AFOQT Aviation Information Part 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/213
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Aviation Terms for AFOQT Examination
Last updated 8:23 PM on 6/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
214 Terms
1
New cards
Primary Flight Display (PFD)
A display that provides increased situational awareness to the pilot by replacing the traditional six instruments used for instrument flight with an easy-to-scan display that provides the horizon, airspeed, altitude, vertical speed, trend, trim, and rate of turn among other key relevant indications.
Procedure Turn
Procedure Turn
2
New cards
Procedure Turn
A maneuver prescribed when it is necessary to reverse direction to establish an aircraft on the intermediate approach segment or final approach course.
3
New cards
Profile View
Side view of an IAP chart illustrating the vertical approach path altitudes, headings, distances, and fixes.
4
New cards
Prohibited Area
Designated airspace within which flight of aircraft is prohibited.
5
New cards
Propeller
A device for propelling an aircraft that, when rotated, produces by its action on the air, a thrust approximately perpendicular to its plane of rotation. It includes the control components normally supplied by its manufacturer.
6
New cards
Propeller/Rotor Modulation Error
Certain propeller rpm settings or helicopter rotor speeds can cause the VOR course deviation indicator (CDI) to fluctuate as much as ±6°. Slight changes to the rpm setting will normally smooth out this roughness.
7
New cards
Rabbit, the
High-intensity flasher system installed at many large airports. The flashers consist of a series of brilliant blue-white bursts of light flashing in sequence along the approach lights, giving the effect of a ball of light traveling toward the runway.
8
New cards
Radar
A system that uses electromagnetic waves to identify the range, altitude, direction, or speed of both moving and fixed objects such as aircraft, weather formations, and terrain.
9
New cards
Radar Approach
The controller provides vectors while monitoring the progress of the flight with radar, guiding the pilot through the descent to the airport/heliport or to a specific runway.
10
New cards
Radar Summary Chart
A weather product derived from the national radar network that graphically displays a summary of radar weather reports.
11
New cards
Radar Weather Report (SD)
A report issued by radar stations at 35 minutes after the hour, and special reports as needed. Provides information on the type, intensity, and location of the echo tops of the precipitation.
12
New cards
Radials
The courses oriented from a station.
13
New cards
Radio or Radar Altimeter
An electronic altimeter that determines the height of an aircraft above the terrain by measuring the time needed for a pulse of radio-frequency energy to travel from the aircraft to the ground and return.
14
New cards
Radio Frequency (RF)
A term that refers to alternating current (AC) having characteristics such that, if the current is input to antenna, an electromagnetic (EM) field is generated suitable for wireless broadcasting and/or communications.
15
New cards
Radio Magnetic Indicator (RMI)
An electronic navigation instrument that combines a magnetic compass with an ADF or VOR. The card of the RMI acts as a gyro-stabilized magnetic compass, and shows the magnetic heading the aircraft is flying.
16
New cards
Radiosonde
A weather instrument that observes and reports meteorological conditions from the upper atmosphere. This instrument is typically carried into the atmosphere by some form of weather balloon.
17
New cards
Radio Wave
An electromagnetic wave with frequency characteristics useful for radio transmission.
18
New cards
RAM Recovery
The increase in thrust as a result of ram air pressures and density on the front of the engine caused by air velocity.
19
New cards
Random RNAV Routes
Direct routes, based on area navigation capability, between waypoints defined in terms of latitude/longitude coordinates, degree-distance fixes, or offsets from established routes/airways at a specified distance and direction.
20
New cards
Ranging Signals
Transmitted from the GPS satellite, signals allowing the aircraft's receiver to determine range (distance) from each satellite.
21
New cards
Rapid Decompression
The almost instantaneous loss of cabin pressure in aircraft with a pressurized cockpit or cabin.
22
New cards
Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM)
A system used to verify the usability of the received GPS signals and warns the pilot of any malfunction in the navigation system. This system is required for IFR-certified GPS units.
23
New cards
Recommended Altitude
An altitude depicted on an instrument approach chart with the altitude value neither underscored nor overscored. The depicted value is an advisory value.
24
New cards
Receiver-Transmitter (RT)
A system that receives and transmits a signal and an indicator.
25
New cards
Reduced Vertical Separation Minimum (RVSM)
Reduces the vertical separation between flight levels (FL) 290 and 410 from 2,000 feet to 1,000 feet, and makes six additional FLs available for operation.
