Electric fields questions
1/23
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
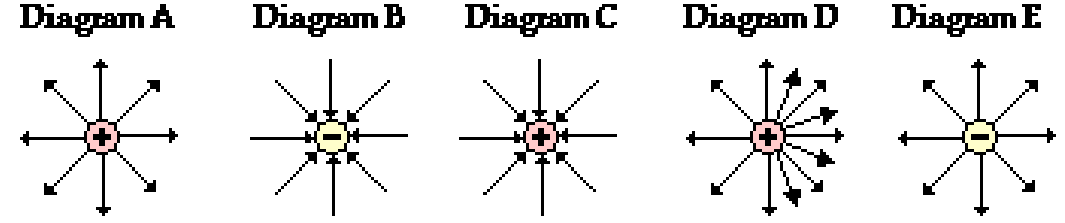
Which of these electric field lines is incorrect and why?
C, D and E
In C, the lines are directed towards a positively charged object.
In D, the lines are not symmetrically positioned, despite the fact that the object is a symmetrical sphere.
In E, the lines are directed away from a negative charge.

What is wrong with this diagram?
Electric field lines should never intersect each other. They cross here.
From the diagram, it is apparent that object A is ____ and object B is ____ (what charge do they have?)
a) + +
b) - -
c) + -
d) - +
D - Electric field lines are directed towards object A so object A must be negative. They are directed away from object B so object B must be positive
a) Sketch the field lines between two oppositely
charged parallel plates.
b) E = F/Q but E = V/d for parallel plates. You need to do work to move an electron from the positive to negative side. Can you derive E = V/d from E = F/Q?
a) shown in diagram
b) F = QE
Move a charge from positive to negative
W = F x d = QEd
V = W/Q = QEd/Q = Ed
So E = V/d
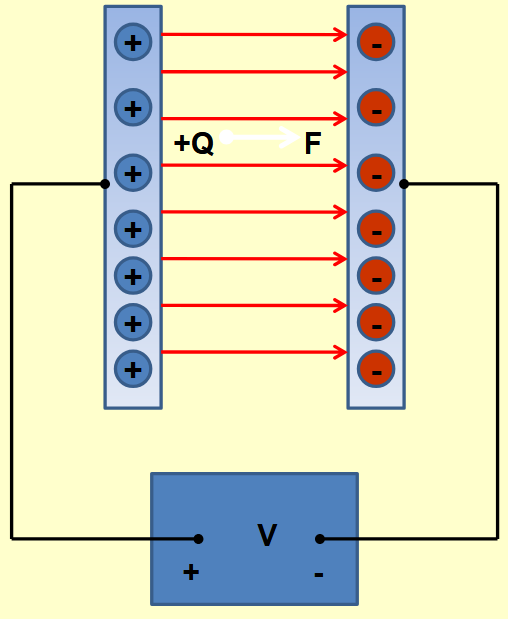

E = V/d and E = F/Q
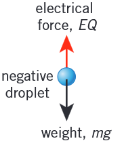
A tiny negatively charged oil drop is held stationary in an electric field between two horizontal parallel plated as shown. The mass of the oil drop is 2.5x10-10 kg.
(a) Draw a labelled free-body force diagram for the drop.
(b) Why is it stationary?
(c) What is the charge on the oil drop?
a) The force acting downwards is the weight. The upwards force is the force of electrostatic attraction
b) The two forces are in equilibrium; weight = electric force; W = Fe
c) E = V/d = 3000 V / 0.025 m = 1.2x105 Vm-1 (or NC-1)
E = F/Q so Q = Fe/E and as Fe = W = mg
Q = (2.5x10-10 kg x 9.81 N kg-1) / 120 000 N C-1 = 2.04x10-14 C
Draw a sketch of the electric field lines around point positive and a point negative charge adjacent to each other

