Biology
1/140
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
what are the 4 key points of cell theory
all living things are composed of living cells
the cell is the basic functional unit of life
cells arise from preexisting cells
cells carry genetic information in the form of DNA. this genetic material is passed on from parent to daughter cell
Why are viruses not considered living organisms (2)
replicate by invading other organisms
they use RNA as their genetic information
what do eukaryotic cells have that prokaryotes dont
could be multicellular
has a nucleus enclosed in a membrane
membrane bound organelles
what do prokaryotes cells have that eukaryotes dont
unicellular only
no nucleus
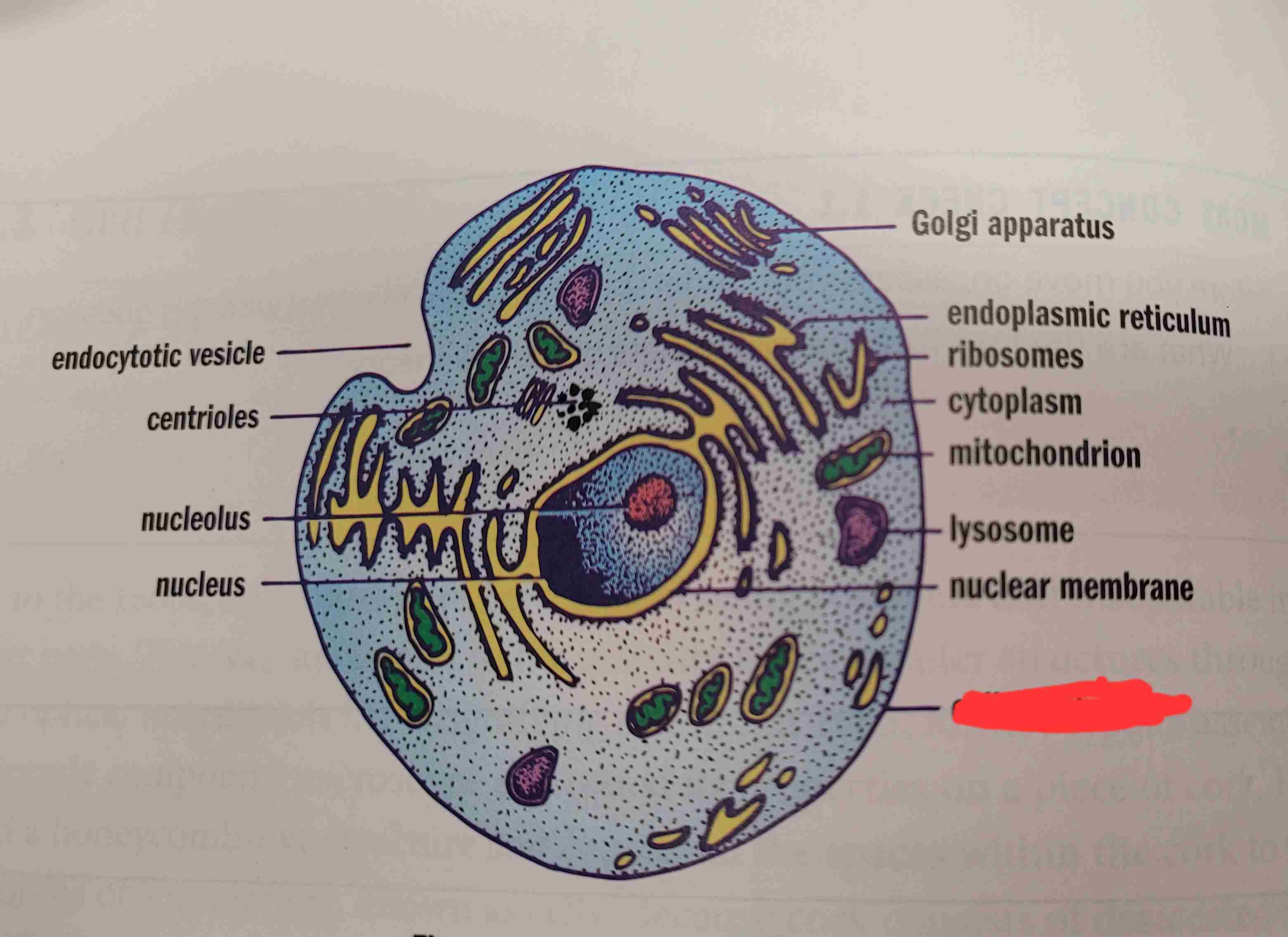
what is it
cell membrane
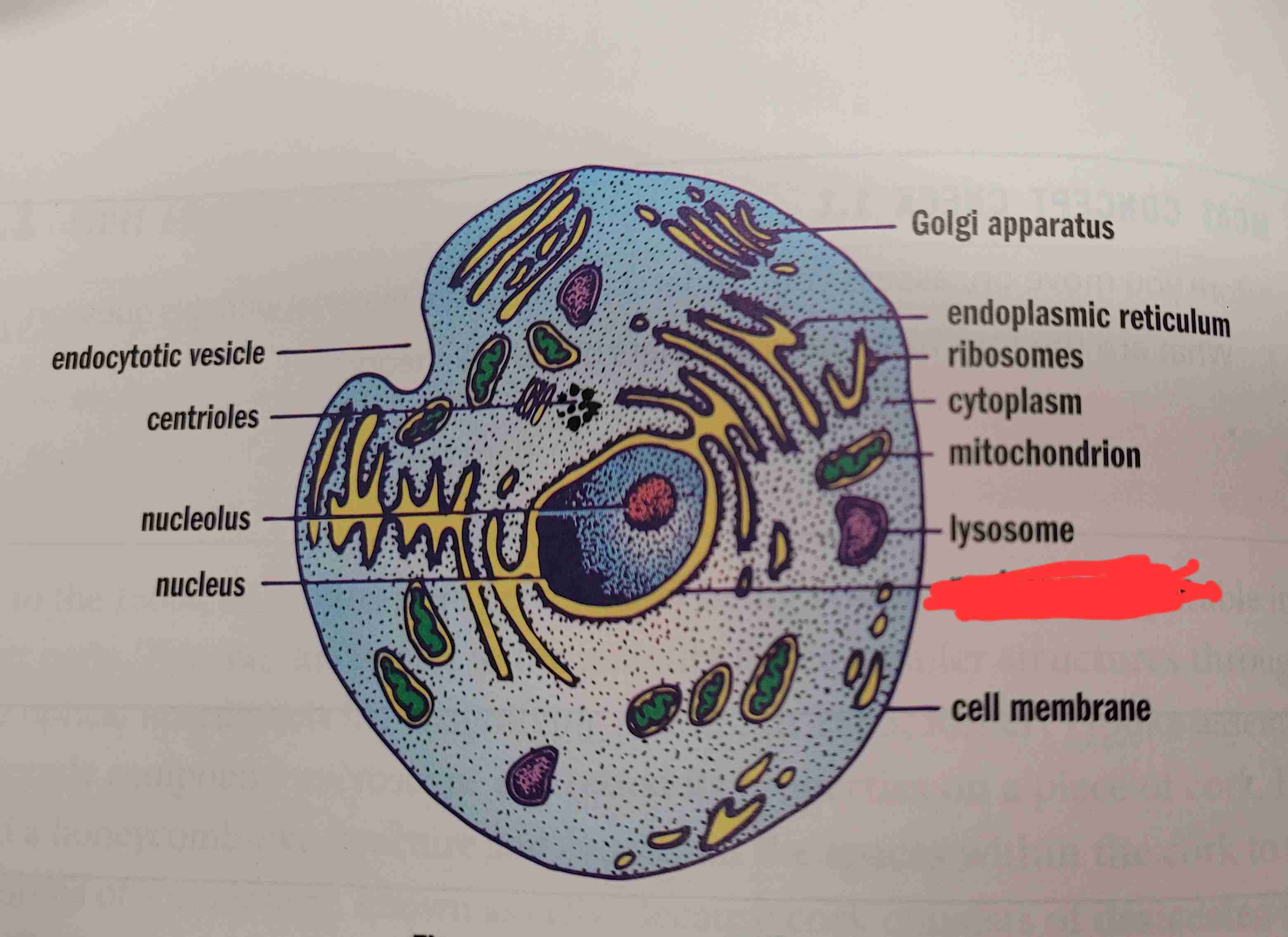
what is it
nuclear membrane
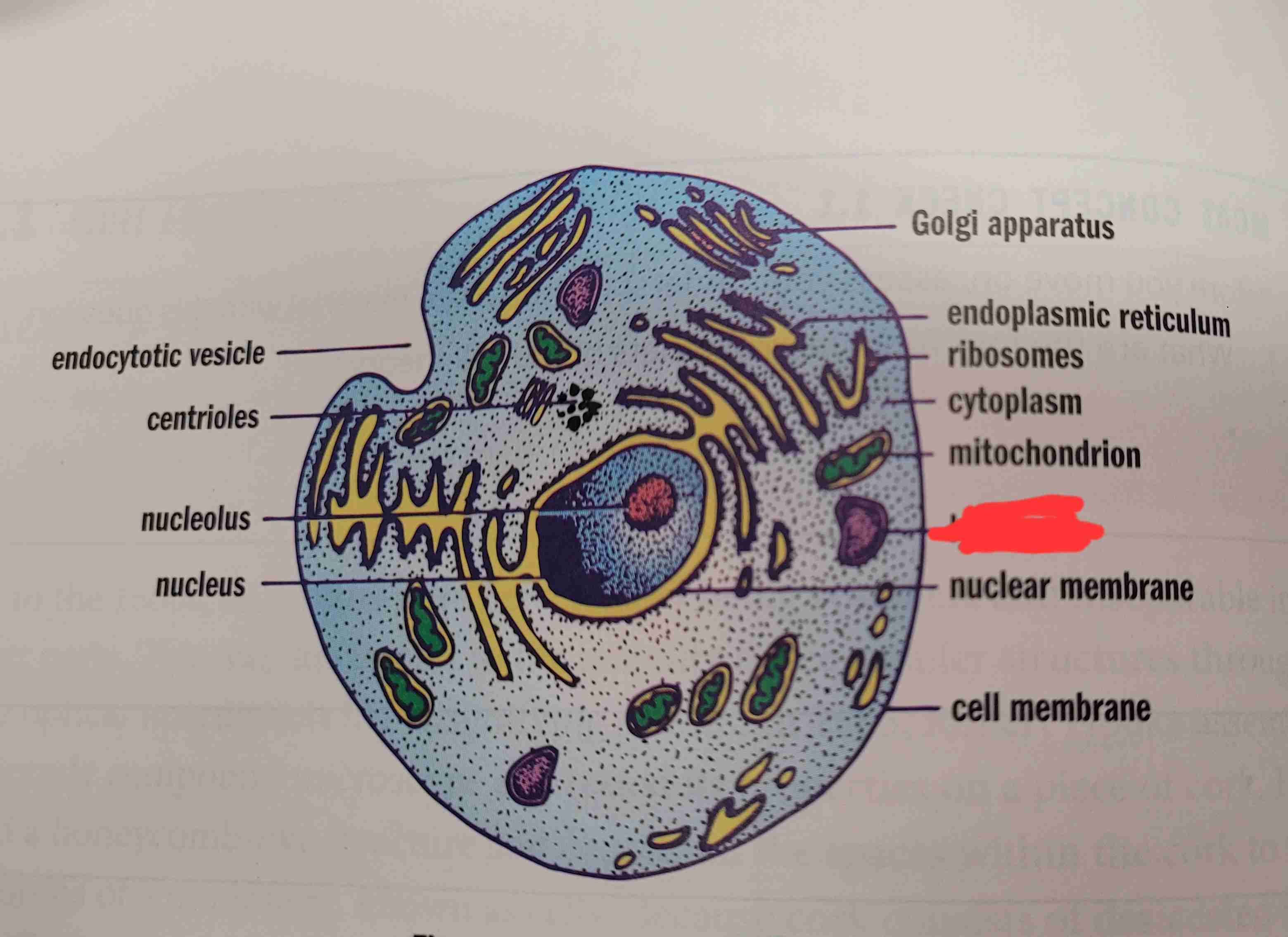
what is it
lysosome
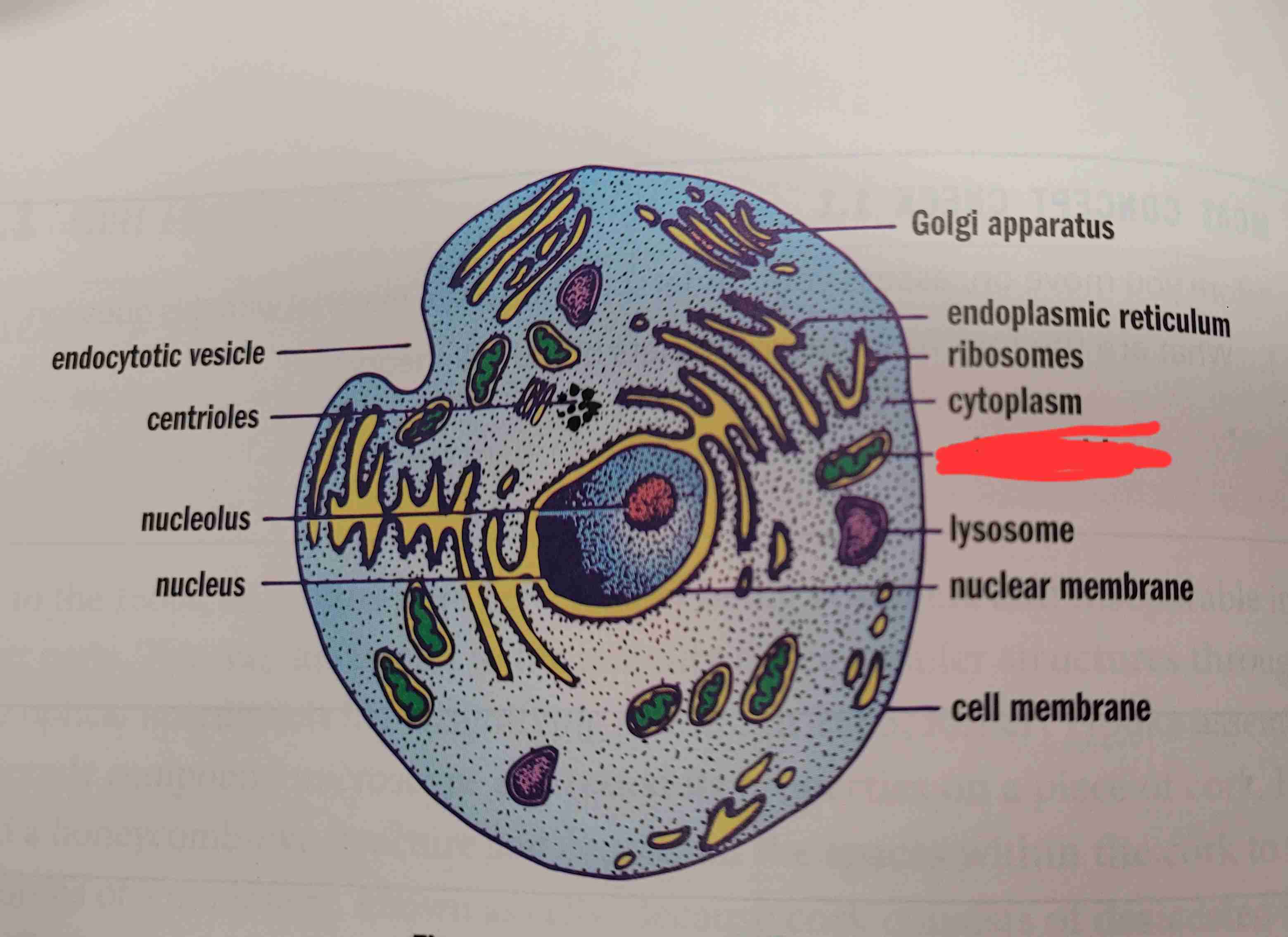
what is it
mitochondrion
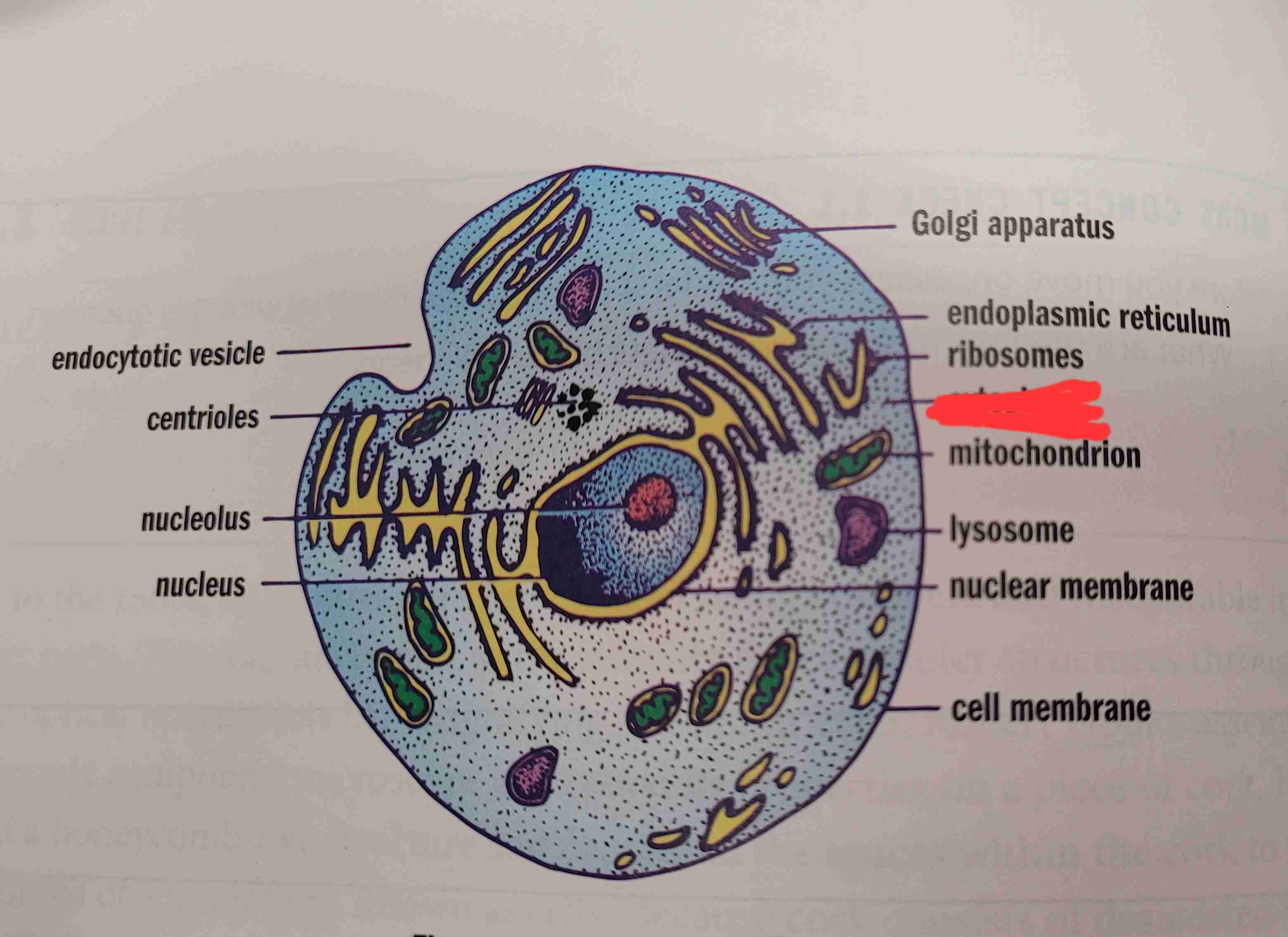
what is it
cytoplasm
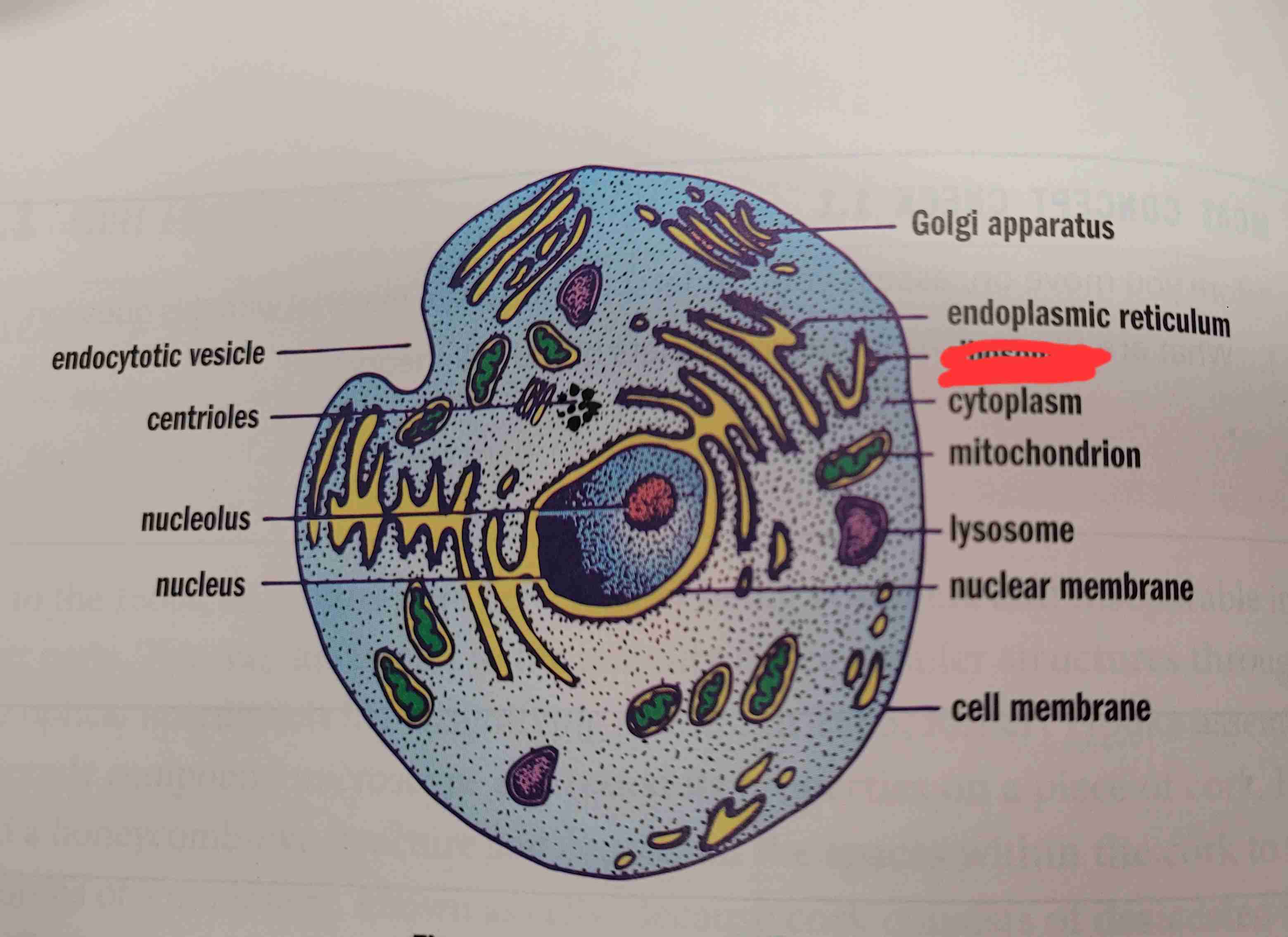
what is it
ribosomes
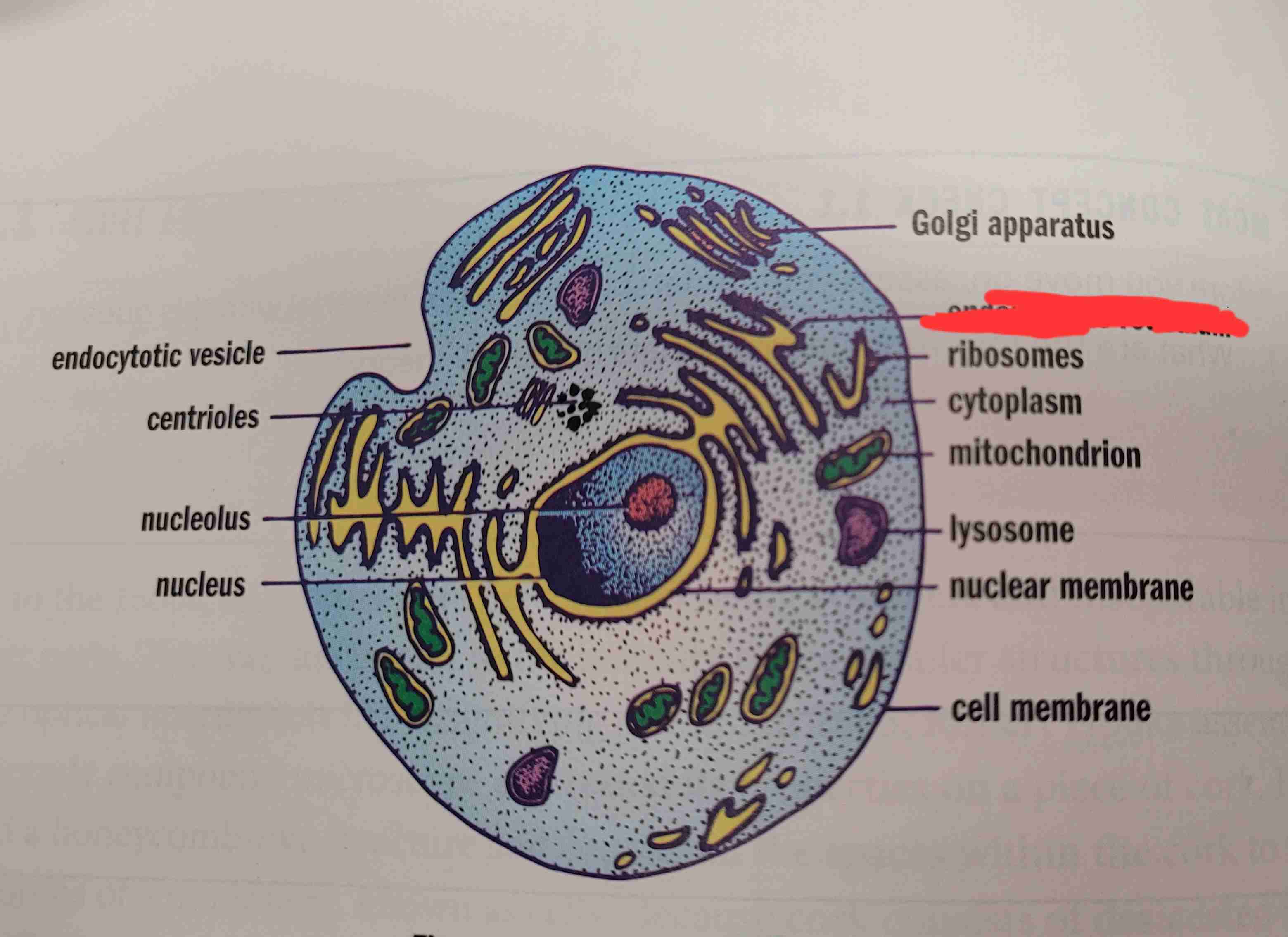
what is it
endoplasmic reticulum
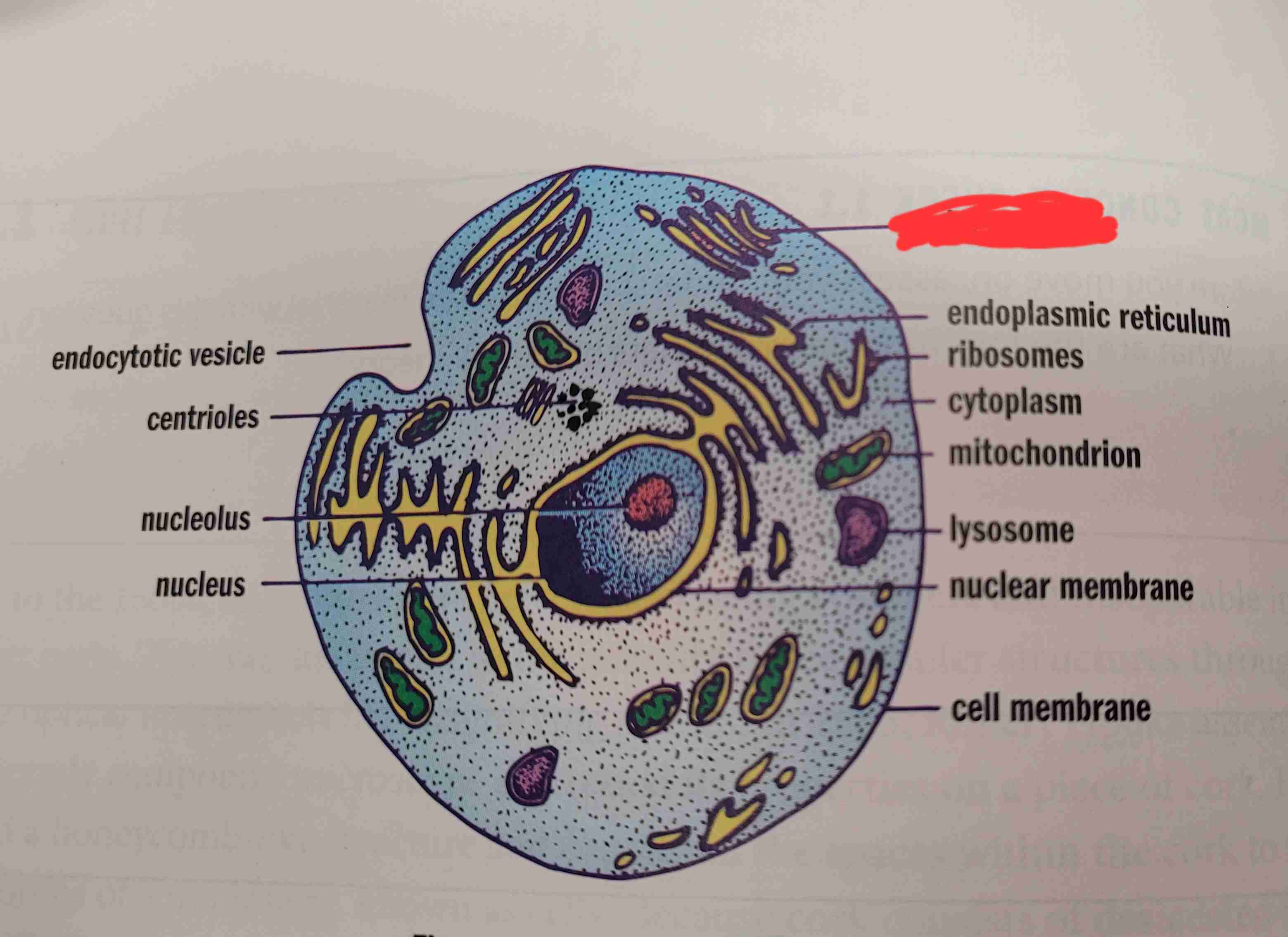
what is it
golgi appratus
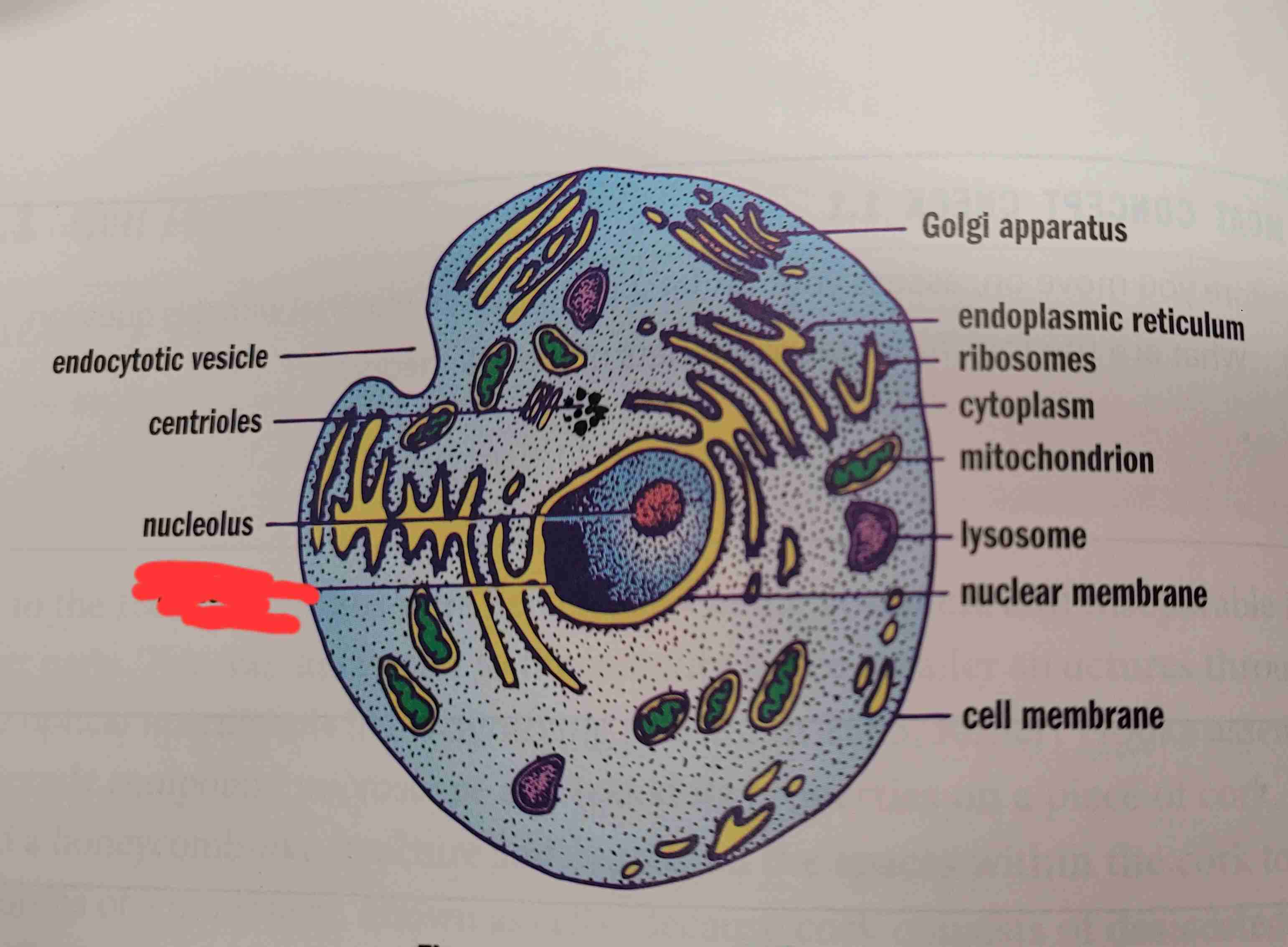
what is it
nucleus
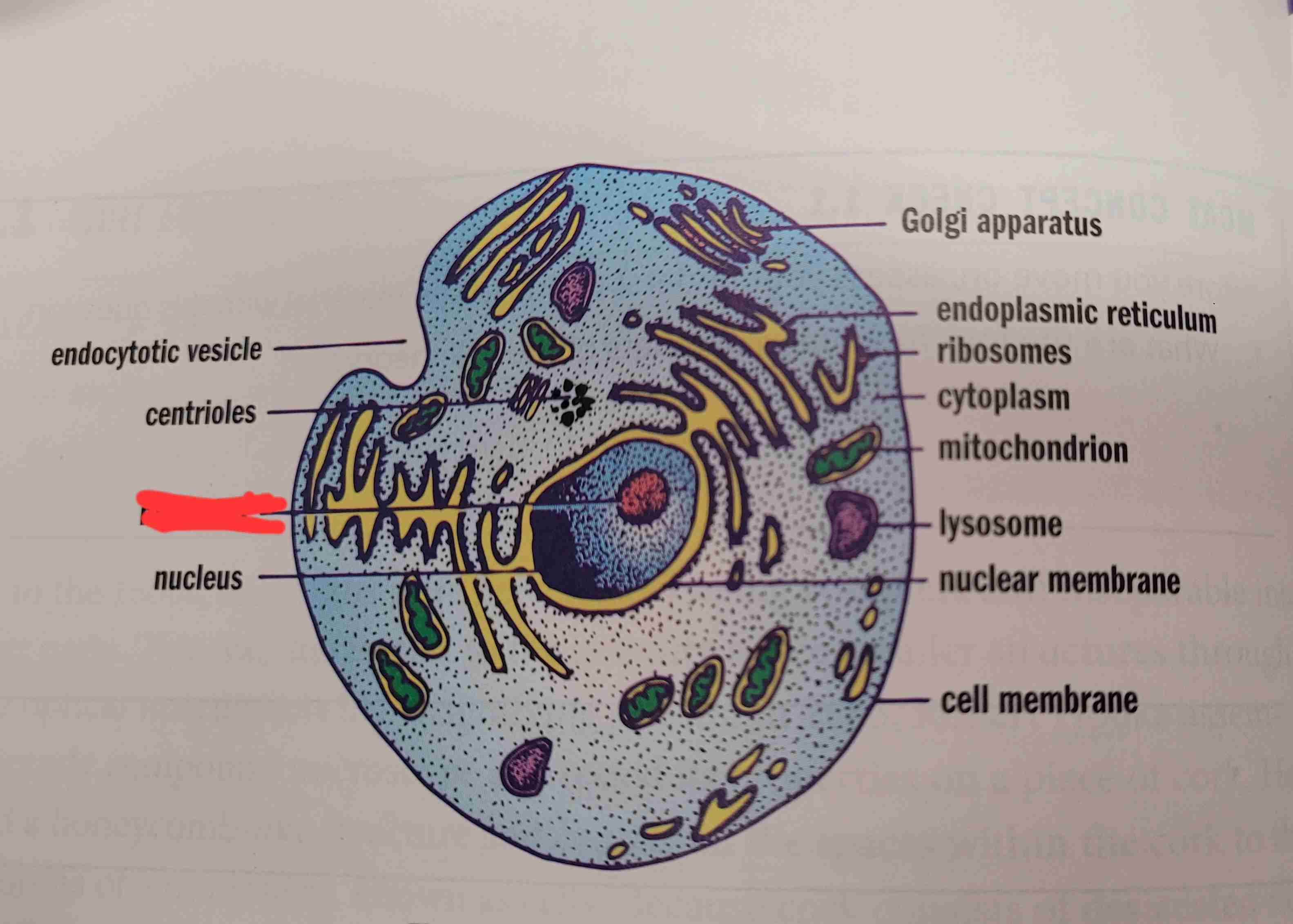
