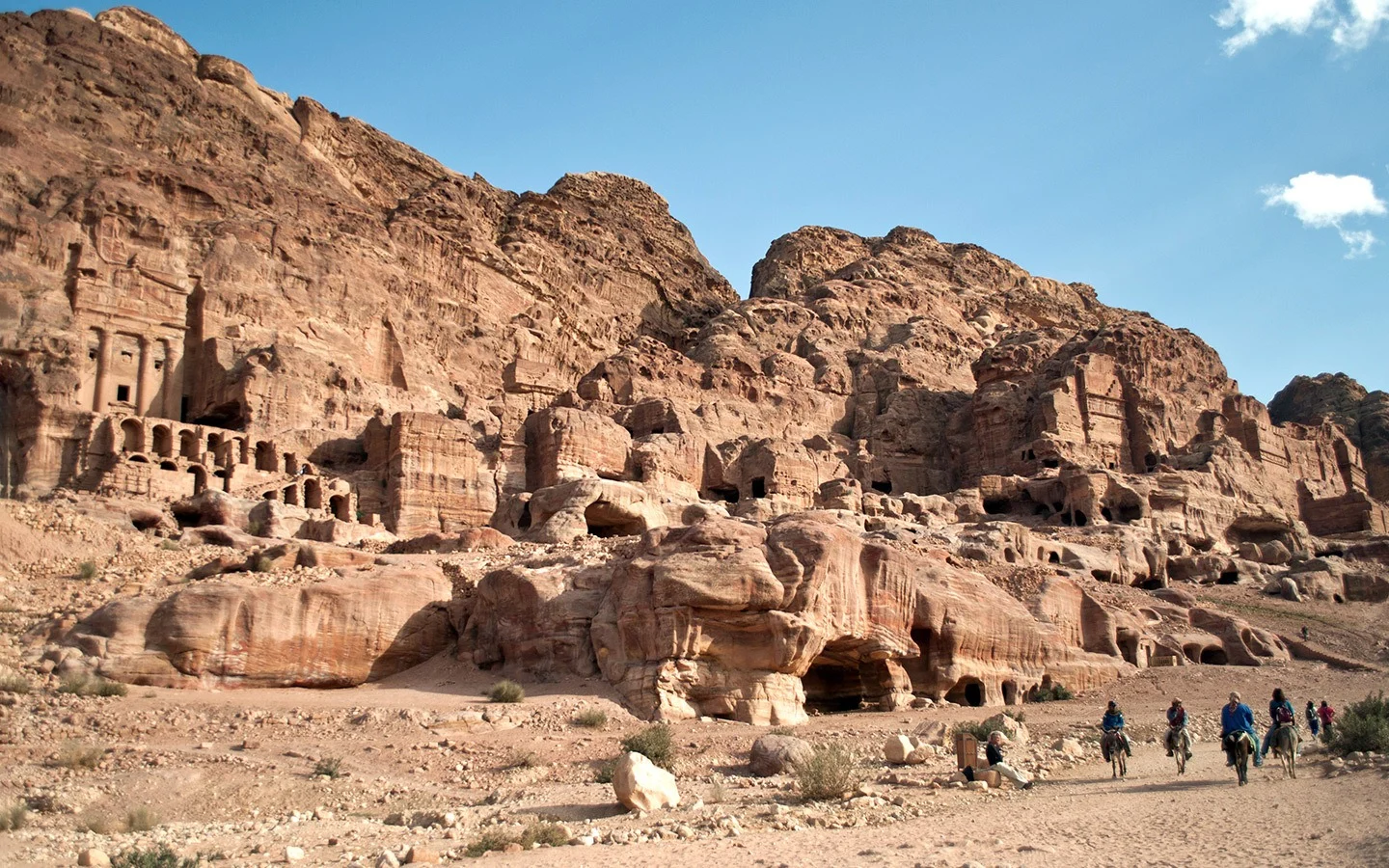

Great Temple of Petra
* Nabataean concept and Roman features such as Corinthian columns.
