Conflict Theory flashcards
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
Terms: conflict
direct confrontation between individuals or groups over scarce resources; occurs when people use controversial means to obtain their goals, or have incompatible goals, or some combo of both
2
New cards
Terms: conflict theory
examines conflict that exists within families and other social relationships
3
New cards
terms: competition
one wins and other loses; members realize they can take turns winning and losing and make decisions where members jointly win or lose, depending on their willingness to negotiate, cooperate, and seek compromise
4
New cards
terms: conflict management
strategies to keep conflict form escalating; dealing with conflict while acknowledging the continued existence of the underlying competitive structure
5
New cards
terms: compromise
an accepted idea is eventually challenged by its opposite until a middle ground is reached
6
New cards
terms: negotiation and bargaining
exchange process
7
New cards
terms: conflict resoution
reach a stable resolution; parties no longer see the issue as competition for scarce resources
8
New cards
terms: consensus
all agree “see things the same way”; stable state in which society, groups, or families exist, sharing common awareness or knowledge of given issues, values, and norms; conflict management seeks the consensus
9
New cards
terms: power
ability to control the course of action of others; can be used positively (authority or privilege) or negatively (unduly control others); can also be a function of personality and temperament, because some people tend to be more persuasive
10
New cards
terms: Assertion
acting in a way that affirms one’s rights and positions but not necessarily at the expense of others
11
New cards
terms: aggression
use of power to get others to behave to one’s advantage even at expense of others
12
New cards
terms: threats
messages that imply punishment if demands are not met
13
New cards
terms: promises
messages that communicate the delivery of something positive/rewarding if demands are met
14
New cards
Assumptions: nature of individuals is that they are self-oriented
