2.4 - Motivation and Demotivation - Motivation Theories
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This unit is so long.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Motivation
The desire, effort, and passion to achieve something. The willingness to complete a task or job with intent and purpose
Generic Benefits of increased worker motivation
Higher staff morale and job satisfaction → higher productivity and quality
Better industrial relations → reduce the chance of conflict in workplace
Lower absenteeism → staff have incentives to turn up to work
Lower staff turnover → reduced cost of replacing staff
Improves corporate image → helps attract customers and potential employees
Higher profitability → from combining all the benefits above
Warning signs of poor motivation in the workplace
High absenteeism rate (% of workforce that miss work without valid reasons)
High labour turnover rate (number of staff who leave as a % of the total workforce, per year)
High wastage level (high % of defective output or substandard work)
High number of customer complaints (due to poorer quality output and lack of customer service
Low quality output (workers are more likely to make mistakes and care less about quality)
Poor punctuality (poor timekeeping and missed deadlines)
More disciplinary problems (corrective measures required to deal with less productive staff)
What are the motivation theories?
Taylor, Maslow, Herzberg, McClelland, Deci and Ryan, Equity and expectancy
Intrinsic Motivation
Motivation that is driven by an interest. Exists within the individual.
Ex: autonomy, belonging, curiosity, love, learning, mastery, meaning
Extrinsic Motivation
Comes from outside of an individual
Ex: badges, competition, fear of failure, fear of punishment, gold stars, money, points, rewards
Taylor’s Scientific Management (1911)
Essentially assumes that employees are primarily motivated by money and that productivity could be improved by setting output and efficiency targets related to pay
Promotes the use of division of labour (breaking down different parts of a job/task and assigning different people to each particular part of work
Advocated for the use of differentiated piecework where workers are paid normally if they reach the standard level of output, but then recieve a higher rate of pay, if they exceed the benchmark. He believed that workers should be scientifically selected for their jobs, based on their ability
How does Taylor (1911) work?
Managers plan the work using division of labour → Conduct a work study to identify the best way of completing the task → Train and develop each employee → Provide detailed instructions and supervision of each worker → Workers perform the work in a standardized fashion → Workers recieve payment based on their output (piece rates)
Criticisms of Taylor’s theory
Ignores the non-financial factors
Does not recognize that workers can be independent thinkers
Focus only on extrinsic motivation
Not always possible to measure the output of workers
Can lead to repetitive and monotonous tasks
Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs (1943)
Focuses on the emotional and mental (psychological) needs of workers as he believed people are motivated by more than just their pay. A person must be satisfied with their lower level before moving on to their higher level.
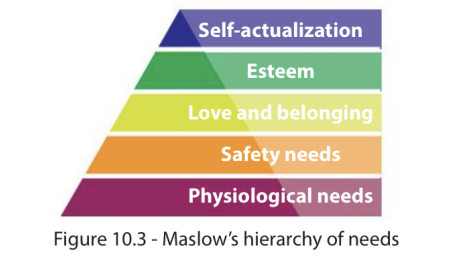
Physiological needs or basic needs
Examples: water, food, air, warmth, sleep
Safety needs
The demands necessary to make people feel safe and stable.
Ex: job security, sick pay, maternity leave, pension
Love and belonging
The human desire to be accepted as part of a friendship group or a family.
Ex: Opportunities to work as a team
Esteem needs
The desires for recognition and self-respect
Ex: Job titles, employee of the month
Self-actualization
The forces that drive people to become the best they can be
Criticisms of Maslow’s theory
Identification of which level workers are currently on the hierarchy is difficult
Assumes that all workers have the same five needs
Self-actualization needs are rarely permanently achieved
Some people may never be able to reach self-actualisation
Herzberg - 2-factor theory
Investigated the factors that cased satisfaction and disatisfaction at work.
