Electric Circuits
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Electric current
Rate of flow of electric charge
Potential difference
Energy transferred per unit charge between two points in a circuit
Resistance
Measure of how difficult it is for charge carriers to pass through a component
Ohm's law
For an ohmic conductor, current is directly proportional to the potential difference across it, given temperature is constant
Principle of charge conservation
The total electric charge in a closed system does not change
Kirchoff's first law
Total current flowing into a junction is equal to the total current flowing out of that junction
Distribution of current in a series circuit
Current is the same everywhere
Distribution of current in a parallel circuit
The sum of currents in each parallel set of branches is equal to the total current
Principle of conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred from one form to another
Kirchoff's second law
The sum of all the voltages in a series circuit is equal to the battery voltage
Distribution of potential differences in a series circuit
The total sum of the voltages across all elements is equal to the supply p.d
Distribution of potential differences in a parallel circuit
The p.d across each branch is the same
Distribution of resistance in a series circuit
Rₜ = R₁ + R₂ + R₃ + ...
Derivation of resistance in series
V = V₁ + V₂ + V₃
V = IR₁ + IR₂ + IR₃
V = I(R₁ + R₂ + R₃)
R = R₁ + R₂ + R₃
Distribution of resistance in a parallel circuit
1/R = 1/R₁ + 1/R₂ = 1/R₃ + ...
Derivation of resistance in parallel
I = I₁ + I₂ + I₃
I = V/R₁ + V/R₂ + V/R₃
I = V(1/R₁ + 1/R₂ + 1/R₃)
1/R = 1/R₁ + 1/R₂ + 1/R₃
Power
Rate of transfer of energy
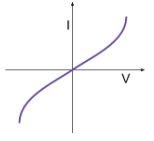
Current-voltage graph of an ohmic conductor
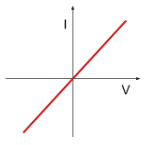
Current-voltage graph of a diode
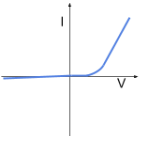
Current-voltage graph of a filament bulb
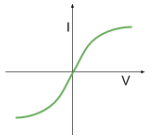
Current-voltage graph of a (Negative Temperature Coefficient) thermistor
Resistivity
A measure of how easily a material conducts electricity
What are the variables in the equation ρ = RA/l?
ρ: Resistivity
R: Resistance
A: Cross-sectional area
l: Length
What are the variables in the equation I = nAve?
I: Current
n: Charge carrier density (number of electrons per unit volume)
A: Cross-sectional area
v: mean drift velocity
e: electron charge
How does length of a wire affect p.d?
Because R = ρl/A, as length increases, resistance increases. Using Ohm's law (V = IR), as resistance increases, potential difference also increases
Potential divider circuits
A circuit with several resistors in series connected across a voltage source used to produce a fraction of the source p.d
Variable potential divider circuits
A potential divider circuits where one resistor is a variable resistor, meaning you can vary the potential difference output
Electromotive force
The energy transferred by a cell per coulomb of charge that passes through it
Internal resistance
Energy lost due to electrons colliding with atoms inside the battery
Terminal potential difference
The p.d across the resistance R
Lost volts
The p.d across the resistance r
Lattice structure
Provides a medium for vibration of the atoms about their equilibrium position. As temperature of the solid increases, intensity of the vibration of atoms also increases
How does lattice vibrations affect resistance?
The more intense the vibrations, electrons are more likely to collide with the atoms, causing them to slow down. This in turn increases the resistance of the material
Temperature increase in a semiconductor
As temperature increases, its atoms gain energy and once they gain enough energy they begin to release electrons. This increases the number of charge carriers available which decreases resistance
Negative temperature coefficient thermistors
As temperature increases, resistance decreases
Metallic conductors
As temperature increases, resistance increases
Light-dependant resistors
Made from photoconductive materials. Because of the photoelectric effect, as light intensity increases, electrons are released and resistance decreases