Business Management Unit 2 - Human Resource Management
1/166
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
Define Human Resources
The people who work for a business.
Define workforce planning
A continual process used to align the needs and priorities of the organization with those of its workforce.It involves forecasting future workforce needs and ensuring the right number of employees with the right skills are in place.
Define labour turnover
The proportion of a firm's workforce that leaves during the course of a year.
Define demographics
Statistical data relating to the population and particular groups within it.
Define labour mobility
The degree to which people are able and willing to move from one job to another
Define recruitment
The action of finding new people to fill a specific position in a business
Define 360-degree feedback
A process through which feedback from an employee's subordinates, colleagues, and supervisor, as well as a self-evaluation by the employee themselves is gathered.It provides a comprehensive view of performance and areas for improvement.
Define self-appraisal
An act or instance of evaluating one's own worth, significance, or status
Define redundancy
This is when a job is no longer required so the employee doing this job becomes redundant through no fault of his or her own.
Define Human Resource Management
This is the management process of anticipating a firm's current and future staffing needs.
What is the equation for labour turnover?
(employees who left/Average number of employees)x100
What does it mean if labour turnover is high?
This could be a sign of: difficult working conditions, a poorly managed organizational culture or outright management failure
What are some costs associated with high labour turnover?
Need to pay for advertisements to recruit new staff, firing costs(golden handshake), Hiring costs, cost of training workersand potential loss of productivity during the transition period.
Name some external factors affecting workforce planning
Technological changes, government regulations, demographic change, social trends, state of economy, changes in education, labour mobility
Name some internal factors affecting workforce planning
Changes in business organisation, changes in labour relations, changes in business strategy, changes in business finance
Describe the recruitment process
Identify the vacancy, define the role, person Specification, advertise, short list candidates, interview, check references, test them, offer job
Define internal recruitment
Recruiting someone who already works in the company to fill a vacant position.
Define external recruitment
Recruiting someone who doesn't already work at the company
Name some advantages of internal recruitment
Less risky as the person is already well known, cost effective, motivation for the person to get a promotion, no need to go through the tedious recruitment process, person will have pre existing knowledge of what to do, no need to do reference check
Name some disadvantages of internal recruitment
Fewer applicants, time consuming, might be harder to get new ideas, internal politics
Name some advantages of external recruitment
More applicants, may have more experience, may positively impact workers, can bring new ideas
Name some disadvantages of external recruitment
Greater degree of uncertainty, time consuming, expensive
Define on the job training
Involves instruction at the place of work
Define induction training
Given to all new recruits and aims to introduce them t the people which they will be working closely with
Define off-the-job training
Entails any course of instruction away from the place of work
Define cognitive training
Aims to develop both the physical skill base of their workers through on-the-job training and their mental capabilities through the use of cognitive exercises
Define behavioural training
Allows employees to grow their skill base so that they can be more productive for an organiazation
Name some advantages of on-the-job training
Cheap, targeted, fewer disruptions, location is convenient
Name some disadvantages of on-the-job training
May pick up bad working practices, Trainers may lack the most up to date training experience and skills.
Name some advantages of induction training
Establishes clear expectations, helps new recruits to understand the corporate culture, morale boosted as new staff feel welcome
Name some disadvantages of induction training
Time consuming key staff need to be freed from their duties to conduct induction training, information overload, may take too long
Name some advantages of off-the-job training
Experts who might not exist internally are used to provide training, a wider range of training can be provided, no distractions, networking can take place
Name some disadvantages of off-the-job training
loss of workers whilst they attend such trainings, expensive, some of the skills learnt may not be relevant and transferable
Define appraisal
A way of judging an employee's performance
Describe some of the positive consequences associated with appraisal
The employer has the opportunity to restate objectives, can praise high performance, get a chance to voice concerns,opportunity to channel frustrations
Define summative appraisal
occurs at the end of a training period or a year
Name some reasons for making employees redundent
No need for the role anymore, not in the financial position to have so many employees, competition
Explain how privatisation affects employees
increased stress due to less stable position in the business and longer working hours
Explain how increased migration affects employees
Less payment, different ideas, more diverse
Define full time
guaranteed a minimum amount of working hours a week
Define permanent contract
Work there for the rest of your life
Define part time
for only part of the usual working day or week.