* The city was built along a caravan route.
* Approached through a propylaeum and a grand staircase that leads to a colonnade terrace in the lower precincts.
* The city was built along a caravan route.
* Approached through a propylaeum and a grand staircase that leads to a colonnade terrace in the lower precincts.
41
New cards
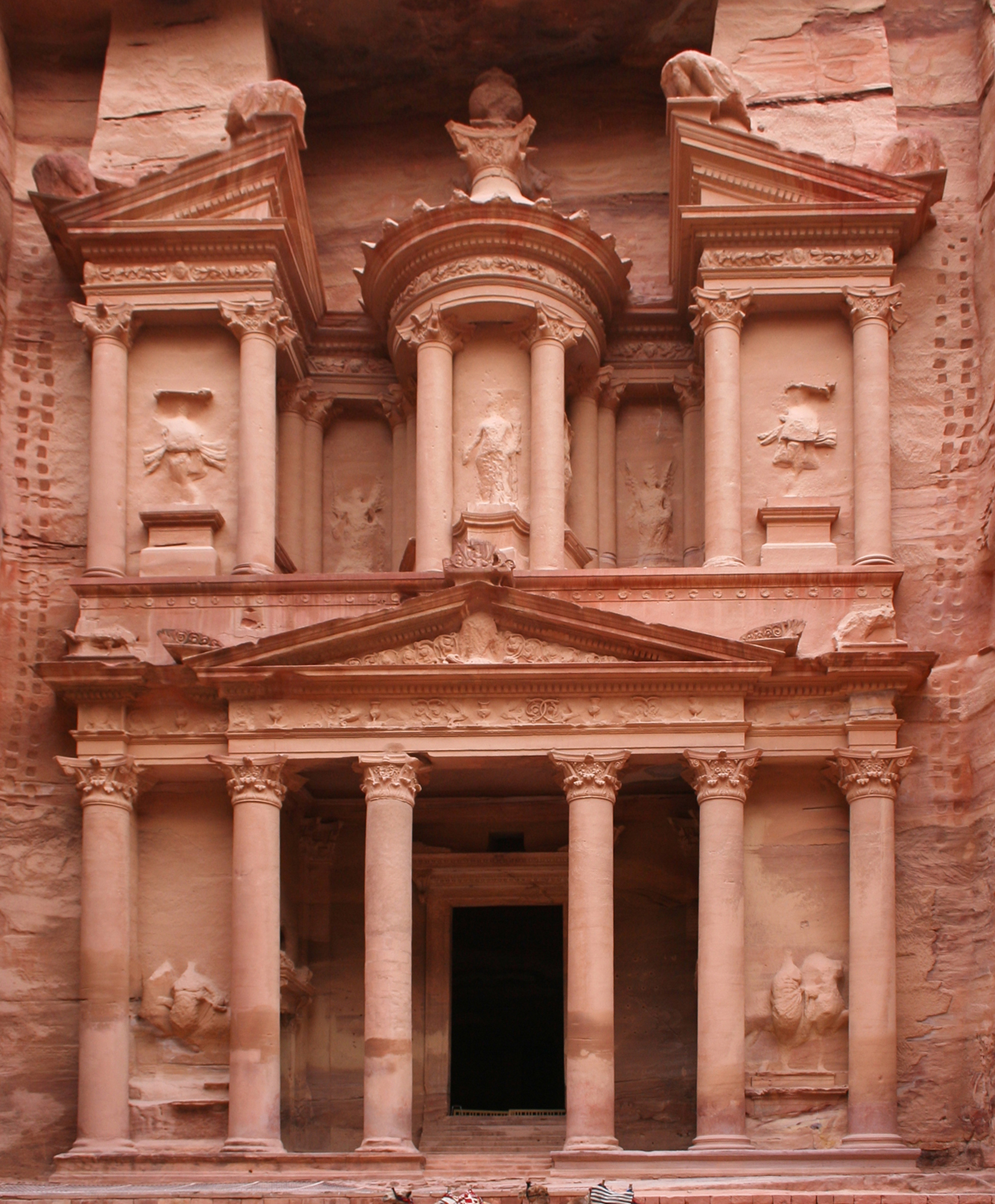

Treasury of Temple (Petra)
* In reality, it was a tomb, not a “treasury,” as the name implies.
