MLS Clinical Chemistry Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 12:23 AM on 9/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
176 Terms
1
New cards
What is a standard deviation?
the measure of the variance around a mean
2
New cards
how is a standard deviation useful
to termine if a value should be considered normal or not
3
New cards
What percent of values are found within two standard devations of the mean
95%
4
New cards
Why is it important to know what percentage of values are found within two standard devations of the mean
to consider whether that value should be considered normal or not
5
New cards
what is the coefficient of variation
a measurement of the dispersal of points around a mean
6
New cards
what is the formula to calcuate the coeffcient of variation for a population
SD/x-bar * 100
7
New cards
How does resistivity relate to the grade of reagent-grade water
the higher the grade, the higher the resistivity
8
New cards
T/F: ultra pure water conducts a current
F
9
New cards
How resistant does water need to be to be considered reagent grade
>1 megaohm
10
New cards
What is analytical sensitivty
how little of a compound a test can measure
11
New cards
what is analytical specificity
the ability of a test to correctly identify a compound amongst other compounds
12
New cards
What does it mean when a test has a high sensitivity
it is able to detect a compound even when there is very little of it
13
New cards
what does it mean when a test has a low sensitivity
it is not able to detect a compound until there is a lot of it
14
New cards
what does it mean when a test has high specificity
it is able to pick out a specific compound amongst several other compounds of similar structure
15
New cards
what does it mean when a test has low specificity
it often cross-reacts with compound it was not meant to detect but have similar structure to the desired compound
16
New cards
What is diagnostic sensitivity
the ability to correctly identify individuals with a disease
17
New cards
what is diagnostic specificity
the ability to correctly identify individuals without a disease
18
New cards
what is the formula for diagnostic sensitivity
TP/(TP+FN)
19
New cards
what is the formula for diagnostic specificity
TN/(TN+FP)
20
New cards
What is the purpose of a ROC curve
the determine which test has the best values of sensitivity and specificity
21
New cards
Which axis of a ROC curve is used to find the false-positive rate (false alarm rate)
x-axis
22
New cards
What does the area under the ROC tell us?
how much diagnstic ability a test has; a larger area is better diagnostic ability
