Biomechanics Exam 3
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Force
A mechanical disturbance or load that may deform a body or change its state of motion
Is force a vector or scalar quantity?
Vector
Has:
Magnitude
Direction
Point of application
Line of action (line of application)
Point of application
Where to the tendon attaches to the bone for internal forces
For external forces, point of application is where body is in contact with some external body (ex: ground reaction force)
Examples of contact forces
Ground reaction forces
Joint reaction force
Friction
Fluid resistance
Muscle force
Examples of non-contact forces
Gravity
Centripetal
Newton’s First Law
Law of Inertia
A body will maintain a state of rest or constant velocity unless acted on by an external force that changes the state
In absence of net force, the state of motion of an object will not change
Inertia depends on ______
mass of object
What is inertia
Inertia is the resistance of an object to changes in its state of motion
Newton’s Second Law
Law of Acceleration
Acceleration of an object is:
Directly proportional to the net force
Inversely proportional to the mass
In the same direction as net force
Defined by the equation: F=ma
If net force is increased, what happens to acceleration?
It increases (F= ma)
Newton’s Third Law
Law of reaction
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
Law of Gravitation
All bodies are attracted to one another with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them
Ex: weight (W = mg)
Ground Reaction Force (GRF)
The equal and opposite reaction force the ground exerts on the body during stance (stance phase of walking)
How do you measure GRF
Force plate used to measure GRF
GRF is assumed to act on the center of
mass of the individual
If a person is standing still on a force plate, what would their GRF read?
It would be equal to their weight (need acceleration to change the GRF)
Center of mass (COM)
object's mass is equally distributed in all directions
When acceleration is negative = vertical GRF is….
less than a person’s bodyweight
When calculating GRF, is gravity negative or positive?
Positive
Describe vertical GRF in walking
Highest in stance phases
Highest in the pre-swing phase, specifically
When acceleration is positive = vertical GRF is….
greater than a person’s bodyweight
Speed impact on GRF
Stance phase is shortened with greater speeds
Max GRF is higher in running than in walking
Steeper slope with greater speed
With running, one defined peak whereas walking has two peaks
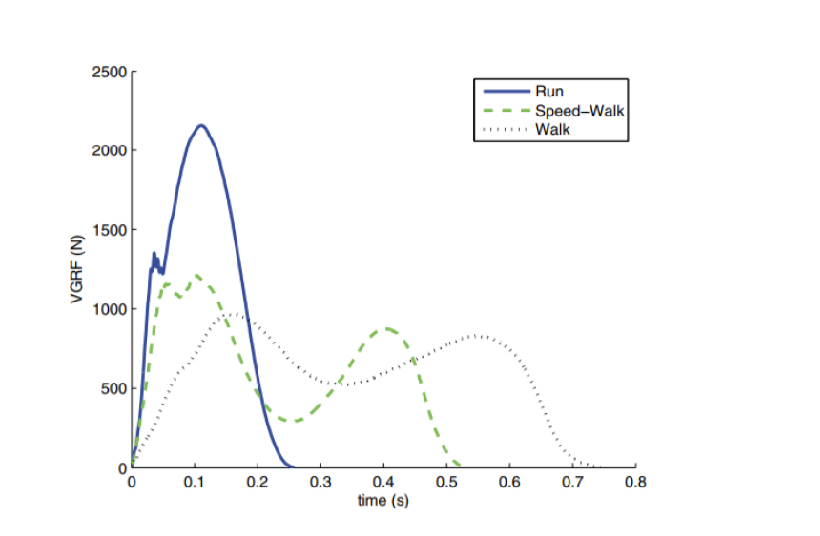
Why is there only one peak in the vertical ground reaction force graph of running?
Heel does not hit ground
How does mass affect GRF?
Larger mass means higher max values for VGRF
Shape of graph does not change with mass
Joint Reaction Force
Equal and opposite force between two articulating bones (ie joint) caused by the weight and inertial force on the bones
From compressive force and shear force, we can calculate joint reaction force (resultant joint reaction force)
Muscle Force
Resultant of all forces generated by muscle force
Friction
force acting at the area of contact between two surfaces in the direction opposite that of motion or motion tendency
What kind of force is friction?
contact
Factors affecting friction
Force acting perpendicular to the surface
Ground reaction force
Properties of the surface
coefficient of friction
Order these from lowest to highest coefficient of friction: ice, gravel, concrete
ice < gravel < concrete
Smaller coefficient of friction is easier or harder to move across?
easier
Static friction
When applied force is exerted on object/body, but no movement occurs; static friction resists the applied force
Maximal static friction
Eventually, you get to a point where you have applied enough force to overcome the static friction and make the object/body movement — this is the max static friction
Static friction just before applied force exceeds friction
For static bodies, friction is equal to ______
applied force
Kinetic friction
AKA dynamic friction
Applied force exceeds friction force, creating movement
The friction that is experienced by a moving object/body
For kinetic bodies, friction is ______ applied force
less than
Is it easier to get an object to start moving or to keep it moving? Explain.
