Edexcel IGCSE Physics - Stellar Evolution
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what is the colour of a star caused by?
the visible light it emits
what determines how much visible light of each frequency a star emits?
its surface temperature
what colour light has the lowest frequency?
red
what colour light has the highest frequency?
blue
what frequency of light do very hot stars emit?
high
what frequency of light do cooler stars emit?
low
what are the 5 colours used to classify stars?
red, orange, yellow, blue, white
what is the order of star colours from hottest to coolest (1 is hottest)?
blue
white
yellow
orange
red
why are some stars white?
they emit roughly equal amounts of all colours of light
what are the 2 kinds of star evolution cycle?
evolution of stars with a similar mass to the sun
evolution of stars with a higher mass than the sun
what are the stages of evolution of stars with a similar mass to the sun?
nebula
protostar
main sequence star
red giant
white dwarf
what are the stages of evolution of stars with a higher mass than the sun?
nebula
protostar
main sequence star
red supergiant
supernova
neutron star OR black hole
what is a nebula?
a cloud of dust and gas
describe the change from a nebula to a protostar
the force of gravity pulls the dust and gas together to form a protostar
the temperature rises as the star gets denser
describe the change from a protostar to a main sequence star
when the temperature and pressure become high enough, hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium nuclei
this releases a lot of energy, keeping the core of the star hot
a star is born
describe the stage of being a main sequence star
the outward pressure caused by nuclear fusion balances the force of gravity pulling everything inwards
this stage lasts for a very long time
the heavier the mass, the shorter the stage
describe the change from a main sequence star to a red giant
the hydrogen is used up and the centre of the star collapses due to the lack of outward pressure (force of gravity is greater)
it becomes extremely dense and hot, so the energy and pressure cause the outer layers to expand greatly to become a red giant
the star becomes red because the surface cools
describe the change from a red giant to a white dwarf
the red giant star becomes unstable - outer layers of dust and gas are ejected
the centre of the star compresses and it becomes very hot and dense
the next stage is a black dwarf where the star cools and becomes more dense - only theoretical
describe the change from a main sequence star to a red super giant
the hydrogen is used up and the centre of the star collapses due to the lack of outward pressure (force of gravity is greater)
it becomes extremely dense and hot, so the energy and pressure cause the outer layers to expand massively to become a red super giant
the star becomes red because the surface cools
describe the change from a red super giant to a supernova
more fusion begins to take place to make heavier elements, going up to iron
the stars expand and contract as the balance shifts between gravity and thermal pressure
the stars explode in a supernova
describe the change from a supernova to a neutron star or black hole
the supernova throws layers of dust and gas into space
this leaves a very dense core called a neutron star
if the star is massive enough, it will collapse and become a black hole - incredibly dense point that no light can escape from
what does apparent magnitude mean?
the perceived brightness of a star as seen from Earth - the closer the star the brighter it appears
what does absolute magnitude mean?
how bright a star would be if it was at a fixed distance from earth
what is the rough absolute magnitude of the sun?
+5
what is the relationship between absolute magnitude and brightness of a star?
the lower (more negative) the absolute magnitude, the more bright a star is
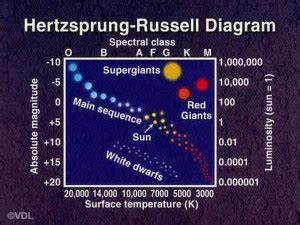
what diagrams are used to show different types of star?
Hertzsprung-Russel Diagrams
what are the axis on a Hertzsprung-Russel diagram?
y-axis → (decreasing as upwards) absolute magnitude
x-axis → (decreasing as right) temperature
where are main sequence, red giants/super giants, and white dwarfs located on a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram?
ignore luminosity and spectral class
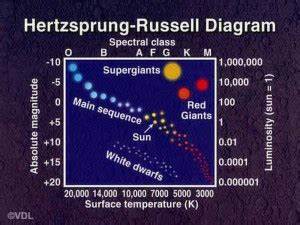
where is the sun on a Hertzsprung-Russel diagram?