Independent assortment + Non-disjunction T3 W4
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
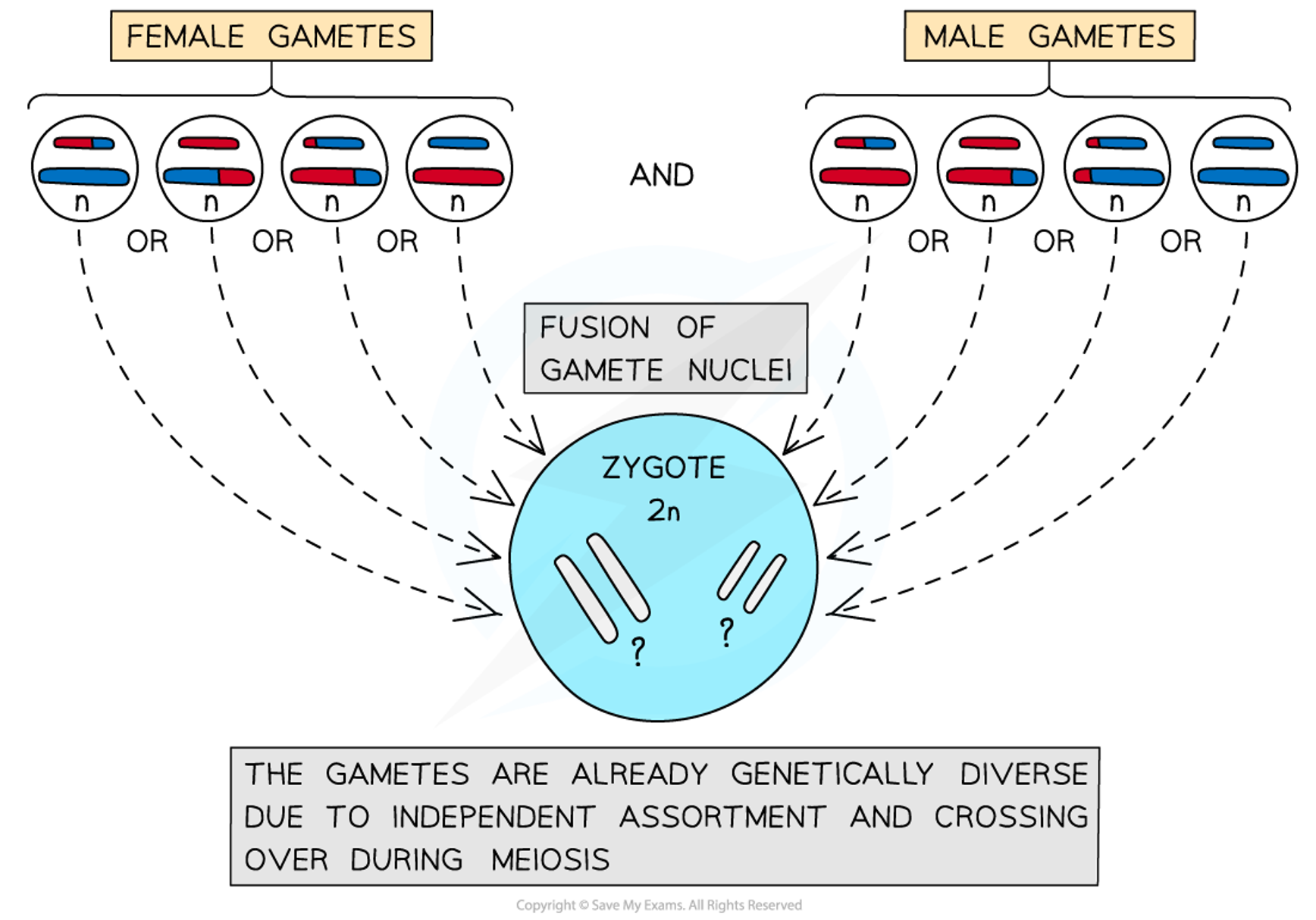
Independent assortment
A genetic principle that states that the alleles of two genes will seperate into daughter cells independent of one another
