Chapter 2 Anatomy (chem)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Matter
Anything that occupies space and has mass
Energy
Capacity to do work
Kinetic energy
active energy
Potential energy
Inactive energy
Chemical, electric, mechanical, radiant
Types of energy
Proton
Positively charged, resides in nucleus of an atom
Neutron
Neutral and resides in the nucleus of an atom
Electrons
Negatively charged, orbits nucleus in electron cloud
Atomic number
Number of protons in the nucleus
Mass number
Sum of masses of the protons and neutrons
Isotope
Same number of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons
Atomic weight
average mass of numbers of all isotopes of an element
Radioactivity
the process of atomic decay. Alpha, beta, or gamma particles are ejected from the atomic nucleus
Quarks
Components of nuclear particles—what composes protons and neutrons
Half-life
The time is takes for a radioisotyope to lose one half of its activity
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by a chemical bond
Compound
two or more different types of atoms held together by chemical bonds
Mixtures
two or more substances whose components are physically intermixed. Types include solutions, colloids, and suspensions
Solution
Solute particles are very tiny and do not settle out or scatter light. Ex. mineral water
Colloid
Solute particles are larger than in a solution and scatter light; does not settle out. Can change from fluid state to solid state (sol-gel transformations) Ex. Jello
Suspension
Solute particles are very large, settle out, and may scatter light. Ex. blood
Valence shell
Indicates an atom’s outermost energy level. Shell 1 is occupied with 2 electrons, shell 2 is occupied with 8
Rule of eight
Atoms tend to interact so they have 8 electrons in their valence shell
Ionic bonds
Formed by the transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another. (anions and cations)
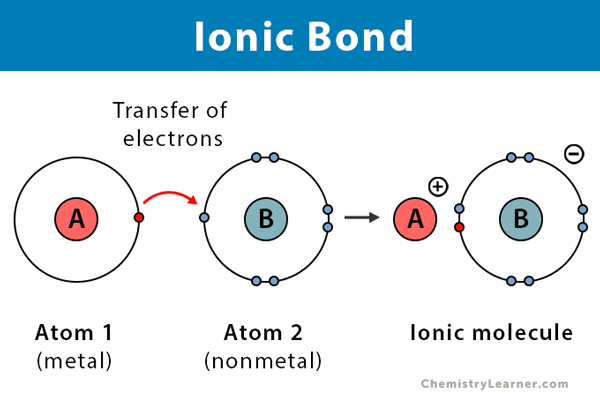
Anion
A type of ionic bond that’s an electron acceptor. Gains a negative net charge
Cation
A type of ionic bond that’s an electron donor. Gains a net positive charge
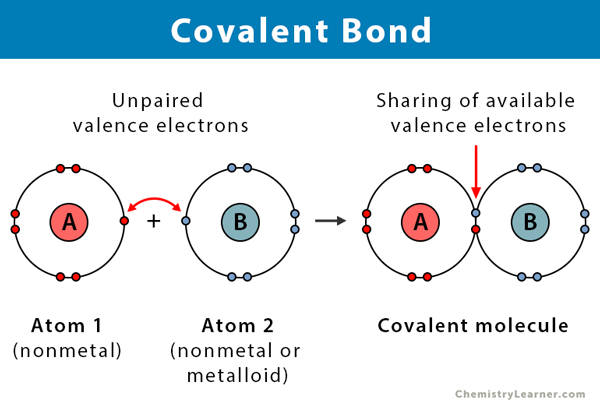
Covalent bond
Shared electrons occupy an outer electron shell common to both atoms.