23
New cards
What does this SPEP chart indicate
Normal
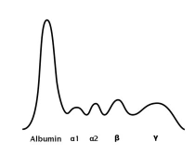
24
New cards
What does this SPEP chart indicate
increased alpha zones; acute inflammation
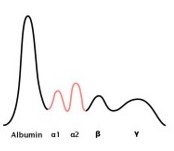
25
New cards
What does this SPEP chart indicate
decreased alpha 1; emphysema, lung and liver disease
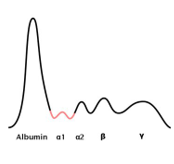
26
New cards
What does this SPEP chart indicate
increased albumin, bridge from gamma to beta; cirrhosis
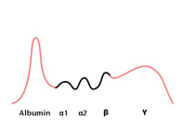
27
New cards
What does this SPEP chart indicate
Spike in gamma (M spike); multiple myeloma
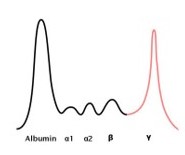
28
New cards
What does this UPEP chart indicate
increased albumin, alpha 2, beta, gamma; nephrosis

29
New cards
What type of SPEP would be seen in polyclonal gammopathy
larger gamma diffraction with no spike
30
New cards
Where in an SPEP would you find albumin
albumin band
31
New cards
Where in an SPEP would you find antitrypsin
alpha-1 band
32
New cards
where would you find haptoglobin in an SPEP
beta band
33
New cards
where would you find transferrin in an SPEP
beta band
34
New cards
where would you find LDL in an SPEP
beta band
35
New cards
where would you find C3 in an SPEP
beta band
36
New cards
where would you find IgA immunoglobulin in an SPEP