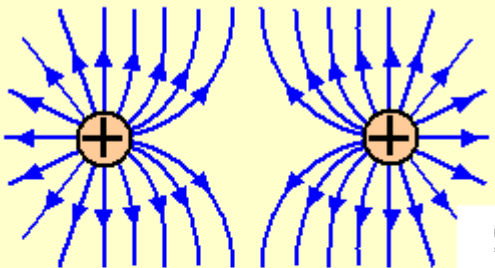
Draw a sketch of the electric field lines around two adjacent positive charges
Draw a sketch of the electric field lines between a point positive charge and a plate of negative charge
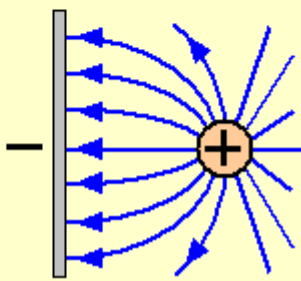
Draw a sketch of the electric field lines between two parallel plates charged positively and negatively

What are equipotential lines?
A line of points that all have the same electric potential
Often shown as a dashed line
Are perpendicular to electric field lines
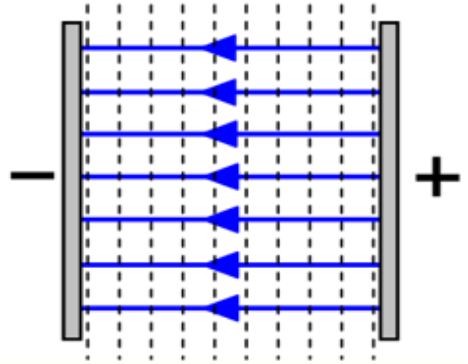
How are electric field lines and equipotential lines geometrically related?
Electric field lines run perpendicular to equipotential lines
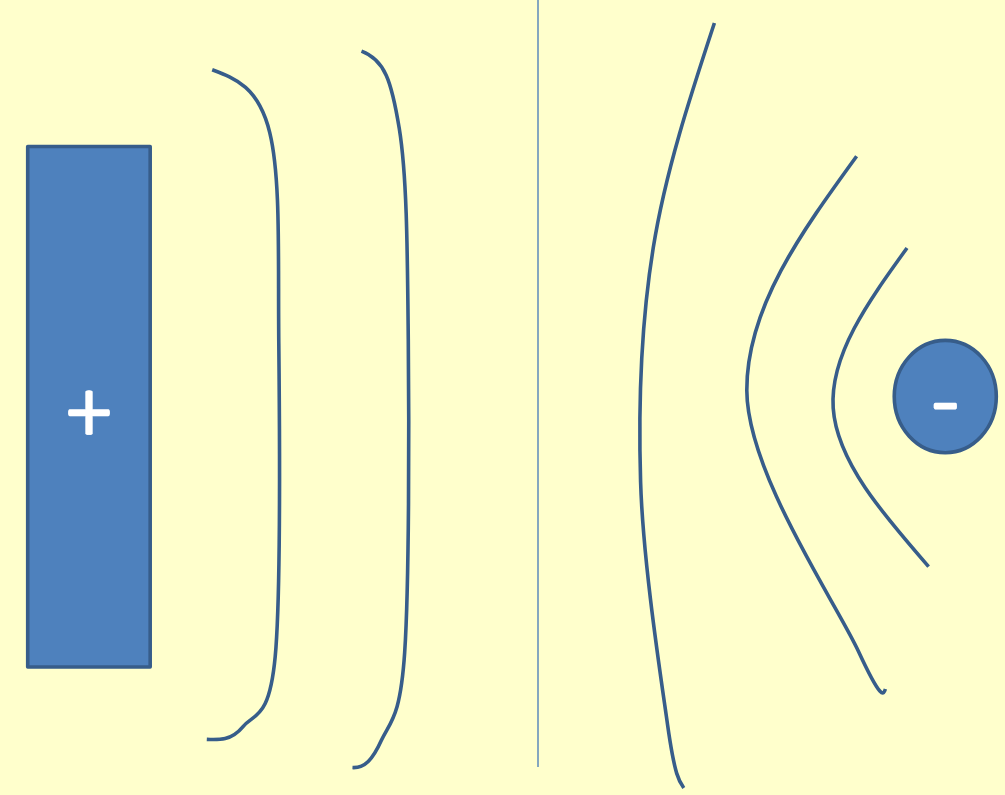
The image shows some equipotential lines. What would the field lines be?


