Topic 4- Waves
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
waves transfer___ but not___
energy but not matter
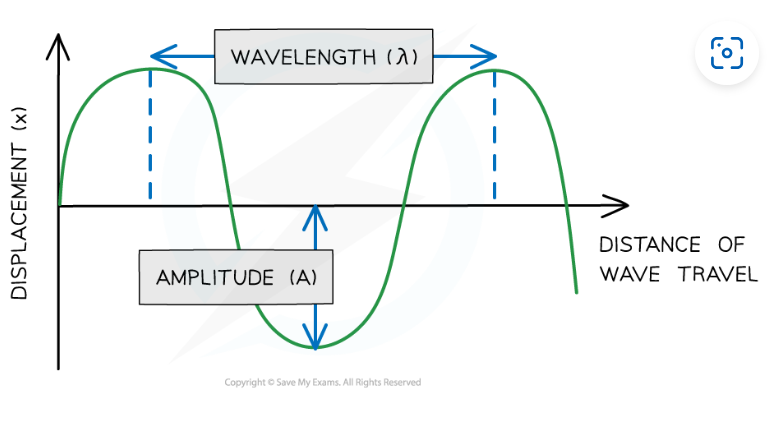
wavelength (lamda)
distance between the same points on 2 consecutive waves
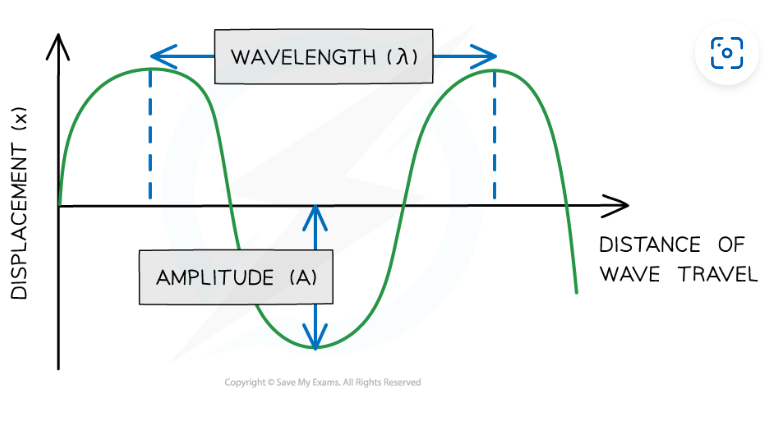
Amplitude (A)
distance from equilibrium line to maximum displacement
Frequency
number of waves that pass a single point per second
Time Period (T)
time taken for a whole wave to completely pass a single point
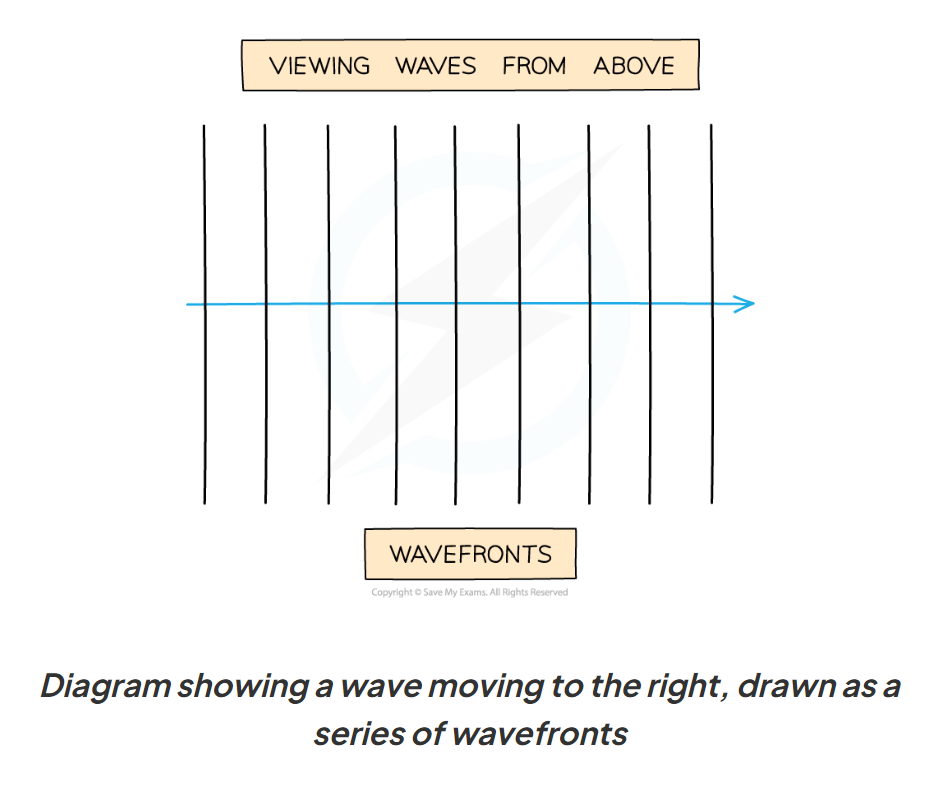
wavefront
a way of picturing waves from above with lines
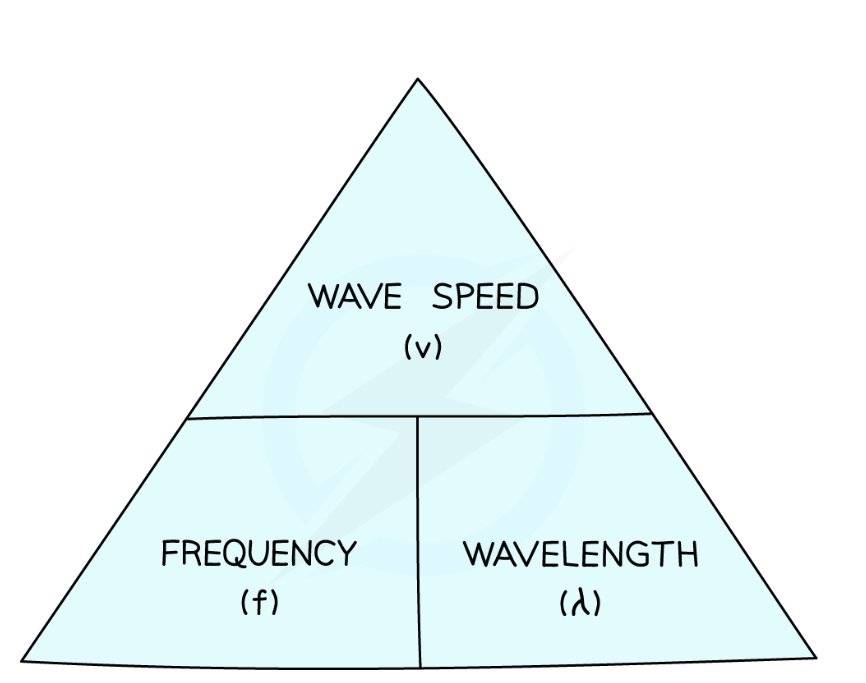
Wave equation
v = f x lamda (velocity(m/s) = frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m))
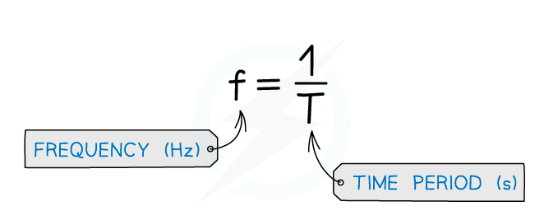
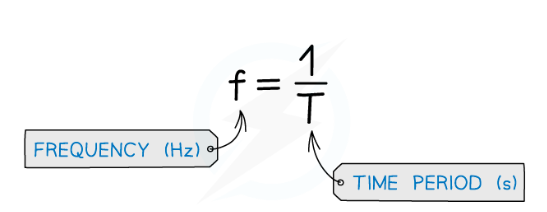
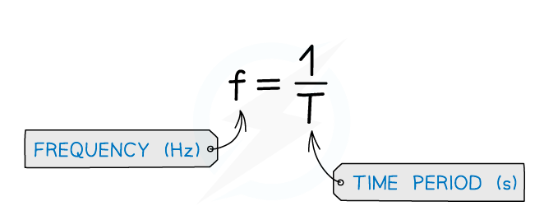
frequency and period relationship
f = 1/T
transverse wave
vibration is perpendicular to direction of wave motion
longitudinal waves
vibration parallel to direction of wave motion
longitudinal waves can’t move in a…
vacuum
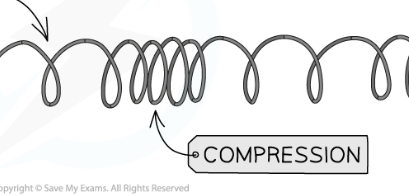
close together bits of a longitudinal waves
compressions
spaced apart bits of longitudinal waves
rarefactions
wavelength of a longitudinal wave
distance between the centre of 1 compression and the next
top and bottom points of a transverse wave
peaks and troughs
symbol for wavelength
lambda
3 ways of measuring speed of sound waves
2 people stand >100m apart and time how long after seeing they hear something (least accurate)
use an echo and stand >50m away from a wall, time how long after seeing they hear something
use an oscilloscope that uses 2 microphones (most accurate)
calculate the distance (x) of something using wave speed and time
x = v x t
calculate depth of water using wave speed and time
depth = ½ x speed in water x time to receive echo
reflection
a wave hits a boundary between 2 media but doesn’t pass through and is reflected back
flat, smooth surfaces are ___ reflectors
good
rough surfaces are ___ reflectors because they ___ light
bad, scatter
which surfaces always reflect some light (some is absorbed)?
