psychology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:39 PM on 2/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
1
New cards
psychology
the study of mind and behavior
2
New cards
behavior
actions that can be directly measured/observed
3
New cards
mind/mental process
thoughts, feelings, motives that cannot be observed
4
New cards
Wilhem Wundt
1st psych lab in germany, studied introspection: peoples awareness of immediate experience
5
New cards
E.B. Titchener
student of Wundt, founded structuralism: broke down the mind into structures of mental process, what of the mind
6
New cards
William James
1st U.S. psychologist, founded functionalism: interaction between the mind and the environment, why of the mind
7
New cards
Studied psychology using the multicultural approach
francis cecil sumner, george sanchez, and the clarks
8
New cards
Mary Calkins
1st female psychologist, harvard denied degree
9
New cards
Margaret F. Washburn
1st woman to earn a Ph.D in psychology
10
New cards
psychology approaches (7)
psychoanalytic, biological, behavioral, humanistic, cognitive, evolutionary, multicultural/cross cultural
11
New cards
psychoanalytic approach
focuses on the unconscious mind (wishes/desires/motivations that we didn’t know were there), conflict between instincts and societies demands, early childhood experiences; sigmund freud founded psychoanalysis, early interactions with parents and unfulfilled wishes lead to our personality
12
New cards
biological approach
focuses on the nervous system and the structures of the mind, thoughts and behavior have a physical basis in our body, stimulus to response
13
New cards
behavioral approach
focuses on observable/measurable behavior, stimulus=environment, response=behavior, reinforced with rewards or punishments
14
New cards
humanistic approach
feel good approach, focuses on the positive qualities of people and believe humans are born good
15
New cards
cognitive approach
focuses on information processing/how people process information (memory, learning, reading, social cues)
16
New cards
evolutionary approach
focuses on ideas such as “survival of the fittest”, adaptation, and genetics; behaviors that increase reproductive success
17
New cards
multicultural/cross-cultural approach
focuses on differences between cultures and how cultural and social influences affect our behavior
18
New cards
eclectic approach
selects and uses components in each approach
19
New cards
social cognitive theory
albert bandura; stimulus, organism, response
20
New cards
positive approaches to psychology
valuable experiences, positive individual traits, positive values
21
New cards
spears 2007 article
decrease in behaviorism, increase in cognitive neuroscience, no approach is dominant
22
New cards
two major organizations
American Psychological Association 1892 (APA), American Association for Psychological Science 1988 (AAPS)
23
New cards
hindsight bias
i knew it all along
24
New cards
false consensus effect
overestimating
25
New cards
overconfidence
think we know more than we do
26
New cards
theory
a set of well dell developed ideas that explain and predict observations
27
New cards
hypothesis
testable prediction made by a theory
28
New cards
5 steps of the scientific methods
1. observe phenomenon, 2. generate data, 3. collect data, 4. analyze data, 5. summarize data and evaluate the theory
29
New cards
variable
anything that can change
30
New cards
operational variable
(list, very specific, measurable) description of variable
31
New cards
types of descriptive research
observational, surveys, case study, archival
32
New cards
observational
observing/recording behavior
33
New cards
surveys
list of questions
34
New cards
case study
in depth look at one person; phineas gage
35
New cards
archival
using existing records to answer questions
36
New cards
experimental research
independent variable, dependent variable, experimental group, control group, random assignment
37
New cards
independent variable
the cause, manipulated and influenced factor
38
New cards
dependent variable
factor that is measured, can changed based on the IV
39
New cards
experimental group
group who receives the IV
40
New cards
control group
group that does not receive the IV
41
New cards
random assignment
assigning groups by chance
42
New cards
experimenter bias
researchers expectations influence the outcome of a study
43
New cards
participant bias
participants behavior changes because they know they are in a study
44
New cards
double blind experiment
no one knows what group the participants are in
45
New cards
ethnic gloss
researcher assumes all people in the group are the same
46
New cards
Central Nervous System
