Unit 4 AOS 1
1/147
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
Pathogen
An agent that causes disease.
Antigen
Any molecule that may trigger an immune response.
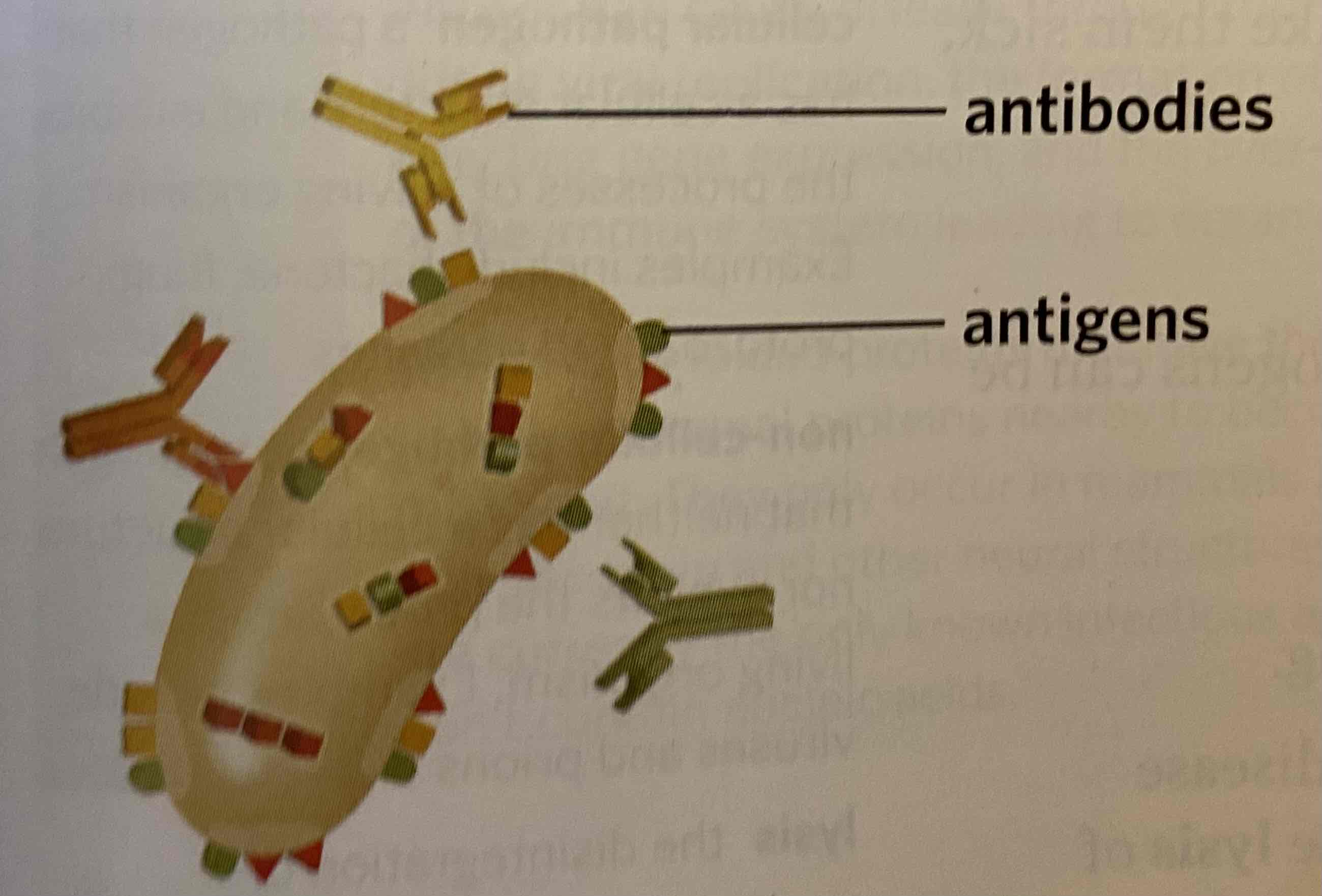
Non-self antigen
A molecule from outside the body that is recognised by the immune system and initiates an immune response. Also known as a foreign antigen.
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) markers
A groups of proteins present on the surface of all self-cells hat enables the immune system to distinguish it from non-self material. Also known as MHC proteins, MHC molecules or self-antigens.