what is it
nucleolus
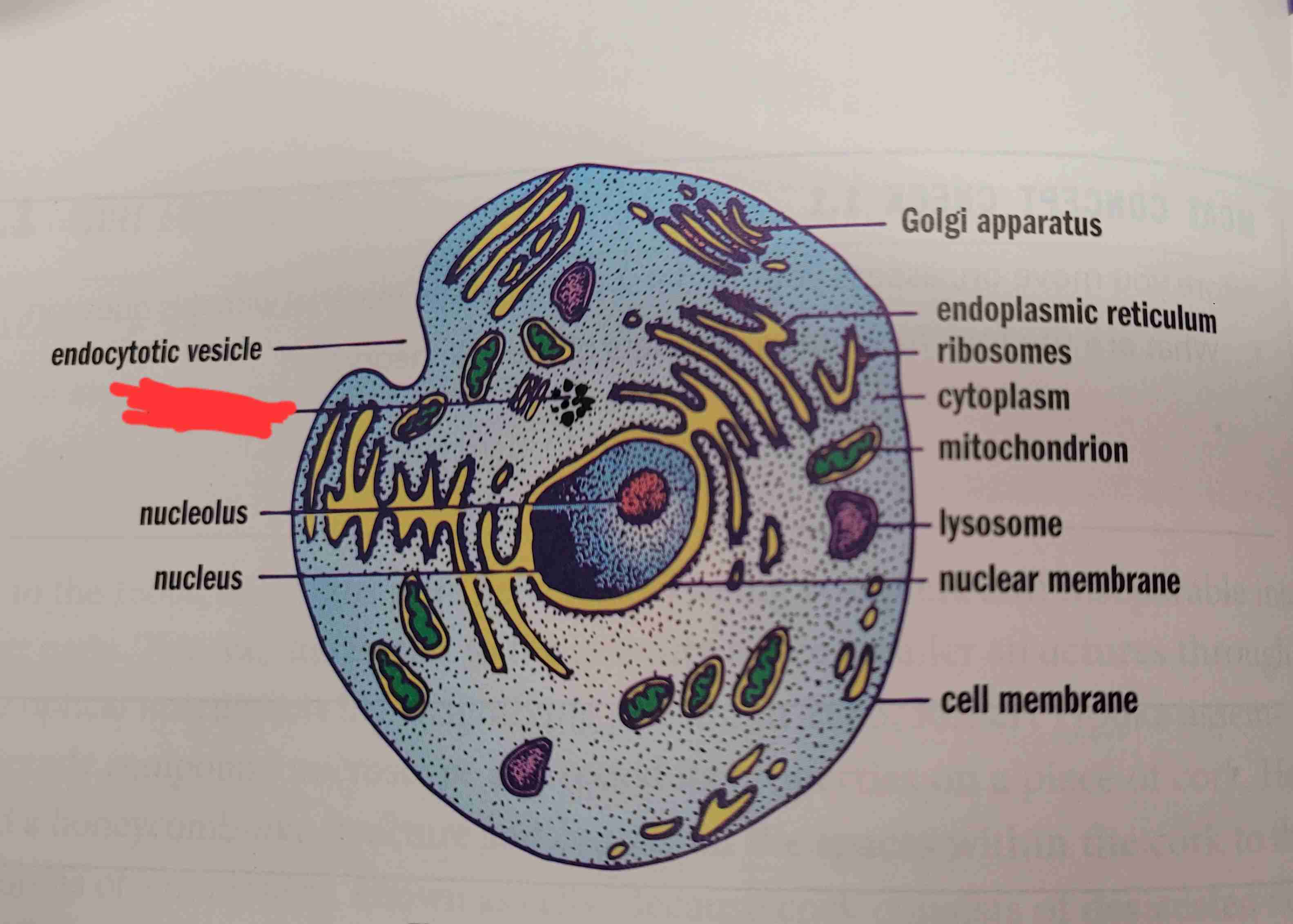
what is it
centrioles
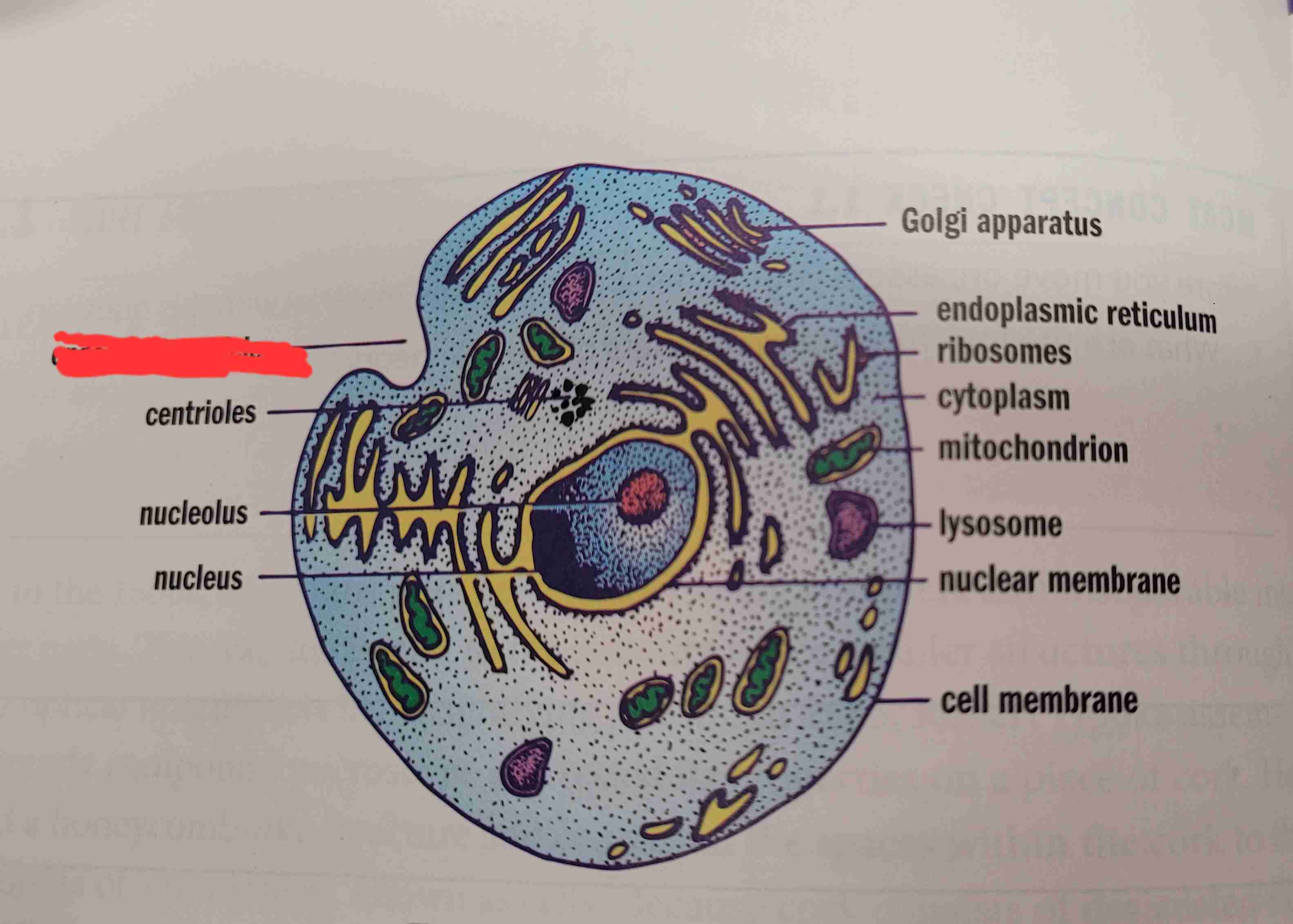
what is it
endocytotic vesicle
what are organelles suspended in, in eukaryotic cells
semifluid cytosol
what are membranes of eukaryotic cells made of
phospholipid bilayer
what is the cytosol
allows from the diffusion of molecules throughout the cell
what happens in the nucleus
genetic material is encoded in DNA, ehich is organized in chromosomes
how do eukaryotic cells reproduce
mitosis
what surrounds the nucleus
nuclear membrane aka envelope
what is the nuclear membrane
a double membrane that maintains a nuclear enviroment seprate and distinct from the cytoplasm
what are nuclear pores
are in the nuclear membrane and allows selective two-way exchange of material between cytoplasm and the nucleus
what are genes
coding regions for DNA
what are hitsones
Linear DNA that is wound around organizing proteins
what are chromsomes
hostones that are wound further
what is the nucleolus
a subsection of the nucleus where RNA is synthesized
What are the 2 layers of the mitochonrion
outer membrane and inner membrane
what is the outer membrane
is a barrier between cytosol and inner membranes
what is inner membrane
is arreanged in cristae, and containes the moleculles and enzymes of the electron transport chain
