Adrenal Disorders
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
glucocorticoids (cortisol), cortex
Cushing’ s syndrome/disease is a overproduction of __________ in the ____________
inhibit glucose uptake/metabolism, decrease protein synthesis, increase release of AA, lactate
What effect does cortisol have on the muscles
increase lipolysis
What is the effect of cortisol on the fat?
suppression, anti-inflammatory
What is the effect of cortisol on the immune system?
increase CO, increase peripheral vascular tone (HTN)
What is the effect of cortisol on the cardiovascular system?
increase gluconeogenesis, increase glycogen synthesis
What is the effect of cortisol on the liver
increase GFR, aid in water regulation and electrolyte balance
What is the effect of cortisol on the renal system?
increase blood glucose
Other effects of cortisol
Cushing syndrome
clinical manifestations (S/S) due to excessive glucocorticoids either from exogenous steroid use or spontaneous production of excess corticosteroids by the adrenal cortex
Cushing Disease
ACTH hypersecretion from the anterior pituitary due to a benign pituitary adenoma
central obesity, buffalo hump, supraclavicular fat pad, moon fascies
Cushings presentation - weight gain
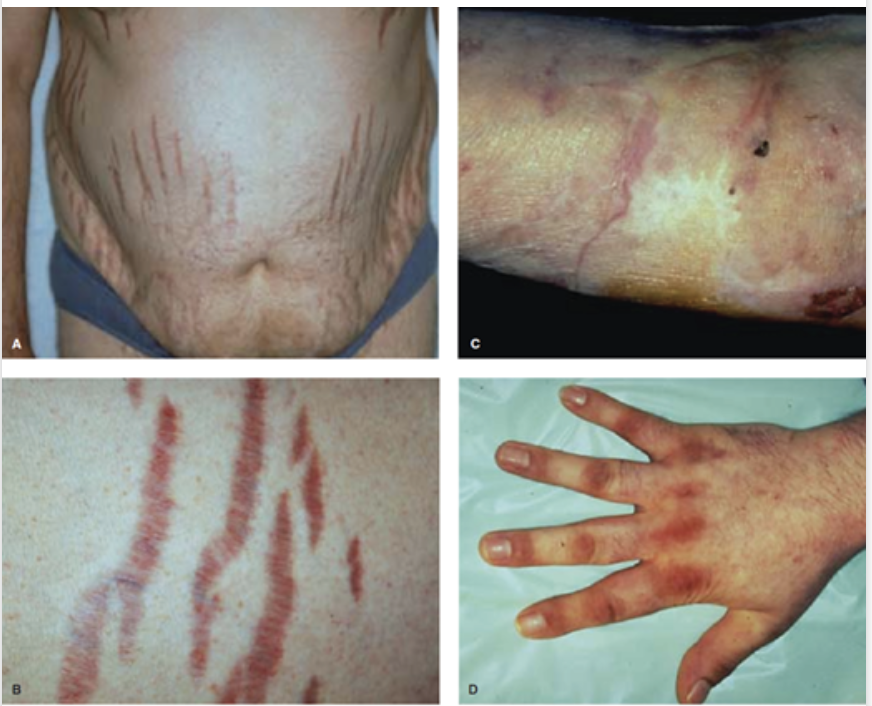
purple striae (loss of collagen), easy bruising, thin skin, slow wound healing, unusual bacterial/funga; infections
Cushings presentation - Skin changes
proximal muscle weakness, emotional lability, depression, osteoporosis, HA (pituitary tumor)
Cushings presentation - Neuro and musculoskeletal
HTN
Cushings presentation - CV and renal
DM, menstrual irregularities, decrease libido, infertility, ED
Cushings presentation - Endrocrine
Serum and urinary cortisol, ACTH, CMP (glucose, K), UA (glucose), CBC (leukocytosis)
35 y/o female presents to the clinic for muscle weakness and fatigue. On a physical exam you note central obesity, purple striae on the upper extremities and abdomen. Vitals are stable with the exception of 150/90. What labs do you want?