Hygiene factor
Do not motivate but must be met to prevent dissatisfaction
Example: job security, organizational policies/rules/regulations, pay, physical security, good working conditions, coordination
Motivators
Factors that can lead to psychological growth of workers and hence increase satisfaction and performance at work
Example: achievement, recognition, responsibility, promotion, advancement, personal growth, interesting tasks
Criticisms of Herzberg’s theory
Hygiene factors can be taken for granted
Does not apply to low-skilled jobs as the study was limited to engineers and accountants
Employees may not want the extra responsibility and stress from having enriched/more demanding jobs
McLelland’s Acquired Needs Theory (1961)
Three types of needs must be satisfied to boost motivation and productivity
need for achievement (nAch)
need for affliation (nAff)
need for power (nPow)
_______ believed that all three are present, but the intensity varies
Need for Achievement (nAch)
_________ motivated people tend to be moderate risk takers. Prefer to work on tasks where they hold key responsibilities or work alongside high ________. More interested in personal success.
Should be given challenging but achievable tasks
Need for Power (nPow)
Power-motivated people like to influence the behaviour of others so tend to be very strong willed, either personal or institutional power. They use their authority to bring out the best in their team.
Should be given opportunities to manage and lead different teams of people
Need for Affiliation (nAff)
People who need _______ seek to have a good social and working relationship with colleagues and the senior management team. Tend to conform to group norms and avoid conflict. Prefer to favour opportunites for social interactions such as teamworking or customer relations
Should be given a cooperative and collaborative working environment to gain their best performance
Deci and Ryan’s self-determination theory (1985)
States that people can achieve intrinsic (autonomous) motivation when their needs of competence, autonomy, and relatedness are satisfied
Autonomy
The need or the drive to have control over what a person does. When completed, the person feels a sense of integrity and authenticity with their actions. When uncompleted, person feels frustrated and pressured in an unwanted direction
Competence
The need or drive to feel confident and competent in doing a particular task or job role. Can be achieved through providing and developing opportunities to use and extend people’s skills and expertise. When this need is not met, the person experiences a sense of ineffectiveness, vulnerability, and failure.
Relatedness
Refers to the need to interact, be connected to, and experience caring for others. This is satisfied when people develop meaningful relationships and inteactions with others. If not met, people feel socially alienated, excluded and lonely, which then have an impact on motivation and productivity.
John Stacey Adams - Equity Theory (1963)
The key premise of the theory is that workers will be motivated if they percieve that there is equity between themselves and relevant others.
People need to feel that there is a fair balance between their contributions and rewards in comparison to relevant others
Individuals seek a fair balance between what we put into our job (input/contributions) and what we get out of it in return (outputs/benefits)
Workers will only be motivated if their input to output ratio is deemed to be equitable in relation to that of others in the workplace. If they feel that they are not being fairly rewarded, they will seek to redress the balance
Equity
Percieved fairness or making adjustments to imbalances
Inputs/Contributions according to the Equity theory
Effort
Performance
Loyalty
Commitment
Skill
Outputs/Rewards according to the Equity theory
Pay
Recognition
Reputation
Status
Praise
Training
Opportunities
Promotion
Vroom’s Expectancy Theory (1964)
States that a person’s motivation is determined by:
The individual’s assessment of the likelihood that the effort will lead to expected performance (Expectancy)
The belief that the performance will lead to reward (Instrumentality)
How much an individual wants a reward (Valence)
Vroom believes that if any of the factors are low, workers will be demotivated.
Motivation =
Expectancy x Instrumentality x Valence
The higher the number, the more motivated employees are likely to be.
How can workers be motivated according to Vroom’s Expectancy Theory?
Expectancy - Setting goals/targets that employees believe are achieveable
Instrumentality - Following through on promises
Valence - Offering a reward that is valued by the employees
Criticism of Vroom’s Expectancy Theory
It does not provide any specific suggestions on how to motivate employees
Labour Turnover
The number of workers leaving a company per year as a percentage of the average number of workers employed during that period of time

Acronym of why people leave their job
Challenge
Location
Advancement
Money
Pride
Job Security
CLAMPS
Impact of high labour turnover
Loss of experience
Damage to morale
Diminished customer service
Increased costs
Decreased productivity
Difficulty attracting talent
Added stress
Key causes of high labour turnover
Recruitment of workers who are not the right fit for the job
Lack of recognition for job performance
Poor relationships with co-worker
Dangerous work environment
Unchallenged by the work itself
Lack of promotion opportunities
Poor relationship with managers
Poor pay
Nature of the work itself
Why do firms recruit?