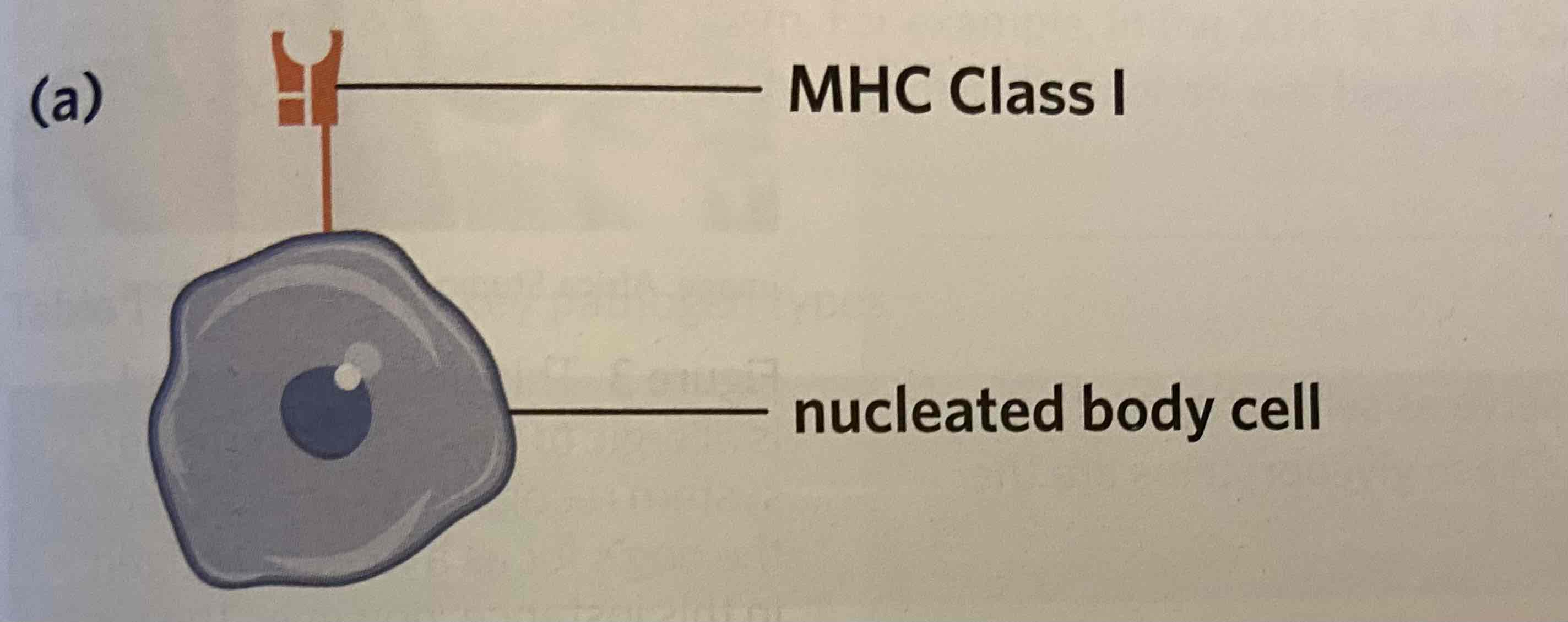
Major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC class I) markers
Expressed on all nucleated cells in the body. These mark cells as “self” so that the immune system doesn’t attack them.
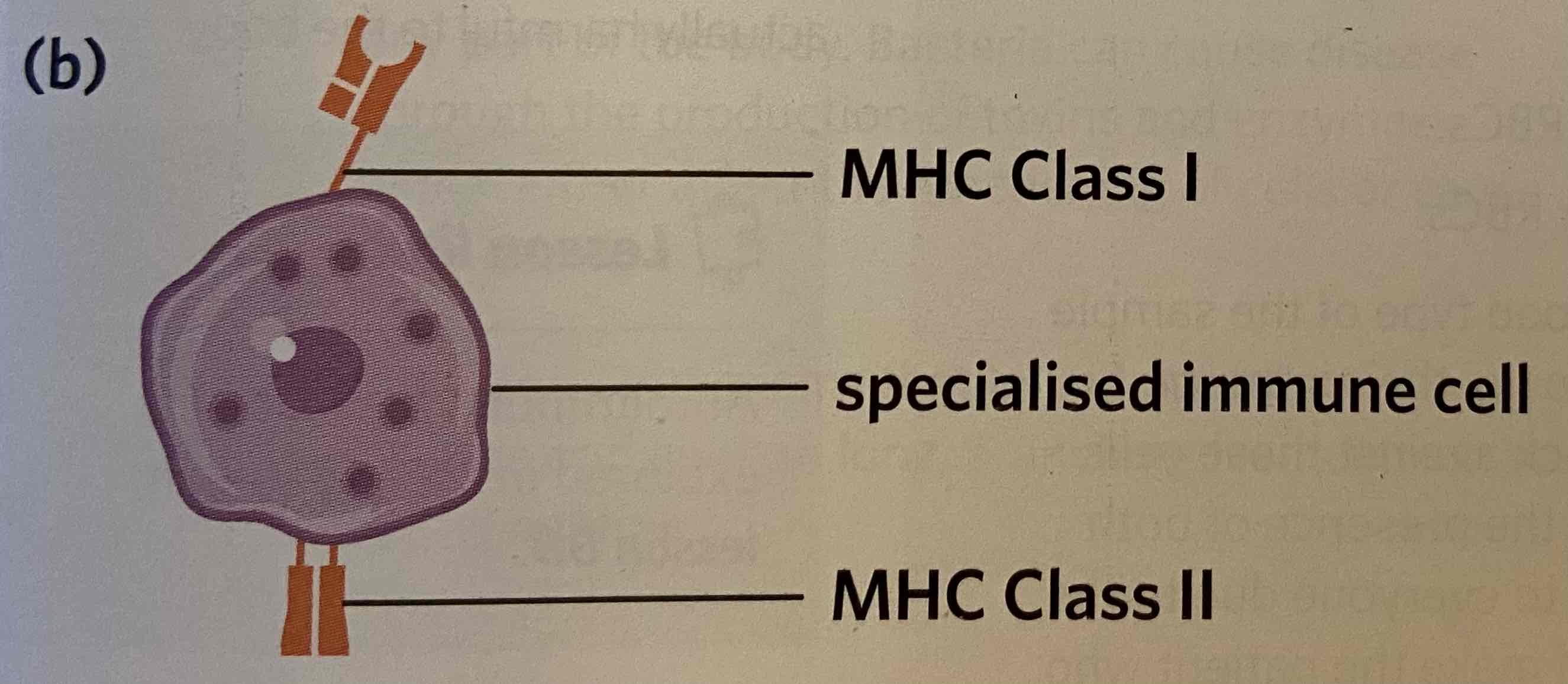
Major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC class II) markers
Expressed in antigen-presenting cells, which interact with T helper cells in the process of antigen-presentation.
Autoimmune disease