or focused on self-interests; individuals are symbol-producing, they are able to ascribe value to things → sets up the competition → resort to interpersonal aggression
15
New cards
Assumptions: societies (families) operate with a scarcity of resources
societies = organized systems for species survival; lead to perpetual scarcity of resources → perpetual confrontations
16
New cards
Assumptions: conflict is a confrontation over control of scarce resources
internal (between individuals, families or societies) or external conflict ( originated from outside system)
17
New cards
Assumptions: group dynamics are different in families than in other groups
family illness will stress its resources while in a group it will not; membership is involuntary in families, they can’t just leave the group
18
New cards
Assumptions: conflict has a positive aspect
people come to new understanding of each other and the compromise might be the best decision; allows growth to occur when they learn new things about each other
19
New cards
Assumptions: conflict can be classified
1. macro social perspective - issues of conflict between groups of people who have privilege and those who are disadvantaged (haves vs. have nots)
2. micro social perspective - elements within family that bring conflict (marital conflict, adolescent individuation)
20
New cards
Underlying sources of conflict in marriage
1. role expectations → household tasks
2. competing needs for connectedness and separateness → time spent with family v. other
3. fairness and equity → “that’s not fair”
4. power → ability to control actions of others; structures in families give authority to parents over children
21
New cards
work-family conflict (dual-career familes)
work-family conflict conception → work and family are incompatible; roles more difficult as a result of participation in both
1. increase in health risks
2. decreased parenting performance
3. decreased work performance
4. decreased life satisfaction
1. increase in health risks
2. decreased parenting performance
3. decreased work performance
4. decreased life satisfaction
22
New cards
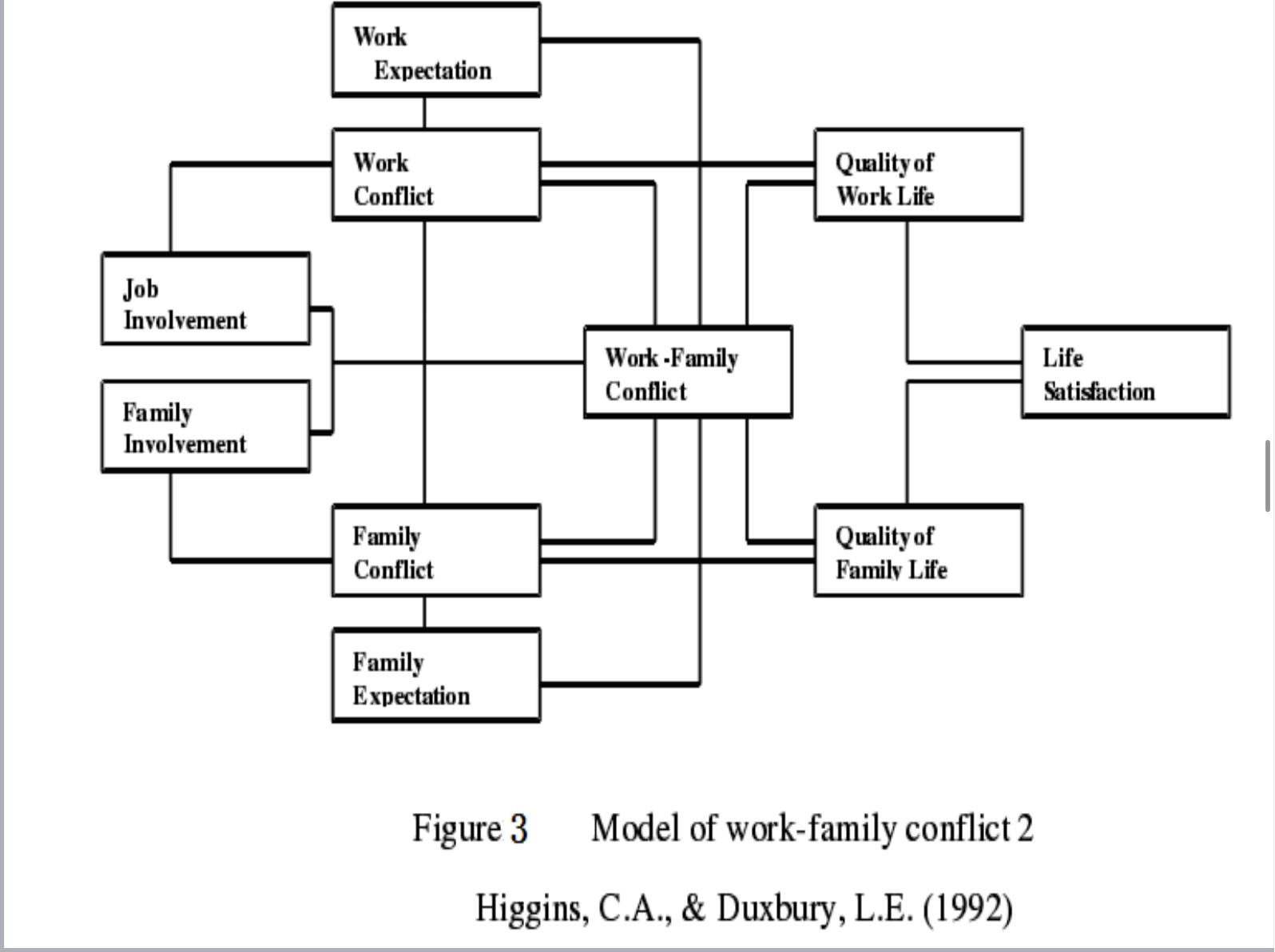
Conflict Items Examples
1. demands of my work interfere with my home and family
2. the amount of time my job takes up makes it difficult to fulfill family responsibilits
