bio sex linked traits packet quiz
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/25
Last updated 10:45 PM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
sex chromosomes
the pair of chromosomes that determine the sex of an individual
- the 23rd pair in humans are the sex chromosomes
- the 23rd pair in humans are the sex chromosomes
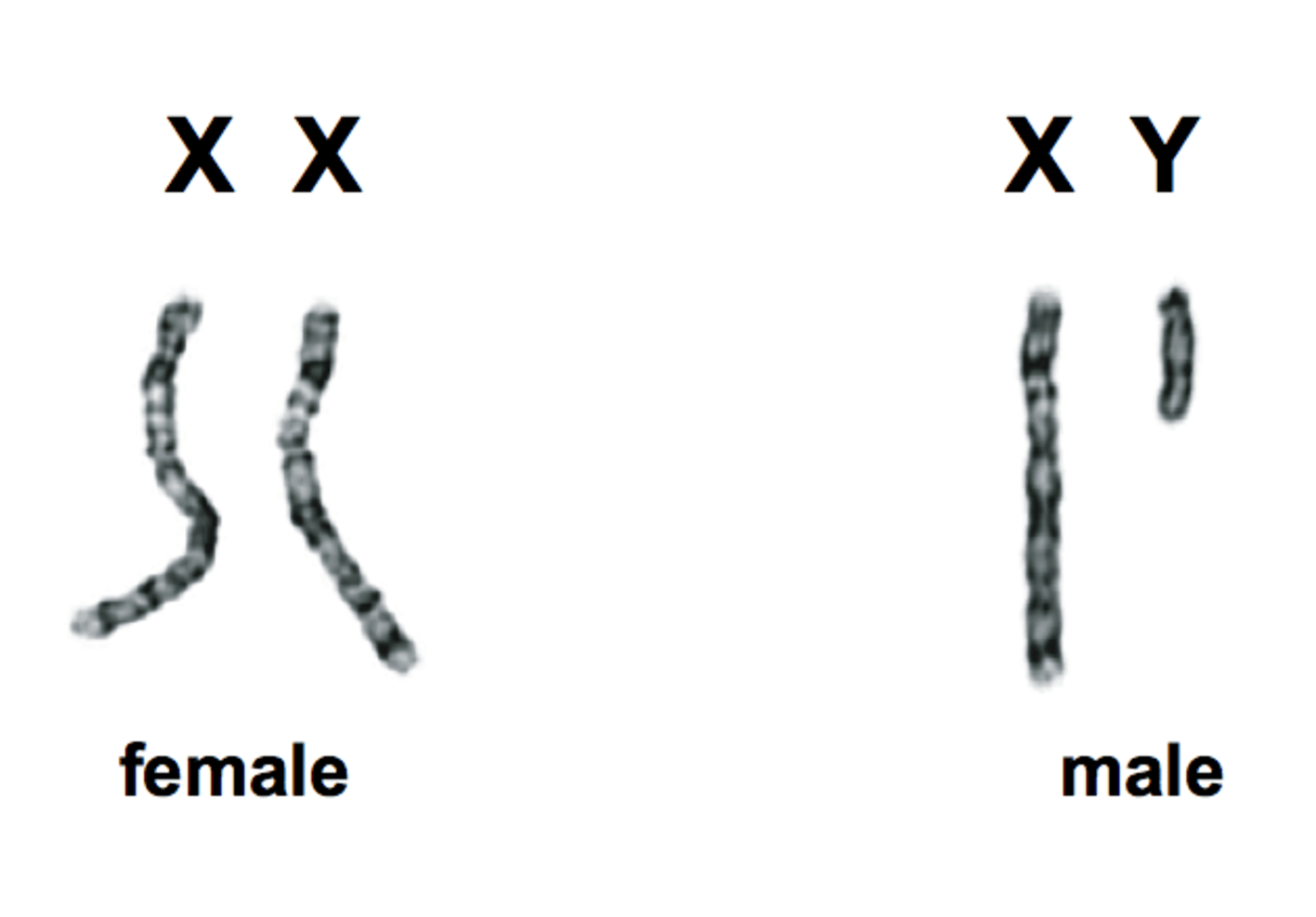
2
New cards
female
xx
3
New cards
male
xy
4
New cards
autosomes
all other chromosomes other than sex cells
- 1st through 22nd pair in humans
- 1st through 22nd pair in humans
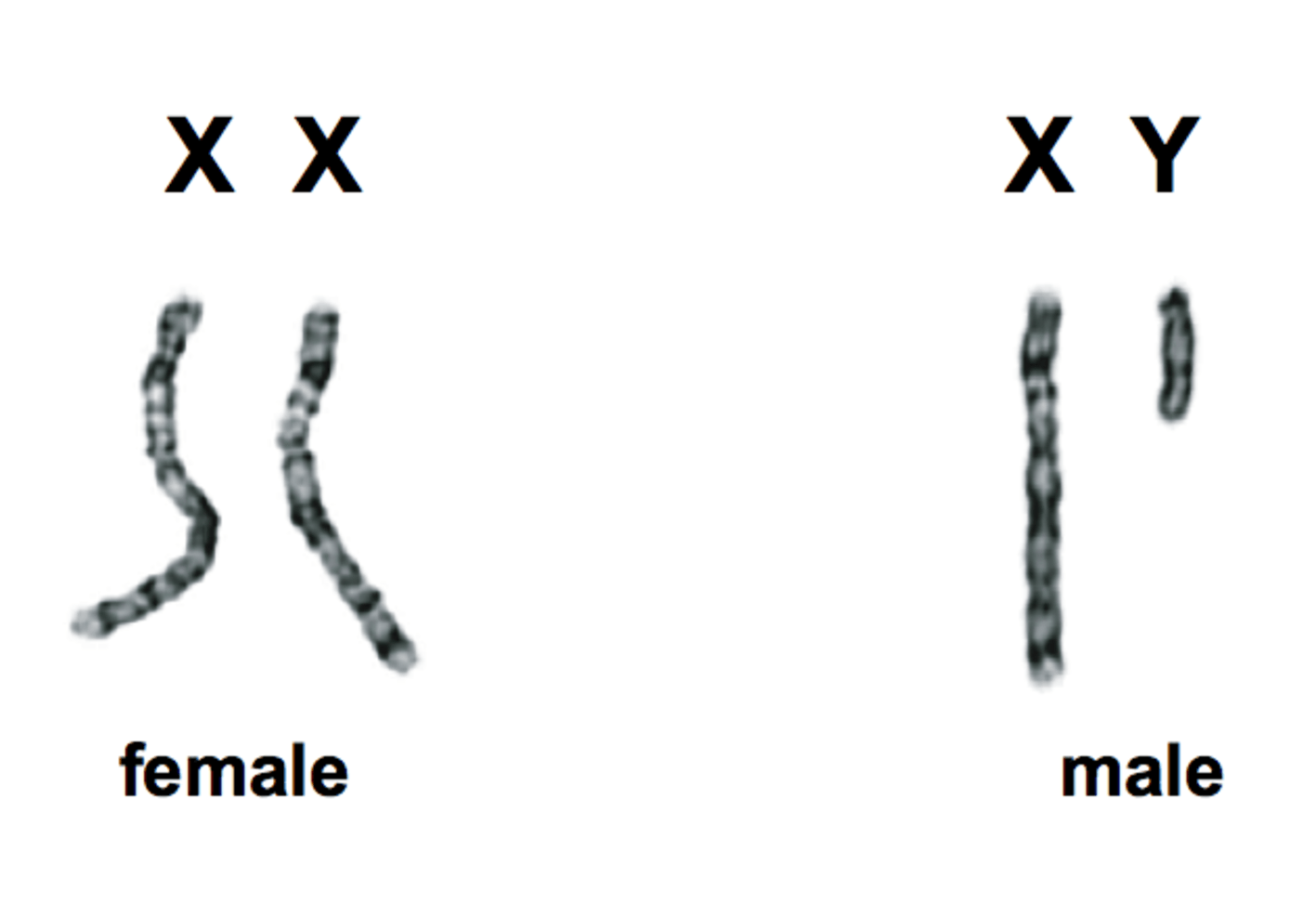
5
New cards
sex-linked
also called x-linked/x-traits; traits that are determined by genes on the x chromosomes