26
New cards
Reference Circle (Distance Circle)
The circle depicted in the plan view of an IAP chart that typically has a 10 NM radius, within which chart the elements are drawn to scale.
27
New cards
Regions of Command
The "regions of normal and reversed command" refers to the relationship between speed and the power required to maintain or change that speed in flight.
28
New cards
Region of Reverse Command
Flight regime in which flight at a higher airspeed requires a lower power setting and a lower airspeed requires a higher power setting in order to maintain altitude.
29
New cards
Relative Bearing (RB)
The angular difference between the aircraft heading and the direction to the station, measured clockwise from the nose of the aircraft.
30
New cards
Relative Bearing Indicator (RBI)
Also known as the fixed-card ADF, zero is always indicated at the top of the instrument and the needle indicates the relative bearing to the station.
31
New cards
Relative Wind
The direction of airflow by an object moving through the air. The relative wind for an airplane in flight flows in a direction parallel with and opposite to the direction of flight; therefore, the actual flight path of the airplane determines the direction of the relative wind.
32
New cards
Remote Communications Outlet (RCO)
An unmanned communications facility that is remotely controlled by air traffic personnel.
33
New cards
Required Navigation Performance (RNP)
A specified level of accuracy defined by a lateral area of confined airspace in which an RNP-certified aircraft operates.
34
New cards
Restricted Area
Airspace designated under 14 CFR part 73 within which the flight of aircraft, while not wholly prohibited, is subject to restriction.
35
New cards
Reverse Sensing
The VOR needle appearing to indicate the reverse of normal operation.
36
New cards
RF
Radio Frequency
37
New cards
Rigging
The final adjustment and alignment of an aircraft and its flight control system that provides the proper aerodynamic characteristics.
38
New cards
Rigidity
The characteristic of a gyroscope that prevents its axis of rotation tilting as the Earth rotates.
39
New cards
Rigidity in Space
The principle that a wheel with a heavily weighted rim spun rapidly will remain in a fixed position in the plane in which it is spinning
40
New cards
Risk Elements
There are four fundamental risk elements in aviation: the pilot, the aircraft, the environment, and the type of operation that comprise any given aviation situation.
41
New cards
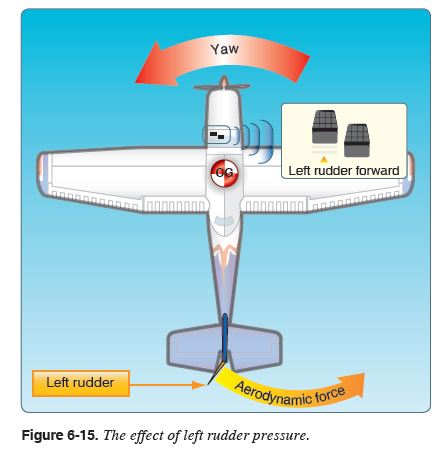
Rudder
The movable primary control surface mounted on the trailing edge of the vertical fin of an airplane. Movement of the rudder rotates the airplane about its vertical axis.
42
New cards
Ruddervator
A pair of control surfaces on the tail of an aircraft arranged in the form of a V. These surfaces, when moved together by the control wheel, serve as elevators, and when moved differentially by the rudder pedals, serve as a rudder.
43
New cards
Runway Centerline Lights
Runway lighting which consists of flush centerline lights spaced at 50-foot intervals beginning 75 feet from the landing threshold.
44
New cards
Runway Edge Lights
A component of the runway lighting system that is used to outline the edges of runways at night or during low visibility conditions. These lights classified according to the intensity they are capable of producing.
45
New cards
Runway End Identifier Lights (REIL)
A pair of synchronized flashing lights, located laterally on each side of the runway threshold, providing rapid and positive identification of the approach end of a runway.
46
New cards
Runway Visibility Value (RVV)
The visibility determined for a particular runway by a transmissometer.
47
New cards
Runway Visual Range (RVR)
The instrumentally derived horizontal distance a pilot should be able to see down the runway from the approach end, based on either the sighting of the high-intensity runway lights, or the visual contrast of other objects.
48
New cards
St. Elmo’s Fire
A corona discharge which lights up the aircraft surface areas where maximum static discharge occurs.
49
New cards
Satellite Ephemeris Data
Data broadcast by the GPS satellite containing very accurate orbital data for that satellite, atmospheric propagation data, and satellite clock error data.