opaque
Refraction
a wave changes speed at the boundary between 2 media of different densities, sometimes causes wave to change direction
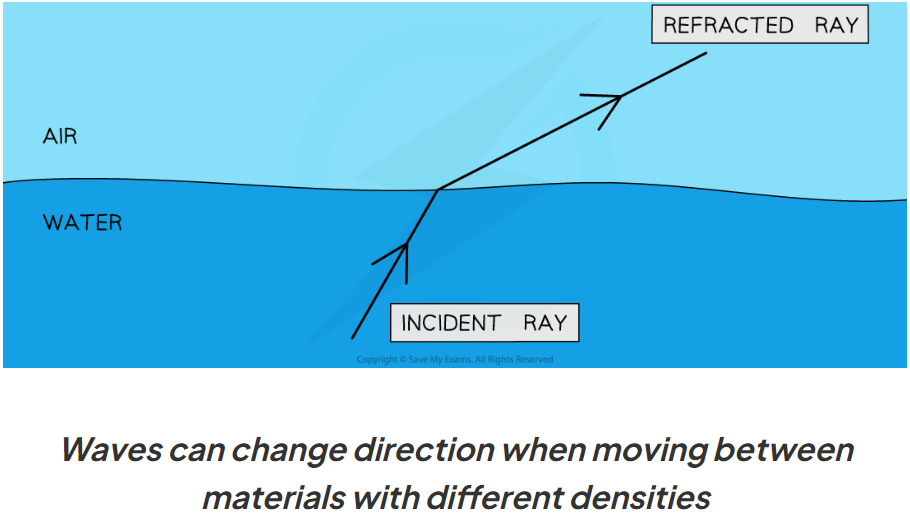
which types of waves can be refracted?
sound
seismic
water
electromagnetic
Transmission
a wave passes through a substance (must emerge other side)
what happens to a wave when it is transmitted?
partially absorbed (usually)
amplitude may decrease (e.g. sound waves quieter through a wall)
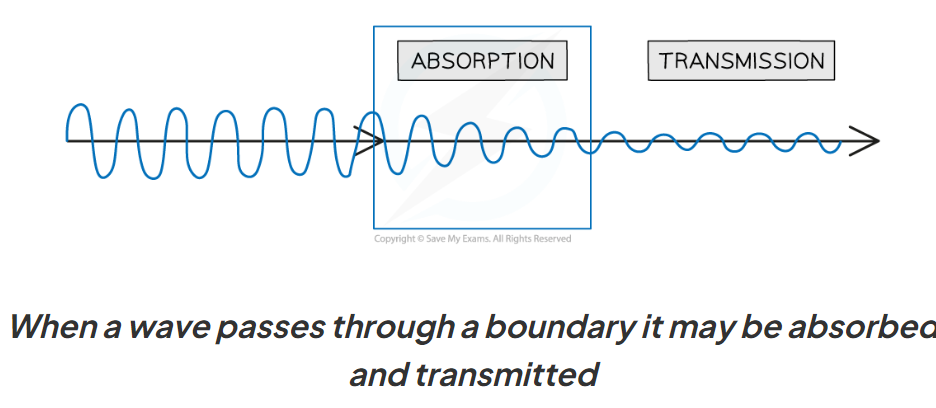
Absorption
energy is transferred from the wave into the particles of a substance
Why do some waves change direction when they are refracted?
different parts of the wave enter denser medium at different times, causing a difference in speed within the wave. causes it to bend.
