LIFESCI 3K03 Topic 5 Part III: Spinal Interneurons
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/11
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
1
New cards
spinal interneurons
- most input to alpha motor neurons mediated by a complex network of spinal interneurons
- this intricate network of interneurons can design simple to highly complex patterns of movement based on input from primary sensory axons, descending axons from brain, collaterals of lower motor neuron axons, other interneurons
- this intricate network of interneurons can design simple to highly complex patterns of movement based on input from primary sensory axons, descending axons from brain, collaterals of lower motor neuron axons, other interneurons
2
New cards
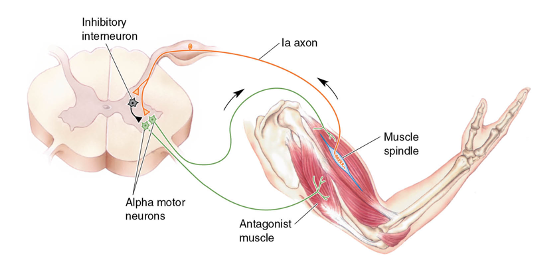
reciprocal inhibition
reflex arc using spinal interneurons to support simple monosynaptic reflexes (e.g. stretch reflex)
- contraction of one muscle accompanied by relaxation of its antagonish muscle
- contraction of one muscle accompanied by relaxation of its antagonish muscle
3
New cards
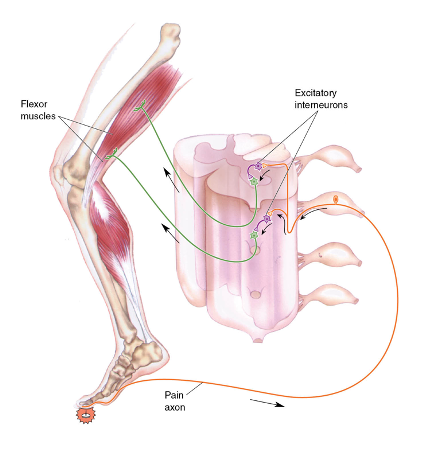
withdrawal reflex
reflex arc used to withdraw limb from aversive stimulus
- excitatory input for multiple ipsilateral motor units
- excitatory input for multiple ipsilateral motor units
4
New cards
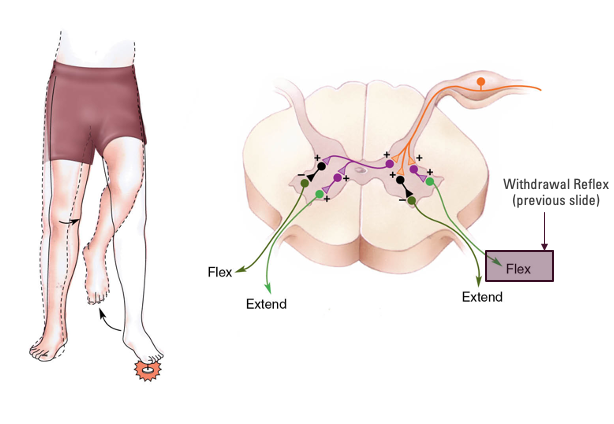
crossed-extensor reflex
reflex arc for extensors and flexors on opposite side
- excitatory and inhibitory for ipsilaterial and contralateral motor units
- excitatory and inhibitory for ipsilaterial and contralateral motor units
5
New cards
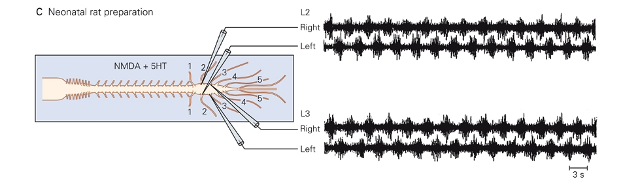
what are central pattern generators
- circuitry for many rhythmic movements resides in spinal cord
- complex network of sensory, motor, and interneurons
- evidence from animal spinal transections
- measured bursts of rhythmic and coordinated activity arising for input that was constant
- complex network of sensory, motor, and interneurons
- evidence from animal spinal transections
- measured bursts of rhythmic and coordinated activity arising for input that was constant
6
New cards
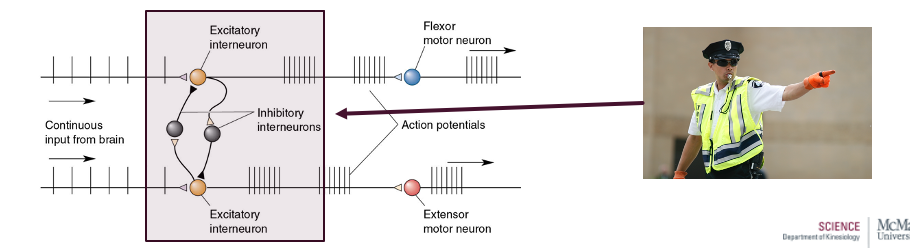
what are central pattern generators controlled by?