gamma band
37
New cards
Where would you find IgG immunoglobulin in an SPEP
gamma band
38
New cards
Where would you find IgD immunoglobulin in an SPEP
gamma band
39
New cards
Where would you find IgE immunoglobulin in an SPEP
gamma band
40
New cards
What substances are in the gamma band of an SPEP
immunoglobluin (IgA, IgG, IgE, IgD, IgM)
41
New cards
Where would you find IgM immunoglobulin in an SPEP
gamma band
42
New cards
What types of substances would you find in the beta region of an SPEP
LDL, C3, haptoglobin, transferrin
43
New cards
What substances are in the alpha bands of an SPEP
antitrypsin
44
New cards
What substances are in the albumin band of an SPEP
albumin
45
New cards
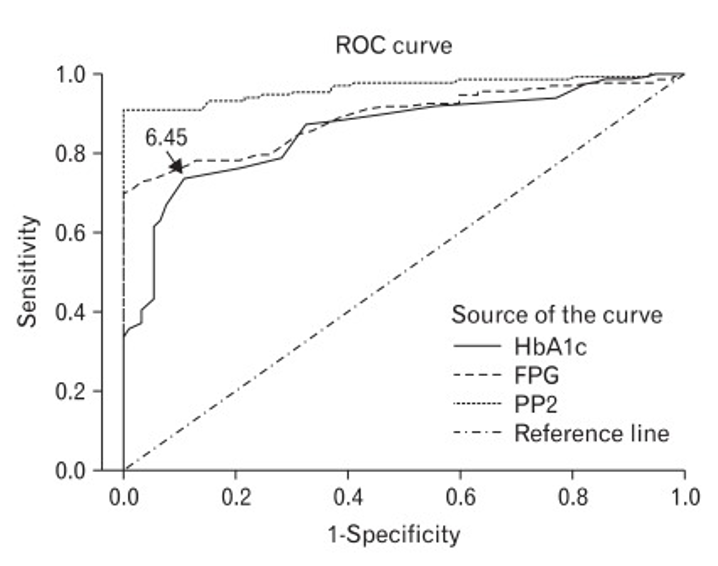
Identify the test with the best overall diagnostic efficiency
PP2
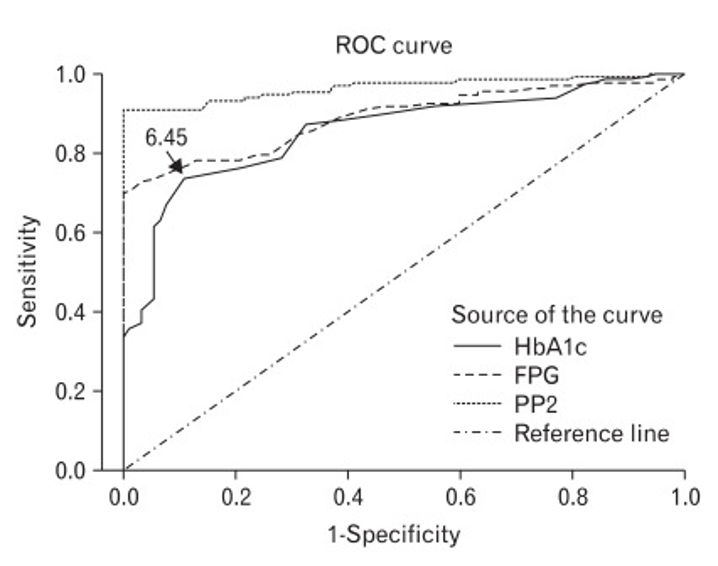
46
New cards
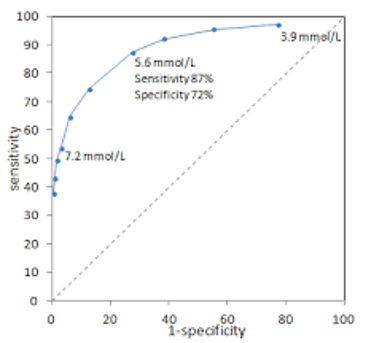
What is the sensitivity of the A1c test at the given point
~72%
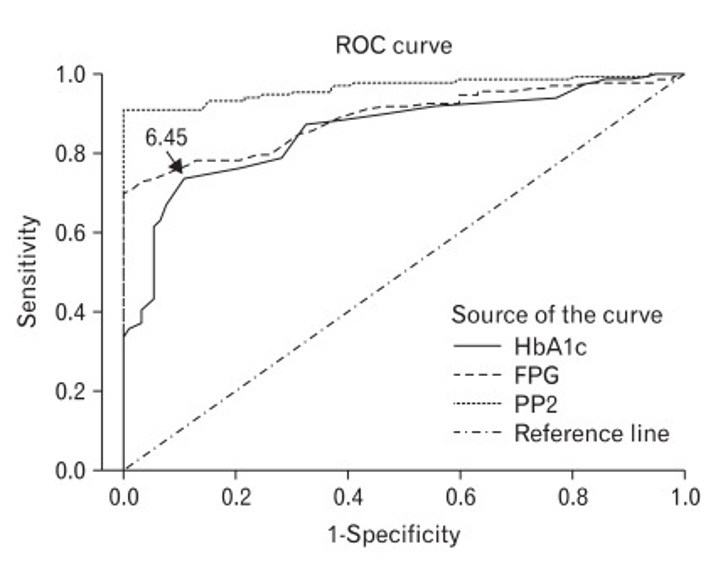
47
New cards
What is the specificity of the A1c tetst at the given point
~85%
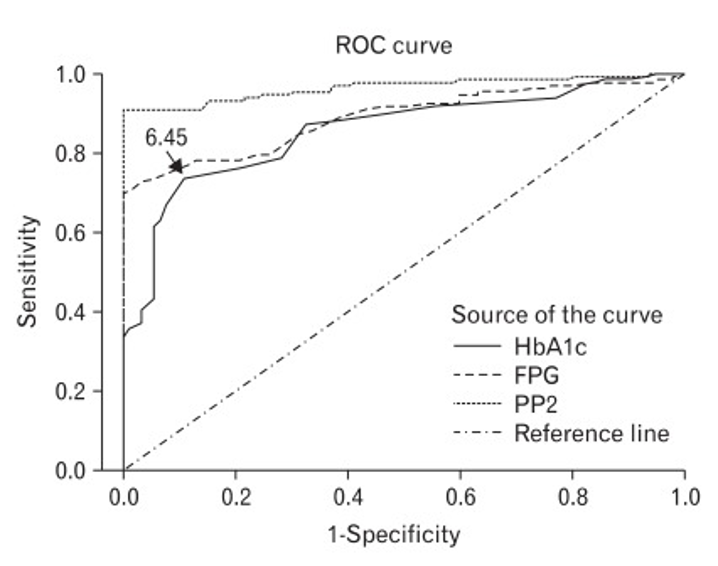
48
New cards
What is the false-positive rate of the A1c test at the given point
~15%
49
New cards
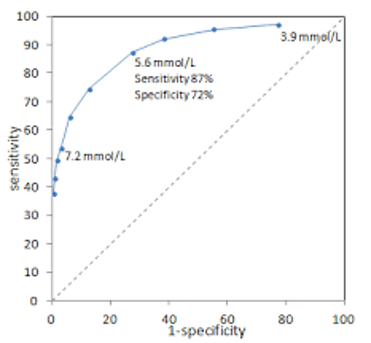