A diseases in which an indivdiual’s immune system initiates an immune response against their own cells.
Allergen
A non-pathogenic antigen that triggers an allergic reaction.
Allergic reaction
An overreaction of the immune system to a non-pathogenic antigen.
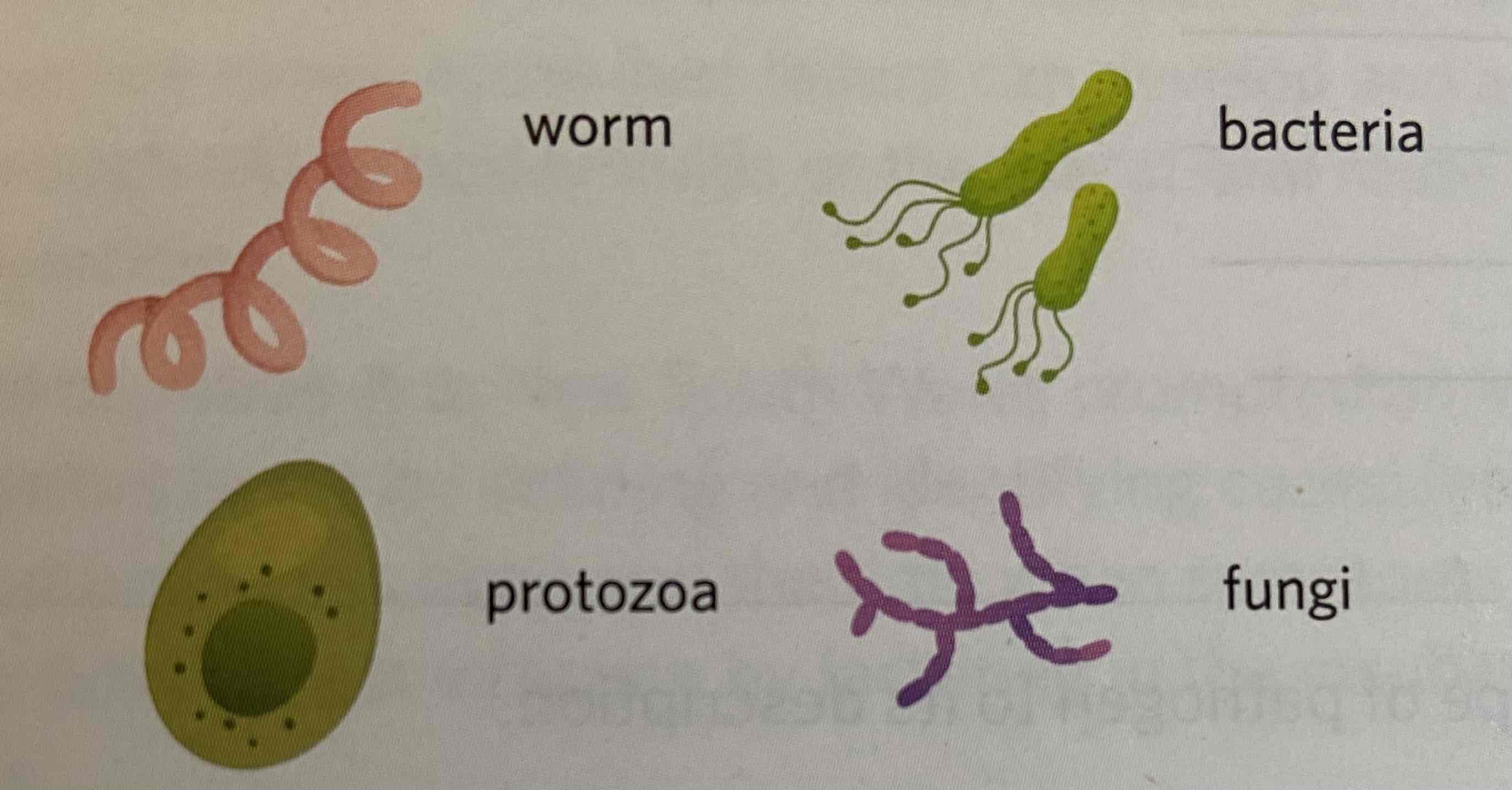
Cellular pathogen
A pathogen that has a cellular structure and exhibits the processes of a living organism. Examples include bacteria, fungi, protozoa and parasites.

Non-cellular pathogen
A pathogen that doesn’t have a cellular structure and doesn’t exhibit the processes of a living organism. Examples include viruses and prions.