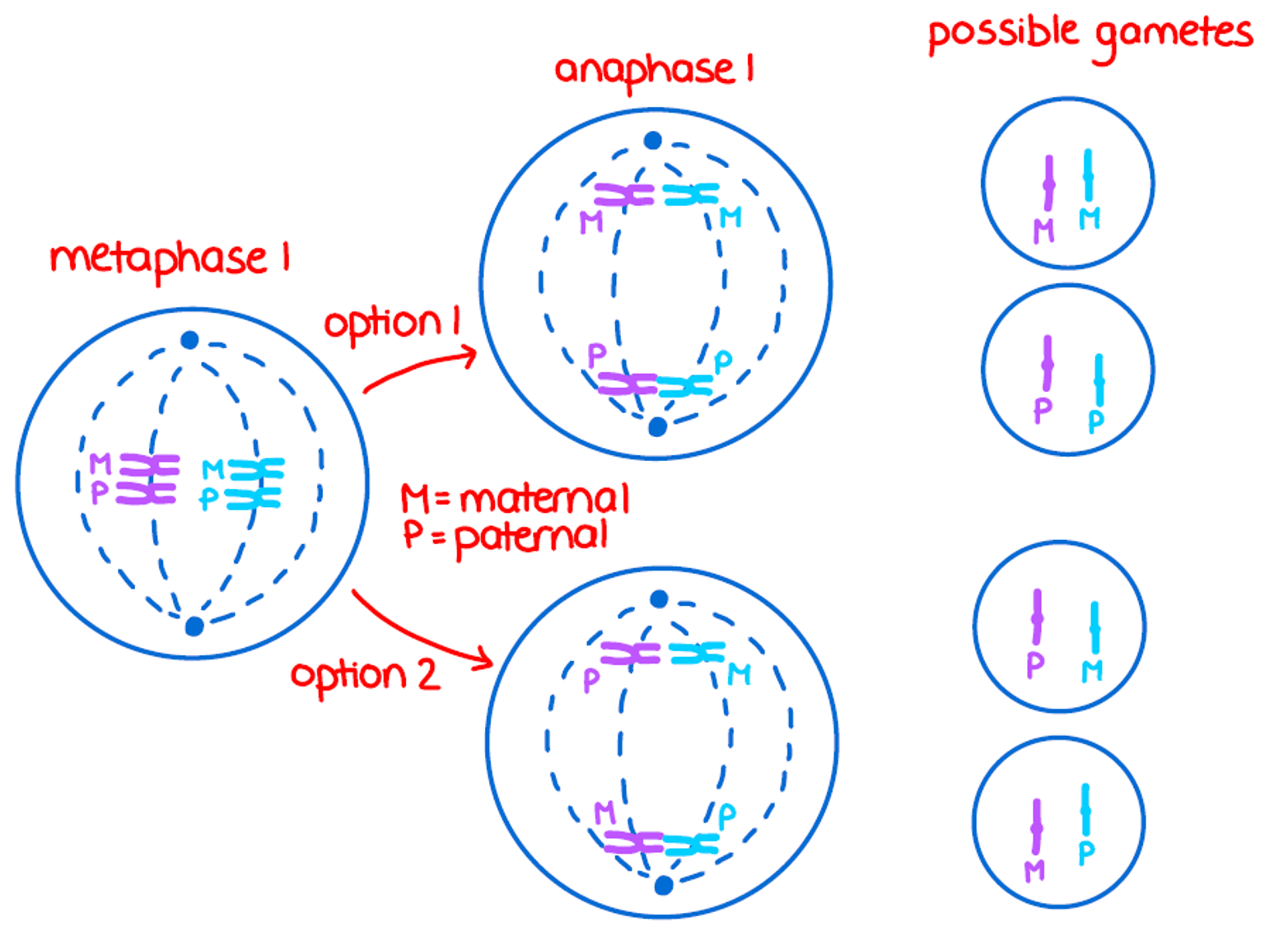
Independent assortment during anaphase 1
•During anaphase I in meiosis I, the homologous pairs of chromosomes (paternal and maternal) separate.
•One member of each pair moves to one pole of the cell, and the other moves in the opposite direction.