Plot a sketch of how the potential (V) changes as the distance (d) increases from the negative plate (0V) to the positive plate.
How does this graph show that E is constant?
Graph shown in image
E = ∆V/∆d = gradient. Gradient is constant so E is constant.

Draw the equipotential lines for a radial field around a positive charge?
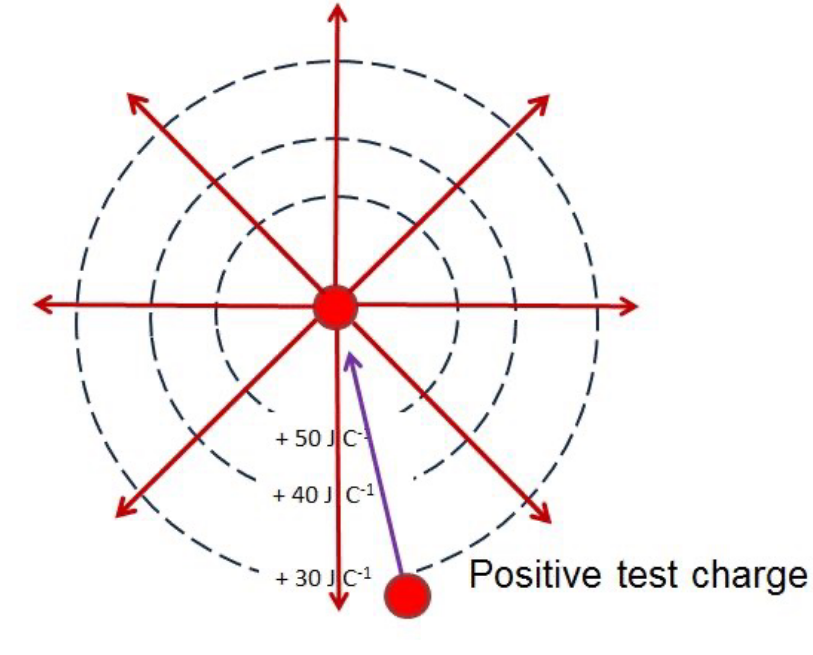
Why do the equipotentials become further apart as you move away from the centre of a radial fields?
The force of repulsion between two positive charges decreases as their separation, r, increases.
Work done = Force x displacement = F ∆r
The work done between equipotentials is constant, so as F decreases, ∆r increases.

Two metal spheres are touching. They are on insulating bases. Draw diagrams to show the charges within the spheres when…
a. A negatively charged balloon is brought close to sphere A.
b. While the balloon is near A, A and B are separated.
c. Describe the processes.


Two metal spheres are touching. They are on insulating bases. Draw diagrams to show the charges within the spheres when…
a. A positively charged balloon is brought close to sphere A.
b. While the balloon is near A, A and B are separated.
c. Describe the processes.


A carbon coated ball hangs freely between two parallel plates connected to a high potential difference.
The ball is pulled across so that it touches one of the plates and is then released.
The ball bounces between the two plates.
a. Describe the electric field within the plates.
b. What happens when you touch the ball to one plate?
c. Explain how and why the ball moves? Ignore the weight of the ball.
d. What happens at the other plate?
Uniform electric field between plates
When the ball touches the a plate, charge is transferred from plate to ball
Ball is repelled from plate it touches and attracted to opposite plate
Ball accelerates to the other plate. Uniform field so constant force -> constant acceleration (F=ma).