Lysis
The disintegration or rupturing of a cell.
Hyphae
Branching filaments of a fungus which help absorb nutrients from the environment.
Parasite
An organism that lives in or on another organism, usually deriving nutrition from the host organism.
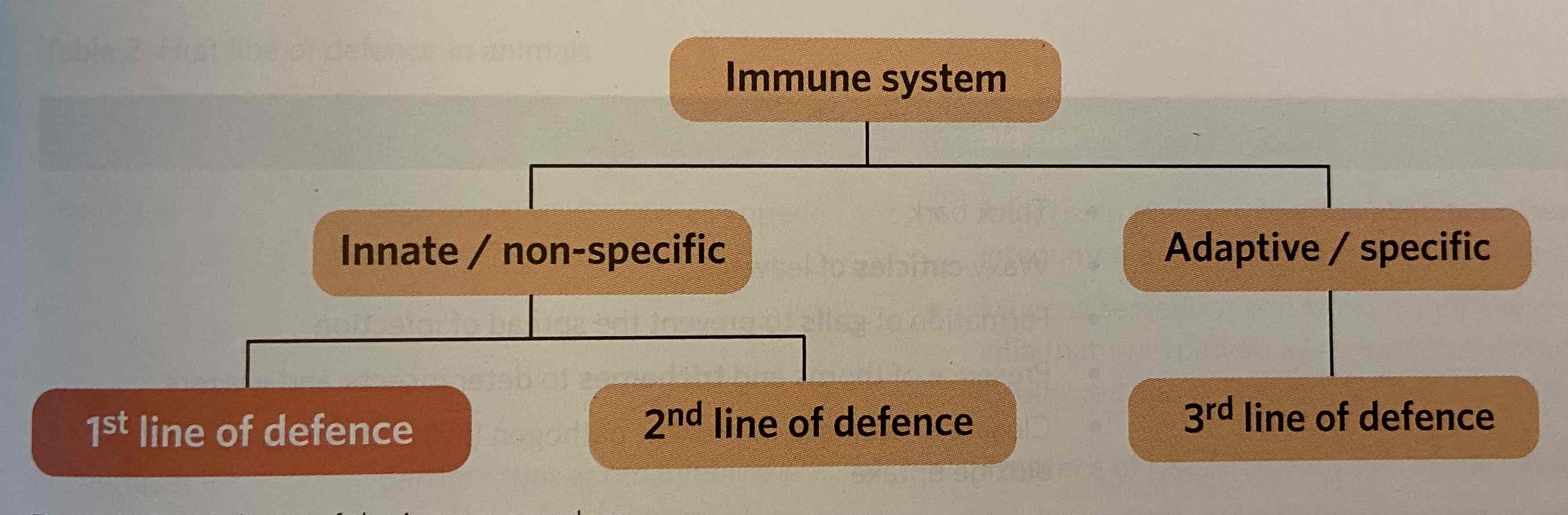
Innate immune system
A component of the immune system that is composed of generalised and non-specific defences and/or responses to pathogens. Also known as the non-specific immune system.