* Greek, Egyptian, and Assyrian gods on the façade.
* Monuments carved in traditional Nabataean rock-cut cliff walls.
* Greek, Egyptian, and Assyrian gods on the façade.
* Monuments carved in traditional Nabataean rock-cut cliff walls.
42
New cards
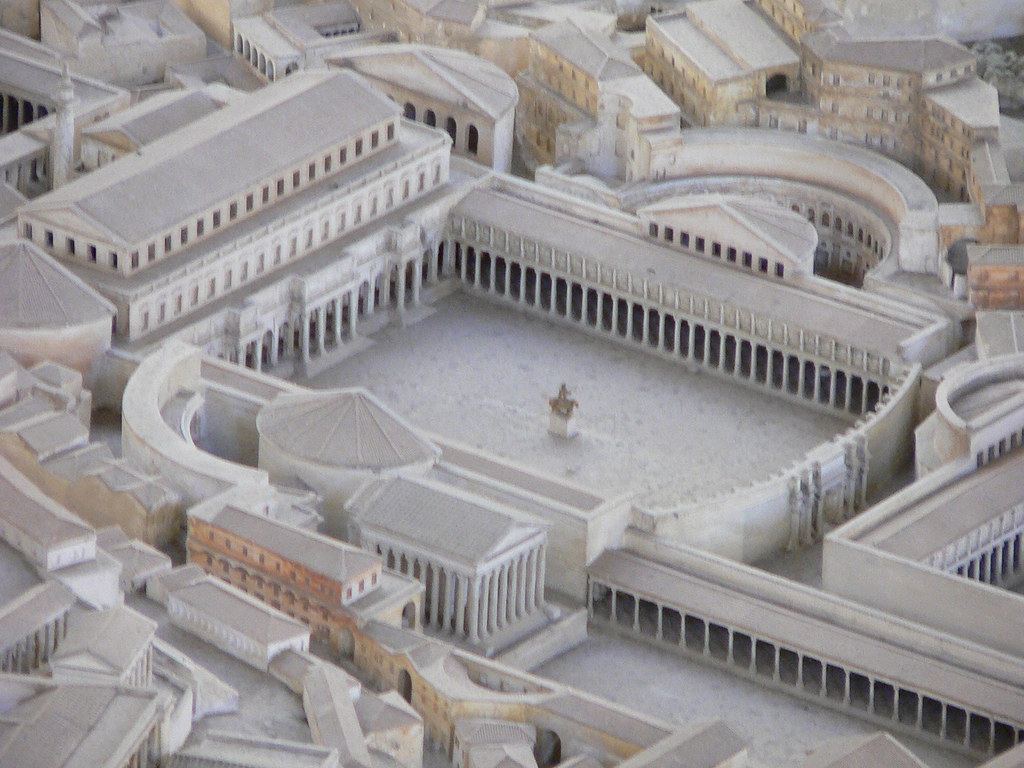

Forum of Trajan
* Large central plaza flanked by stoa-like buildings on each side.
* Originally held an equestrian monument dedicated to Trajan in the center.
* Built with booty collected from Trajan’s victory over the Dacians.
* Originally held an equestrian monument dedicated to Trajan in the center.
* Built with booty collected from Trajan’s victory over the Dacians.