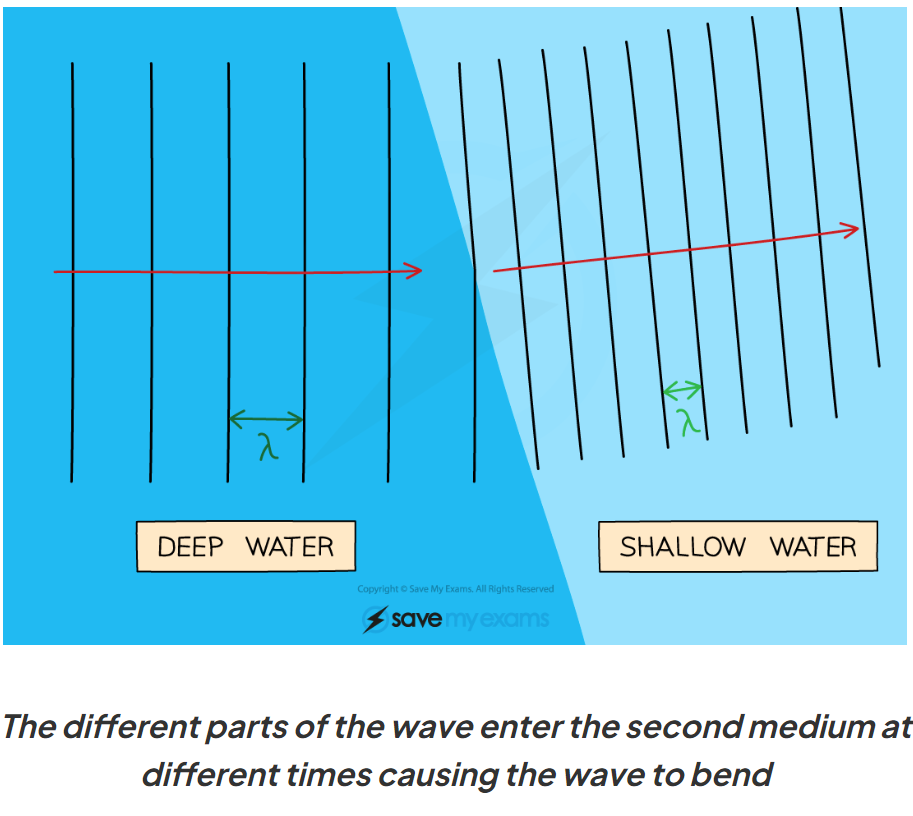
what affects how materials interact with waves?
wavelength
measure speed of water waves by creating ripples
choose a clam, flat water surface
measure distance between 2 people
1 person disturbs water, the other times how long it takes to get to them
repeat 10 times and find average
calculate speed (d/t)
rarefactions and compressions create changes in…
pressure
how do sound waves cause vibrations in solids?
fluctuating pressure of waves hits solids and causes particles to vibrate
natural frequency of a solid
the frequency a solid tends to vibrate at
how does natural frequency change affect of sounds waves on solids?
sound waves with frequency close to natural frequency cause larger vibrations compared to sound waves with much higher or lower frequencies (to natural frequency)
therefore some frequencies are transferred more efficiently to the solid
why can sound waves be heard by human ears
they are transferred efficiently to solid components of ear
why does transmission of sound to human ear only work in a limited frequency range?