First line of defence
A component of the innate immune system characterised by the presence of physical, chemical and microbiological barriers to keep pathogens out of the host organism.
Second line of defence
A component of the innate immune system characterised by the non-specific response to injury and/or pathogens by a variety of cells and molecules.
Non-specific
Described a component of the immune system that responds the same way to all pathogens.
Physical barrier
A component of the first line of defence that features solid or fluid obstacles that block pathogen entry such as skin or mucus.
Chemical barrier
A component of the first line of defence that features the use of enzymes, toxins and acids to protect against pathogen invasion.
Cuticle
A waxy protective film covering the surface of a plant leaf.
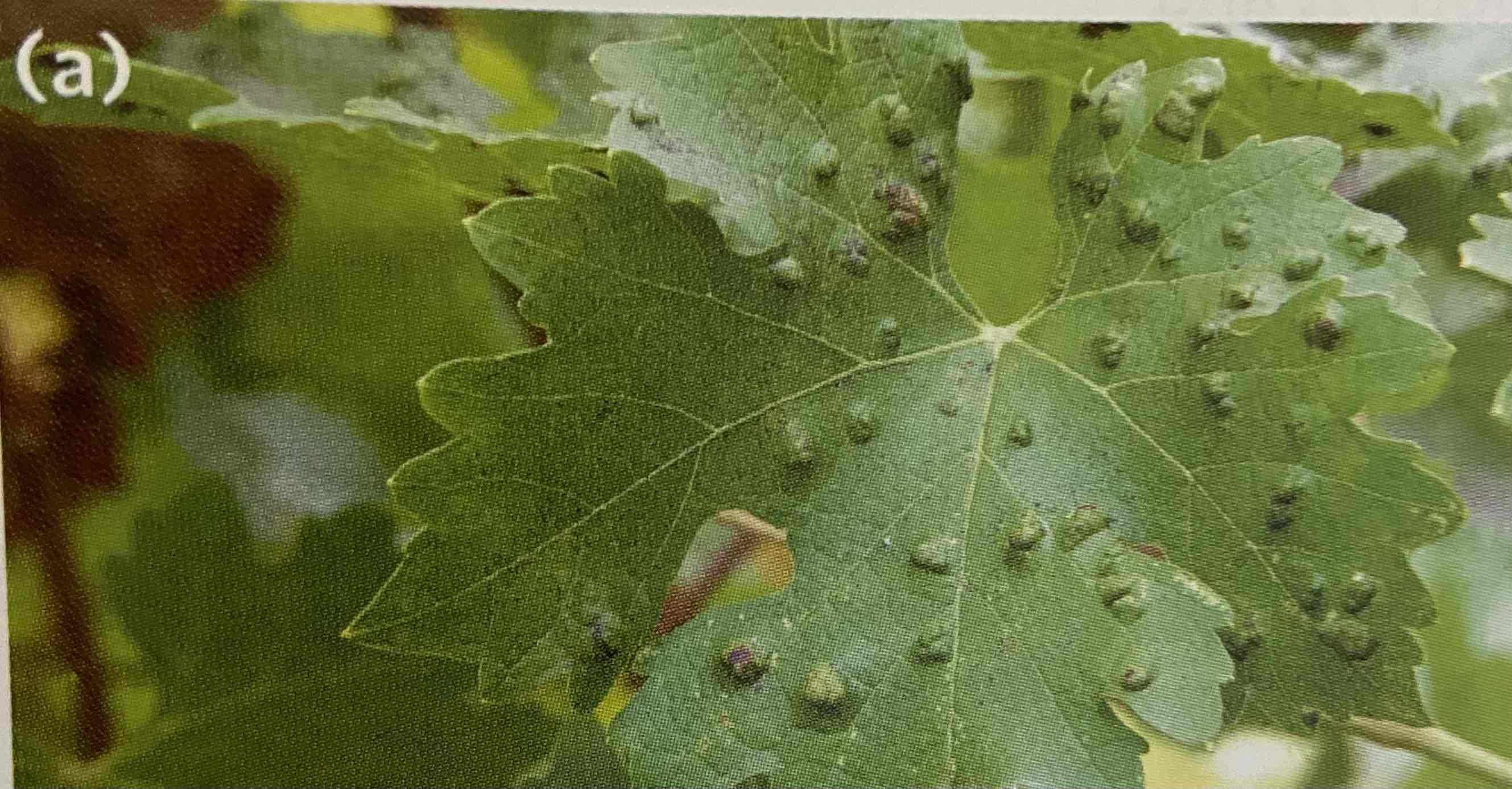

Gall
An abnormal outgrowth of tissue in plants designed to limit the spread of an invading pathogen.