43
New cards
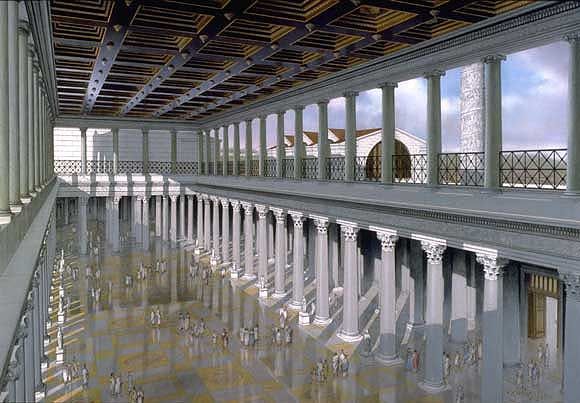

Basilica of Ulpia
* Law courts held here; apses were a setting for judges.
* Said to have been paid for by Trajan’s spoils taken from the defeat of the Dacians.
* Grand interior space (385 feet by 182 feet) with two apses.
* Said to have been paid for by Trajan’s spoils taken from the defeat of the Dacians.
* Grand interior space (385 feet by 182 feet) with two apses.
44
New cards
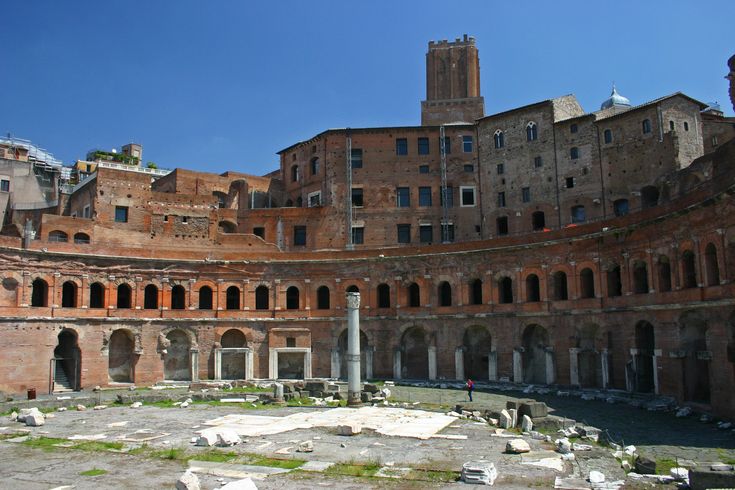

Trajan Markets
* Semicircular building held several levels of shops.
* Main space is groin vaulted; barrel vaulted area with the shops.
* Multilevel mall.
* Original market had 150 shops.
* Main space is groin vaulted; barrel vaulted area with the shops.
* Multilevel mall.
* Original market had 150 shops.
45
New cards