How do homologous pairs seperate in indepdent assortment
•All homologous pairs of chromosomes separate independently, i.e., the way one homologous pair separates is unaffected by the way any of the other pairs separate; and randomly, i.e., towards which pole the maternal and paternal chromosomes travel of each pair is by chance.
Non-disjuction
The failure of one or more pairs of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate normally during nuclear division, usually resulting in an abnormal distribution of chromosomes in the daughter nuclei.
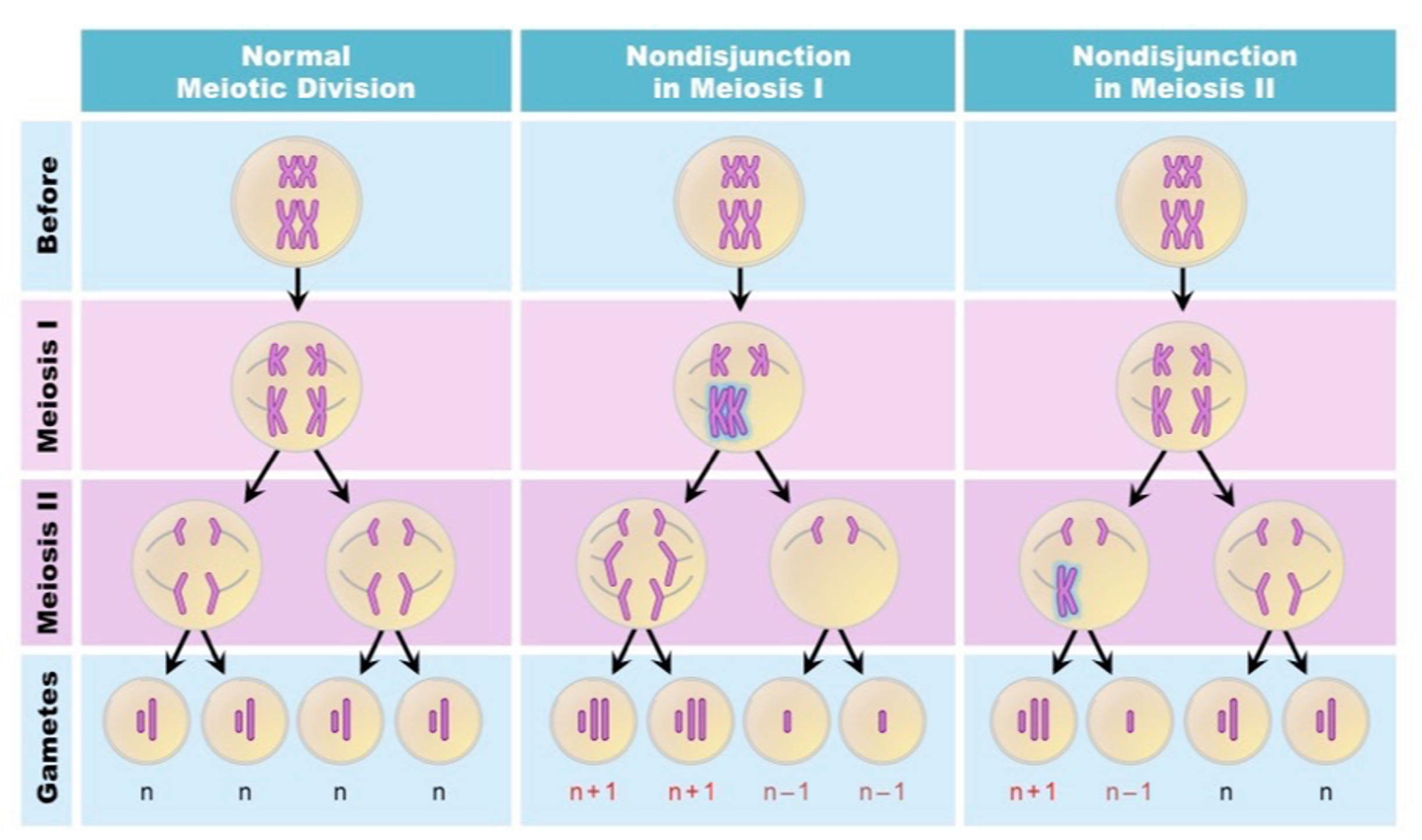
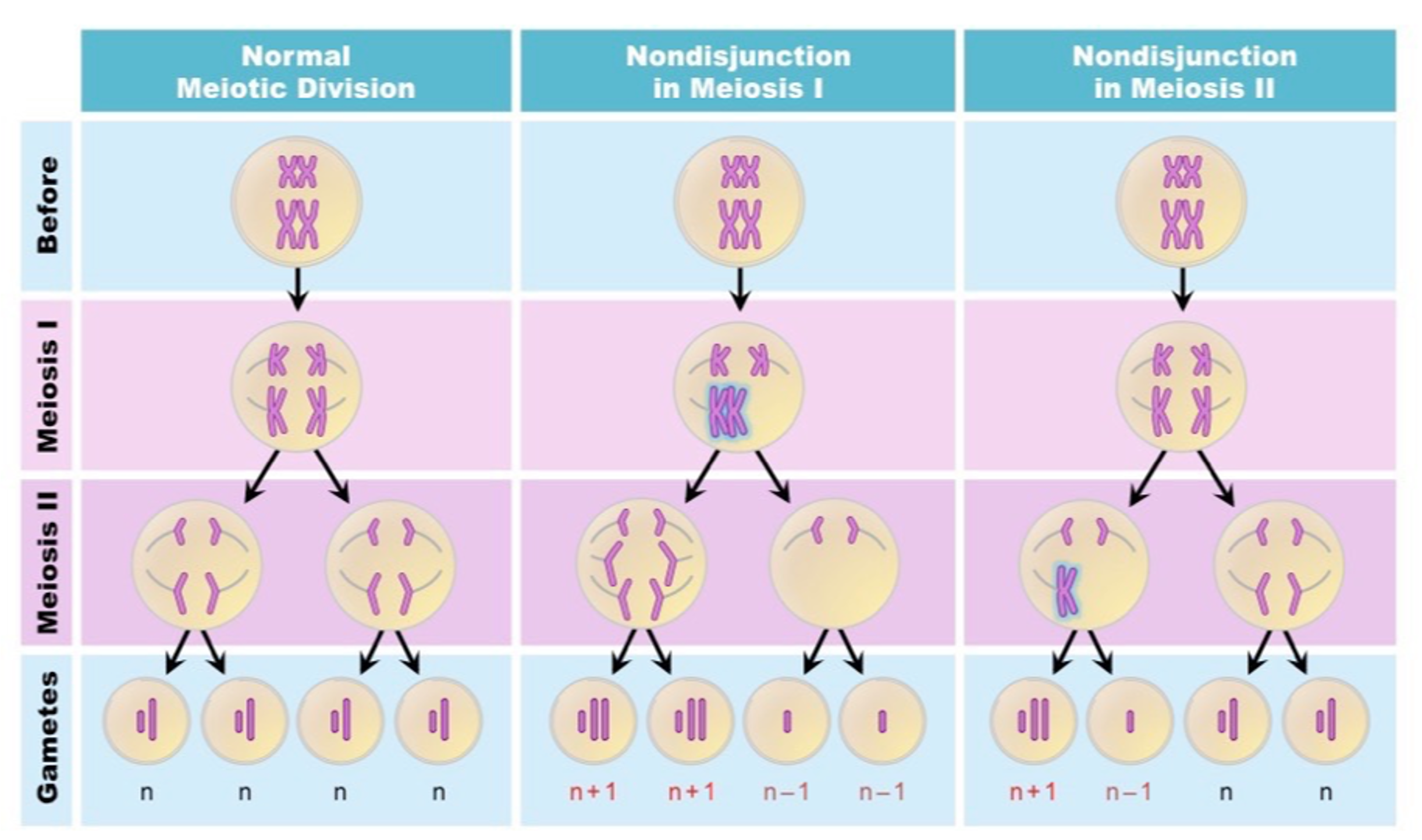
Non-disjunction in meiosis 1
⚬During metaphase I homologous chromosomes pair on the equator of the cell and are then separated during anaphase I.