what is the space in between the outer and inner membrane called
inter-membrane space
what is the space in the inner membrane called
intermatrix
what is cristae
multiple infoldings
what is the proton motive force
these protons flow through ATP synthase to generate ATP during oxidative phosphorylation
how do mitochondria replicate
binary fission
what establishes proton motive force
the pumping of protons from the mitochondrial matric to the intermembrane space
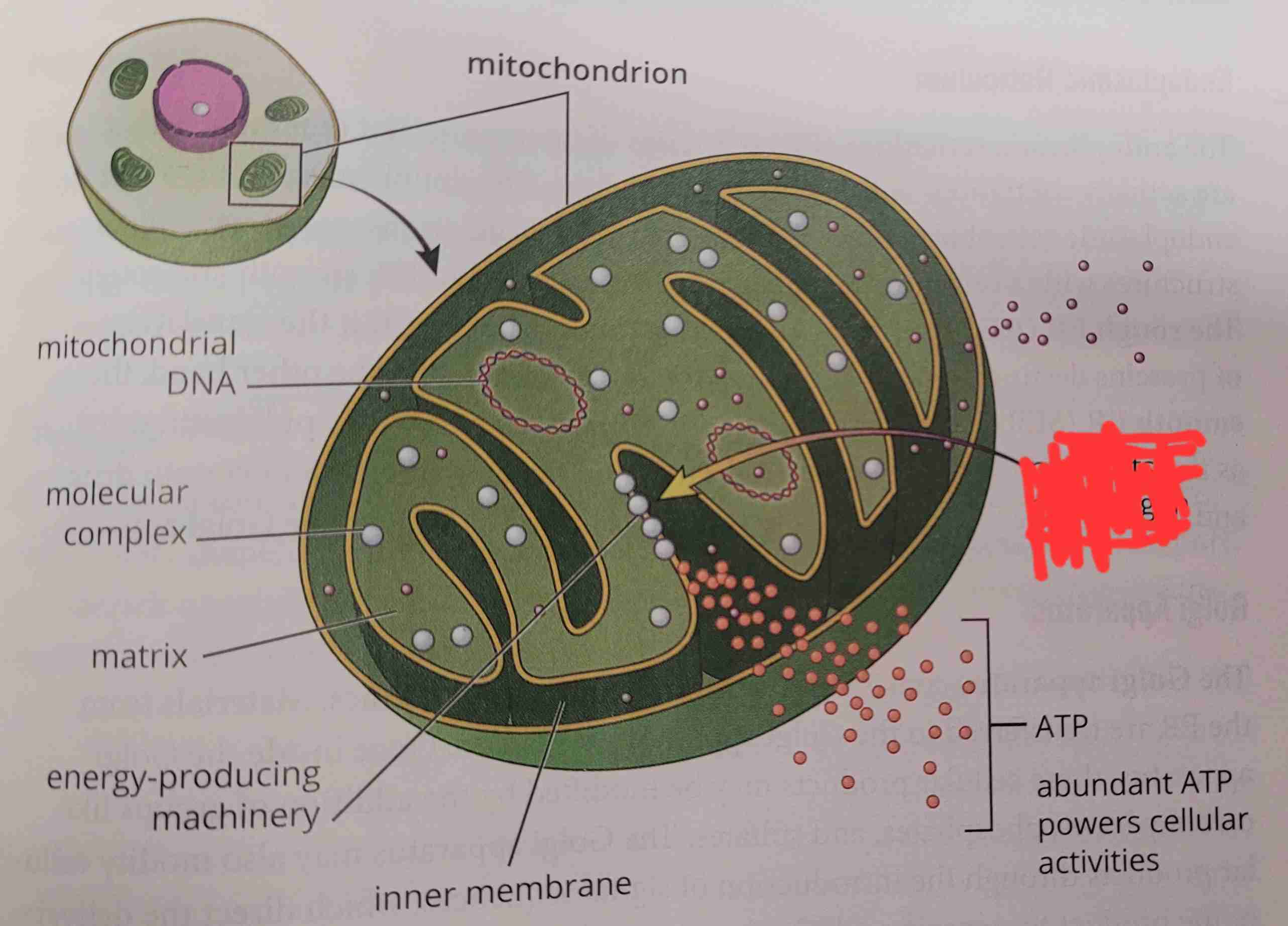
what is it
nutrients and oxygen
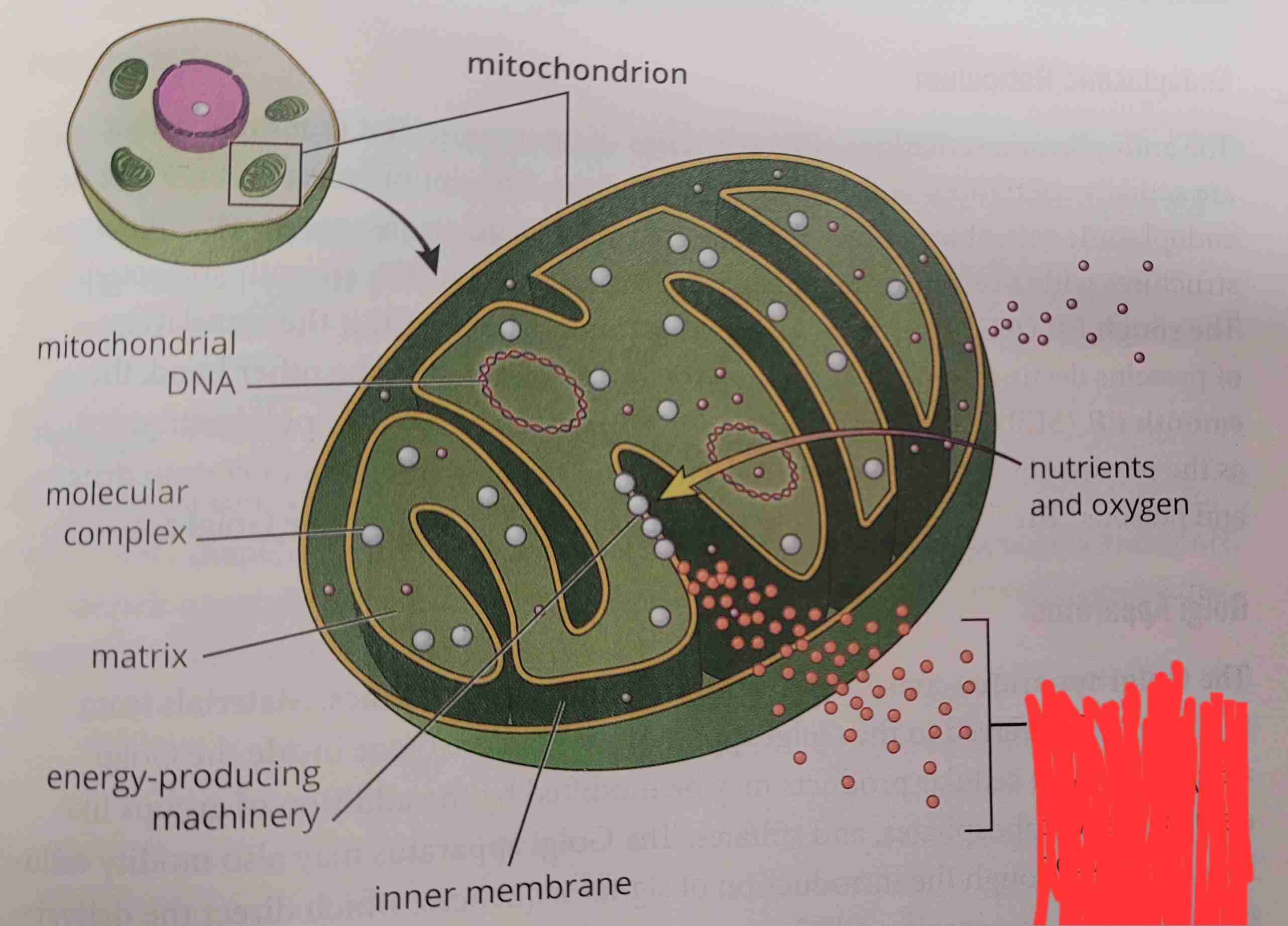
what is it
ATP
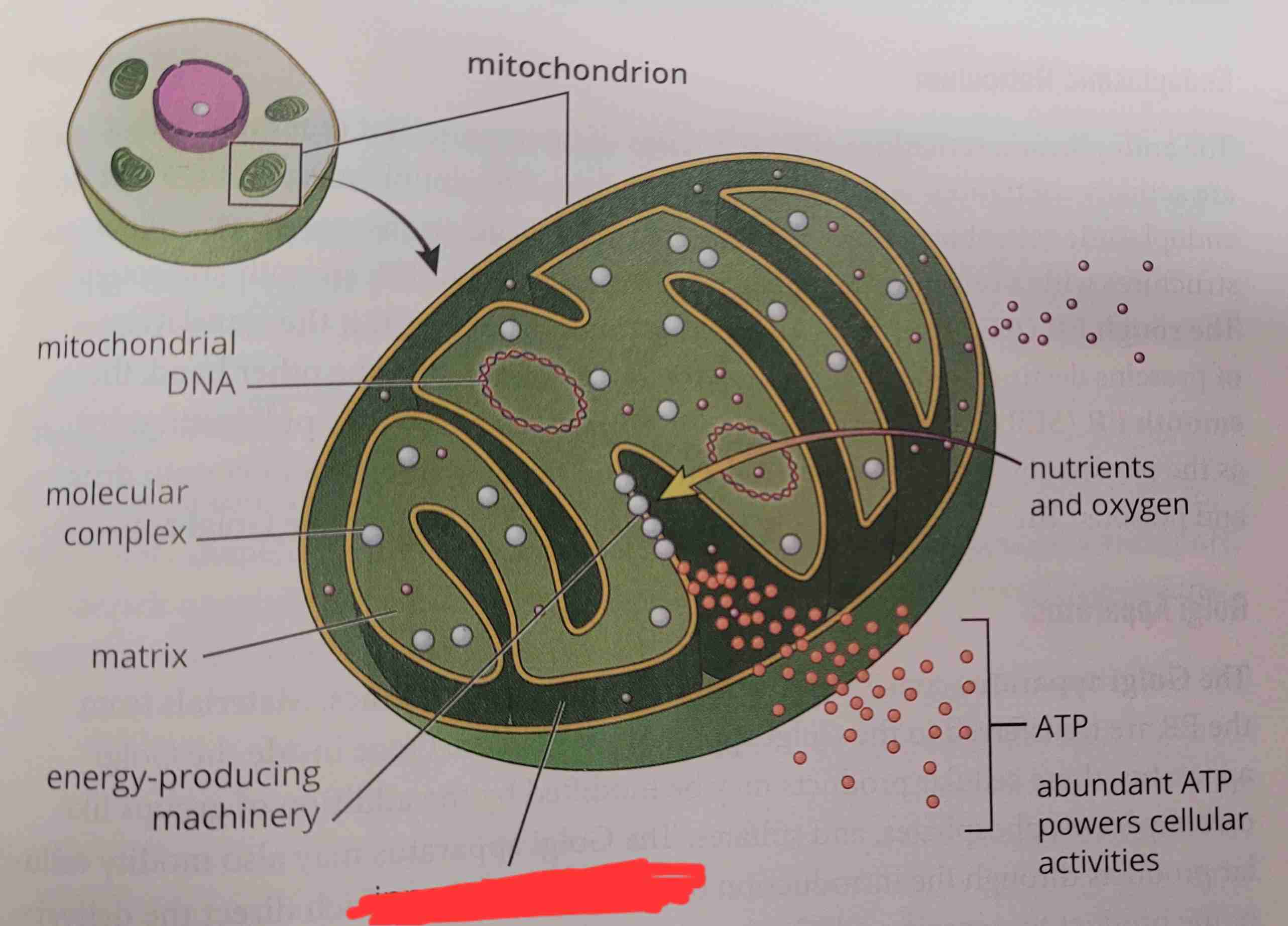
what is it
inner membrane
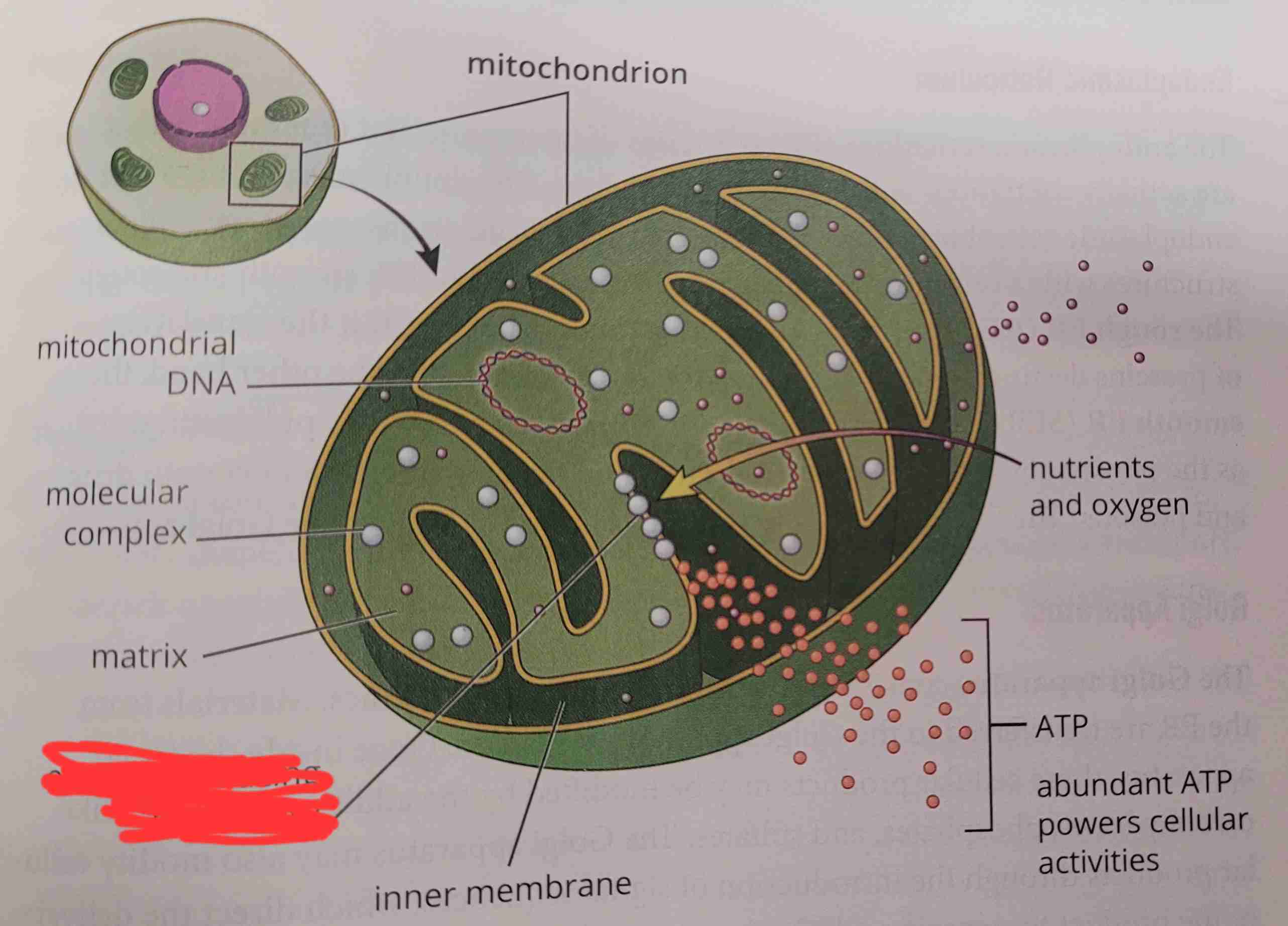
what is it
energy-producing machinery
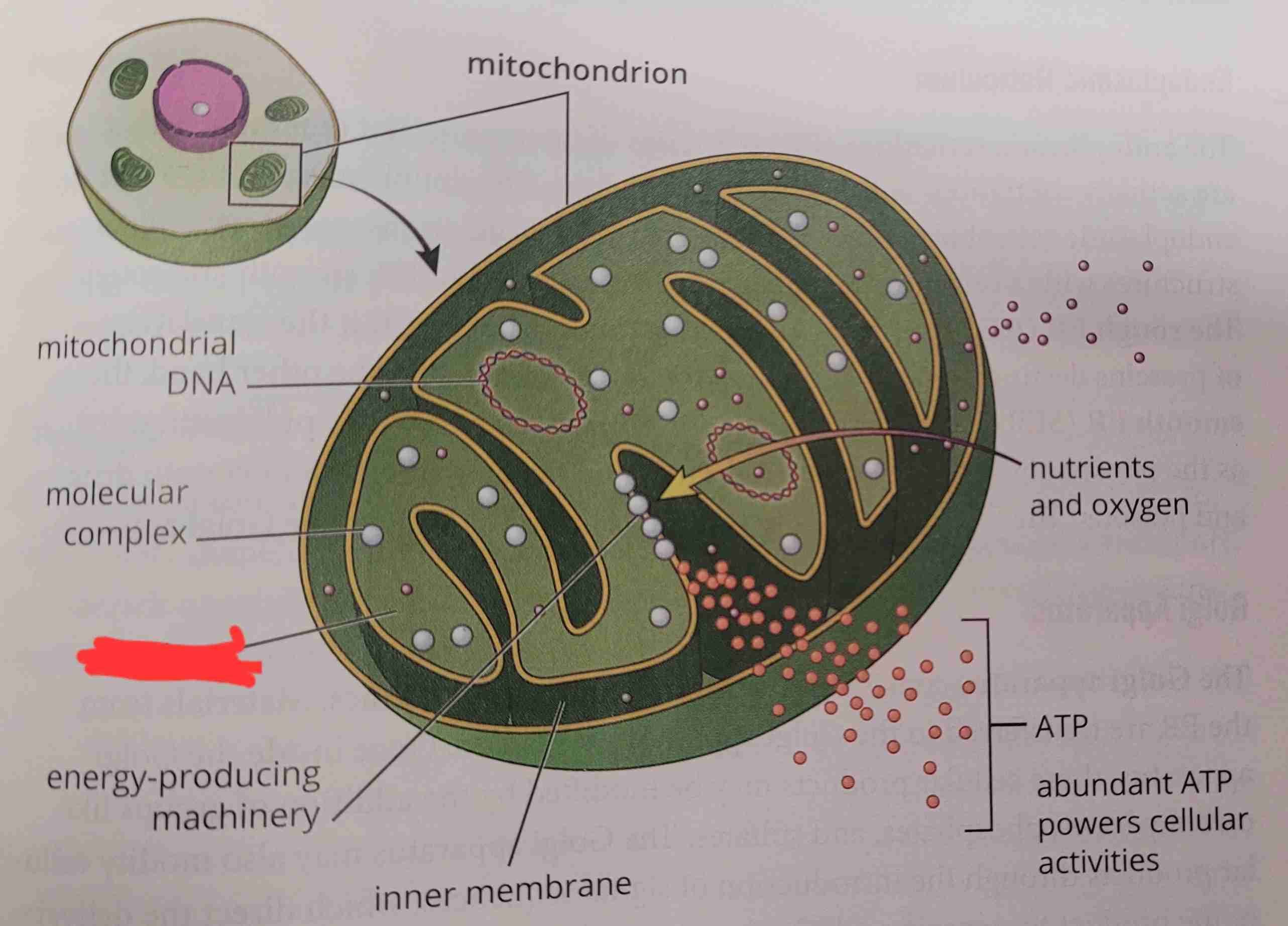
what is it
matrix
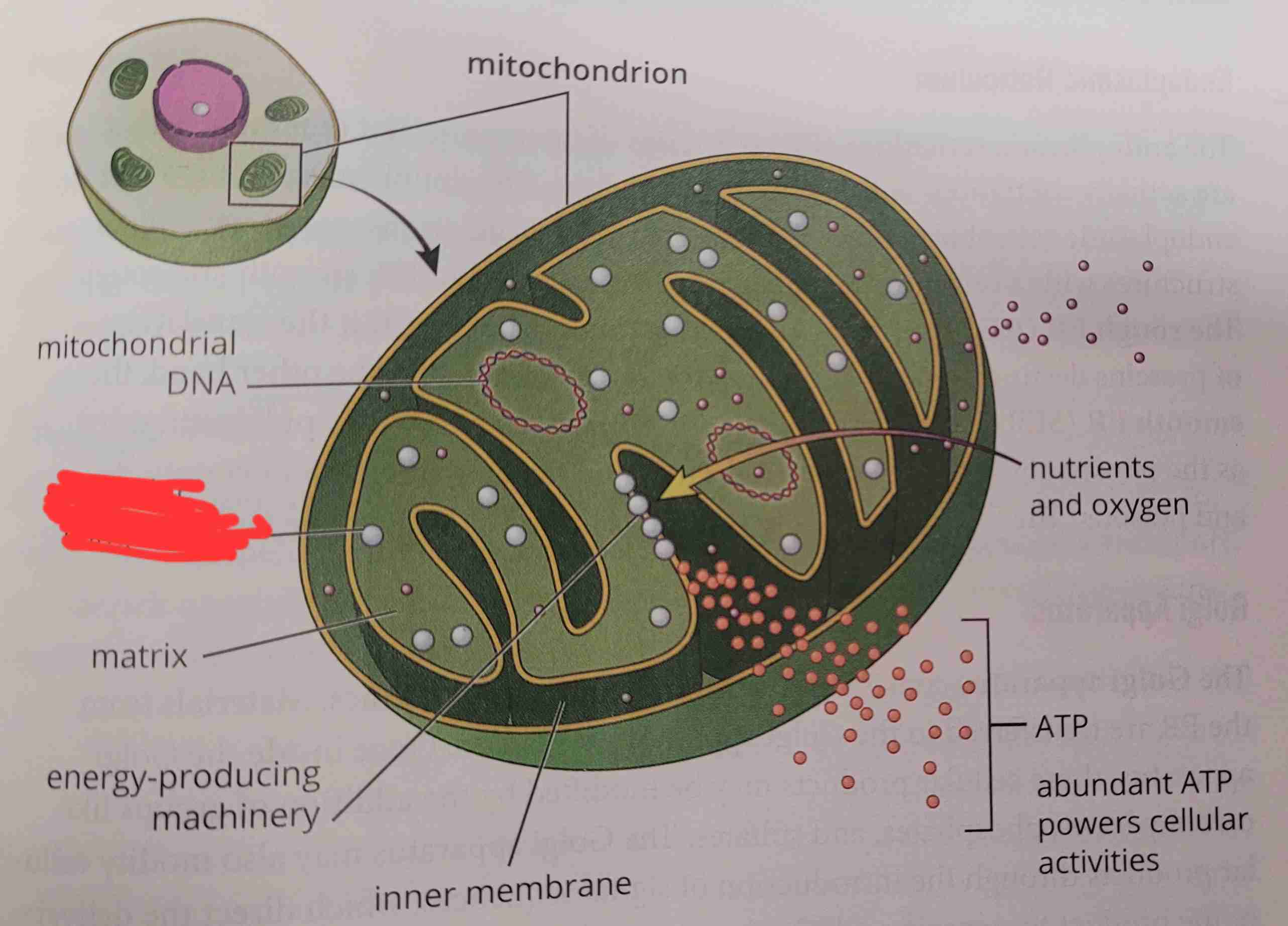
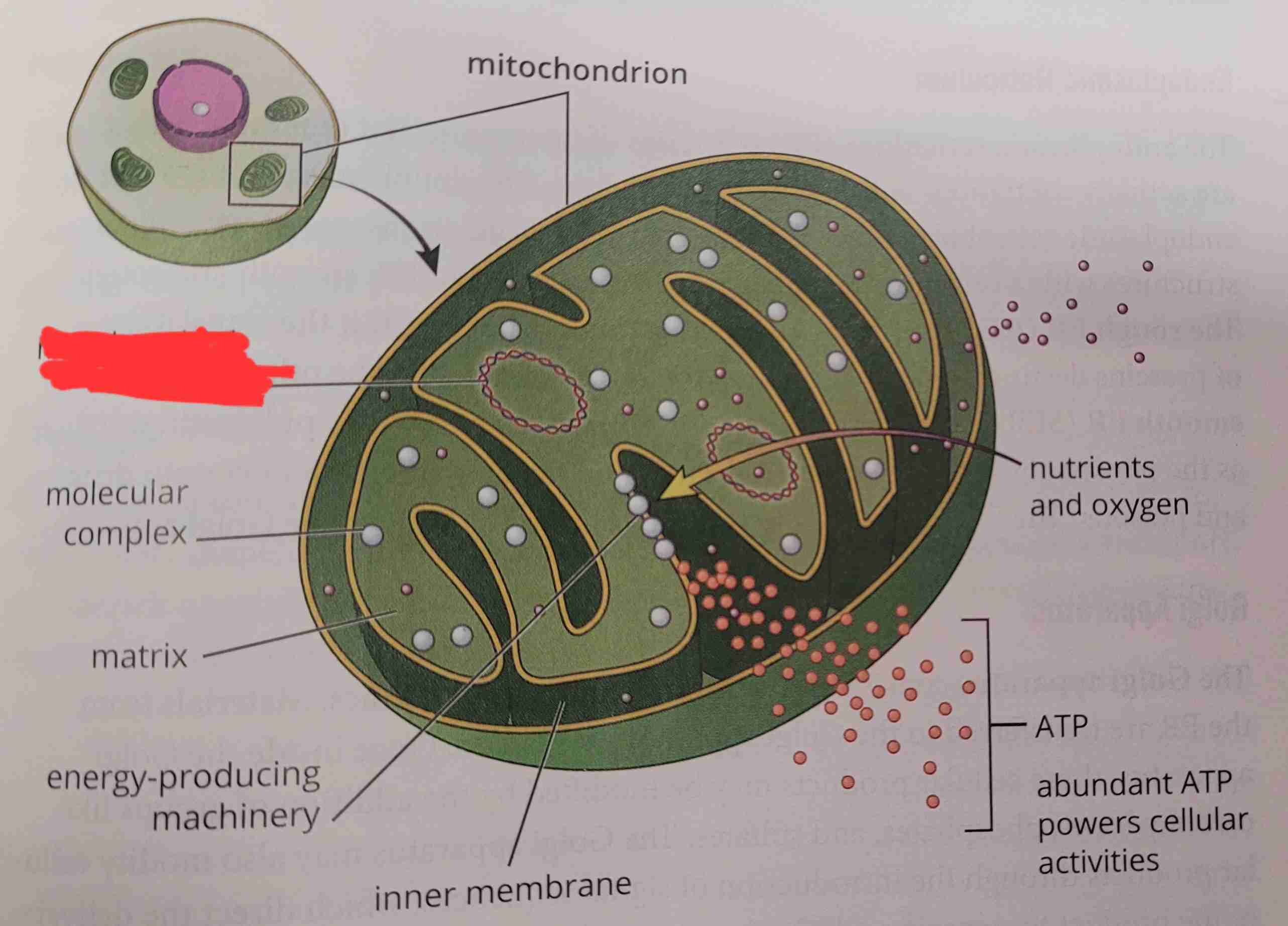
what is it
molecular complex
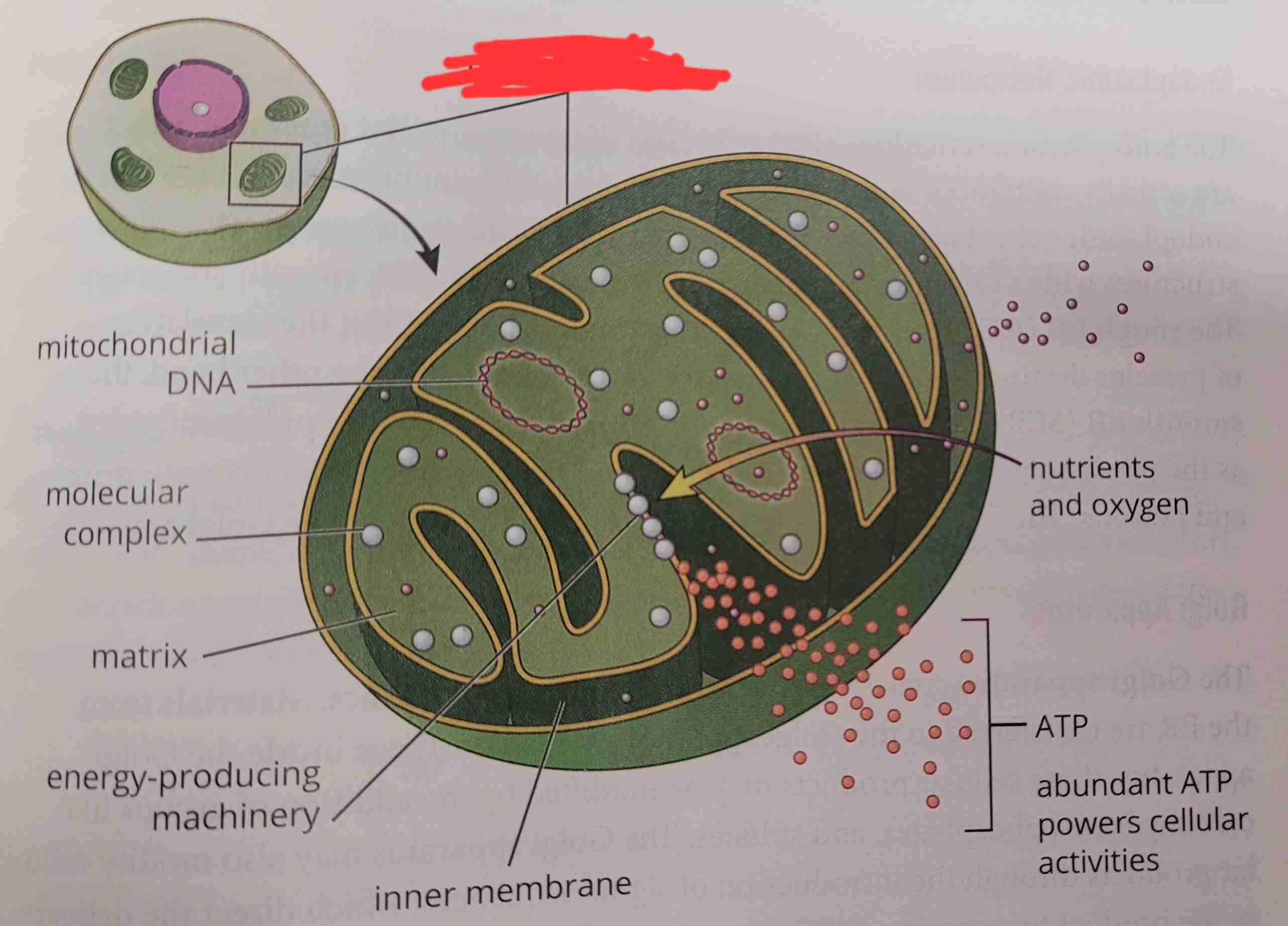
what is it
mitochondrial DNA
what is it
mitochondrion
what is cytoplasmic inheritance aka
extranuclear inheritance
what is cytoplasmic inheritance
the transmission of genetic material independent of the nucleus
what does the mitochondria do
keep the cell alive by providing energy
how do mitochondria cause apoptosis
by releasing enzymes from the electron transport chain