A carbon coated ball hangs freely between two parallel plates connected to a high potential difference.
The ball is pulled across so that it touches one of the plates and is then released.
The ball bounces between the two plates.
The sketch shows the velocity, v, of the ball against time, t, from when it leaves one plate and returns to the same plate.
a. Describe the motion of the ball in each region of the graph
b. Why is there a change in speed?
a:
Constant/uniform acceleration
Changes direction at “vertical” +/- line
Constant/uniform acceleration in opposite direction. Initial velocity of smaller magnitude
b:
Ball accelerates to the other plate. Uniform field so constant force -> constant acceleration (F=ma).
Inelastic collision - less energy after impact
What force will an electron feel in the field of an X-ray machine with strength 4.5 x 105 Vm-1?
E = F/Q
F = EQ = 4.5x105 x 1.6x10-19 = 7.2x10-14 N
An X-ray machine has a potential difference of 45,000 V between anode and cathode which are 10 cm apart. What is the field strength between these plates?
E = V/d = 45000/0.1 = 4.5x105 Vm-1
In a X-ray machine with field strength 4.5 × 105 Vm-1, how fast will the electron be travelling if the field accelerates it from rest and it is within the field for a distance of 10 cm?
KE = QV = ½ mv2 and E = V/d
Thus v = √(2EQd/m)
v2 = (2 × 4.5×105 × 1.90×10-19 × 0.1)/9.11×10-31
v = 1.26 x 108 ms-1
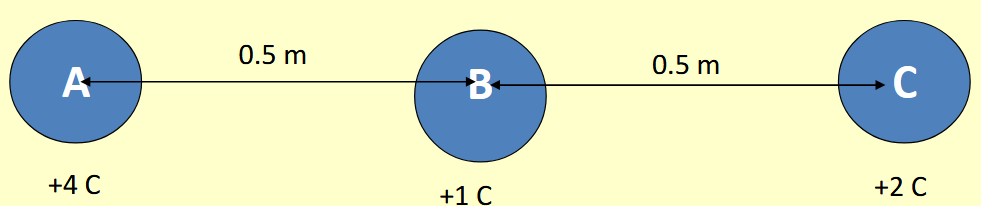
a) The charges A, B and C are spaced apart as shown. Determine the resultant force on B. What assumption do we make about the radius of the charges?
b) How would your answer change if A was negative and B and C were both still positive ?
To be completed
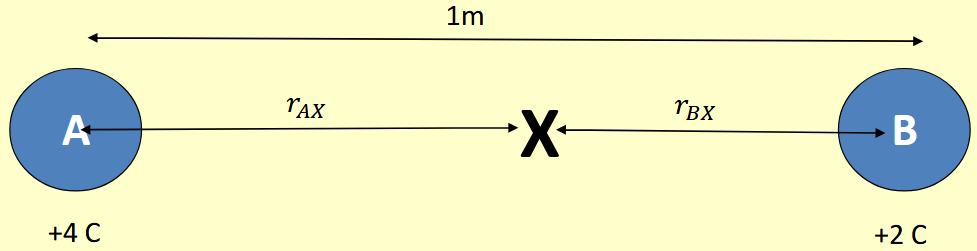
There is a point X between the two charges shown where the electric field strength is zero. How far is X from A if the two charges are placed 1m apart.
𝐸𝐴𝑋 = 𝐸𝐵𝑋
4 / (rAX2 × 4 𝜋 𝜀𝑜) = 2 / (rBX2 × 4 𝜋 𝜀𝑜)
4 𝜋 𝜀𝑜 cancels on both sides
4 / rAX2 = 2 / rBX2
𝑟𝐴𝑋 + 𝑟𝐵𝑋 = 1 so 𝑟𝐵𝑋 = ( 1 − 𝑟𝐴𝑋 ). Dubstitute this in the above equation:
4 / rAX2 = 2 / (1-rAX)2
Square root everything (could expand but that is more difficult):
2 / rAX = √(2) / (1-rAX)
2 (1-rAX) = √(2) ×rAX
Rearrange to get rAX = 2 - √(2) ≈ 0.59 m