Which point has the best combination of digagnostic sensitivity and specificity
5.6 mmol/L
50
New cards
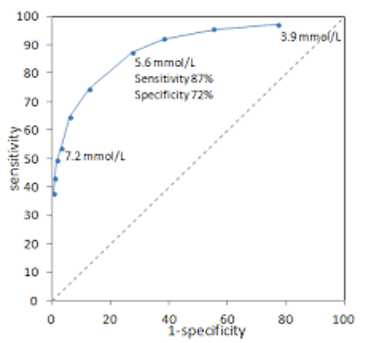
What is the diagnostic sensitivity of 7.2 mmol/L
~53%
51
New cards
What is the diagnostic specificity of 7.2 mmol/L
>95%
52
New cards
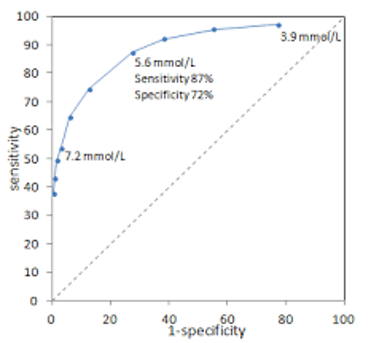
What is the false positive rate of 7.2 mmol/L
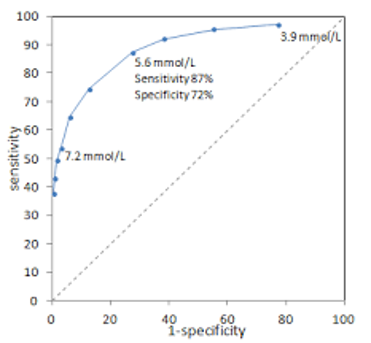
53
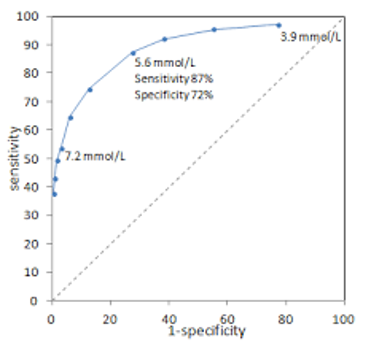
New cards
What is the diagnostic sensitivity of 3.9 mmol/L
~95%
54
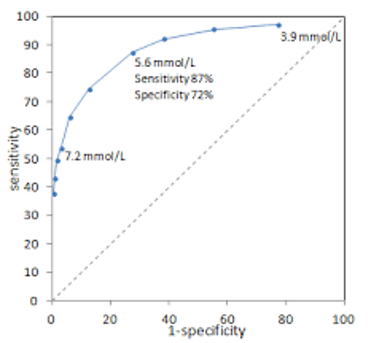
New cards
What is the diagnostic specificity of 3.9 mmol/L
~28%
55
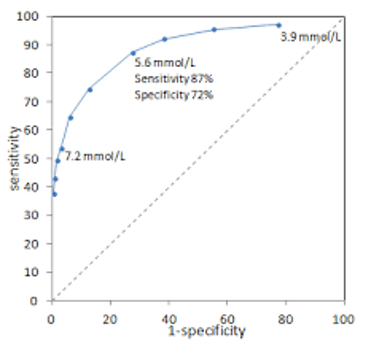
New cards
What is the false positive rate of 3.9 mmol/L
~72%
56
New cards
What is the false positive rate of 5.6 mmol/L
28%
57
New cards
What does a high positive predictive value indicate
the patient is very likely to have a particular diagnosis
58
New cards
what does a high negative predictive value indicate
the patient is very likely to not have a partiular diagnosis
59
New cards
give an example of a test with a high negative predictive value
D-dimer
60
New cards
give an example of a test with a high positive predictive value
M-spike in gamma region of SPEP
61
New cards
What is the formula for the Beer-Lambert Law
A = abc
62
New cards
What is "A" in the Beer-Lambert Law equation
