PRELIM EXAM PRACTICE
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Prelim
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Chemistry
Is the study of matter, its properties, the changes that matter undergoes, and the energy associated with these changes.
Property
The characteristics that give each substance a unique identity
Physical Properties
Properties a substance shows by itself without interacting with another substance
Ex: color, melting point, boiling point, density
Chemical Properties
Properties a substance shows as it interacts with, or transforms into, other substances
Ex: Flammability, corrosiveness
Solid
(States of Matter)
Has a fixed shape and volume.
May be hard or soft, rigid or flexible
Liquid
(States of Matter)
Has a varying shape that conforms to the shape of the container, but a fixed volume.
Has an upper surface
Gas
(States of Matter)
Has no fixed shape or volume and therefore does not have a surface
Element
The simplest type of substance with unique physical and chemical properties.
Consists of only ONE type of atom
It cannot be broken down into any simpler substances by physical or chemical means (Ex: Fe, Cu, Na)
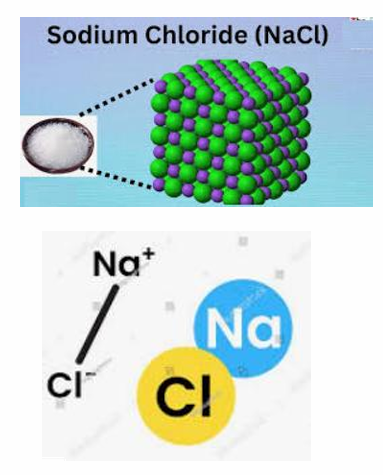
Compound
A substance composed of TWO or MORE elements which are chemically combined
Ex: H20, NaCl, CO)
Mixture
A group of two or more elements and/or compounds that are physically intermingled

Heterogeneous Mixture
(Types of Mixtures)
Has one or more visible boundaries between the components
Ex: Oil and water, gravel and sand
Homogeneous Mixture
(Types of Mixtures)
Has no visible boundaries because the components are mixed as individual atoms, ions, and molecules.
Other term for this is ‘solution’
Ex: NaCl solution, Sugar solution, Coffee
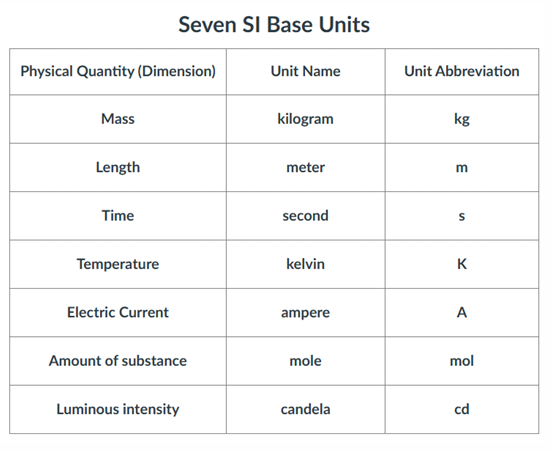
Units
All measured quantities consists of a number and a unit.
Conversion Factor
Is a ratio of equivalent quantities used to express a quantity in different units
Dimensional analysis is used to convert one unit to another

2.0 g/cm3
A stone weighs 3.5 grams and has a volume of 1.75 cm3. Find the density of the stone in g/cm3
96.535 g
A piece of platinum metal with a density of 21.5 g/cm3 has a volume of 4.49 cm3. What is its mass (in grams)?
2.6 g/cm3
In the determination of the density of a rectangular metal bar, a student made the following measurements: length 8.53 cm; width 2.4 cm; height 1.0 cm, mass 52.71 g. Calculate the density of the metal bar
10.5 g/cm3
A silver object with a mass of 194.3 g is placed in a graduated cylinder containing 242.0 mL water. The volume of water with the object now reads 260.5 mL. Determine the density of the silver object in g/cm3
Democritus
Expressed the belief that all matter consists of very small, indivisible particles
‘atomos’ meaning uncuttable or indivisible
John Dalton
Formulated a precise definition of the indivisible building blocks of matter that we call atoms
Atom
Is the basic unit of an element that can enter into chemical combination
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
It postulates that:
1. All matter consists of atoms.
2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element.
3. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from atoms of any other element.
4. Compounds result from the chemical combination of a specific ratio of atoms of different elements
J.J Thomson
He studied electrical discharges in partially evacuated tubes called cathode-ray tubes
He found that when high voltage was applied to the tube, a “ray” he called a cathode ray (because it emanated from the negative electrode, or cathode) was produced
Electrons
Stream of negatively charged particles
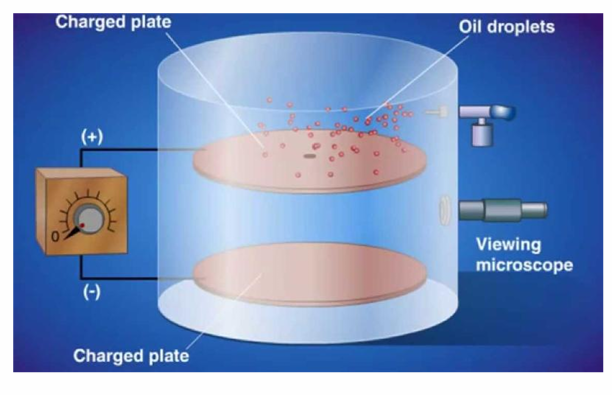
Robert Millikan
Oil-drop experiment
This experiment allowed him to determine the magnitude of the electron charge
Ernest Rutherford
His experiment involved directing alpha particles at a thin sheet of metal foil
He calculated that an atom is mostly space occupied by electrons, but in the center of that space is a tiny region called nucleus
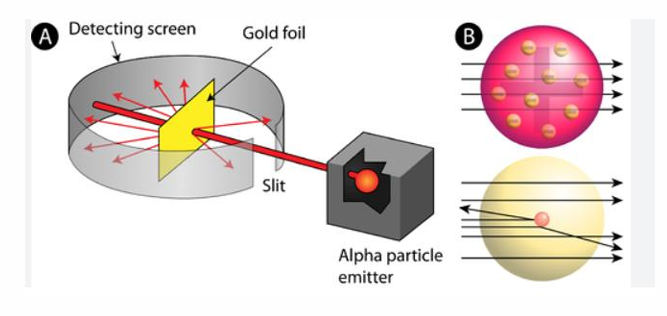
Nucleus
Contains all the positive charge and essentially all the mass of the atom
Contains protons and neutrons
Protons
Positive charged particles
Neutron
An uncharged dense particle that also resides in the nucleus. discovered by James Chadwick
James Chadwick
He discovered the Neutron