Trichomes
Small hairs on the surface of plants that are used to deter pathogens and/or insects.
Stoma
A small pore on the leaf’s surface that opens and closes to regulate gas exchange.
Microbiological barrier
A component of the first line of defence in which the presence of flora limits the growth of pathogenic bacteria. Also known as microbiota barrier.
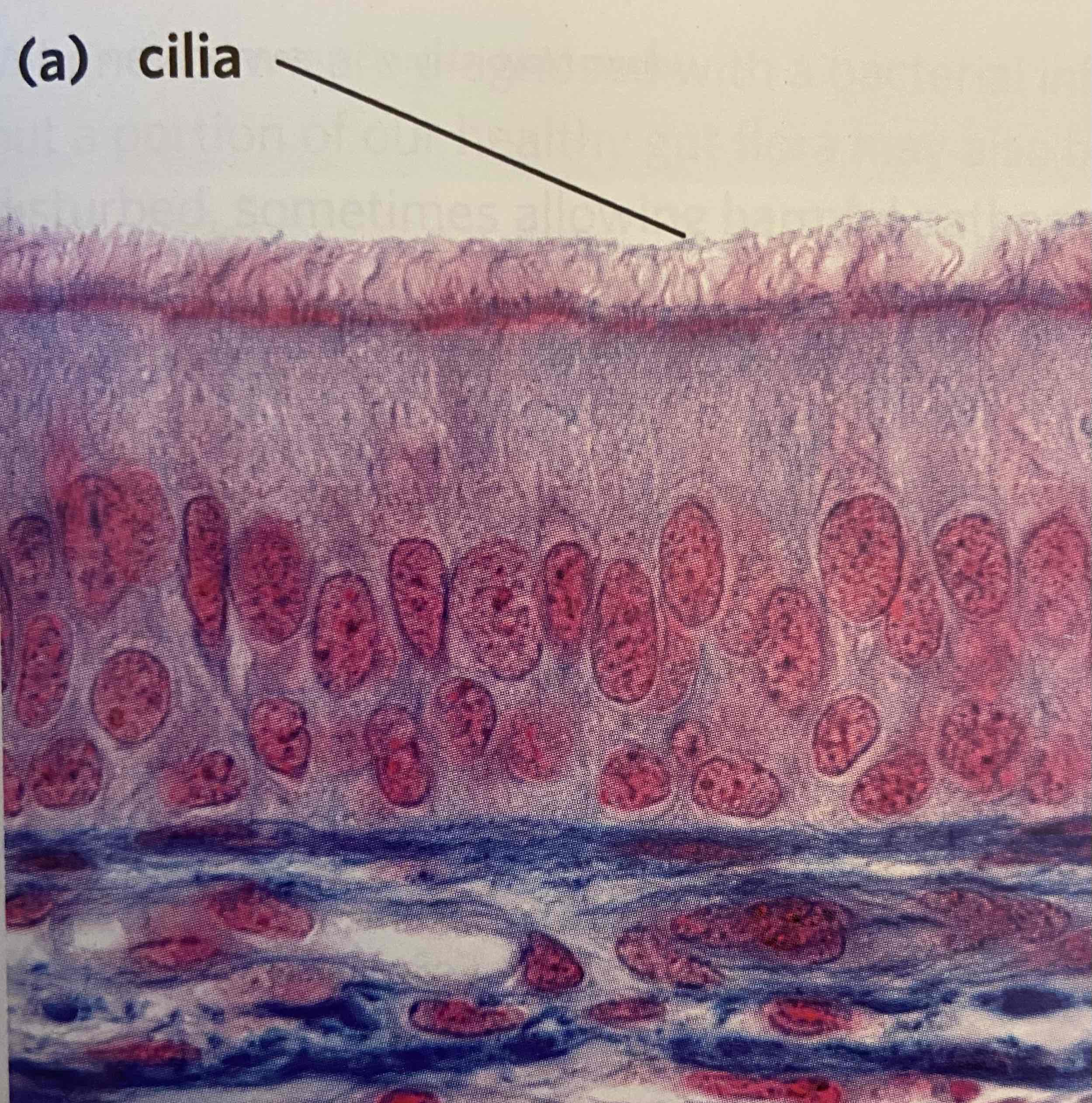
Cilium (pl. cilia)
Thin, hair-like projections that protrude from eukaryotic cells.
