Chemistry- 1 States of matter
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
how are the particles arranged in solid liquid and gas
in solid they are packed very closely together in a fixed and regular pattern in liquid they are close together in irregular arrangement in gas the particles are far apart
how do the particles move in solid liquid and gas
in Solid they vibrate in the places
in Liquid they slowly slide over each other
In Gases they move randomly and freely
intermolecular faces between solid liquid and gas
solid-extremely strong liquid-strong but less than solid gas-very week
shape and volume of solid liquid and gas
solid-fixed shape,fixed volume
liquid-no fixed shape,fixed volume
gas-No fixed shape and no fixed volume
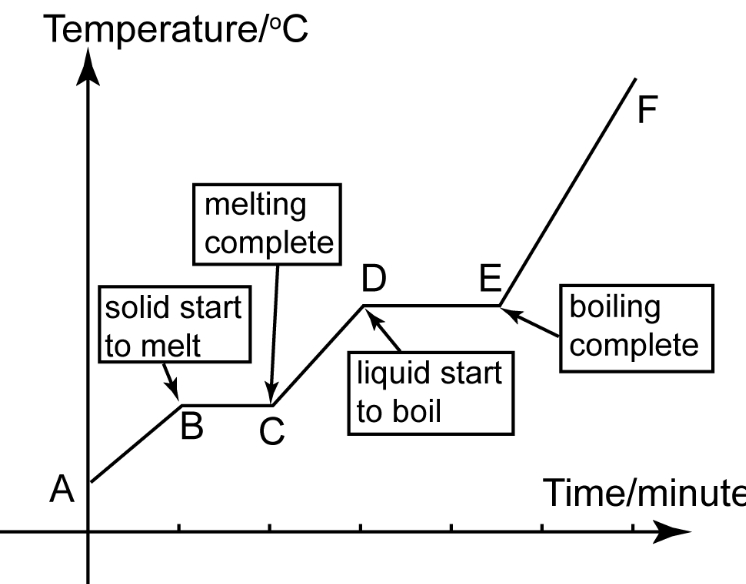
describe the changes of state in melting
anything that takes up space and has mass
matter
what are they three states of matter
solid liquid gas
the kinetic particle theory
all matter is composed of very small invisible particles
the particles move all the time higher the temperature the faster they move
lighter particles move faster than heavier ones
in gas there are alot of space between the particles so they are free to move anywhere
what happens to the meting point and boiling points when impurities are present
it decreases the melting point and increases the boiling point
liquid to gas
evaporation/boiling
gas to liquid
condensation
solid to liquid
melting
liquid to solid
freezing
gas to solid and solid to gas
sublimation
difference between melting point and melting
melting point is the temperature whereas melting is the change of state from solid to liquid by heating
differences between boiling and evaporation
Evaporation happens below the boiling point whereas boiling occurs only at the boiling point
Evaporation only occurs at the surface whereas boiling occurs throughout the liquid
Evaporation doesn’t require any external heat whereas boiling requires heating
no bubbles of vapor are formed while evaoration but in boiling bubbles are formes
what are the factors that increases the rate of evaporation
increasing temperature
increasing surface area
explain diffusion
diffusion is spreading out of liquids and gas it is the movement of particles from low conc to high conc it occurs until the mixture/smell is uniform
what are the factors affecting diffusion how and why?
Molecular Mass (the higher the MR the slower the rate of diffusion as it more heavy therefore takes more time to travel)
Temperature (higher the temperature higher the rate of diffusion as increasing the emp increases the energy therefore particles hit each other more increasing their speed)
what happens to the volume of a gas in respect to temperature density and pressure
As temperature increases gas volume increases. The density decreases as the volume increases Pressure increases as volume decreases
How does temperature affect the volume of a gas
Increasing the temperature increases the kinetic energy of each particle
As the temperature increases, the particles in the gas move faster and spread out more
If the gas particles are inside a container, they will collide with the container walls more frequently
If the container walls are flexible and stretchy then the container will get bigger and bigger, just like the hot air balloon!
How does pressure affect the volume of gas
Pressure is about the number of particles in a given volume
Increasing the pressure means that there are the same number of particles but in a smaller volume
Since the volume is decreased, the gas particles hit the container walls more frequently
describe the changes of state in melting
when a solid is heated the particles get more energy and vibrate more this makes the solid expand At the melting point the particles vibrate so much that they break away from their positions and becomes a liquid
heating curve
cooling curve
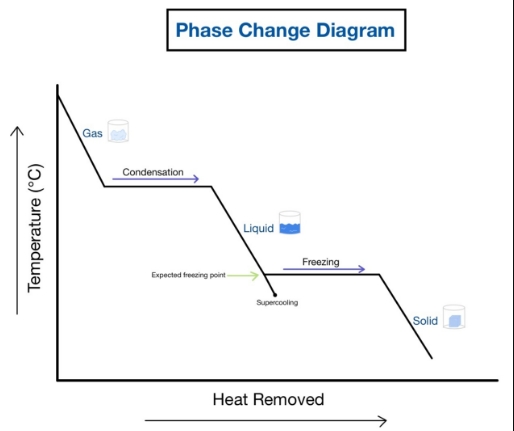
what is the freezing and boiling point of water
freezing point is 0 degrees celcius
boiling point is 100 degrees celcius
what is the freezing and boiling point equal to
freezing point=melting point
boiling point=condensation point
If the melting and boiling point is more than the room temperature what state of matter is it
its a solid
If the melting and boiling point is less than the rtp what state of matter is it
its a gas
If the melting point is less than the room temperature and the boiling point is more than the room temperature.
liquid