Static friction coefficient is greater than dynamic friction
Molecular bonds form between surfaces that are static
When in movement, these bonds can’t form as well
Harder to break the initial bonds
Translational Friction
Object that occurs when there is sliding of an object/body
Rolling friction
Object rolls on surface and point of contact between object and surface changes
Ex: bike wheels
Rotational Friction
Resistance between rotating bodies
The resistance to motion that a rotating body experiences due to friction
Rotational Friction vs Rolling Friction
Rolling friction acts on the point of contact, while rotational friction is a twisting force that affects the object's spin.
Artifical grass vs natural grass
Theory is that artificial turf exerts higher frictional forces on people moving on it than natual grass
Injury risk is higher
Literature is inconclusive
What kind of force is fluid resistance?
contact force
What kind of force is air resistance?
Fluid force (a contact force)
Fluid force
Types of force exerted on object in fluid
Two main types of fluid force
Drag and lift
Drag
Force that resists the movement of object/body
Coefficient of drag
An index of how smooth and streamlined the object/body is
What affects drag?
Coefficient of drag
Projected frontal area of object/body (area facing flow, A)
Fluid densitu (or viscosity)
Velocity of the body/object relative to the fluid
What does the magnitude of C_d depend on?
Shape of object
Orientation of object relative to flow
Streamlining reduces C_d
How to calculate relative velocity?
Relative velocity = velocity of object/body + velocity of fluid
Types of drag force
Surface drag: friction of fluid on object’s surface
Pressure drag: caused by pressure differential between the front and back of the object
Surface Drag
The friction of fluid on an object’s surface
Pressure Drag
Caused by pressure differential between the front and back of the object
Dominant form of drag in human movement
Creates a turbulent wake
Pressure differential = pressure in front of object/body
Turbulent Wake
Non-uniform flow of fluid around an object
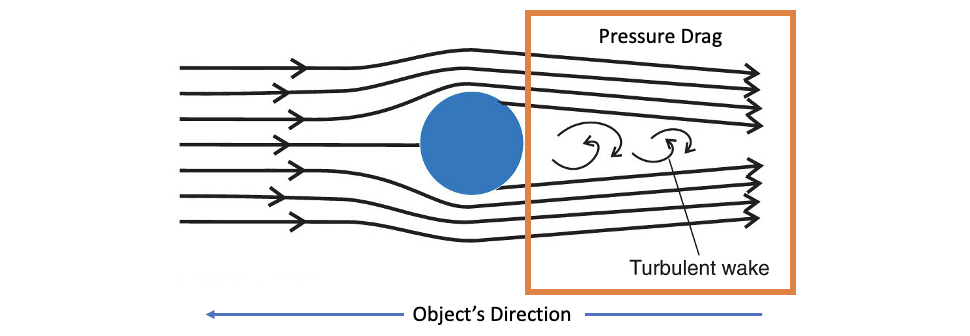
What happens when you increase pressure differential?
Increase in resistance and pressure drag
Describe the pressure differenial and turbulent flow of the highest pressure drage
Highest pressure drag has highest pressure differential and largest turbulent flow
Why do golf balls have dimples
They reduce the turbulent wake which in turn reduces pressure drag
Free body diagrams (FBD)
Sketches of a defined system in isolation with all force vectors acting on the system
Which forces you draw depend on how you define the system
Centripetal force a non-contact or contact force?
non-contact
Centripetal force definition
the net force that causes an object to move in a circular path by constantly pulling it towards the center of the circle; line of application is towards the center of the circle
Momentum definition
effect of force applied over time
Momentum and collision relationship
Momentum is particularly useful in collision analysis
Increases in momentum increases resulting effect of collision
Perfectly inelastic collision definition
collision resulting in the total loss of system velocity
AKA plastic collision
Inelastic collisions
Momentum is conserved and objects stick/move together instead of bouncing apart
Momentum before collision = momentum after the collision
Impulse Definition
Change of momentum over time
How can we maximize jump height
By increasing impulse
I = force * change in time
Can increase force
Can increase time interval
Impulse-momentum relationship
The impulse applied to an object/body is equal to the change in its momentum
How do you decrease an object's force when catching a baseball or softball?
Increase contact time (cushioning or dampening)
Think about impulse formula
How do you minimize forces acting on your body when landing from a jump?
Flexing the hips, knees, and dorsiflexing the ankle allows for more time (greater range of motion)
Think about impulse formula
Kinetics
forces that cause motion
Angular motion
all parts of the body or object do not move through the same distance during the same amount of time
Torque
Tendency of a force to cause rotation about an axis
What directions can act torque be in?