sound waves outside the frequency range are too far from natural frequency of ear components
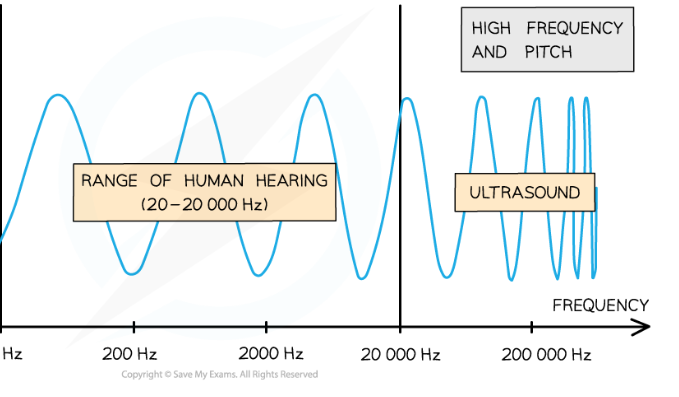
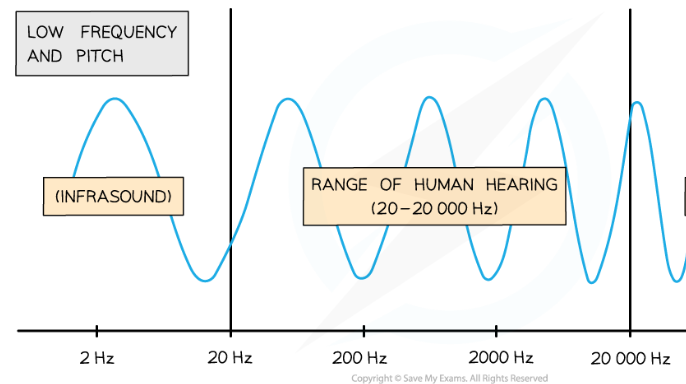
range of human hearing
20 Hz - 20,000 Hz
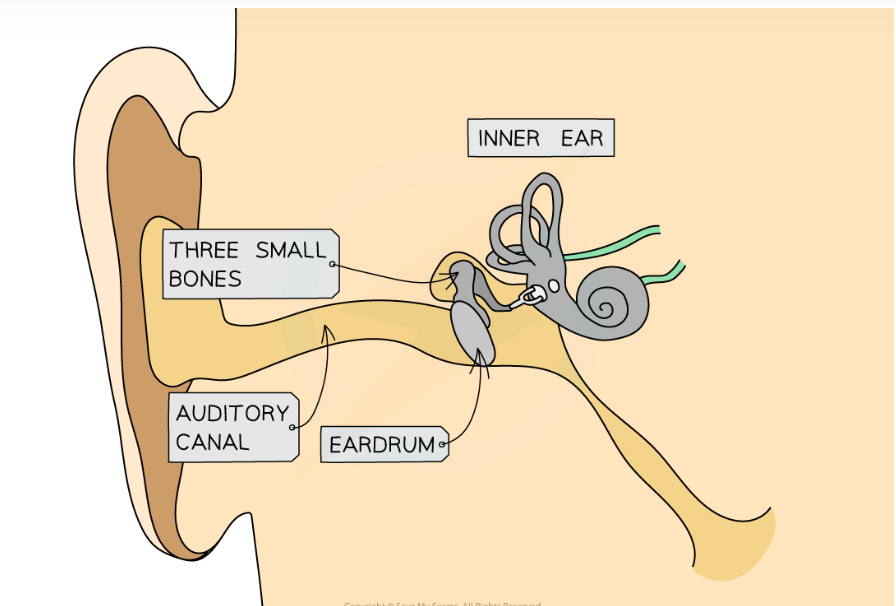
How the ear works
sound waves travel down auditory canal
pressure variations exert varying force causing eardrum to vibrate
vibrations transferred to 3 small bones that amplifies them
vibrations transferred to liquid in cochlea in inner ear
tiny hairs in cochlea detect vibrations create electrical impulses which travel to brain and are interpreted as sound
ultrasound
sounds waves with frequency over 20,000 Hz
Infrasound
sound waves with frequency under 20 Hz
uses of ultrasound in sonar
detects objects underwater
sound wave reflected off ocean floor
time it takes for sound wave to return used to calculate depth of water (unusual variations in depth = object underwater)
uses of ultrasound in foetal scanning
used to construct images of foetus in womb
transducer produces beam of ultrasound into womb
different boundaries between tissues reflect ultrasound back to transducer
electrical signals are sent when echoes are detected, depths and distances calculated
computer builds up an image
non-invasive and harmless