Define freelance
no set job, offers services to employers
Define teleworking
working over the telephone
Define homeworking
Work which can be done at home
Define flexitime
Certain number of hours are required but you can pick when you would like to work
Define job share
sharing a job with another person
Define offshoring
Moving part of a company's operations to another country
Define outsourcing
A business function or operation performed by a third party either onshore or offshore
Define reshoring
A deliberate attempt to move functions back to the country of origin
Name some of the disadvantages of outsourcing
Subcontractors have been known to cut corners by hiring under-aged, illegal and unqualified workers, quality management can become more difficult, Subcontractors need to be monitored, can cause redundancies, unethical practices
Name some of the advantages of outsourcing
Specialists are hired to carry out the work to high quality, subcontractors will bid for the outsourced work, reduce labour costs, improves workforce flexibility
Evaluate how innovation may influence human resource practices.
It is crucial that innovative and motivated workers are recruited to support and stimulate the creative process
Evaluate how ethics may influence human resource practices
As HR plans are based on relationships it is important that ethical guidelines are followedEvaluate how culture may influence human resource practices
Evaluate how culture may influence human resource practices
It is vital in today's world that cultural differences are understanding of and respectful toward diversity
Define delegation
The process of entrusting a subordinate to perform a task for which the manager or superior retains the overall responsability
Define span of control
The number of immediate subordinates one commander or leader can effectively control, supervise, or direct.
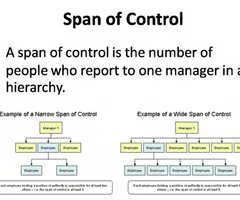
Define levels of hierarchy
The number of levels of formal authority from the top to the bottom of an organization
Define chain of command
Is usually depicted on an organizational chart as a vertical line of authority enabling decision-making or responsibility to be passed down through the layers of hierarchy.
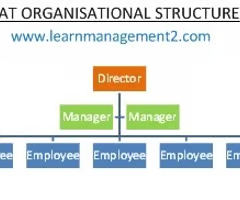
Define bureaucracy in a business context
An administrative system of a business which relies on a set of rules and procedures, separation of functions and a hierarchical structure in implementing controls over an organization
Define centralization
The degree to which decision making is concentrated at upper levels of the organization
Define decentralization
Decision making occurs at all levels of management
Define delayering
A process designed to remove the number of layers in the hierarchy
Name some advantages of delayering
Reduce costs, improves the speed of communication, encourages delegation and empowerment
Name some disadvantages of delayering
Creates a sense of insecurity, overloads staff, decision making can take longer
Name some advantages of a tall hierarchical structures
Quicker and more effective communication within smaller teams, smaller teams are generally easier to control and manage, greater specialisation, more opportunities for people to be promoted which can be very motivating
Name some disadvantages of a flat hierarchical structure
Delegation becomes quite important hence subordinates get the chance to further their career, communication is improved, cheaper to operate, can help to eliminate a 'them and us' culture
Define project teams
People from different fields are put into one team to work on a project together
Name some advantages of project-based organization
Flexibility, productivity, efficiency, motivational
Name some disadvantages of project-based organization
Discontinuity, isolation, inefficiencies, conflicting interests and priorities
Describe handy's shamrock organization
Core workers: full-time employees with trusted experience and are small in number
External subs(contract workers): Are employed on a short-term basis for a specific task
Project workers(periperal workers): Are flexible workers employed on a par-time basis for reasons such as seasonal shifts in operation
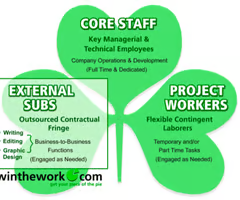
Describe five functions management
Planning: managers are responsible for setting the course of action to achieve organisational objectives. They are involved in setting both tactical plans and strategic plans.
Commanding: managers give instructions and orders to their teams and subordinates in order to achieve business objectives. They should enforce discipline in the workplace to prevent slack and to prevent non-compliance.
Controlling: Managers are responsible for the performance and health and safety of their teams.
Coordinating: Managers have the responsibility for ensuring that all departments strive to achieve the goals of the organisation.