brain and spinal cord, 99% of nerve cells, reflexes- automatic response to stimuli
47
New cards
peripheral nervous system
network of sensory nerves, connects CNS to body, afferent nerves: sensory, carry Info to the brain, efferent nerves: motor, carry info away from the brain
48
New cards
somatic nervous system
controls skeletal muscles, voluntary activities
49
New cards
autonomic nervous system
organs and glands, controls autonomic functions, dual system: sympathetic (arouses the body), parasympathetic (calms the body)
50
New cards
neurons
building block of the nervous system
51
New cards
types of neurons
sensory (carry info may from the CNS), motor (carry Info away from the CNS, interneurons (do both)
52
New cards
glial cells
function like glue, keep neurons running smoothly, provide nutrients, clean up, supportive role to neurons
53
New cards
parts of neurons
soma, dendrite, axon, terminal buttons, synaptic vesicles, myelin sheath
54
New cards
soma
cell body
55
New cards
dendrite
receives info from other neurons (multiple)
56
New cards
axon
carries info away from neuron (only one)
57
New cards
terminal buttons
end of a axon, house synaptic vesicles (multiple)
58
New cards
synaptic vesicles
hold neurotransmitters
59
New cards
myelin sheath
layer of fatty tissue that insulates axons and speeds up impulses / nodes of ranvier
60
New cards
multiple sclerosis
disease where the myelin sheath degenerates, slows down communications to the muscles and eventually leads to loss of muscle control
61
New cards
ions
electrically charges particles, can be positive or negative
62
New cards
ion channel
membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through channel
63
New cards
resting potential
neuron resting, negative inside/ positive outside
64
New cards
threshold
neurons need a strong enough impulse to overcome it
65
New cards
depolarization
neuron becomes more positive, sodium/potassium
66
New cards
actions potential
signal that travels down a neuron when threshold is exceeded, strength does not affect speed
67
New cards
synapse steps
1. electrical impulse converted to chemical energy 2. neurotransmitters released 3. neurotransmitters cross synapse 4. neurotransmitters bind to and stimulate the next neuron
68
New cards
reuptake
reabsorption by a neuron of a neurotransmitter following the transmission of a nerve impulse across the synapse
69
New cards
synapse
junctions between two neurons
70
New cards
synaptic cleft
tiny gap in synapse junction
71
New cards
all or none principle
Neuron either FIRES or it DOESN’T
72
New cards
types of neurotransmitters
**Acetylcholine, Beta-Endorphin, Dopamine, GABA, Glutamate, Norepinephrine, Serotonin**
73
New cards
acetylcholine
muscle action, learning, memory
74
New cards
beta-endorphin
pain, pleasure
75
New cards
dopamine
movement, mood, sleep, learning
76
New cards
GABA
brain function, sleep, low level = anxiety
77
New cards
glutamate
learning and memory
78
New cards
norepinephrine
heart, intestines, alertness; too little = depression, too much = manic state
79
New cards
seretonin
sleep, mood, arousal; depression
80
New cards
cerebral cortex
control center, surface of the brain, divided into two hemispheres
81
New cards
lateralization
specialization of function (right)
82
New cards
longitudinal fissure
left of the brain
83
New cards
corpus callous
connects the two hemispheres
84
New cards
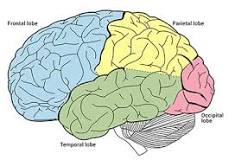
four lobes
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
85
New cards
frontal lobe (prefrontal cortex, motor complex, broca’s area)
reasoning, motor control, emotion, language
86
New cards
parietal (somatosensory cortex)
senses, attention span
87
New cards
occipital (visual cortex)
vision
88
New cards
temporal (auditory cortex, wernicke’s area)
hearing, memory, language processing
89
New cards
forebrain
thamalus, limbic system: amygdala, hippocampus, hypothamulus
90
New cards
thamalus
directs messages to sensory receiving areas in the cortez
91
New cards
amygdala
2 almonds, emotional awareness
92
New cards
hippocampus
stores memory, learning
93
New cards
hypothalamus
hunger, thirst, temp, sexual behavior/ helps endocrine system
94
New cards
midbrain
Reticular formation, substantia nigra, vetral tegmental areas
95
New cards
reticular formation
alertness, arousal, attention, some reflexes
96
New cards
**Substansia Nigra & Ventral tegmental areas**
produce dopamine, involved in movement, mood, rewards, and addiction
97
New cards
hindbrain
medulla, cerebellum, pons, brain stem
98
New cards
medulla
Begins where the spinal cord enters the skull. Helps with breathing and posture
99
New cards
cerebellum
coordinates voluntary movement & muscles
100
New cards
pons
Involved in sleep and arousal