Dexamethasone suppression test, 24 hour urine, midnight serum/salivary cortisol levels
35 y/o female presents to the clinic for muscle weakness and fatigue. On a physical exam you note central obesity, purple striae on the upper extremities and abdomen. Vitals are stable with the exception of 150/90. Labs show elevated serum and urinary cortisol, glycosuria, hypokalemia, and leukocytosis. What are some tests you can use to confirm your diagnosis of Cushings?
Give Dex at 11 pm, check cortisol in the morning if lower than 1.8 the pituitary responded and cushings is excluded
Describe the dexamethasone suppression test
Adrenal CT (adrenal tumor)
In a Cushing’s workup, if serum ACTH is low, what imaging do you want
Pituitary MRI (pituitary tumor), CT of chest/abdomen (ectopic tumor)
In a Cushing’s workup, if serum ACTH is high, what imaging do you want
transphenoidal selective resection of pituitary adenoma
Treatment of choice for Cushing’s disease (ACTH dependent)
unilateral adrenalectomy
Treatment plan for adrenal adenoma/ACTH independent hyercortisolism
hydrocortisone replacement (due to delay in normal CRH/ACTH secretion - then taper it down)
How can we avoid adrenal crisis after treating Cushing’s?
ketoconazole (adrenal enzyme inhibitors)
If surgery is not an option for endogenous Cushing syndrome, what is our 1st line medication?
Adrenocortical insufficiency (Addison’s disease)
Progressive hypofunctioning of the adrenal cortex
mineralcorticoids, glucocorticoids (cortex)
In addison’s disease, what are we deficient in
autoimmune destruction (90% of cases in US), infectious (TB, HIV, CMV), bilateral adrenal hemorrhage, congenital adrenal hyperplasia
What are some causes of Primary adrenal insufficiency
fatigue, anorexia, weight loss, N/V/D, abdominal pain, arthralgias, myalgias, hypotension
What are the most common symptoms of primary adrenal insufficiency?
tachycardia, decreased axillary hair and libido in women, irritability, depression, hyperpigmentation (usually shows up 1st), salt cravings
Less common symptoms of primary adrenal insufficiency
Low AM cortisol, ACTH over 200, low Na, high K, low serum DHEA, anti-adrenal antibodies, elevated plasma renin activity
Labs for primary adrenal insufficiency
Chest CT (TB, fungal infection, cancer), CT adrenals (1st draft pick), FNA (determines etiology)
Imaging for primary adrenal insufficiency
Hydrocortisone (glucocorticoid replacement - could use dex, prednisone), Fludrocortisone (mineralcorticoid replacement), DHEA (in women with refractory symptoms)
Treatment for primary adrenal insufficiency
Stress dose of glucocorticoids for 3 days
What should be done for a patient with adrenal insufficiency who encounters a stressful situation (fever, surgery, etc)
Stress dose IV hydrocortisone 100-300 mg, NS rapid bolus (D50 if hypoglycemic), empiric antibiotics
45 y/o woman presents to the ER with complaints of N/V and abd pain. Vitals are stable with the exception of 90/50 and 104.3 temp. Labs show hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and hypoglycemia. What is your treatment plan?
hydrocortisone
What med do you prioritize in an adrenal crisis
Pheochromocytoma
A tumor in the adrenal medulla that secretes both norepi and epi

HA, palpitations/tachy, diaphoresis
Pheo classic triad
sustained/paroxysmal HTN, orthostatic hypotension, tremor
Other symptoms of pheo
High plasma free metanephrines (most sensitive), urine VMAs, abdominal CT/MRI, nuclear imaging
Diagnostics for pheo
adrenalectomy (1st draft pick), get pressure under control before surgery with alpha blockers or CCBs, Tachycardia can be controlled with a beta blocker AFTER HTN is undercontrol
25 y/o male patient presents to the ER for palpitations stating it feels like “his heart is racing out of his chest.” He also reports HA. On a physical exam you note HTN (180/126), 176 bpm, skin is diaphoretic, and a slight tremor of the hands is noted. Labs show high plasma free metanephrines and high urine VMAs. What is your treatment plan?