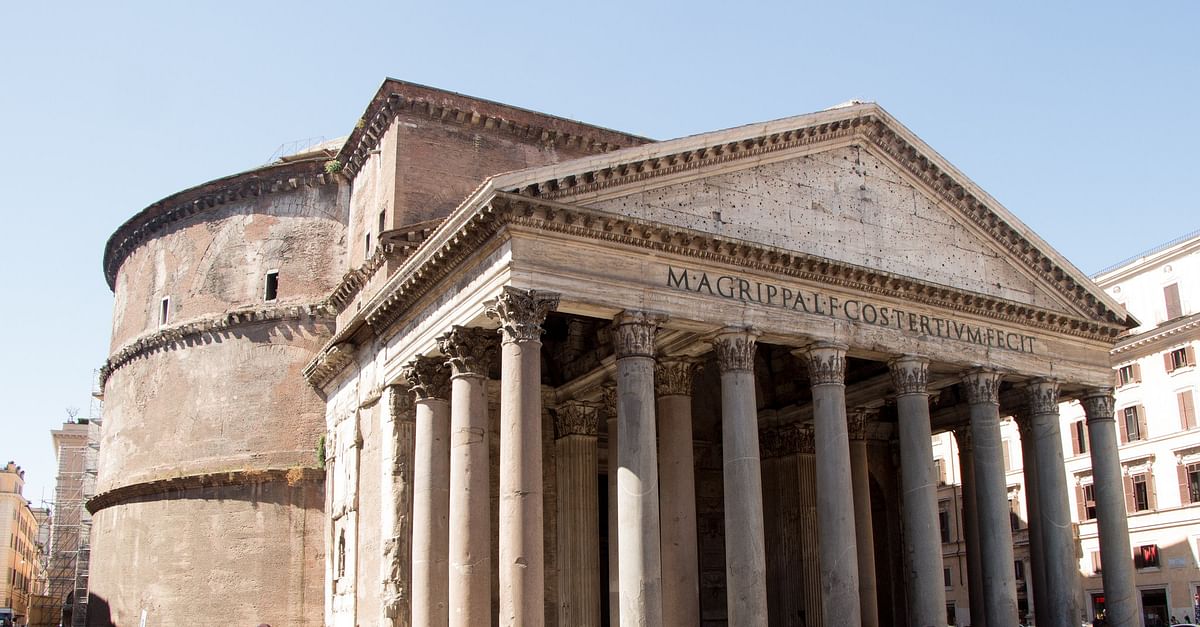

Pantheon
* it was built as a Roman temple dedicated to all the gods.
* it may have been dedicated to a select group of gods and the divine Julius Caesar and/or used for court rituals.
* It is now a Catholic church called Santa Maria Rotonda.
* it may have been dedicated to a select group of gods and the divine Julius Caesar and/or used for court rituals.
* It is now a Catholic church called Santa Maria Rotonda.

46
New cards
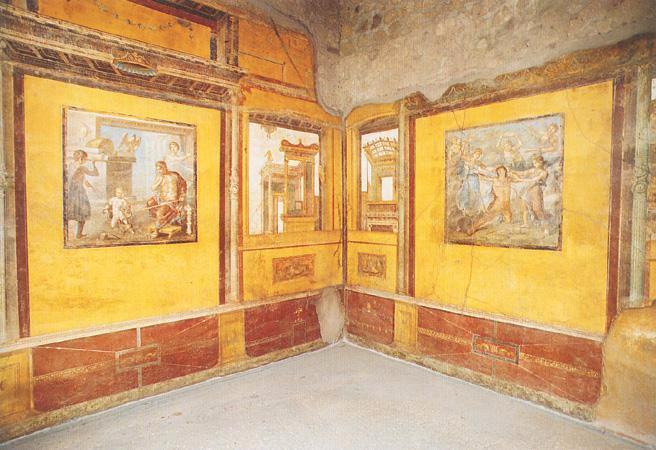

Pentheus Room
* a Triclinium
* Main scene is the death of the Greek hero.
* This painting opens the room with the illusion of windows and a sunny cityscape beyond.
* Main scene is the death of the Greek hero.
* This painting opens the room with the illusion of windows and a sunny cityscape beyond.