⚬Sometimes one or more of the homologous pairs of chromosome pairs may fail to separate.
⚬This results in aneuploidy, where some of the daughter cells receiving an extra chromosome and some receiving one less chromosome.
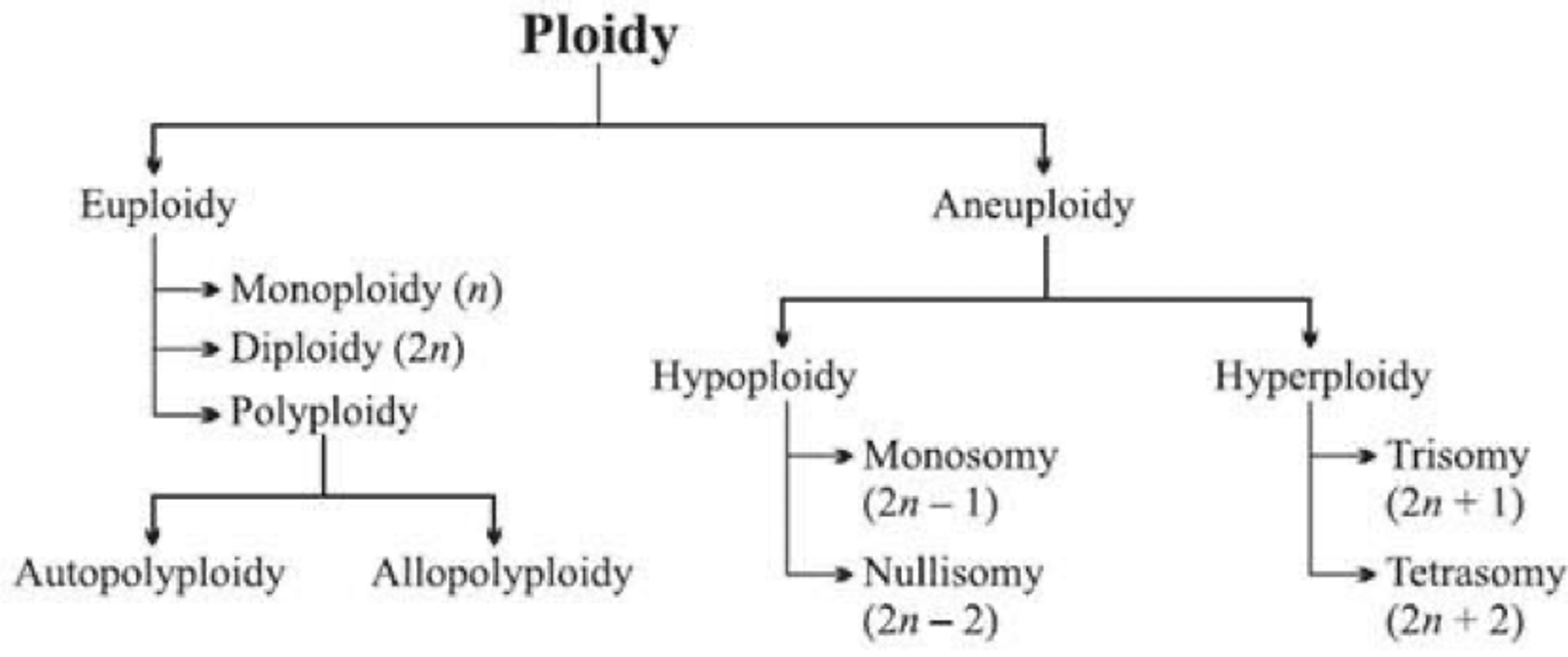
Aneuploidy
A condition of having an abnormal number of chromosomes in a haploid set.
Non-disjunction in meiosis 2
⚬During metaphase II chromosomes line up on the equator of the cell and are then separated during anaphase II with one of each chromatid pulled to an opposite pole.
⚬Sometimes one or more of the chromatids may fail to separate.
⚬This results in some of the daughter cells receiving the correct number of chromosomes, and aneuploidy as some daughter cells receive an extra chromosome and some receive one less chromosome.