Expansion - more workers required
Change - new workers are required with different skills
Replace workers who have left the organisation
Replacing workers who have been promoted
Job Analysis
The process of determining the need to hire workers to verify
the roles and responsibilities of the job
the skills, qualifications, and attributes needed
the rewards needed to attract the right candidates
→ From this ______, the job description and person specification are drawn up
Job Description
Document drawn up to include details about a job
Job title
Working Hours
Duties and responsibilities
Pay
Line Manager
Person Specification
Identifies the characteristics needed of the person to do the job
Could include:
Qualifications
Experience
Skills
Personal Qualities
How are jobs advertised?
Newspaper advertising
Specialist trade publications
Posters/notices
Website/social media
Recruitment websites
Employment agencies
Job centres
University Fairs
Head hunters
Employee referals
How would jobs receive applications?
Either through Application Form or CV/Resume or Covering Letter
Application Form
A standardised document produced by the business for selecting appropriate job applicants
Curriculum Vitae (CV)
Document outlining an applicant’s education, employment history, skills, and professional qualifications
Cover Letter
Introductory letter written by the applicant, stating which position is being applied for and why the applicant should be considered for the job
Shortlisting
Involves reviewing the applications against the person specification and selecting the best ones to take through to the next stage
Job Interview
Conversation which occurs between a potential employer and a job applicant. Can be carried out through telephone, video conferencing, or face-to-face
Purpose of interviews
To find out more information about the candidate
To see if the candidate will fit in with the company culture
To assess if the candidate has the personal qualities needed to do the job
What tests may be required?
Psychometric Tests
Aptitude Tests
Skills Tests
Intelligence Tests
Assessment Centres
Some companies invite candidates in for whole days of assessment activities along with other candidates
References
Written statements about an applicant from an independent source, usually the current or previous employer
Referees
The people who write employment references, may be asked to confirm the strengths and suitability of an applicant
Internal Recruitment
Refers to the filling of job vacancies from within the business
Existing employees are selected rather than employing someone from outside
External Recruitment
Refers to the filling of job vacancies with candidates from outside the business
Advantages of Internal Recruitment
Cost effective - cheaper and quicker to recruit from within the organisation as suitable candidates may be readily available
Less down-time - internal candidates are already familiar with how the business operates and workplace culture
Less risk - recruiting internally might ensure that the job is filled with a more suitable candidate
Motivational - internal recruitment can serve as a form of motivation as it is an opportunity for promotion. it can create employee loyalty and commitment to the business
Disadvantages of internal recruitment
Fewer applicants - limits the number of potential applicants that could possibly be better
Less creativity - new applicants could bring in new ideas to the business
Time consuming - hiring an internal candidate leads to another vacancy within the organisation needing to be filled
Internal politics - resentment and conflict could arise amongst workers who didn’t get the job
Advantages of external recruitment
More creativity - people hired from outside of the organization can bring in new ideas and creative ways of thinking. Can bring in new insights as to how a rival business could have done it
Wider range of experiences - external recruits might be more qualified or more suitable than the internal candidates.
