Human Geog Mid#2
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
What is the principle feature of language?
Spoken
How many languages are currently spoken?
7000
What is an Institutional language?
A language used in education, work, mass media, and government
What is a Stable language?
A language used for face-to-face communications with all generations
What is an endangered language?
A threatened or dying language because it is not being passed to younger generations
Language Family
A collection of languages that existed long before recorded history
Language Branch
A collection of languages within a family related through a common ancestral language that existed several thousand years ago
Language Group
A collection of languages within a branch that share a common origin in the relatively recent past
What language family is most spoken worldwide?
Indo-European
What two language families are spoken by 2/3rds of the worlds population?
Indo-European & Sino-Tibetan
How many writing systems are present around the world?
3856
How many language families have at least 50 million speakers?
12
What is the “taxonomy” of the English language?
Indo-European / Germanic Branch / West Germanic Group
What languages fall under the Uralic group?
Finnish, Estonian, and Hungarian
What is Quentin Atkinson’s theory of language origin?
Believed it spread from West Africa as there is a greater diversity of sounds getting further from W. Africa
What is Marija Gibutas’ theory on language origin?
Kurgan peoples domesticated horses, cattle, and lived in the grasslands. Their ease of migration lead to the spread of language throughout the land they searched for grassland
What is Colin Renfrew’s theory of language origin?
The first speakers lived 2000 years before the Kurgans, in the eastern part of present-day Turkey. Language triumphed due to people becoming more numerous from an Agricultural society vs. Hunting
Lingua franca
A language that is adopted as a common language between speakers whose native languages are different.
Pidgin language
A simplified, “broken” adoption of a Lingua franca
Dialect
A regional variation of a language
Isgloss
The tracking and mapping of a words’s usage boundaries
Creole
A language which forms over time from mixing a colonizer’s language with the indigenous language
Mutual intelligibility
The ability for two unique speakers to understand each other without special effort
Is Catalan a dialect, or a language?
It was a Spanish dialect, but is now classified as a distinct Romance language
What country has the most languages?
Papa New Guinea
What two countries are home to nearly 20% of all the world’s languages?
Papa New Guinea, Indonesia
How many languages are considered Endangered?
3100
50% of endangered languages are located in just _____ countries
8
Ethnicity
identity with a group of people who share the cultural traditions of a particular homeland or hearth
Race
is identity with a group of people who are perceived to share a physiological trait
Nationality
identity with a group of people who share legal attachment to a particular country.
Racism
the belief that race is the primary determinant of human traits and capacities and that racial differences produce an inherent superiority of a particular race.
What pattern of slave trade was developed in the 18th century?
A Triangular pattern
Sharecropper
Someone who works fields rented from a landowner and pays the rent by turning over to the landowner a share of the crops.
Redlining
The process of financial institutions preventing people from lending money to purchase or improve property within a delineated boundary
Ethnic enclave
A place with a high concentration of an ethnic group that is distinct from those in the surrounding area
Ethnoburb
A suburban area with a cluster of a particular ethnic group.
“Separate but Equal”
The idea of giving Whites and Blacks equal treatment, but spatially segregated
Jim Crow Laws
A comprehensive set of separate but equal treatment laws in the southern states
What Supreme Court decision found that separation of Blacks & Whites was unconstitutional?
Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka in 1954
Apartheid
Legal separation of races
When was apartheid abolished?
1990-1991
When did #BlackLivesMatter first appear online?
2013
Nationalism
Loyalty and support for a nationality
Centripetal force
Attitude that unifies people and enhances support for a state
Centrifugal force
Attitude that divides people and reduces support for a state
Who are the Kurds?
Sunni Muslims who live within several countries, principally in Turkey and Iran
Ethnophobia
Fear of people of a particular ethnicity
Xenophobia
which is fear of people who are from other countries.
Ethnic Cleansing
purposeful policy designed by one ethnicity or religious group to remove by violent and terror-inspiring means the civilian population of another ethnic or religious group from certain geographic areas
Genocide
mass killing of a group of people in an attempt to eliminate the entire group from existence
What ethnic group is claimed by the Myanmar government to be living there illegally?