3. the demands of my family or partner interfere with work-related activities
4. I have to put off doing things at work because of demands on my time at home
5. things I want to do at work do not get done because of demands of my family or partner
6. my home life interferes with my responsibilities at work such as getting to work on time, accomplishing daily tasks, and working overtime
7. family-related strain interferes with my ability to perform job-related duties
23
New cards
Conflict Resolution: conflict constructive or destrictvie
1. vertical conflict - objectively is considered conflict; conflict b/t parties in hierarchical relationship
2. contingent - generated by reason that can be solved; arises due to a specific reason/issue
3. displaced - reason for conflict is from other situation
4. poorly attributed - comes from other source
5. latent - not addressed; exists beneath the surface
6. false - misinterpretation, misunderstanding
24
New cards
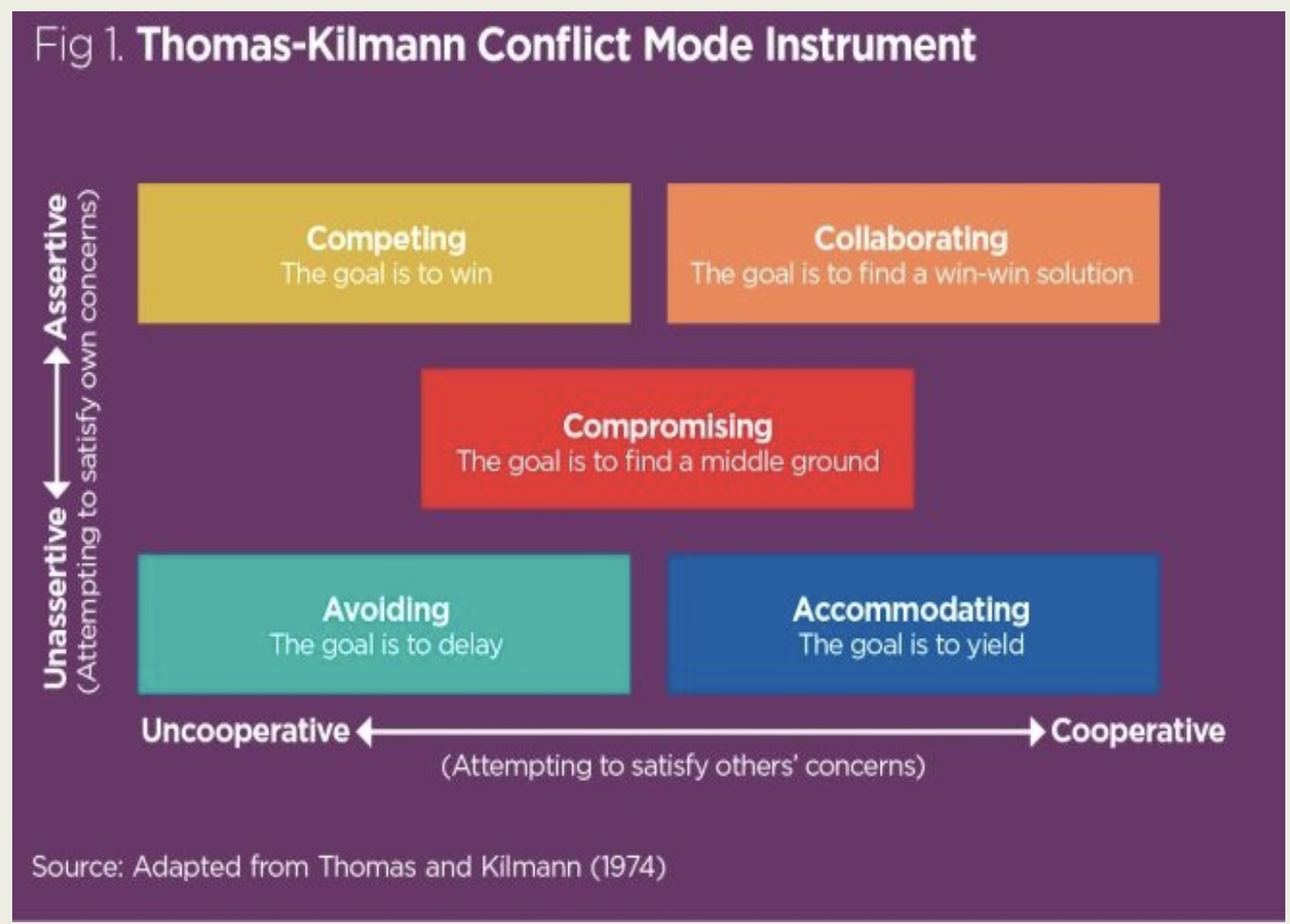
Styles of conflict resolution (Thomas and Kidman) conflict mode instrument (TKI): competing