- controlled by two "half-centers" of spinal neurons
- mutually inhibiting halves that produce alternating bursts of flexor and extensor activity
- rhythmic activity will continue as long as input exists
- circuitry for walking resides in the lumbar/sacaral spinal cord
- Something in spinal cord generating pattern
- Continous input from brain
- Interneuron job to start and stop motion
- Inhibit alternatively
- Extensors: quads
- Flexors: hamstrings
- When A fires, B inhibits, vice versa
- mutually inhibiting halves that produce alternating bursts of flexor and extensor activity
- rhythmic activity will continue as long as input exists
- circuitry for walking resides in the lumbar/sacaral spinal cord
- Something in spinal cord generating pattern
- Continous input from brain
- Interneuron job to start and stop motion
- Inhibit alternatively
- Extensors: quads
- Flexors: hamstrings
- When A fires, B inhibits, vice versa
7
New cards
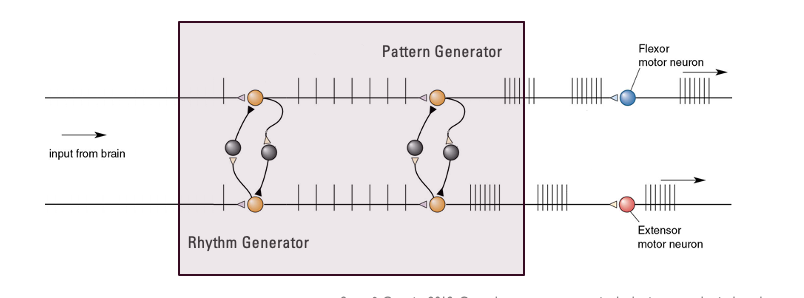
seperating central pattern generators
rhythm generators - setting the timing of patterns to be generated
pattern generators - sending the required pattern of muscles activations
pattern generators - sending the required pattern of muscles activations
8
New cards
what initiates and adapts CPGs?
descending control (input from brain) initiates and adapts CPGs
- can influence both rhythm and pattern genereation neural pools
- can influence both rhythm and pattern genereation neural pools
9
New cards
gait retraining
changing the mechanics of how you walk or run
- easy to override motor patterns or CPGs
- very difficult to "rewrite" them
- Can retrain someone to move differently
- Walk/on toes, hard to rewire i.e. when running for bus
- easy to override motor patterns or CPGs
- very difficult to "rewrite" them
- Can retrain someone to move differently
- Walk/on toes, hard to rewire i.e. when running for bus
10
New cards
sensory information and CPGs
sensory information may also influence BOTH rhythm and pattern
stepping in cats
- proprioception