absorbance
63
New cards
What is "a" in the Beer-Lambert Law
the molar extinction coefficient (constant)
64
New cards
What is "b" in the Beer-Lambert Law
the path length of th elight transmiting cuvette (constant)
65
New cards
What is "c" in the Beer-Lambert Law
concentration of the sample
66
New cards
What is the equation to find absorbance given transmittance
A = -log(T)
67
New cards
What is the dynamic range
range of which the test is reliable
68
New cards
what is the matrix effect
using a test on a medium the test wasn't developed for; results are unusual
69
New cards
What Westgaurd rules are being violated here
2,4s
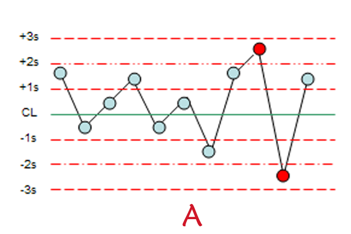
70
New cards
What Westgaurd rules are being violated here
1,3s
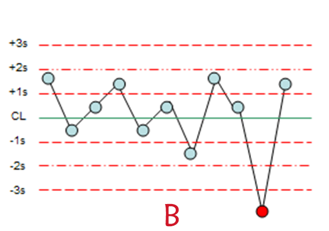
71
New cards
What pattern are these points following
trend
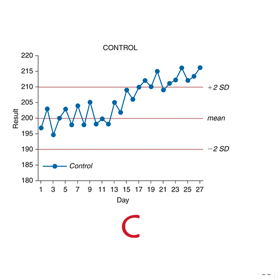
72
New cards
What Westgaurd rules are being violated here
pt 3: 1,2s; Pt. 7-10: 4,1s
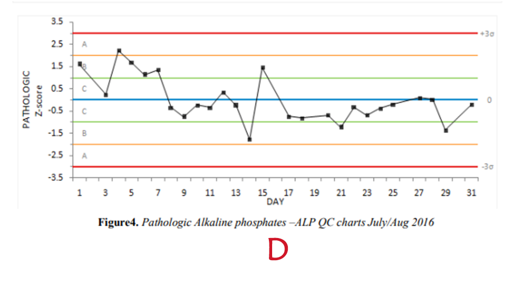
73
New cards
What pattern are points 3-7 following
shift
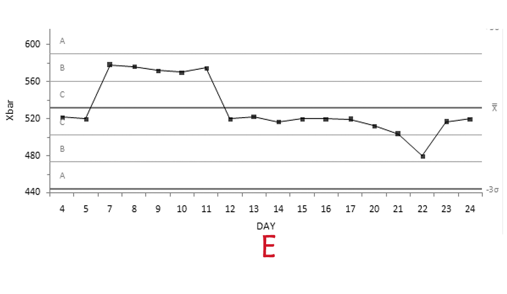
74
New cards
What Westgaurd rule is being violated here
10x
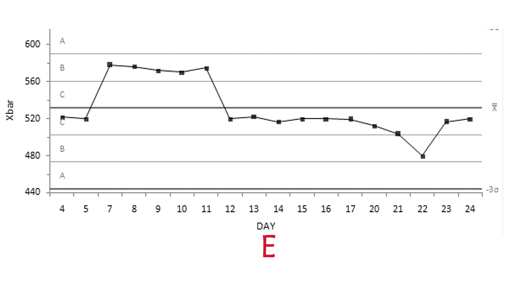
75
New cards
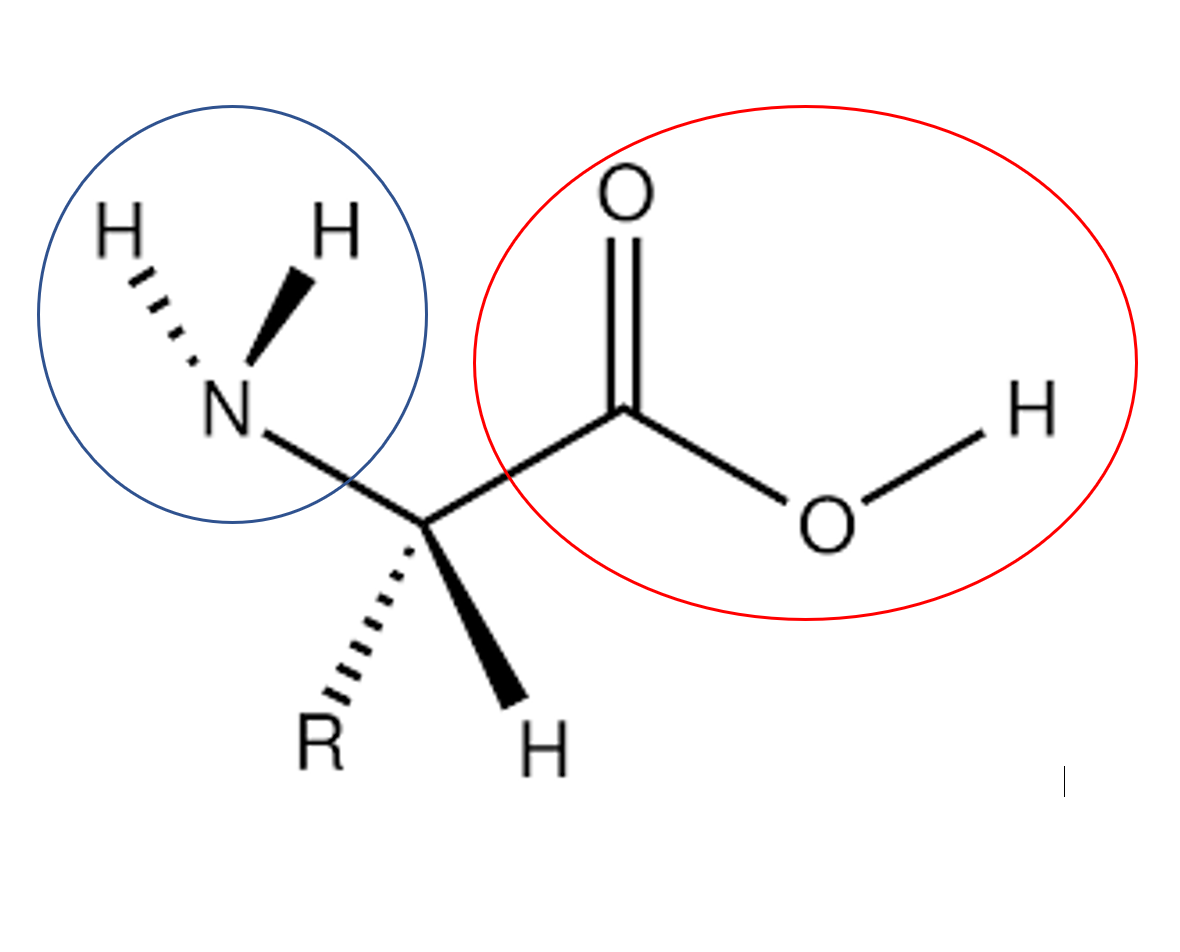
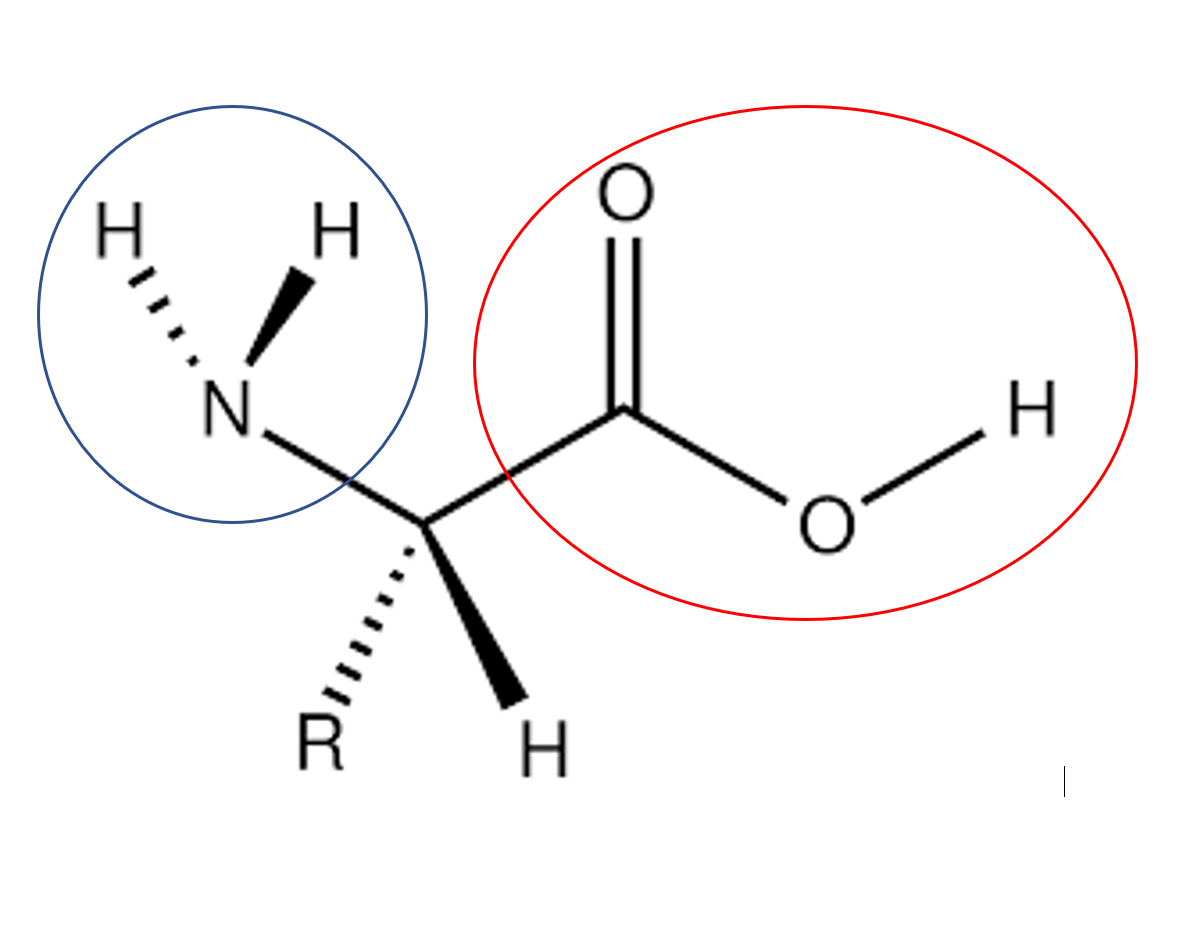