47
New cards
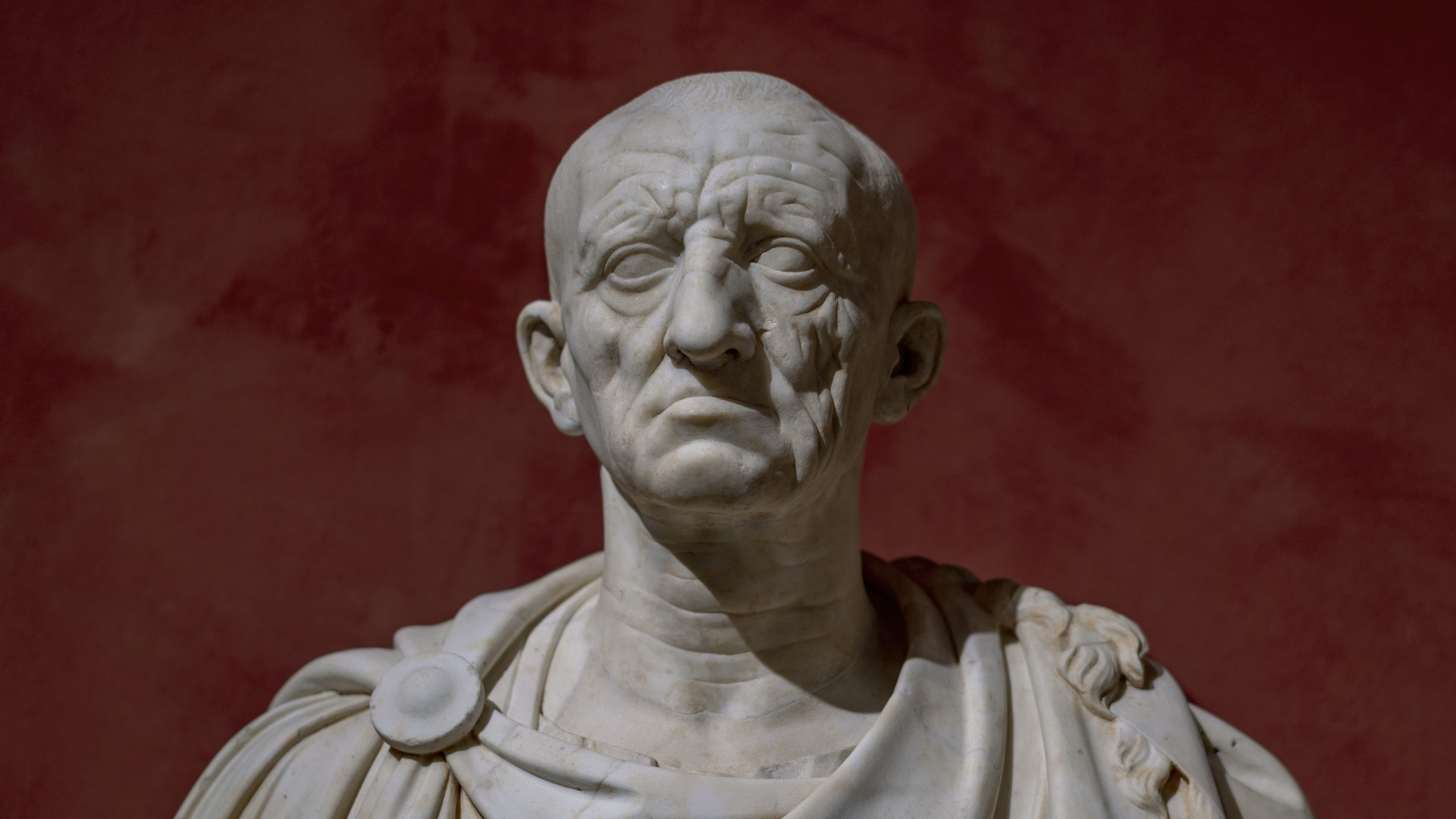

Head of a Roman patrician
* Tradition of wax portrait masks in funeral processions of the upper class to commemorate their history.