50
New cards
Sea Breeze
A coastal breeze blowing from sea to land caused by the temperature difference when the land surface is warmer than the sea surface. The sea breeze usually occurs during the day and alternates with the land breeze that blows in the opposite direction at night.
51
New cards
Sea Level Engine
A reciprocating aircraft engine having a rated takeoff power that is producible only at sea level.
52
New cards
Scan
The first fundamental skill of instrument flight, also known as “cross-check”; the continuous and logical observation of instruments for attitude and performance information.
53
New cards
Sectional Aeronautical Charts
Designed for visual navigation of slow- or medium-speed aircraft. Topographic information on these charts features the portrayal of relief, and a judicious selection of visual check points for VFR flight. Aeronautical information includes visual and radio aids to navigation, airports, controlled airspace, restricted areas, obstructions and related data.
54
New cards
Selective Availability (SA)
A satellite technology permitting the Department of Defense (DoD) to create, in the interest of national security, a significant lock and ephemeris error in the satellites, resulting in a navigation error.
55
New cards
Sensitive Altimeter
A form of multi-pointer pneumatic altimeter with an adjustable barometric scale that allows the reference pressure to be set to any desired level.
56
New cards
Service Ceiling
The maximum density altitude where the best rate-of-climb airspeed will produce a 100-feet-per-minute climb at maximum weight while in a clean configuration with maximum continuous power.
57
New cards
Servo
A motor or other form of actuator which receives a small signal from the control device and exerts a large force to accomplish the desired work.
58
New cards
Servo Tab
An auxiliary control mounted on a primary control surface, which automatically moves in the direction opposite the primary control to provide an aerodynamic assist in the movement of the control.
59
New cards
Significant Meteorological Information (SIGMET)
A weather advisory in abbreviated plain language concerning the occurrence or expected occurrence of potentially hazardous en route weather phenomena that ma affect the safety of aircraft operations. It warns information, hence it is of highest priority among other types of meteorological information provided to the aviation users.
60
New cards
Signal-to-Noise Ratio
An indication of signal strength received compared to background noise, which is a measure of the adequacy of the received signal.
61
New cards
Significant Weather Prognostic
Presents four panels showing forecast significant weather.
62
New cards
Simplex
Transmission and reception on the same frequency.
63
New cards
Simplified Directional Facility (SDF)
A NAVAID used for non-precision instrument approaches. The final approach curse is similar to that of an ILS localizer; however, the SDF course may be offset from the runway, generally not more than 3 degrees, and the course may not be wider than the localizer, resulting in a lower degree of accuracy.
64
New cards
Single-Pilot Resource Management (SRM)
The ability for a pilot to manage all resources effectively to ensure the outcome of the flight is successful.
65
New cards
Situational Awareness
Pilot knowledge of where the aircraft is in regard to location, air traffic control, weather, regulations, aircraft status, and other factors that may affect flight.
66
New cards
Skidding Turn
An uncoordinated turn in which the rate of turn is too great for the angle of bank, pulling the aircraft to the outside of the turn.
67
New cards
Skin Friction Drag
Drag generated between air molecules and the solid surface of the aircraft.
68
New cards
Slant Range
The horizontal distance from the aircraft antenna to the ground station, due to line-of-sight transmission of the DME signal.
69
New cards
Slaved Compass
A system whereby the heading gyro is “slaved to”, or continuously corrected by bring its direction readings into agreement with a remotely located magnetic direction sensing device (usually a flux value or flux gate compass).
70
New cards
Slipping Turn
An uncoordinated turn in which the aircraft is banked too much for the rate of turn, so the horizontal lift component is greater than the centrifugal force, pulling the aircraft toward the inside of the turn.
71
New cards
Small Airplane
An airplane of 12,500 pounds or less maximum certified takeoff weight.
72
New cards
Somatographic Illusion
The misperception of being in a nose-up or nose-down attitude, caused by a rapid acceleration of deceleration while in flight situations that lack visual reference.
73
New cards
Spatial Disorientation
The state of confusion due to misleading information being sent to the brain from various sensory organs, resulting in a lack of awareness of the aircraft position in relation to a specific reference point.
74
New cards
Special Use Airspace
Airspace in which flight activties are subject to restrictions that can create limitations on the mixed us of airspace. Consists of prohibited, restricted, warning, military operations, and alert areas.