P waves
Primary waves- faster than S waves so felt first in an earthquake
longitudinal infrasound waves caused by earthquakes
can pass through solid and liquid layers of earth
refracted as they pass through layers, causing ‘shadow zones’ where they are not detected
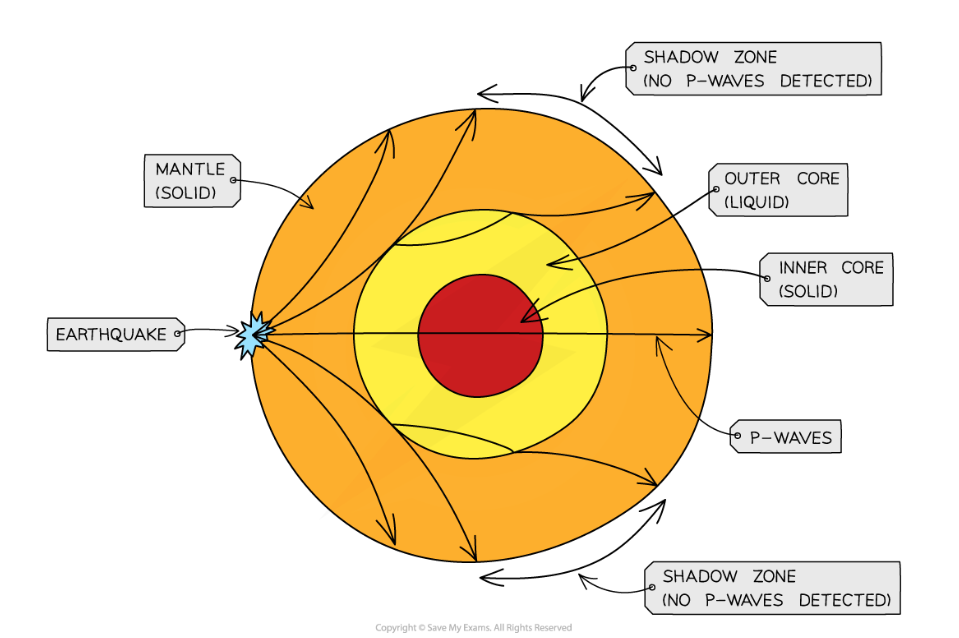
S waves
Secondary waves- slower than P waves so felt 2nd in an earthquake
transverse waves caused by earthquakes
only travels through solids
can’t pass through liquid outer core, so not detected on opposite side of earth’s surface to quake
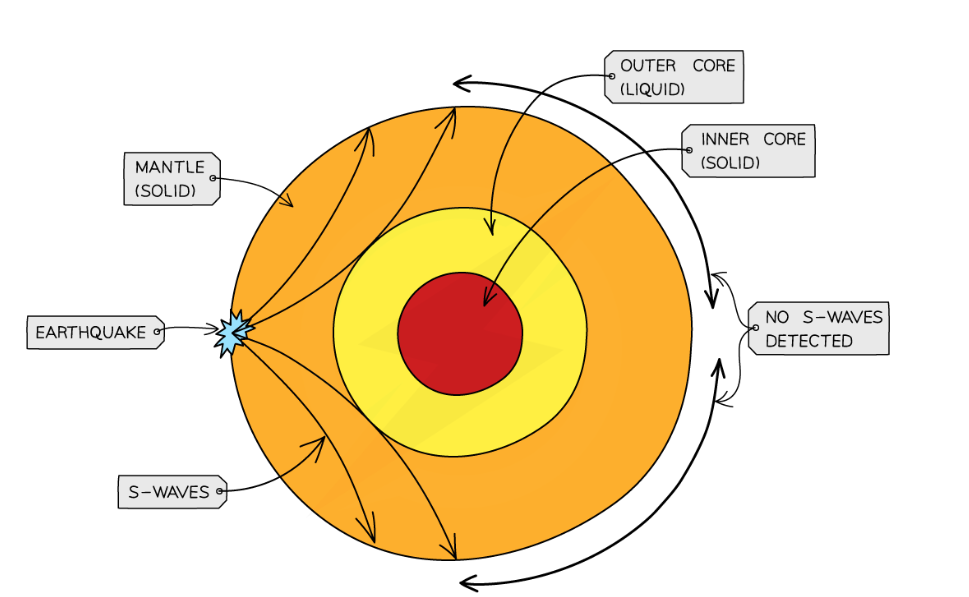
why seismic waves are important to understand structure of Earth
interior of Earth not physically possible to observe so provide evidence about structure
conclusion from discovery that only P-waves are detected on opposite side of Earth to quake
Mantle is solid- both waves can pass through
outer core is liquid- s waves can’t pass through it
why do refractions between layers in the Earth cause 2 shadow zones?
inner core is solid, so large refraction is taking place
what can change about a wave from one medium to another?
wavelength
velocity
frequency
These are all linked by the wave equation, meaning changes in one causes changes in others
sound travels ___ in hot air
faster