Which part of the amino acid is the carboxyl group
red circle
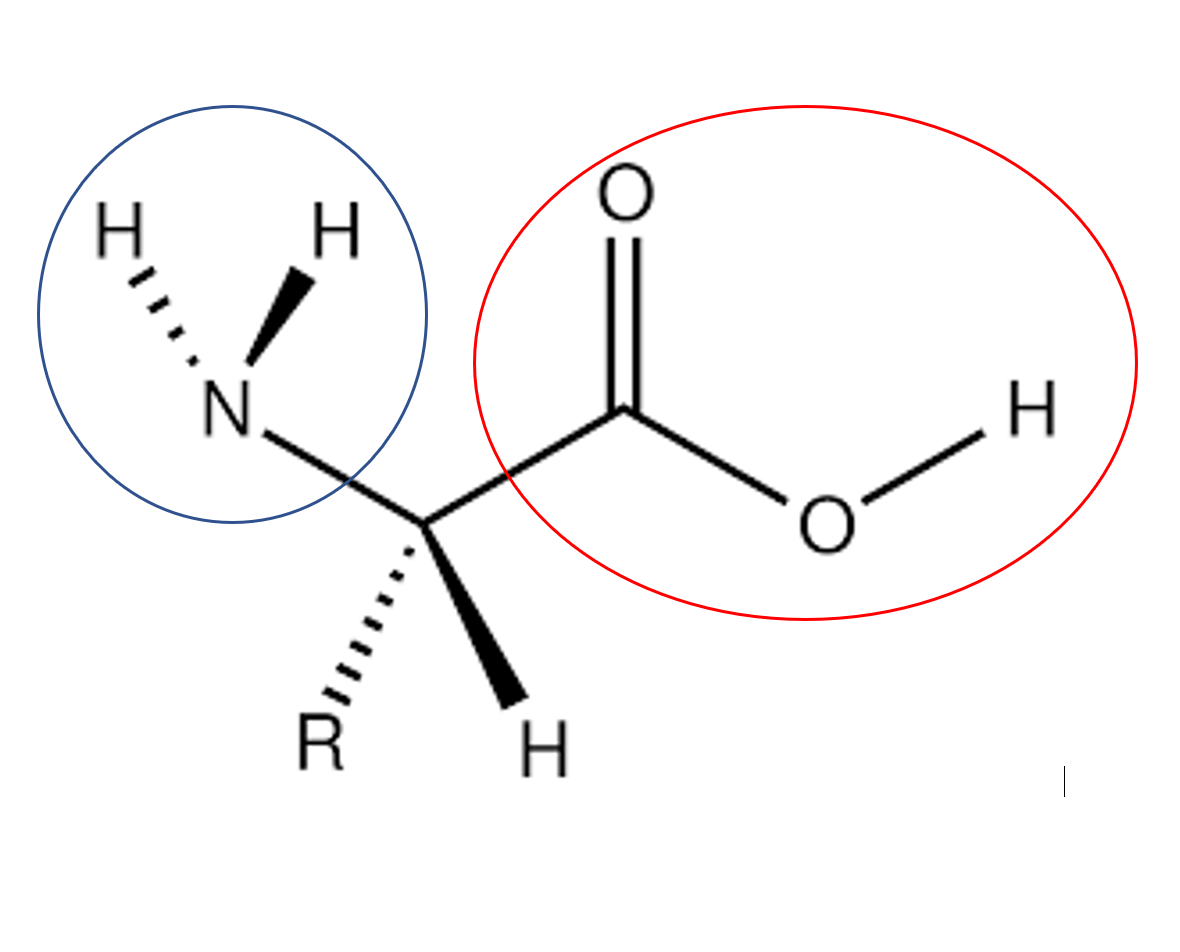
76
New cards
Which part of the amino acid is the amine group
blue circle
77
New cards
What is "R"
The variable side chain
78
New cards
which amino acids are basic
18, 19, 20
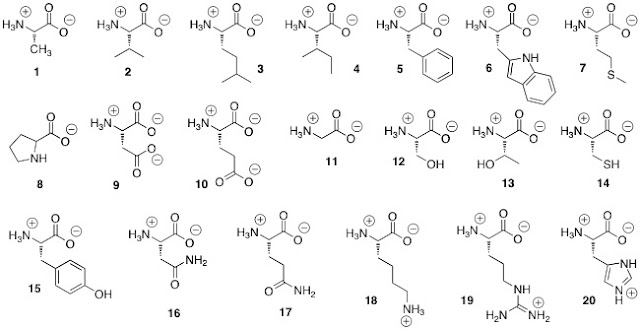
79
New cards
Which amino acids are acidic
9, 10
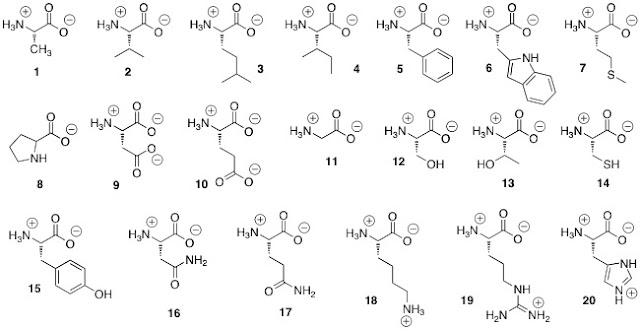
80
New cards
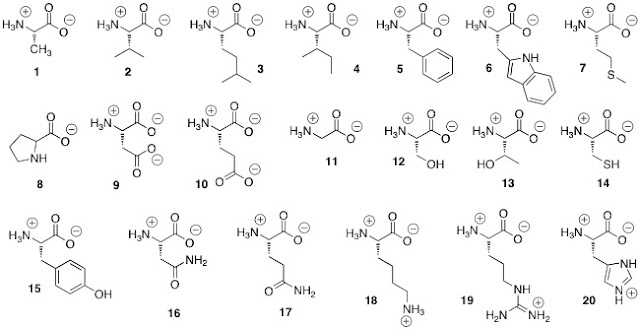
Which amino acids are nonpolar
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 11
81
New cards
Which amino acids are polar, uncharged
12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17
82
New cards
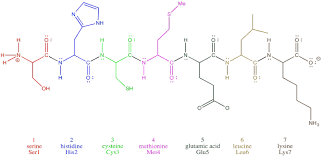
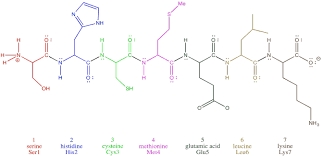
where is the amino terminal
far left, serine, 1
83
New cards
where is the carboxy terminal
far right, lysine, 7
84
New cards
Identify the peptide bonds
OC-NH bonds between amino acids
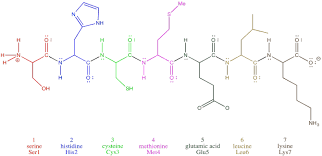
85
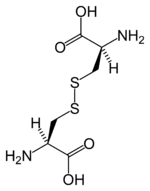
New cards
What kind of bond is this
disulfide
86
New cards
What are the clinical consequences in the lungs of an alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
there is nothing to protect the lungs from neutrophilic toxic granules
87
New cards
What are the clinical consequences in the liver of an alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
lack of antitrypsin causes misfolded proteins, liver is overwhelmed
88
New cards
In Maple Syrup Urine Disease, which amino acids specifically are increased
leucine, isoleucine, valine
89
New cards
In phenylketonuria, which metabolites are increased
toxic metabolites, exact metabolites dependent on where the block is located
90
New cards
in phenylketonuria, which amino acid is decreased
tyrosine
91
New cards
what are the clinical signs of phenylketonuria
secondary tyrosine deficiency, infants have abnormal pigmentation, mousy-smelling urine
92
New cards
Where is albumin synthesized
liver
93
New cards
where is antitrypsin synthesized
liver
94
New cards
where is haptoglobin synthesized
liver
95
New cards
where is transferrin synthesized
liver
96
New cards
where is LDL assembled
liver
97
New cards
where are immunoglobulin synthesized
Bone marrow, plasma cells, b-lymphocytes
98
New cards
How are most plasma proteins charged in a buffer of 7.4
negatively
99
New cards
which amino acids are involved in providing a charge to plasma proteins
acidic-side group amino acids
100
New cards
what are two physiologic functions of albumin
carries insoluble proteins/drugs, retains water through attraction of sodium