- ex of sex-linked diseases: hemophilia, colorblindness, duchenne muscle dystrophy
- ex of sex-linked diseases: hemophilia, colorblindness, duchenne muscle dystrophy
6
New cards
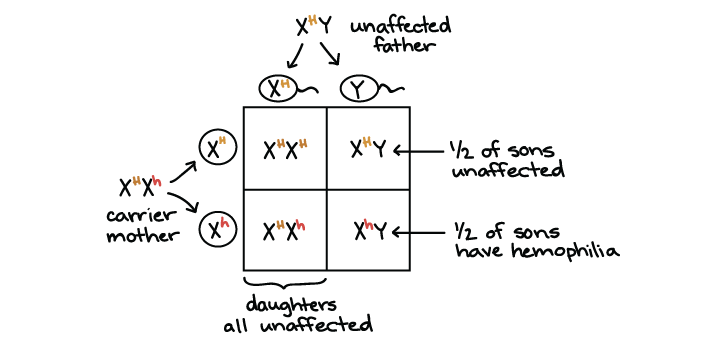
hemophilia
not able to plot blood correctly
-ex:
H= normal h=hemophilia
-- female
X^H X^H - normal
X^H X^h - normal but carrier
X^h X^h - hemophiliac
-- male (can't be carriers)
X^H y - normal
X^h y - hemophiliac
-ex:
H= normal h=hemophilia
-- female
X^H X^H - normal
X^H X^h - normal but carrier
X^h X^h - hemophiliac
-- male (can't be carriers)
X^H y - normal
X^h y - hemophiliac
7
New cards
colorblindness
inability to distinguish between certain colors
- red/green colorblindness and blue/yellow colorblindness
-- H normal h cb.