\
goal is to win (uncooperative; assertive)
goal is to win (uncooperative; assertive)
25
New cards
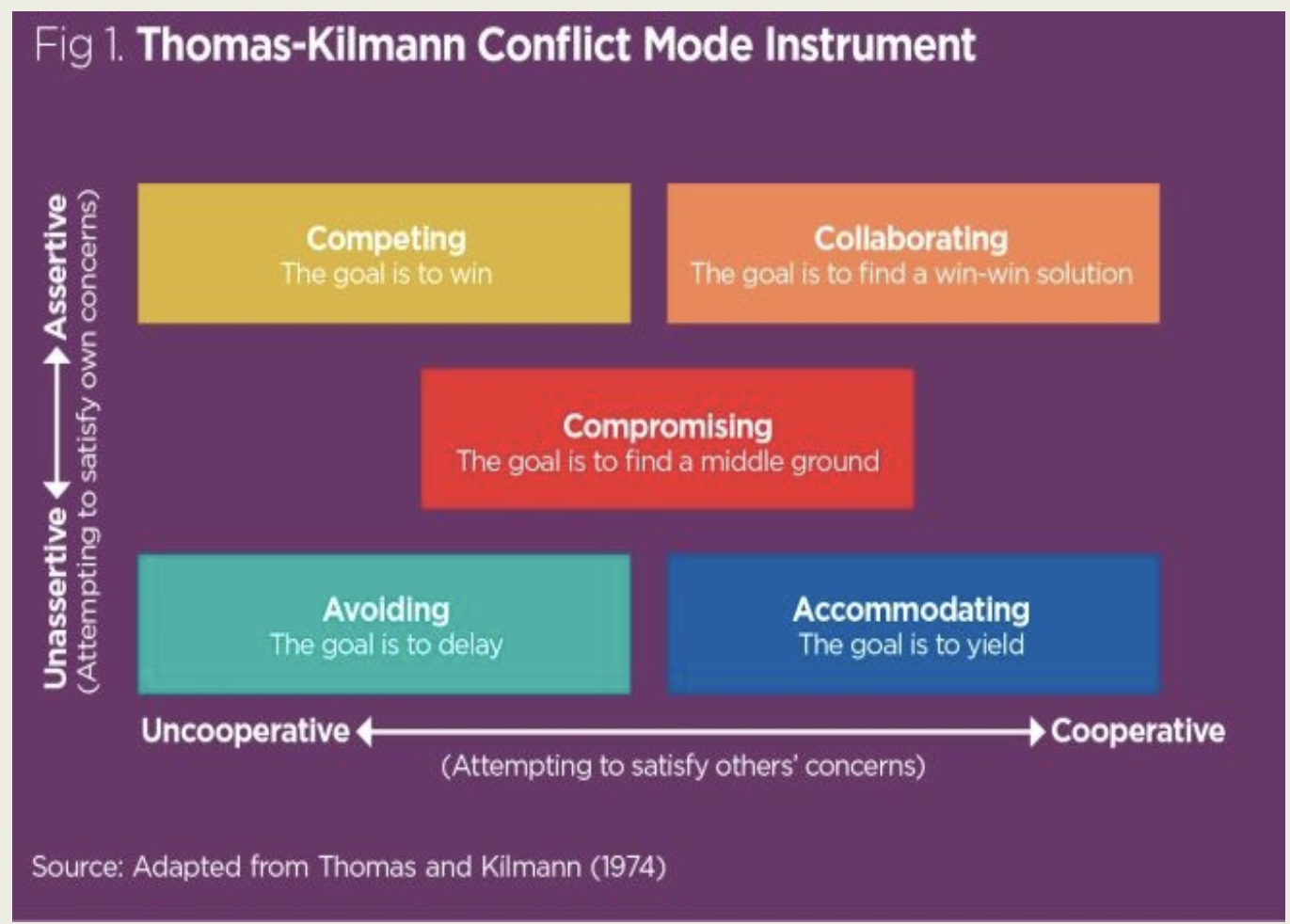
Styles of conflict resolution (Thomas and Kidman) conflict mode instrument (TKI): collaborating
goal is win-win (cooperative; assertive)
26
New cards
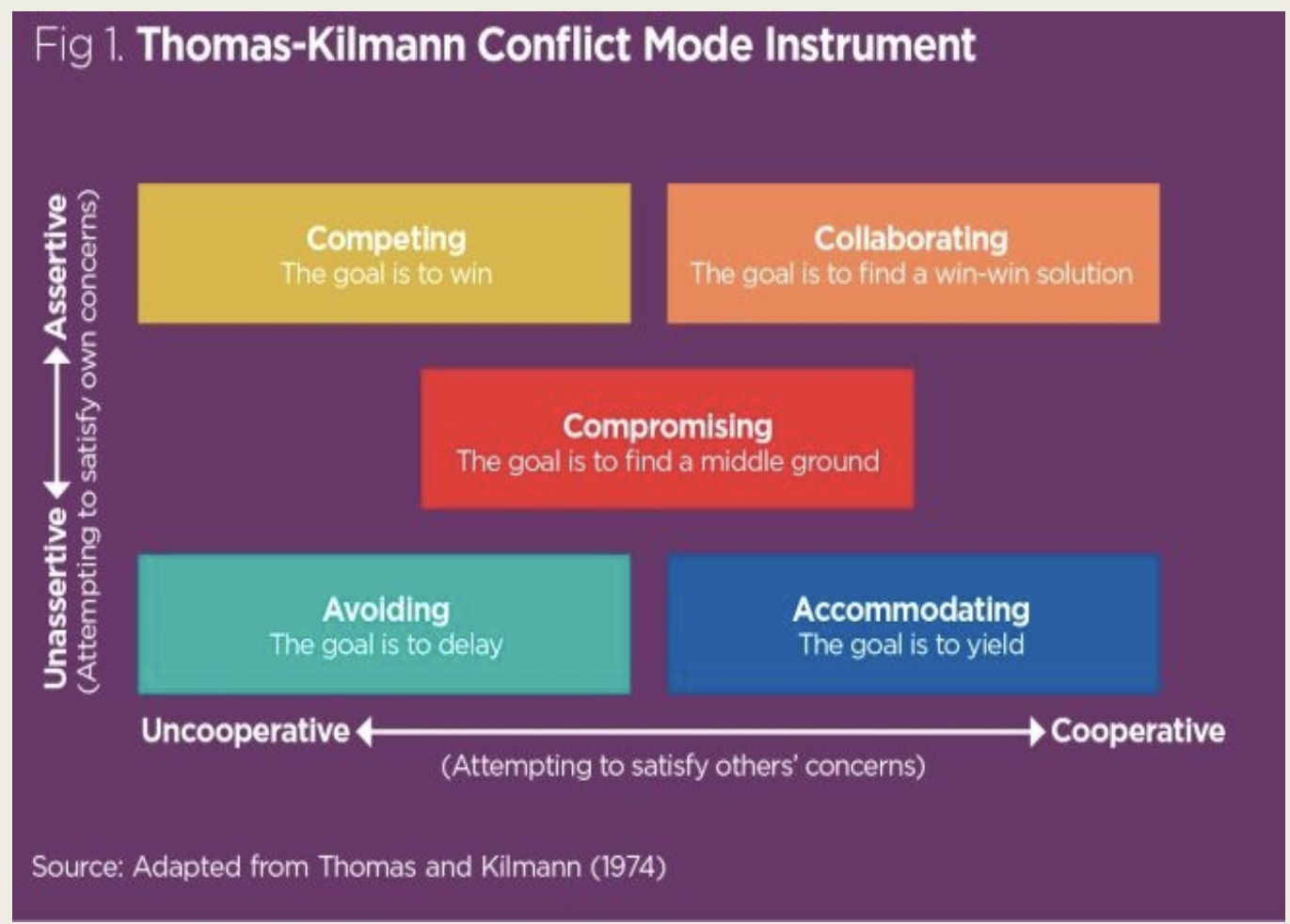
Styles of conflict resolution (Thomas and Kidman) conflict mode instrument (TKI): compromising
goal is middle ground (in between both cooperative-uncooperative and unassertive-assertive)
27
New cards
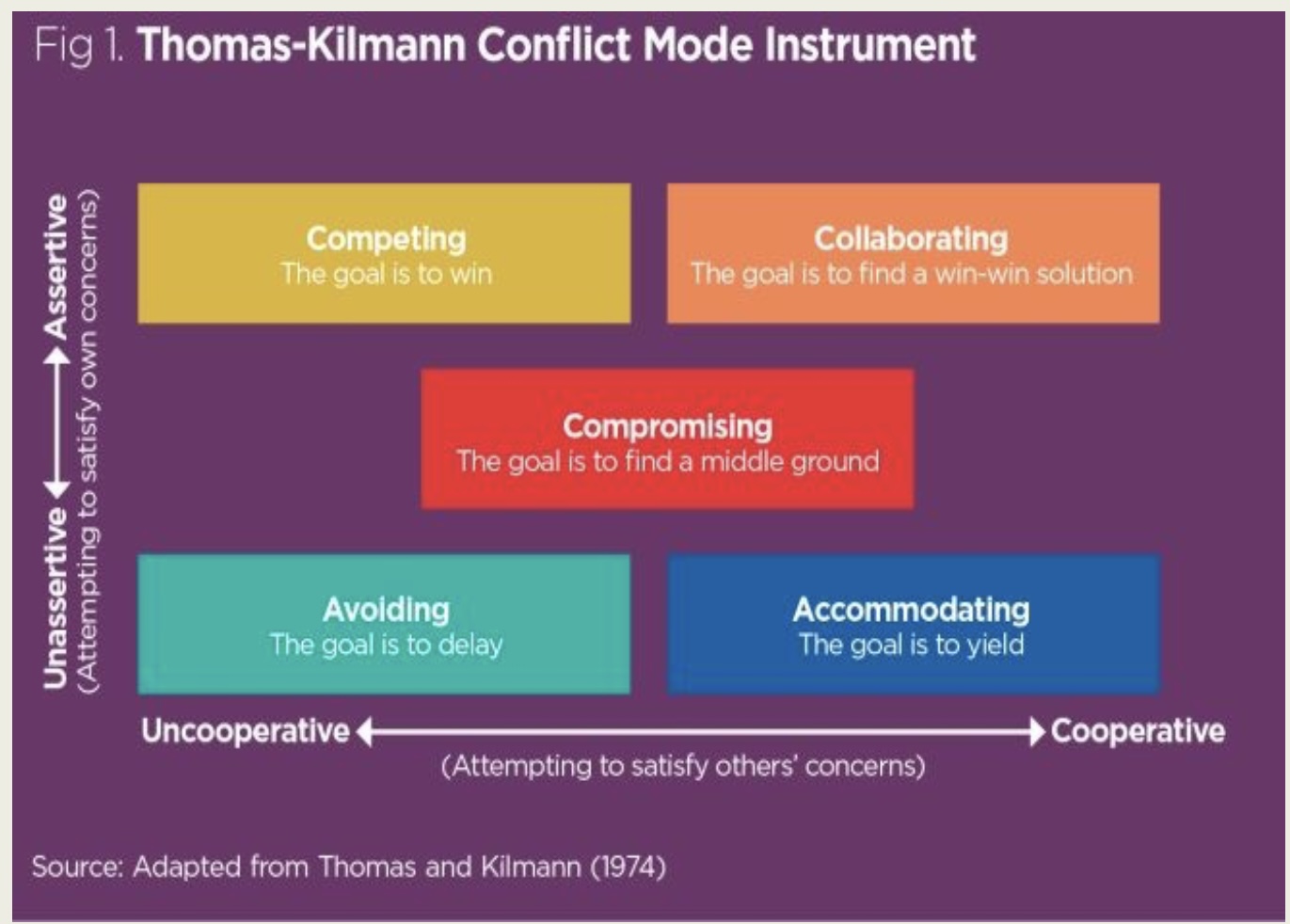
Styles of conflict resolution (Thomas and Kidman) conflict mode instrument (TKI): avoiding
goal is to delay (uncooperative; unassertive)
28
New cards
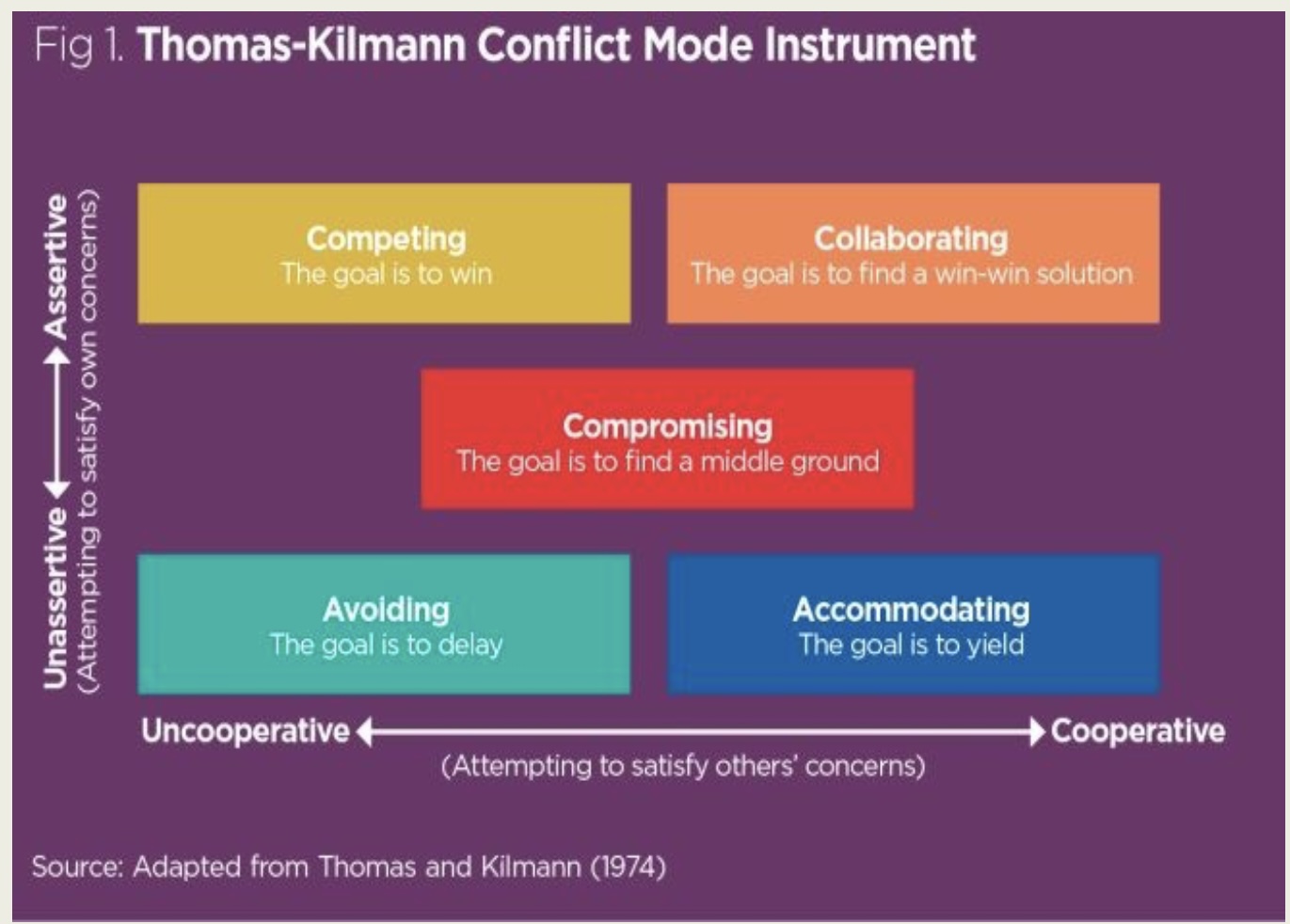
Styles of conflict resolution (Thomas and Kidman) conflict mode instrument (TKI): accommodating
goal is to yield (cooperative; unassertive)
29
New cards
Basic steps for conflict resolution
1. clarify issue
2. determine what each person wants
3. identify alternatives
4. decide on negotiation
5. solidify agreements
6. review and renegotiate
30
New cards
Fair fighting rules
1. avoid ultimatums
2. say what you really mean
3. avoid accusations and attack
4. state your requests clearly
5. repeat the message you think you received
6. resist giving the silent treatment
7. focus on the issue and on the present
8. call time-out and foul
9. always go for closure
31
New cards
Applying conflict theory to research: parents’ and children’s power effectiveness during polyandry family conflict: process and outcome
1. how does this research reflect the application of conflict theory?
* by studying conflict in families and examining power dynamics between parents and children during conflict
2. discuss the assumption: conflict can be classified
* the research focuses on the classification of conflict by studying the types of conflict that arise in polyandry families and how power is used during these conflicts
3. discuss the assumption: group dynamics are different in families than other groups
* the research supports this assumption as it specifically examines conflict in families and the unique power dynamics that exist within them