Primary aldosteronism
What is caused by the autonomous production of aldosterone (mineralocorticoid) by the adrenal cortex due to hyperplasia, adenoma, or carcinoma
increases water retention, increasing Na+ retention
What is the function of aldosterone
Bilateral idiopathic hyperaldosteronism, unilateral aldosterone producing adenoma, unilateral hyperplasia, pure aldosterone producing adrenocortical carcinomas and ectopic aldosterone-secreting tumors
Causes of primary hyperalsoteronism
dehydration, CHF, Cirrhosis, Nephrotic syndrome
Causes of Secondary hyperaldosteronism
Resistant HTN, Hypokalemia (muscle weakness), mild hypernatremia
Symptoms of primary hyperaldosteronism
HTN with hypokalemia, Resistant HTN (3+ meds to manage), Severe HTN, onset of HTN under 30 y/o, HTN with adrenal mass, Family Hx of early onset cardiac issues
Red flags for hyperaldosteronism
CT of adrenal glands, labetalol (HTN emergency), treat hypokalemia
18 y/o male presents to the ER for HA and visual changes. He also reports N/V. Vitals are stable with the exception of BP 180/112. See rhythm strip. Labs show hypokalemia, elevated plasma aldosterone and low plasma renin. What is your next step?
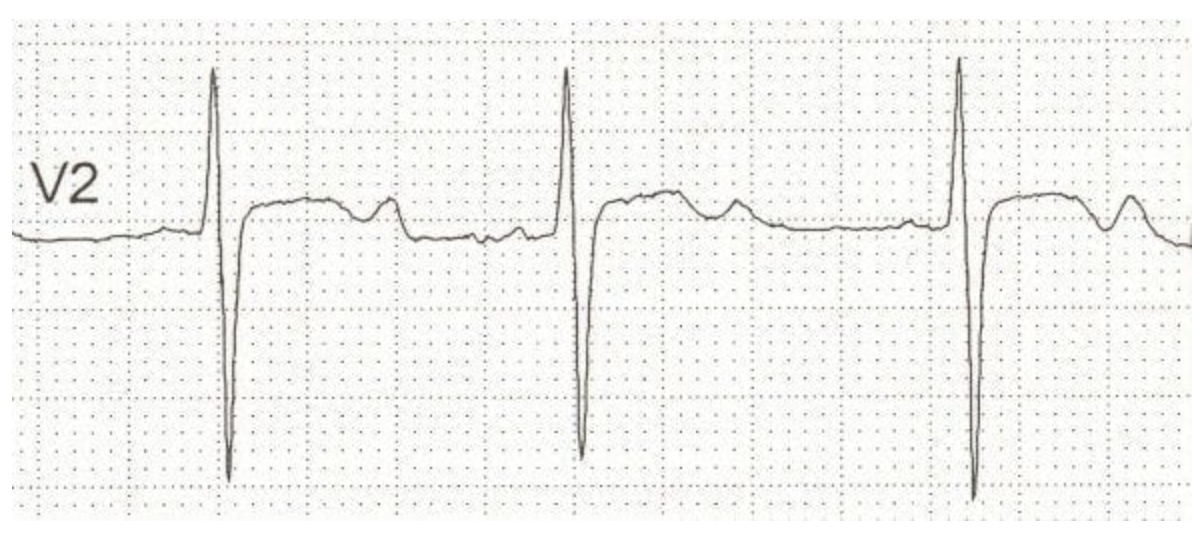
High PAC, Low PRA, PAC:PRA ratio between 20-40
Classic labs for primary hyperalsoteronism
24 hour urine aldosterone, sodium, creatinine on a high sodium diet (5000 mg), fludrocortisone suppression test, saline suppression test
Secondary workup for primary hyperaldosteronism - confirm those suspicions
High PAC, high PRA, PAC:PRA less than 10
Classic labs for secondary hyperalsoteronism
CT/MRI scan of the adrenals, adrenal vein sampling (determine unilateral vs. bilateral)
Imaging to confirm primary hyperaldosteronism
long term aldosterone receptor antagonist (spironolactone, eplernone)
Treatment plan for hyperaldosteronism caused by bilateral adrenal hyperplasia
normalize serum K and blood pressure
Goals of therapy for hyperaldosteronism caused by bilateral adrenal hyperplasia
laparoscopic complete adrenalectomy, monitor for hyperkalemia, spironolactone OR adenoma resection (HTN is improved)
Treatment plan for hyperalsoteronism caused by unilateral adrenal hyperplasia