define invaginations
the action or process of being turned inside out or folded back on itself, to form a cavity or pouch
what are lysosomes
membrane bound structures containing hydrolytic enzymes that are also capable of breaking down many different substrates, including substances ingested by endocytosis and cellular waste products
endosomes do what
transport, package and sort cell material traveling to and from the membrane
lysosomes and endosomes do what
Endosomes are capable of transporting materials to the trans-golgi, to the cell membrane, or the lysosomal pathway for degradation. The lysosomal membrane sequesters these enzymes to prevent damage to the cell
what is autolysis and what does it cause
a process that releases enzymes that can cause damage, it causes apoptosis
True or False. All cells have the same relative distribution of organelles
False. NOT all cells have the same relative distribution of organelles. Form follows functions
What is the endoplasmic reticulum
a series of interconnected membranes that are actually contiguous with the nuclear envelope.
What are the 2 types of endoplasmic reticulum
smooth ER and rough ER
what is the rough ER (RER)
is studded with ribosomes, which permits the translation of proteins destined for secretion directly into its lumen
what is the smooth ER (SER) (3)
is utilized primarily for lipid synthesis and the detoxification of certain drugs and poisons. Also transports proteins from RER to the Golgi apparatus
what is the golgi apparatus
cellular products from the endoplasmic reticulum may be modified by the addition of groups like carbohydrates, phophates, and sulfates. It also can modify cellular products through the introduction of signal sequences, which direct the delivery of the product to a specific cellular location
when is exocytosis used
when the golgi apparatus directs a product for secretion, the secretory vesicle merges with the cell membrane and its contents are released via exocytosis
what is exocytosis
a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
what do peroxisomes do
breakdown very long cahin fatty acids via B-oxidation.
participation in the synthesis of phospholipids and contain some of the enzymes involved in pentose phophate pathway
what does the cytoskeleton do
provides structure to the cell and helps it to maintain its shape and is also a conduit for the transport of materials around the cell
what are the 3 components of cytoskeleton
microfialments
microtubules
intermediate filaments
what are microfilaments made up of