Organising: Managers organise resources in order to achieve corporate objectives. This might include delegating or allocating tasks to workers to ensure that deadlines are met
Define a leader
Someone who influences and inspires others to get things done. Fostering motivation, respect, trust and loyalty from the workforce.
Define a manager
Tend to focus on achieving goals within a period of time
Define autocratic leadership
Autocratic leadership is one person in charge who makes all or most of the decisions.
Define paternalistic leadership
Treat their employees as if they were family members by guiding them through a consultation process and acting in the best interest of their subordinates
Define democratic leadership
Someone who involves employees in the decision-making process.
Define situational leadership
Unlike any other style of leadership it is not based on any single dominant approach. In essence it is using the right leadership style for the right situation.
Define Laissez-faire leadership
Leaders who have a minimal direct input in the work of employees
Name the 5 styles of leadership
1.Autocratic
2.Democratic
3.Situational
4.Paternalistic
5.Laissez-faire
Describe Taylor's scientific management
1. Identify most efficient method of production
2. Spot the most efficient workers and see why they are so good
3. Train the remaining workers to work like the best
4.Pay workers based on productivity(piece rates)

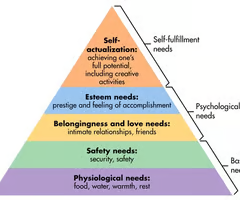
Describe Maslow's hierarchy of needs
Emphasizes an individual's motivation in the continuous quest for self-actualization. The lower needs requiring fulfillment before those at higher levels can be achieved, with self-actualization being fulfillment of one's highest potential.
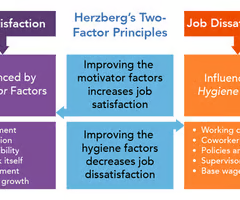
Describe Herzberg's two factor principles
Job dissatisfaction is influenced by hygiene factors such as: working conditions, coworker relations, policies and rules, supervisor quality, base wage and salary. Job satisfaction is influenced by motivator factors such as: achievement, recognition, responsibility, work itself, advancement, personal growth. Improving the motivator factors increases job satisfaction. Improving hygiene factors decreases job dissatisfaction
Describe Adams' Equity Theory
Inputs and outputs should be equal as people become demotivated when they feel their inputs are not being fairly rewarded.
Inputs: Time, effort, ability, loyalty, tolerance, flexibility, integrity, commitment, reliability, heart and soul, personal sacrifice.
Outputs: Pay, bonus, perks, benefits, security, recognition, praise, responsibility, enjoyment.
Describe Pink's motivational theory
Autonomy+Mastery+Purpose=Motivation
Autonomy: Being able to manage their own time
Mastery: Having the correct competence, experience, tasks, support and time to become good at it.
Purpose: Is it worthy for me, the task, the department, the company
Define financial rewards
Methods that a business can use to motivate workers with monetary payment.
Define salaries
Financial rewards set at a fixed annual rate but paid on a monthly basis. e.g. a person earning $36,000 per year is paid $3000 per month
Advantages of salaries
Can improve a firm's cash flow, good when output or productivity is not easy to measure
Disadvantages of salaries
Difficult to reward those who are more productive, little incentive to work harder as pay will stay the same
Define wages(time)
A reward for labour services, usually expressed as an hourly rate
Define wages(piece rate)
A reward for labour services, usually expressed as a measurable quantity of output
Advantages of wages
Straightforward method, more motivating for workers
Disadvantages of wages
Workers not rewarded for their efforts but for their time. This is not true for piece rates of course. a disadvantage of piece rates may that you may as a result sacrifice quality for quantity.
Define commission
Pays workers based on a percentage of sales or output contributed by the worker. For example, real estate agents might get paid 1% (the commision) of the value of each property personally sold.
Advantages of commission
Acts as an incentive to sell more
Disadvantages of commission
Added pressure on workers, tasks can be repetitive, difficult to meet security needs as workers do not know how much they will be paid
Define profit related pay
As a form of financial motivation, this method involves linking pay to the level of profit in the firm.
Advantages of profit related pay
Can foster team spirit and loyalty, hence boosting labour efficiency and decreasing conflict between workers
Disadvantages of profit related pay
The proportion of profit paid to the employees may be too small to act as an incentive to work any harder.
Define performance related pay
A system which rewards employees(as individuals, teams or as a whole workforce) who meet certain goals.