- bc males only have one x chromosome, any recessive allele on the x chromosome will be expressed
-- thus males, are MORE LIKELY to express sex-linked recessive traits
- red/green colorblindness and blue/yellow colorblindness
-- H normal h cb.
- bc males only have one x chromosome, any recessive allele on the x chromosome will be expressed
-- thus males, are MORE LIKELY to express sex-linked recessive traits
8
New cards
duchenne muscular dystrophy
- gradual weakening and wasting away of muscle tissue
-- muscle types: skeletal, smooth and cardiac
- usual onset before age 6, chair-ridden by 12, dead by 20
-- muscle types: skeletal, smooth and cardiac
- usual onset before age 6, chair-ridden by 12, dead by 20
9
New cards
incomplete dominance
a blending of traits in which neither allele is completely dominant over the other
- ex: snapdragons, hypercholesterolemia (elevated cholesterol)
H - normal H^1 - HC.
- ex: snapdragons, hypercholesterolemia (elevated cholesterol)
H - normal H^1 - HC.
10
New cards
multiple allele trait
aka codominance; the existence of more than 2 alleles for a given trait
- ex: blood type in humans
- ex: blood type in humans
11
New cards
blood type in humans
3 different alleles: I^A, I^B, i
-- corresponds to the presence of antigens on the surface of red blood cells
- AB, A, B, and O
-- the I^A allele and I^B allele are said to be CODOMINANT to the i allele
-- corresponds to the presence of antigens on the surface of red blood cells
- AB, A, B, and O
-- the I^A allele and I^B allele are said to be CODOMINANT to the i allele
12
New cards
AB
phenotype: AB
genotypes: I^A I^B
antigens (surface): A and B
antibodies (in blood): none
special: universal recipient
genotypes: I^A I^B
antigens (surface): A and B
antibodies (in blood): none
special: universal recipient
13
New cards
antigen
protein marker on RBC; on surface
14
New cards
antibodies
in blood
15
New cards
A
phenotype: A
genotypes: I^A I^A or I^A i
antigens: A
antibodies: B
special: none
genotypes: I^A I^A or I^A i
antigens: A
antibodies: B
special: none
16
New cards
B
phenotype: B
genotypes: I^B I^B or I^B i
antigens: B
antibodies: A
special: none
genotypes: I^B I^B or I^B i
antigens: B
antibodies: A
special: none
17
New cards
O
phenotype: O
genotype: ii
antigens: none
antibodies: both A and B
special: universal donor
genotype: ii
antigens: none
antibodies: both A and B
special: universal donor
18
New cards
+
presence of RH factor
19
New cards
-
absence of RH factor
20
New cards
RH factor
protein/antigen
O+ = 70%
A- = 0.8%
O+ = 70%
A- = 0.8%
21
New cards
pleiotropy
the impact of a single gene on more than one characteristic
ex: sickle cell anemia
ex: sickle cell anemia
22
New cards
sickle cell anemia
tow abnormal copies of hemoglobin gene result in a variety of different symptoms including: weakness, organ damage, kidney failure, pain, and others
23
New cards
polygenic inheritance
the additive effects of two or more genes on a single characteristic
- skin color, height, eye color in humans
- skin color and eye color based on amount of melanin
- skin color, height, eye color in humans
- skin color and eye color based on amount of melanin
24
New cards
environmental affects on gene expression and phenotype
himalayan rabbits and siamese (black ears, tail, paws, and nose; keeping warmth) cats carry an enzyme for melanin production that is heat-sensitive
- enzyme is less active at the surface of warm body parts
- fur color is darker in cooler parts such as ears, limbs, and tail
- enzyme is less active at the surface of warm body parts
- fur color is darker in cooler parts such as ears, limbs, and tail

25
New cards
female
picture
26
New cards
male
picture