Reactions between organometallic nucleophiles and C-based electrophiles
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
turn alkynes into alkanes
H2, Pd (cat)
turns alkynes into cis alkenes
H2, Lindlar’s catalyst (Pd/BaSO4)
turns alkynes into trans alkenes
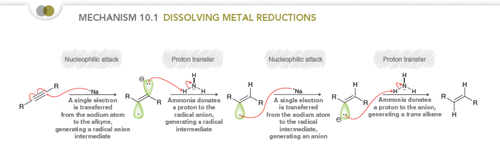
K, NH3 or Na,NH3 (dissolving metal reduction)
turns alkynes into ketones
HgSO4, H2O, H2SO4
turnes alkynes into aldehydes
1. (Sia)2BH, THF 2. H2O2, OH-, H20
turns alkynes into geminal dihalides
HBr (2 eq.) or HCl (2 eq.)
turns alkynes into vicinal dihalides
1. H2, Lindlar’s cat 2. Br2, CHCl2
turns ketones into secondary alcohols
NaBH4, EtOH
turns Aldehyde/Acid chlorides into primary alcohols
NaBH4
turns acid chlorides into aldehydes
Li(tBuo)3AlH
turns acid chlorides into ketones
-CuLi-
synthesis of lithium dialkyl cuprates (Gilman’s reagent)
Br2, hv
Li
CuI (0.5 eq.)
turn acetylide ion into internal alkynes
NaNH2, NH3 (1)
primary alkyl halide
turn acetylide ion into alcohol where OH group is attached to C atom directly bonded to triple bonded C atom
NaNH2, NH3 (1)
ketone/aldehyde
H3O+ (dilute) H2O
turn acetylide ion into alcohol where the OH group is two C atoms removed from the triple bonded C
NaNH2, NH3 (1)
epoxide
H3O+ (dilute), H2O
turn acetylide ion into a tertiary alcohol (unreliable/uncommon)
NaNH2, NH3 (1)
ester/acid chloride
H3O+ (dilute), H2O
turn aldehyde/ketone into alcohol where the OH is attached to the C atoms in the new C-C bond
-MgBr
H3O+ (dilute), H2O
turn epoxides into alcohols where the OH group is adjacent to the new C-C bond
—Li or —MgBr
H3O+ (dilute), H2O
turn ester/acid chloride into a tertiary alcohol through an addition/elimination mechanism
—MgBr (2 eq.) or —Li (2 eq.)
H3O+ (dilute), H2O
substitute LG of vinyl halides/alkyl halide with new C— bond
—Cu— (-), Li (+), THF
Gilman reagents (lithium dialkyl cuprates) are typically not reactive toward…
aldehydes and ketones
turn epoxides into alcohols where the OH group is 2 C atoms removed from the new C-C bond
—CuLi—
H3O+ (dilute), H2O
turn acid chlorides (but not esters) into ketones (which do not react further)
-CuLi-, Et2O
cleaves alkyne creating one OH group and one =O group
KMnO4, H3O+, heat. or 1. O3, 78 degrees C 2. H20
cleaves alkyne creating two =O groups
KMnO4, pH=7, 5 degrees C