* Bulldog-like tenacity of features
* Features may have been exaggerated
* Bulldog-like tenacity of features
* Features may have been exaggerated
48
New cards
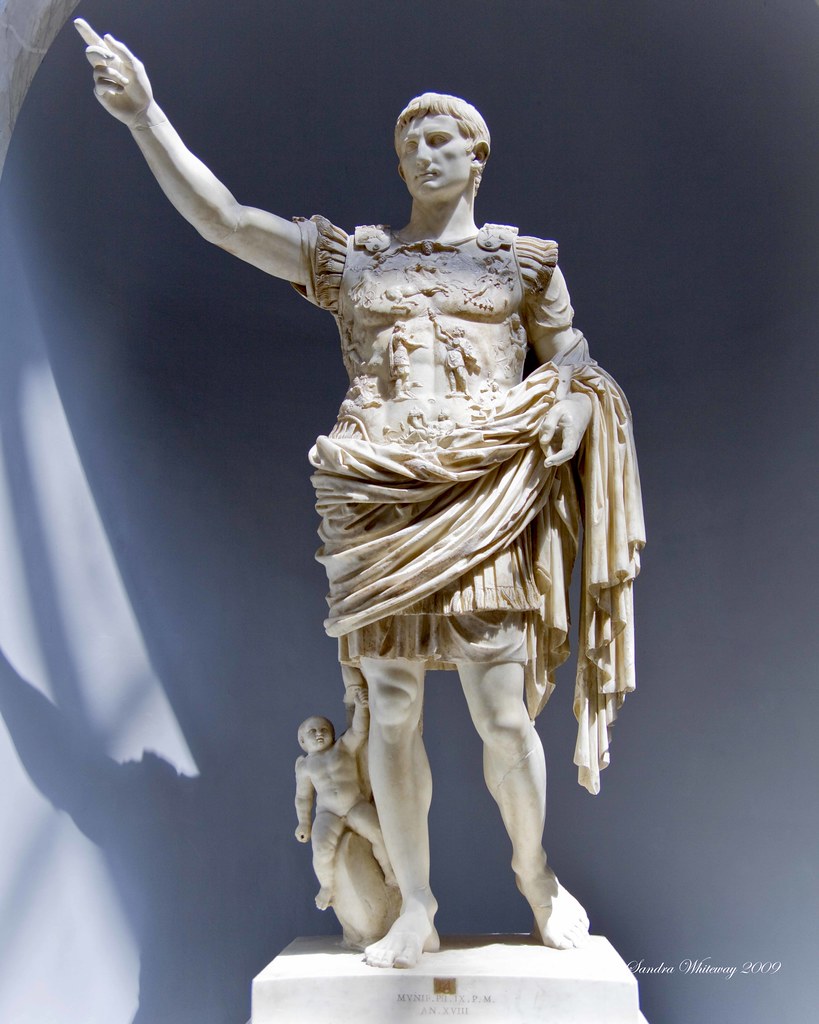

Augustus of Prima Porta
* Contrapposto.
* References Polykleitos’s Doryphoros.
* Found in the villa of Livia, Augustus’s wife
* May have been commissioned by Emperor Tiberius
* References Polykleitos’s Doryphoros.
* Found in the villa of Livia, Augustus’s wife
* May have been commissioned by Emperor Tiberius
49
New cards
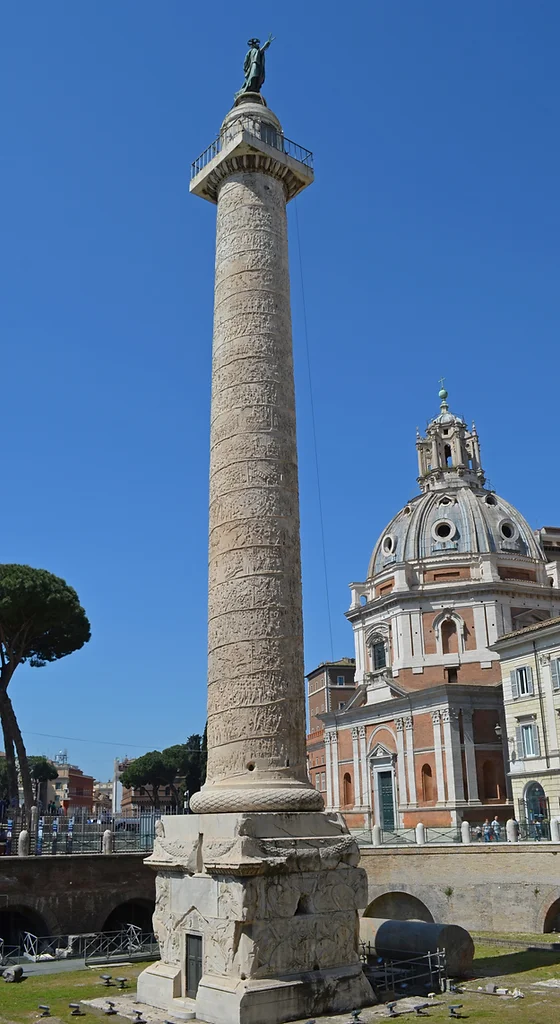

Column of Trajan
* A 625-foot narrative cycle (128 feet high) wrapped around it
* 150 episodes, 2,662 figures, 23 registers—continuous narrative.