made up of solid polymerized rods of actin and resistant to compression and fracture, proving protection for the cell. The actin filaments can also use ATP to generate force for movement by interacting with myosin
whats myosin
a fibrous protein that forms (together with actin) the contractile filaments of muscle cells and is also involved in motion in other types of cells.
What do microfilaments do
play a role in cytokinesis'
cleavage furrow is made from microfilaments
what is cleavage furrow
the cleavage furrow is the indentation of the cell's surface that begins the progression of cleavage
what are microtubules made of
hollow polymers of tubulin proteins
what is the role of microtubules in cytoskeleton
provides the primary pathways along which motor proteins like kinesin and dynein carry vesicles
what is cilia
are projections from a cell that are primarily involved in the movement of materials along the surface of a cell
what is is cilia made of
microtubules
what is flagella made of
microtubules
what is flagella
structures involved in the movement of the cell itself
what are centrioles
they are organizing centers for microtubuls
where are centrioles found
in the centrosome
what are some intermediate filaments
keratin, desmin, vimentin, and lamins
what do intermediate filaments do (3)
many are involved in cell-cell adhesion
maintenance of overall integrity of cytoskeleton
help anchor other organelles
what are the 4 typyes of tissue
epithial tissue
cennective tissue
muscle tissue
nervous tissue
what is epithelial tissue (3)
covers the body and lines its cavities,
providing a means for protection against pathogen invasion and desiccation.
Are also involved in absorption, secretion, and sensation
what is basement membrane
the underlying layer of connective tissues that connects epithial cells that are tightly joined to each other
define parenchyma
the functional parts of the organ
what does it mean when epithial cells are polarized
one side faces a lumen or the outside world , while the other side interacts with underlying bood vessels and strucutal cells
how many layers of epithial cells does simple epithelia have
1
how many layers of epithial cells does stratified epithelia have
multiple layers
how many layers of epithial cells does pseudostratified epithelia have
appear to have multiple layers due to difference in height
what is the cuboidal shape of epithial cells
cube-shaped
what is the columnar shape of epithial cells
cells are long and thin
what is the squamous shape of epithial cells
cells are flat and scale-like
What is the connective tissue
supports body and provides framwork for epithial cells to carry ou their functions
main contributers to stroma ot support structure
most cells in connective tissues produce and secrete materials such as collagen and elastin to form the extracellular matrix
A child is diagnosed with an enzyme defiicency that prevents the production of hydrogen peroxide. What would the likley outcome be of such a deficiency
Peroxisomes are dependent on hydrogen peroxide for their function, so an enzyme deffiecincy that results in an inability to form hydrogen peroxide would likley result in an inability to digest very long chain fatty acids. These fatty acids would build in peroxisomes until they displaced cellular contents, ultimatly resulting in cell death
what are the 3 overarching somains
archea, bacteria, and euaryka
what are archaea creatures
single-celled organisms and have genes and metabolic pathways. They use alternative sources of energy
define extremophiles
most commonly isolated from harsh enviroments with extreme high temperature, high salinity, or no light
what are bacteria organisms
all bacteria contain a cell membrane and cytoplasm, while some have flagella or frimbae
define mutulistic symbiotes
both humans and bacteria benefit from the relationship
define pathogens/parasites
they provide no advantage or benefit to the host, but rather cause disease
what are the 3 shapes of bacteria
cocci, bacilli, and spirilli
what bacteria shape is cocci
spherical bacteria