Larger pool of applicants - increased chance of finding their ideal person for the job
Disadvantages of external recruitment
Greater degree of uncertainty - managers take a risk when hiring external recruits as they don’t really know the candidate, they might not even fit in the corporate culture
Time consuming - the lengthy process of advertising, shortlisting, interviewing and checking reference takes up time
Expensive - expensive to advertise and opportunity cost of management time during the recruitment process
Training
The process of increasing the knowledge and skills of an employee for doing a particular job. It seeks to improve the job performance and work behaviour of those trained
Reasons to train employees
To introduce new staff to the business
To provide workers with the skills to do their jobs
To create a flexible workforce
To attract good quality applicants
To provide workers with increased opportunities for personal growth
To improve worker’s skills and knowledge to make them more efficient
To prepare staff for changes
To prepare workers for promotion
Induction training
Type of training aimed at introducing new employees to the organization
Purpose is to help new recruits feel confident and supported in their new job
Ensures that new employees are familiar with the procedures or codes of behaviour required to carry out their duties
Can also help new recruits to integrate into the corporate culture of the organization
Typical Induction Training Activities
Information about the firm - History, Mission and vision, how it is organised
Tour of site to help workers find their way around
Conditions of employment explained
Health and safety and fire training
Introduced to new colleagues and key personnel
Learning about the role of the job
Training in the skills required to do the job
Advantages of induction training
Establishes clear expectations and good working habits from the start
Helps new recruits to understand the corporate culture of the organisation
By settling in quicker, new recruits can contribute to the organization more promptly
Morale is boosted as new staff feel welcome and are more confident + competent in their new jobs
Disadvantages of induction training
Planning, delivering, and overseeing an _____ can be time consuming
Trainers cannot carry out their other duties as they are involved in providing induction
Information overload is counter-productive for new staff who have to absorb so much information
The length of ____ programmes can be very long, especially in large and disparate organizations
On-the-job training
Training that is carried out whilst in the immediate workplace
Often delivered by a more experience or senior member of staff
Often involves “Learning by doing”
Could include: demonstrating, instruction, shadowing, monitoring, mentoring/coaching
Advantages of on-the-job training
Can be relatively cheap as the firm uses in-house specialists to run and facilitate the training
Relevant as the training targeted at issues directly to firm’s needs
Fewer disruptions to the firm’s daily operations
Can help to develop professional relationships and collegiality at work since team working is involved
The location is convenient for workers and trainers, they don’t have to go off-site
Disadvantages of on-the-job training
Trainees may pick up bad working practices from the trainer
Internal trainers may lack the most up-to-date training experience and skills
Trainers will not be able to do their own work whilst facilitating the training. Means _____ training can be more expensive than expected
Labour productivity is intially lower as workers undergo the process of learning new skills and need time to develop
Off-the-job training
Training carried out, away from the immediate workplace. Can either be delivered by internal trainers or outsourced providers. Can take place on-site or at outside conference/training centres
Workers sometimes may take time away from their jobs to complete the training, or may do it in their own time. May be asked to cascade what they learnt to other colleagues
Can be face-to-face, online synchronous, or online self-pace
Can include:
Classroom lectures/discussions
Audio-Visual
Simulations
Case Studies
Role playing
Assignments
Advantages of off-the-job training
Experts are used to provide the training
Wide range of training courses can be provided
There are no distractions from colleagues and workers as the training is usually conducted off-site
Networking can take place
Morale is boosted as new staff feel welcome and are more confident + competent in their new job roles
Disadvantages of off-the-job training
Potential loss of productivity
Hiring a suitable venue and specialist trainers can be very expensive, especially with transportation and accommodation costs
It is debateable whether all the skills and knowledge learnt are relevent and therefore transferable to the organisation
Finding the time for staff to cascade the information and knowledge from the training course can be difficult
The length of an induction programme can be very long
Appraisal
Formal assessment of an employee’s performance in fulfilling their job based on the tasks and responsibilities set out in their job description
Usually carried out in annual cycles
Often carried out by line managers for their subordinates
Appraisal meetings take place at points throughout the cycle
A written record is usually kept
Can also be referred to as Performance Management
Aims of Appraisals
To improve performance by setting “stretching” goals
To give opportunity to provide feedback
As the basis for bonus/pay increases
To identify performance gaps
To identify training/development needs
To identify candidates for promotion/demotion
Appraisal Meetings