Counterclockwise
Clockwise
Gravitational Torque (in human movement)
A rotational movement that a person experiences due to gravity
Muscle torque
Using muscle force to produce a rotational movement
Ex: trunk flexion
Ground Reaction Force Torque
When ground reaction force acts on a person causes them to have a rotational movement
A person doing a backflip
Line of action/pull (torque)
Straight line in the direction of which the force is acting
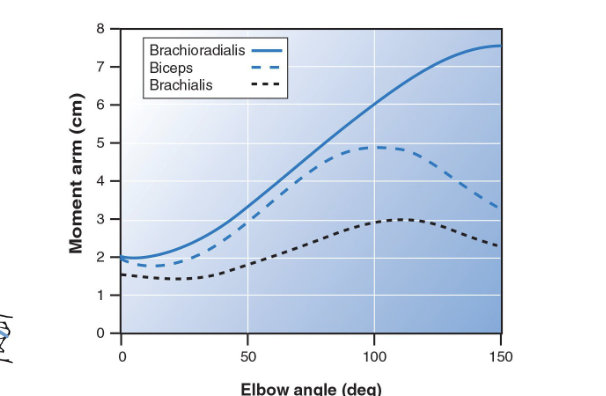
Moment arm
perpendicular distance from the line of action of a force to the axis
In other words: the distance from the application of the forces to the center of mass of the segment
Relationship between moment arm and joint angle
Moment arm is a function of joint angle
Changes non-linear with joint angle
Also affected by angle of attachment
This is the same relationship for muscular and gravitational torque
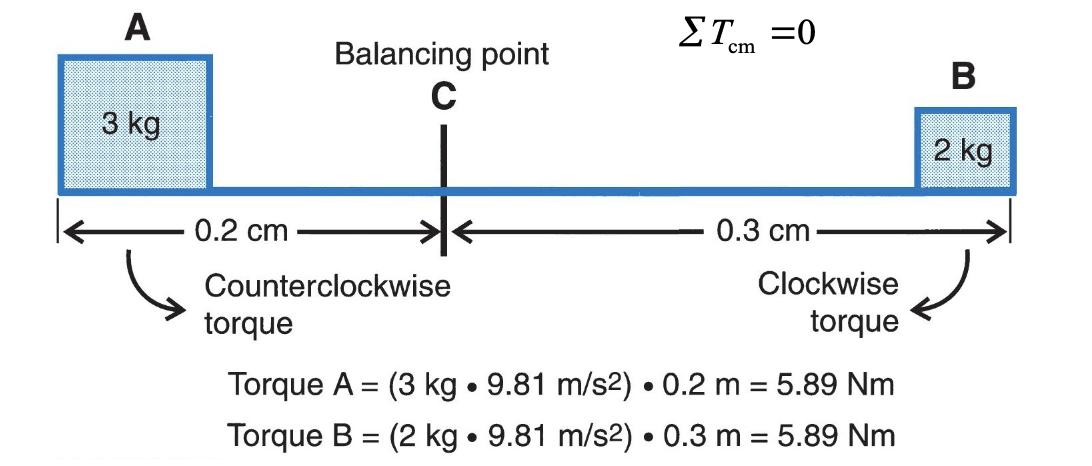
Center of mass
The point at which the sum of torques is equal to zero
The point at which a body’s mass (weight) is evenly distributed (balanced)
Think: seesaw
Center of gravity
The projected position of the center of mass vertically on the ground
Is the center of mass always inside the body/object? Explain.
The calculated center of mass might not always be inside the body
Eg. The Fosbury flop (jump used in high jump)
Curved body makes center of mass below the cross bar
Requires less force in jumping
Center of mass relationship with gravitational torque
force acts on center of mass
Muscular torque and center of gravity relationship
Muscular torque is counteracting the center of gravity
Calculating muscular torque vs gravitational
Do not need to use the sin function in gravitational torque because line of pull of gravitational force is likely perpendicular to moment arm so sin(theta) is not needed (sin(90) =1)
Do need sin function to calculate muscular
Why are the center of masses of humans hard to calculate? How do we overcome this?
Difficult to compute COM for human bodies because the various material of the human body have different densities
Also changes from instant to instant
Segmental method is how we overcome this
We break down body into segments
Calculate the center of mass of each segment using literature values that tell you what percent of the bone from the proximal end the COM is
Can use all the centers of masses of the segments to find the COM of the entire body
How can you use center of mass to calculate moment arm?
Moment arm = horizontal distance between COM and axis of rotation
If net force = 0, then change in velocity =
0
Weight needs to be in what units when calculating gravitational torque
Newtons (N)
Lever definition
simple machines consisting of a relatively rigid bar-like body that may be made to rotate about an axis
What are the parts of a lever
effort/force arm, resistance arm, fulcrum
Force arm
perpendicular distance from line of action to effort force
Resistance arm
perpendicular distance from the line of action to resistance (or load) force
Fulcrum
the point of support or axis about which a lever may be made to rotate
Describe the biceps brachii as parts of a lever
Fulcrum = axis of rotation at the elbow
Effort force = muscle force of biceps
Resistance force = gravitational force on the forearm
What is mechanical advantage?
mechanical effectiveness of a lever calculated by taking the effort arm/resistance arm
What affects mechanical advantage
Muscle length
Cross-sectional area of muscle
Moment arm
Angle of attachment of muscle
Shortening velocity of muscle
Training
Fatigue
Mechanical advantage > 1 means…
It’s easier to lift something
Can generate more force with less effort
Mechanical advantage < 1 means…
It’s harder to lift something
Requires more effort to produce force
Can be advantageous when you need to have greater speed or distance/endurance rather than greater force
1st class lever
Effort force and resistance force are on opposite sides of the fulcrum