- amount of stretching can regulate the stance phase
- cats can match speed of treadmill, through CPG alone (after trained/electrical/drug stim)
- Cats have limited use of back legs, overtime can get back legs to start walking again
- sensory information from the skin
- stimulus to dorsal side of paw causes pattern with increased flexion to avoid a tripping hazard
- only impacts during swing
stepping in cats
- proprioception
- amount of stretching can regulate the stance phase
- cats can match speed of treadmill, through CPG alone (after trained/electrical/drug stim)
- Cats have limited use of back legs, overtime can get back legs to start walking again
- sensory information from the skin
- stimulus to dorsal side of paw causes pattern with increased flexion to avoid a tripping hazard
- only impacts during swing
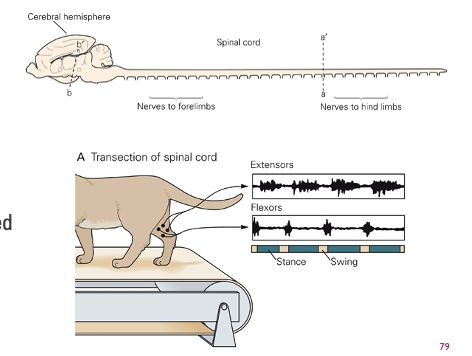
11
New cards
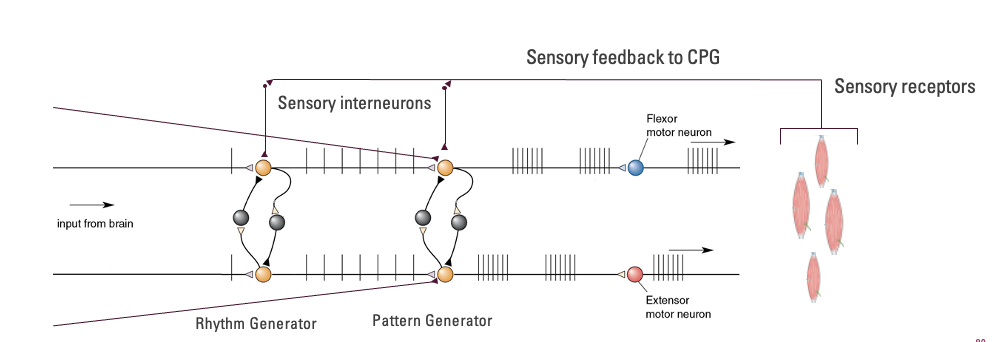
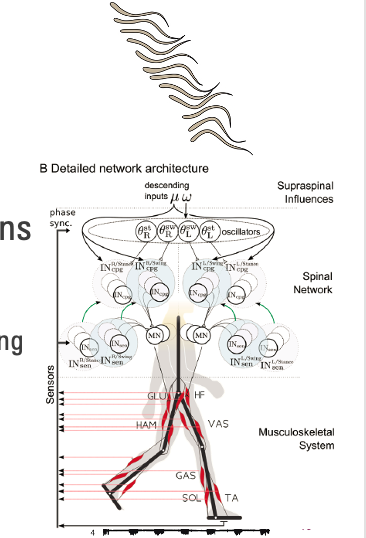
explain this diagram
- patterns are continually adjusted from higher and lower inputs
- Central input from brain, muscle spindles provide CPGs
Rhythm example
- Can edit how fast you’re walking/running
Pattern example
- Generating walking pattern, see puddle and avoid puddle, tweaks to pattern
- Injury --> brain says it hurts, change walking pattern
- How quickly, speed, extensor flexor: rhythm
- Directly firing extensor and flexor: pattern
- Central input from brain, muscle spindles provide CPGs
Rhythm example
- Can edit how fast you’re walking/running
Pattern example
- Generating walking pattern, see puddle and avoid puddle, tweaks to pattern
- Injury --> brain says it hurts, change walking pattern
- How quickly, speed, extensor flexor: rhythm
- Directly firing extensor and flexor: pattern
12
New cards
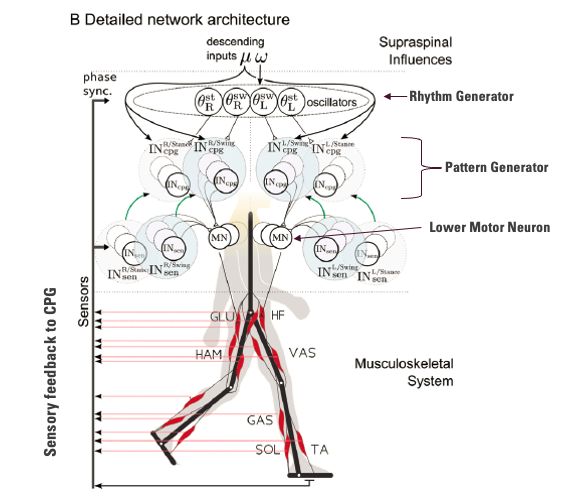
explain this diagram
- Descending input from brain, neurons are rhythm generators which exist in spinal cord
- Pattern generators connect to alpha motor neuron go to muscle
- Pattern generators connect to alpha motor neuron go to muscle