Take place with an employee and their line manager
Might take place at the beginning during a cycle (formative) and at the end of a cycle (summative)
Discussion Points
Review previous performance (strengths and weaknesses)
Target setting
Support needs
Planning strategies
Progress review
Appraisal Documentation
Businesses often design their own bespoke templates to accompany their appraisal process
Actions following an unsatisfactory summative appraisal
Issue an advisory letter
Provide advice/support/training
Closer monitoring
Dismissal (eventually if needed)
Appraisal Methods
Formative
Summative
360º Feedback
Self Appraisal
Formative Appraisal
Aim is to provide feedback on their performance
Aim to:
monitor the learning and performance of employees
help employees identify their strengths and weaknesses
help managers to recognise areas where staff are struggling to provide coaching/mentoring/training in order to help employees improve
Generally low stakes and supportive
Summative Appraisal
Aim is to evaluate/judge employee performance at the end of an appraisal cycle by comparing it against set goals or standards
Often a written summary of the workers acheivements/performance
May include some recommendations for improvements
Can be used to inform decisions regarding progression and pay rise
Often high stakes, with rewards or sanctions based on the results
Self Appraisal
Involves employees appraising themselves based on a set of pre-determined criteria
Employees are expected to be honest about their strengths and weaknesses
They also need to set realistic targets for improvement
This then may be compared with their line managers assessment of their performance as a basis for discussion
360º Feedback
A process through which feedback is collected from an employee’s subordinates, colleagues, supervisor(s), or even suppliers/customers
Opinions and feedback comments about the employee’s performance are usually obtained by the use of questionnaires or interviews
Advantage of appraisals
Used to set targets, leading to positive changes and professional development of employees
Allow managers to objectively praise staff on their strengths and for their contributions in the workplace
Managers can use ______ to provide constructive feedback to employees, which enables staff to focus on areas for improvement
Can be a useful way of getting valuable feedback from employees to help the organization adapt and improve
Managers often aggregate the findings of _____ to identify common strengths and areas in need of development. Allows training and development needs to be better planned for the organization
Can be used as part of the process to determine levels of pay. Can be done by looking at different tasks, responsibilities, skills, qualifications, and challenges. Allows the business to objectively reward more demanding roles with higher rates of pay
Disadvantages of appraisals
Time consuming to conduct properly, so are costly
Confidential feedback must be given and follow-up action requires funding and monitoring if the process is purposeful
Can be rather subjective as perceptions and relationships at work can interfere with the process
Employees may get offended by some of the feedback comments, especially about weakenesses
Many appraisers lack the skills, experience or confidence to carry out appraisals effectively. Diminishes the credibility of the process and the feedback
Employees can experience unnecessary anxiety and stress if the appraisal process is directly linked to pay
Salary
Financial rewards set at a fixed annual rate but paid on a regular basis.
Wages - Time rates
Determined based on per hour, per week or per month
Wages - Piece rates
Paid based on output
Commission
Workers are paid based on a % proportion of the sales that they make. They often receive a basic salary in addition to ensure their physiological needs are met
Profit related pay
The situation in which the pay of employees is related to the profit made by the employer.
Higher profit = Higher Pay
Performance related pay
Financial reward for workers based on personal performance
Employee Share ownership Schemes
Workers, managers, directors are either given shares in the company or sold then at discounted rates. This enables them to have a direct stake in the success of the business
Fringe Benefits
Benefits with financial value Eg. gym memberships, insurance
Job enrichment
Motivational technique that occurs when a job is given additional tasks that are challenging and are usually done by managers. Hence workers have greater autonomy and authority and more interesting work
Job rotation
When employees are regularly rotated into different positions in an organisation, which allows the employees to gain experience and acquire new skills.
Job enlargement
Technique of job design whereby many tasks associated with a job are officially added to the job description. The additional tasks are horizontal in terms of skill and difficulty level.
Empowerment
Involves granting workers the authority to be in charge of their own jobs and to execute their own ideas to solve business problems. Hence, workers have some autonomy in decision-making so can decide for themselves the best way to deal with a task or issue.
(Non Financial Reward)
Purpose/Opportunity to make a difference
Some employees are altruistic and see the purpose of work being to make a positive change in other people’s lives.
Examples of jobs where there is an opportunity to make a difference might be teachers, nurses, doctors, social workers, charity workers etc.
(Non Financial Reward)
Teamwork
Involves organising the business in a way that allows employees to work collaboratively with each other and feel a sense of belonging within a group