Flora
Naturally occurring non-pathogenic bacteria present in an organism.
second line of defence
A component of the innate immune system characterised by the non-specific and immediate response to injury and pathogens by a variety of cells and molecules.
Leukocytes
A group of blood cells responsible for protecting the body against pathogens and foreign material. Also known as white blood cells.
Phagocyte
A group of leukocytes responsible for the endocytosis and destruction of pathogens, foreign material, and cell debris.
Neutrophil
The most common type of leukocyte in the body. Engages in phagocytosis of pathogens and foreign material, as well as the release of cytokines.
Macrophage
A type of leukocyte found throughout the body that engages in phagocytosis and antigen presentation.
Dendritic cell
A type of leukocyte that engages in phagocytosis and antigen presentation.
Antigen-presenting cell
A sub-group of phagocytes that display antigens from consumed pathogens on their surface and interact with the adaptive immune system. also known as professional antigen-presenting cell.
Cytokine
A signalling molecule released by cells (typically in the immune system) which aids in the communication between cells and helps protect against pathogens.
Natural Killer (NK)
A type of leukocyte responsible for the recognition and destruction of damaged and/or infected host cells.
Mast cell
A type of leukocyte responsible for releasing histamine during allergic and inflammatory responses.
Degranulation
The release of granule contents from a cell.
Histamine
A molecule released by mast cells that plays a key role in inflammation.
Inflammatory process
A series of biochemical events that occur in the body as a result of infection, swelling or trauma. Characterised by swelling, redness, pain and heat in the affected area.
Eosinophil
A large granular leukocyte responsible for the release of toxic chemical mediators.
Interferon
A cytokine released by virally infected cells that increases the viral resistance of neighbouring uninfected cells.
Complement protein
A number of different types of proteins found in the blood that opsonise, cause lysis and attract phagocytes to invading pathogens.
Complement cascade
A complex sequence of events which occurs after the activation of complement proteins.
Opsonisation
the mechanism by which complement proteins attach to the surface of pathogens, making them easier to phagocytose.
Chemotaxis
the attraction of phagocytes towards a pathogen.
Lysis
the disintegration or rupturing of a cell.
Membrane attack complex (MAC)
A pore formed by complement proteins in the cell membranes of a pathogen, disrupting the membrane and leading to the pathogen’s destruction.
Vasodilation
The widening of blood vessels.
Lymphatic system
A large network of vessels and tissues throughout the body that form an important component of both the circulatory and immune systems.
Lymph node
A small secondary lymphoid tissue of the lymphatic system where antigen-presenting cells activate the adaptive immune system.
third line of defence
A subset of the immune system within vertebrates that is composed of the humoral and cell-mediated responses which create a specific immune response and form immunological memory. Also known as the adaptive immune system or specific immune response.
Immunological memory
The ability of the immune system to quickly and aggressively combat a previously encountered pathogen due to the presence of T and B memory cells.
T lymphocyte
A type of lymphocyte that plays an important role in cell-mediated immunity. It differentiates into cytotoxic T cells, t memory cells, and T helper cells.
T helper cell (Th)
A type of differentiated T lymphocyte that that supports the functioning of a number of different immune cells, including the cloning and differentiation of selected T and B cells.
humoral immunity
An adaptive immune response in which extracellular pathogens are targeted by specific antibodies produced by plasma cells Also known as B cell immunity.
Cell mediated immunity
An adaptive immune response in which infected or abnormal cells are destroyed by cytotoxic T cells. also known as T cell immunity.
B lymphocyte
A type of lymphocyte that plays an important role in humoral immunity and differentiates into plasma cells and b memory cells.
Antibody
a protein produced by plasma cells during the adaptive immune response that is specific to an antigen and combats pathogens in a variety of ways. Also known as immunoglobulin.