75
New cards
Special Fuel Consumption
Th amount of fuel in pounds per hour consumed or required by an engine per brake horsepower or per pound of thrust.
76
New cards
Spin
An aggravated stall that results in an airplane descending in a helical, or corkscrew path.
77
New cards
Spiral Instability
A condition that exists when the static directional stability of the airplane is very strong as compared to the effect of its dihedral in maintaining lateral equilibrium.
78
New cards
Spiraling Slipstream
The slipstream of a propeller-driven airplane rotates around the airplane. The slipstream strikes the left side of the vertical fin, causing the aircraft to yaw slightly. Rudder offset is sometimes used by aircraft designers to counteract this tendency.
79
New cards
Spoilers
High-drag devices that can be raised into the air flowing over an airfoil, reducing lift and increasing drag. Spoilers are used for roll control on some aircraft. Deploying spoilers on both wings at the same time allows the aircraft to descend without gaining speed. Spoilers are also used to shorten the ground roll after landing.

80
New cards
Stabilator
A single-piece horizontal tail surface on an airplane that pivots around a central hinge point. A stabilator serves the purposes of both the horizontal stabilizer and the elevators.
81
New cards
Stability
The inherent quality of an airplane to correct for conditions that may disturb its equilibrium, and to return or to continue on the original flight path. It is primarily an airplane design characteristic.
82
New cards
Stagnant Hypoxia
A type of hypoxia that results when the oxygen-rich blood in the lungs is not moving to the tissues that need it.
83
New cards
Stall
A rapid decrease in lift caused by the seperation of airflow from the wing’s surface, brought on by exceeding the critical angle of attack. A stall can occur at any pitch attitude or airspeed.
84
New cards
Standard Atmosphere
At sea level, this has a barometric pressure of 29.92 inches of mercury (Hg) or 1013.2 millibars, and a temperature of 15 C (59 F). Pressure and temperature normally decrease as altitude increases. The standard lapse rate in the lower atmosphere for each 1,000 feet of altitude is approximately 1 “Hg” and 2 C (3.5 F).
85
New cards
Standard Empty Weight (GAMA)
This weight consists of the airframe, engines, and all items of operating equipment that have fixed locations and are permanently installed in the airplane including fixed ballast, hydraulic fluid, unusable fuel, and full engine oil.
86
New cards
Standard Holding Pattern
A holding pattern in which all turns are made to the right.
87
New cards
Standard Instrument Departure Procedures (SIDS)
Published procedures to expedite clearance dilvery and to facilitate transition between takeoff and en route operations.
88
New cards
Standard Rate Turn
A turn in which an aircraft changes its direction at a rate of 3 degrees per second (360 degrees in 2 minutes) for low- or medium-speed aircraft. For high-speed aircraft, the standard rate turn is 1.5 degrees per second (360 degrees in 4 minutes).
89
New cards
Standard Service Volume (SSV)
Defines the limits of the volume of airspace which the VOR serves.
90
New cards
Standard Terminal Arrival Route (STAR)
A preplanned IFR ATC arrival procedure published for pilt use in graphic and/or textual form.
91
New cards
Standard Weights
Weights estabished for numerous items involved in weight and balance computations. These weights should not be used if actual weights are available.
92
New cards
Static Longitudinal Stability
The aerodynamic pitching moments required to return the aircraft to the equilibrium angle of attack.
93
New cards
Static Pressure
Pressure of air that is still or not moving, measured perpendicular to the equilibrium.
94
New cards
Static Stability
The intial tendency an aircraft displays when disturbed from a state of equilibrium.
95
New cards
Station
A location in the airplane that is identified by a number designating its distance in inches from the datum. The datum is, therefore, identified as station zero. An item located at station +50 would have an arm of 50 inches.
96
New cards
Stationary Front
A front that is moving at a speed of less than 5 knots.
97
New cards
Steep Turns
In instrument flight, any turn greater than standard rate; in visual flight, anything greater than a 45 degree bank.
98
New cards
Stepdown Fix
The point after which additional descent is permitted within a segment of an IAP.
99
New cards
Stratoshere
A layer of the atmosphere above the tropopause extending to a height of approximately 160,000 feet.
100
New cards
Supercooled Water Droplets
Water droplets that have been cooled below the freezing point, but are still in a liquid state.