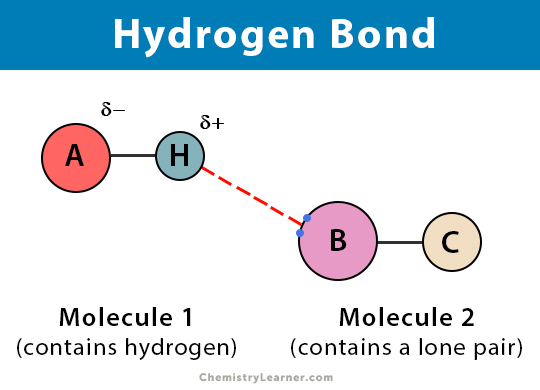
Hydrogen bonds
When hydrogen is covalently linked to another atom and is attracted by another atom and forms a bridge between them
Chemical reaction
Occurs when chemical bonds are formed, rearrange, or broken
Chemical equation
Describes what happens in a reaction and has reactants and products. ex. synthesis and decomposition reactions
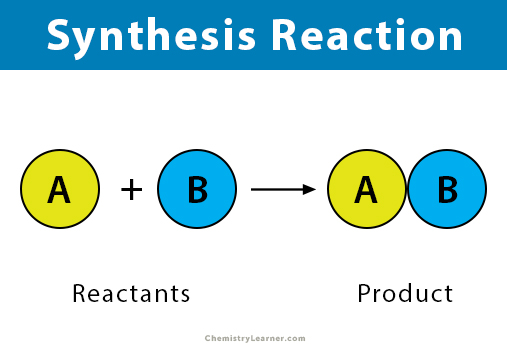
Synthesis reaction
Anabolic chemical reaction where where two or more simple substances, or reactants, combine to form a single, more complex product
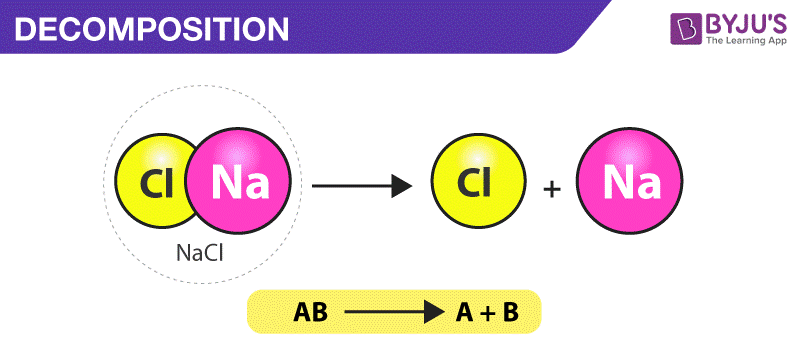
Decomposition reaction
Catabolic chemical reaction where a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler products, often requiring an input of energy
temperature, concentration, particle size, catalysts (enzymes that speed up reactions)
Factors influencing chemical reactions
Biochemistry
the study of chemical compositions and reaction of living matter
Organic compounds
Contain carbon, all have covalent bonds. Includes carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Carbohydrates
Organic compound that includes starches and sugar. Functions to be easily used source of cellular fuel
Lipids
Organic compound that includes fatty acids and glycerol. Functions to be most efficient at storing usable energy fuel. Is insoluble in water and readily dissolves in other lipids.
Proteins
Organic compound that includes amino acids containing carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen. Formed by peptide bonds arranged in an alpha helix, beta-pleated sheet, tertiary structure, or quaternary structure
Nucleic acids
Organic compound that includes DNA and is composed of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorous. Is the largest molecule of the body.
DNA
Long, double-stranded polymer, “double helix.” Found in nucleus and contains genetic material that replicates itself. Provides instructions for building protein
RNA
Single strands of nucleotides. Found outside the nucleus and carries out orders for protein synthesis given by DNA
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Type of organic compound that is the smallest, easy energy immediately usable by all body cells. Very unstable
Inorganic compounds
Includes water, salts, acids, bases, neutralization, and buffers.
Water
The most abundant inorganic compound that makes up 60-80% of the volume of most living cells. Has high heat capacity/vaporization, is universal solvent, and is a biological colloid (ex. blood. protein/water mixture)
Salts
Type of inorganic compound that contains cations except hydrogen ions and anions except hydroxyl ions. Dissolve in water and disassociate into their component ions, creating electrolytes. (all ions are electrolytes)
Acids
Inorganic compound that releases hydrogen ions, H+, in detectable amounts. When dissolved in water, releases protons and anions. Number of protons determine acidity, while anions have little affect on acidity
Bases
Inorganic compound that takes up hydrogen ions, H+, in detectable amount. Are proton acceptors!! Has bitter taste, feels slippery.
pH Scale
Runs fro 0-14. 7 is neutral, hydrogen ions = hydroxyl ions. Below 0-7 is acidic and above 7-14 is basic.
Neutralization
A chemical reaction between an acid and a base that produces a salt and water
Buffers
An inorganic compound that resists abrupt changes in pH. Releases hydrogen ions when pH rises, and binds hydrogen ions when pH drops. Kidneys and lungs regulate blood pH
7.35-7.45
Blood pH range that is physiologically neutral (even though its technically slightly basic)