nucleus quick flashcards
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
what are the functions of the nucleus
storage & maintenance of most of the cell’s genetic info
control of gene expression through transcription
regulation of protein synthesis machinery through: synthesis of rRNA & assembly of ribosomes in nucleolus
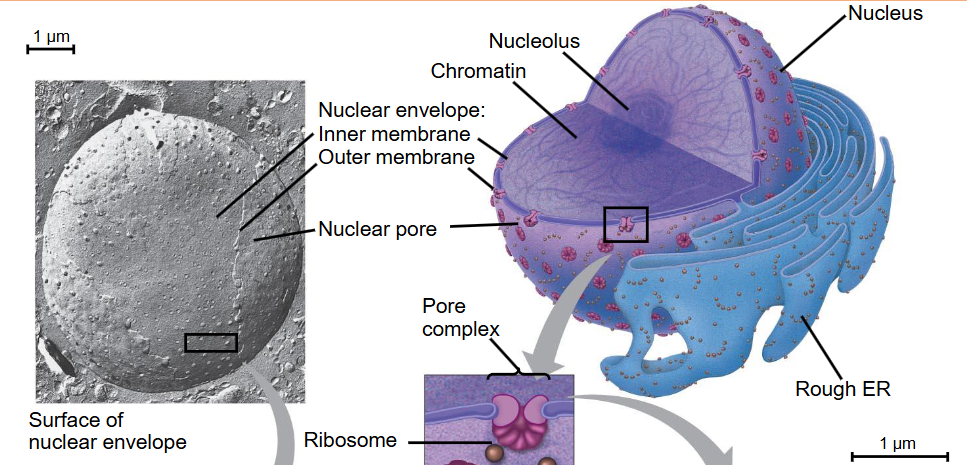
what is the nuclear envelope
consists of two lipid bilayers
inner nuclear membrane is in contact with chromatic
outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the rough ER
what are nuclear pores
inner & outer membrane fused together
facilitate the bidirectional transit of materials between nucleus & cytoplasm
eg. RNAs exit nucleus, proteins, carbs, etc enter nucleus
what are nuclear lamina
line the inner side of nuclear envelope
are a network of intermediate protein filaments that maintain the shape of the nucleus
also anchors interphase chromatin at nuclear periphery
what are chromosomes
one long DNA molecule associated with proteins
some of the proteins help coil DNA and package it within the nucleus
what is chromatin
material that makes up a chromosome that contains DNA and protein
major proteins in chromatin are called histones (packaging elements for the DNA)
chromatin wraps DNA in very tight coil
what is a gene
a length of DNA that codes for a protein
what is a nucleosome
segment of DNA wrapped around 8 histone proteins
2 copies of histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 allows DNA to be organized and packed into the nucleus
what are transcription factors
DNA binding proteins that regulate gene expression
what is euchromatin and heterochromatin
euchromatin - less condensed, expressed genes
heterochromatin - more condensed, silent/no genes
what is the nucleolus
site of rRNA synthesis, rRNA processing and assembly of ribosomal subunits
what can be said if there is a large nucleolus
it is typical of cells that produce large amounts of protein
what are ribosomes
made of rRNA and protein
carry out protein synthesis (translation)
high rate of protein synthesis = large numbers of ribosomes
where do proteins made in free ribosomes go
they function in the cytoplasm
where do proteins made in bound ribosomes go
they are either inserted into membranes/organelles or secreted