* Scenes depict the preparation for battle
* Visitors who entered were meant to wander up the interior spiral staircase to the viewing platform at the top
* 150 episodes, 2,662 figures, 23 registers—continuous narrative.
* Scenes depict the preparation for battle
* Visitors who entered were meant to wander up the interior spiral staircase to the viewing platform at the top
50
New cards
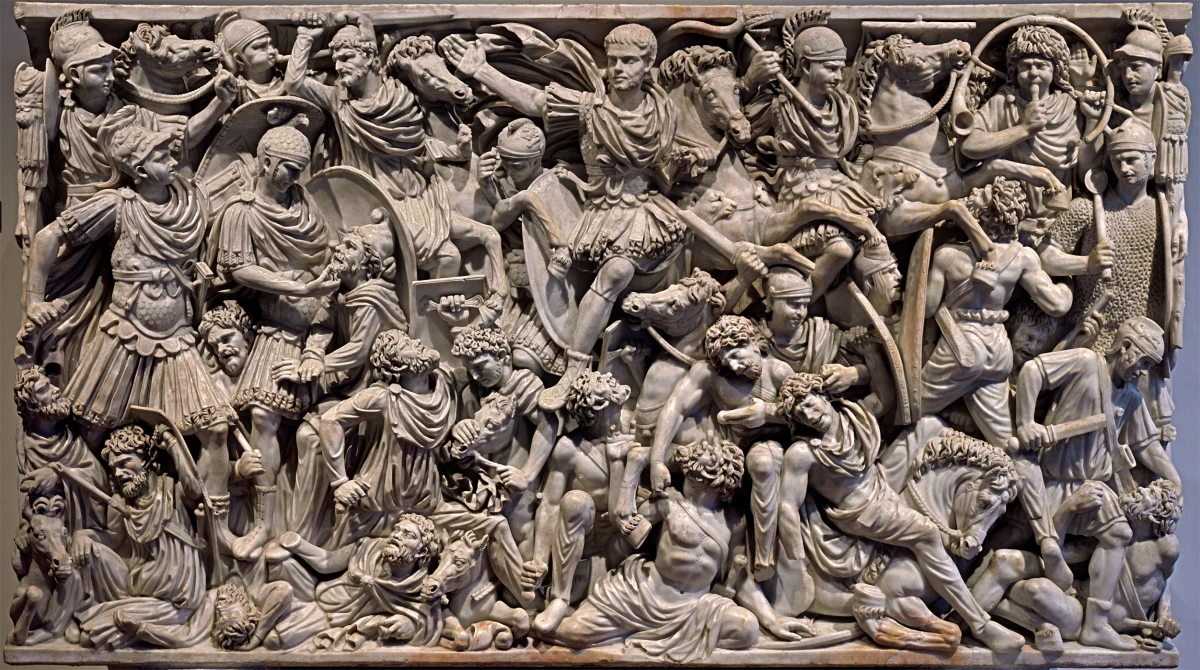

Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus
* Extremely crowded surface with figures piled atop one another; horror vacui.
* Interment of the dead; rich carving suggests a wealthy patron with a military background.
* Confusion of battle is suggested by congested composition.
* Interment of the dead; rich carving suggests a wealthy patron with a military background.
* Confusion of battle is suggested by congested composition.