Rohingya
What has been a primary agent for ethnic violence within contemporary Africa?
European imposed boundaries in the 19th century with little regard to ethnic distributions created a host of 20th century nations with a large collection of dissimilar ethnicities.
What triggered the conflict in Sudan?
southern ethnicities attempting to resist northerners’ attempts to impose a legal system based on Muslim religious practice
Which ethnicity did the Belgians use to rule Rwanda indirectly?
Tutsi’s
When Rwanda gained independence in 1962, which group gained power and undertook ethnic cleansing?
Hutu’s
What event triggered the 1994 Rwanda genocide?
The shooting down of a plane carrying the presidents of Rwanda and Burundi
What state was created to unite the Balkan peoples after WWI?
Yugoslavia
Why did Serbia ethnically cleanse the Albanians?
Because they were the dominant ethnic group of Kosovo, a state that Serbia holds a historical claim to.
Why did the Serbs and Croats of Bosnia & Herzegovina want to unite with Serbia and Croatia?
They did not want to live in an independent multi-ethnic state with a Muslim plurality
What is a state?
an area organized into a political unit and ruled by an established government that has control over its internal and foreign affairs
How many UN member states are there?
193, in 2011
What is sovereignty?
independence from control of its internal affairs by other states.
Unitary government
most power is placed in the hands of central government officials
Federal government
strong power is allocated to units of local government
Devolution
process of transferring or delegating power to a lower level, especially by a national government to local or regional administration
What did most states look like in Ancient times?
City States
Nation
large group of people who are united by common cultural characteristics, such as language and ethnicity, or by shared history
Nation-state
is a state whose territory corresponds to that occupied by a particular nation.
Self-determination
The concept that nations have the right to govern themselves
What are the stages of nation-state development?
City states → Empires → Feudal states → Nation states
Which nation-states are known as the “Baltic Sisters”?
Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania
Multinational state
a state that contains more than one nation
Irredentism
Historical claim over a territory
Colony
A territory that is legally tied to a sovereign state rather than being completely independent
Colonialism
An effort by one country to establish settlements in a territory and impose its political, economic, and cultural principles on that territory.
What three reasons are the basis of colonialism?
Promote Christianity, extract resources, and enhance world power through control of territory and dominance over people
Frontier
A zone where no state exercises complete political control
Boundary
an invisible line that marks the extent of a state’s territory
Physical Boundary
coincide with significant features of the natural landscape
Cultural boundaries
Follow the distribution of cultural characteristics
Geometric boundaries
based on human constructs, such as straight lines.
Territorial waters
12 Nautical miles
Contiguous zone
12-24 nautical miles
Exclusive Economic Zone
24-200 nautical miles
Superimposed boundary
Drawn on an area by a conquering or colonizing power that ignores existing cultural patterns.
Subsequent boundary
Established after the settlement in an area and is changed to accommodate developments such as war
Relic boundary
one that no longer functions but can still be detected on the cultural landscape
Consequent boundary
drawn in order to separate groups based on ethnic, linguistic, religious, or economic differences.
What three nations claim conflicting sovereignty over five uninhabited islands in the East China Sea, going insofar as to establish air defence zones?
China, Taiwan, and Japan
What region is there a boundary dispute between India and Pakistan?
Kashmir
What is a landlocked state?
A state lacking a direct outlet to a sea because it is completely surrounded by other countries.
What is an advantage for a compact state?
Efficiency; distance to any boundary from the centre is not highly variable
Perforated state
A state completely surrounding another
Prorupted state
An otherwise compact state with a large projecting extension
Elongated state
A long and narrow shaped state
A fragmented state
A state with discontinuous pieces of territory
Gerrymandering
Redrawing of legislative boundaries to benefit the party in power

What form of Gerrymandering is this?
Cracking, where like-minded voters are spread across several districts to reduce their power
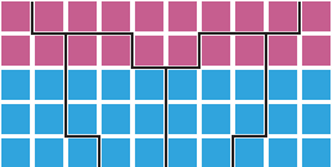
What form of gerrymandering is this?
Packing, where like-minded voters are clustered in a few districts to reduce their impact on other elections