Cytokine
A signalling molecule released by cells (typically in the immune system) which aids in communication between immune cells and helps protect against pathogens.
Clonal expansion
The process in which many copies of a lymphocyte are generated.
Clonal selection
The process in which B and T cells encounter an antigen that matches their antigen binding site, and then generate many copies of themselves. also known as clonal selection theory.
Differentiation
the process in which cells develop specialised characteristics, typically transforming them from one cell type to another more specialised cell type.
B memory cell
A differentiated B lymphocyte that is responsible for providing long-lasting immunological memory of an antigen
Effector cell
A cell that responds to a signal and produces a response.
Plasma cell
A differentiated B lymphocyte that is responsible for the generation and secretion of antibodies during the humoral response.
Disulphide Bond
A strong covalent bond between two sulphur atoms.
Agglutination
The clumping of particles together. in the immune system, antibodies can help clump pathogens together.
Antigen-antibody complex
A structure formed by the complementary binding between antigen and antibody molecules.
Rhesus antigen
An antigen on the surface of red blood cells that can cause an immune response if not matched correctly between donor and receiver.
Cytotoxic T cell (Tc)
A differentiated T lymphocyte that is responsible for the destruction of infected or abnormal cells.
T memory cell
A differentiated T lymphocyte that is responsible for providing long-lasting immunological memory.
Apoptosis
The controlled death of cells in the body. Also known as programmed cell death.
Circulatory System
A collection f tissues and organs involved in the transportation of substances around the body. Composed of the lymphatic and cardiovascular systems.
Lymphatic System
a large network of vessels and tissues throughout the body that form an important component of both the circulatory and immune systems.
antigen-presenting cell
A subgroup of phagocytes that display the antigens from consumed pathogens on their surface and interact with the adaptive immune system.
Secondary lymphoid tissue
Components of the lymphatic system that are responsible for the maintenance of matures lymphocytes and the activation of the adaptive immune response. Includes lymph nodes and the spleen.
primary lymphoid tissue
Components of the lymphatic system that are responsible for the production and maturation of lymphocytes. includes bone marrow and thymus.
Lymph
A pale fluid that flows through the lymphatic system and has a high concentration of leukocytes.
Bone marrow
semi-sold tissue found within bones. Serves as the primary site of the creation of red blood cells and leukocytes.
Thymus
A primary lymphoid tissue found throughout the body where antigen-presenting cells activate the adaptive immune system.
Lymph Node
A small secondary lymphoid tissue found throughout the body where antigen-presenting cells activate the adaptive immune system
Tonsils
The name given to the two lymph nodes that reside at the back of the throat.
Spleen
an organ located in the upper abdomen that serves a variety of functions in the immune system and the regulation of red blood cells.
Clonal selection
The process in which B and T cells encounter an antigen that matches their antigen-binding site, and then generate many copies of themselves.
Lymphatic capillaries
The smallest form of lymphatic vessel. Located in the spaces between cells.
Afferent lymphatic vessel
Thin-walled structures that collect lymph from the tissues of the body and deliver it to lymph nodes
Efferent Lymphatic vessels
Thin-walled structures that collect lymph that has drained through lymph nodes, returning it back to circulation
natural immunity
Protection against a disease formed without medical intervention
Artificial immunity
Protection against a disease formed as a result of medical intervention. Also known as induced immunity
Active immunity
Protection against a disease created by antibodies and memory cells formed by a person’s own adaptive immune system.
Natural active immunity
Protection against a disease created by antibodies and memory cells produced by an individual’s own immune system without medical intervention. Also known as naturally acquired active immunity
Natural Passive immunity
Protection against a disease created by antibodies from an external non-medical source. Also known as naturally acquired passive immunity.
Artificial active immunity
Protection against a disease created by antibodies and memory cells produced by an individual’s own immune system after medical intervention. Also known as artificially acquired active immunity
Vaccine
A medical treatment typically containing antigens designed to stimulate a person’s adaptive immune system to create immunity to a pathogen without actually causing disease.
Primary immune response
The reaction of the adaptive immune system to an antigen it has not previously been exposed to
Secondary immune response
The heightened reaction of the adaptive immune system to an antigen it has previously been exposed to
Vaccination program
A series of vaccinations designed to create long-term immunity to a disease. Also known as a vaccination schedule
Booster vaccine
A vaccination given to a person later in time after they have completed their initial vaccination program to enhance their existing immunity against a disease. Also known as a booster shot
Artificial passive immunity
Protection against a disease created by antibodies from an external medical source. Also known as artificially acquired passive immunity