Psychoanalytic Perspective
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:52 PM on 3/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
Personality Psychology
The scientific study of the __whole person__
* Defined as an individual’s unique, relatively consistent pattern of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors
* Defined as an individual’s unique, relatively consistent pattern of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors
2
New cards
Sigmund Freud
The father of psychoanalysis
* One of the most influential and controversial minds of the 20th century
* One of the most influential and controversial minds of the 20th century
3
New cards
Psychoanalytic Theories
Sigmund Freud developed theory of personality development, human behavior and experience are determined by forces out of our control that we are not aware of
* The iceberg
* The iceberg
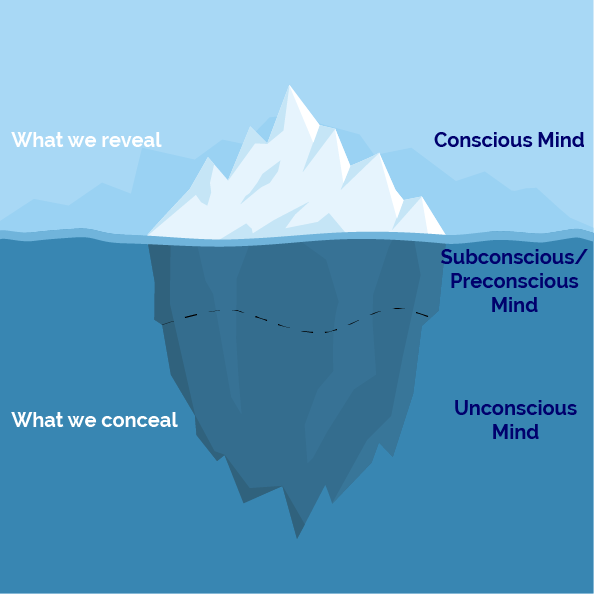
4
New cards
Unconscious
A reservoir of mostly unacceptable thoughts, wishes, and memories
* Our biological drives, instincts, and urges
* Some of these we temporarily store in a precocious area to conscious awareness
* Our biological drives, instincts, and urges
* Some of these we temporarily store in a precocious area to conscious awareness
5
New cards
ID
Part of the human personality that is made up of all our inborn biological urges that seeks out immediate gratification
* Exists at birth and contains our instincts and energy
* Operates on the __pleasure principle__
* Exists at birth and contains our instincts and energy
* Operates on the __pleasure principle__

6
New cards
Pleasure principle
The need to act for instant gratification
7
New cards
Ego
The largely conscious, “executive” part of the personality that mediates between the id, superego, and reality
* Operates on the __reality principle__
* Contains our partially conscious thoughts
* Operates on the __reality principle__
* Contains our partially conscious thoughts

8
New cards
Reality principle
The need to satisfy the id’s desires in ways that will realistically bring pleasure rather than pain
9
New cards
Super-ego
The part of the personality that represents internalized ideals and is our conscience + standards for future aspirations
* Operates on the __morality principle__
* Appears around age 4-5
* Operates on the __morality principle__
* Appears around age 4-5

10
New cards
Morality principle
Our need to comply with parental and other authority figures
11
New cards
Psychosexual Stages
The childhood stages of development (oral, anal, phallic, latency, genital) where the Id’s pleasure seeking energies focus on distinct erogenous zones
* Freud believed that personality formed in the first few years of life
* Sexuality meant *anything* that brought pleasire
* Freud believed that personality formed in the first few years of life
* Sexuality meant *anything* that brought pleasire
12
New cards
Oedipus Complex
Freud -- A boy’s sexual desire towards his mother and feelings of jealously and hatred for the rival father
* Comes from the phallic stage
* Children will eventually cope w/ these feelings by repressing them and becoming like the rival father (identification)
* Comes from the phallic stage
* Children will eventually cope w/ these feelings by repressing them and becoming like the rival father (identification)
13
New cards
Identification
Freud -- The process children incorporate their same sex parents’ values into their developing superegos
* The baseline for what we know as __gender identity__ now
* The baseline for what we know as __gender identity__ now
14
New cards
Fixation
Freud -- A lingering focus on pleasure-seeking energies at an earlier psychosexual stage, where conflicts were unresolved
* Makes the energy occur to adulthood
* Can also result from trauma
* Makes the energy occur to adulthood
* Can also result from trauma
15
New cards
Psychoanalysis
Freud’s techniques in treating psychological disorders by seeking to expose and interpret unconscious tensions
16
New cards
Free Association
In psychoanalysis, a method of exploring the unconscious in which where the person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind
17
New cards
Freudian Slip
When we say the wrong association out loud, and to Freud, it’s the truth resurfacing
18
New cards
Interpretation of Dreams
Freud analyzed dreams, and viewed dreams as significant hidden material
* The manifest content is what we remember in a dream
* Latent content is what we don’t remember in a dream, and what Freud was interested in
* The manifest content is what we remember in a dream
* Latent content is what we don’t remember in a dream, and what Freud was interested in
19
New cards
Defense Mechanisms
Freud -- Proposed that the ego protects itself w/ tactics to reduce or redirect anxiety by distorting reality
* Thought to safeguard the mind against feelings and thoughts to difficult to cope with
* Thought to safeguard the mind against feelings and thoughts to difficult to cope with
20
New cards
Repression
Acts to keep information out of conscious awareness
* Thought these memories, feeling, or desires come out through dreams and Freudian slips
* Thought these memories, feeling, or desires come out through dreams and Freudian slips
21
New cards
Displacement
Involves taking out our frustration, feelings, and impulses on other people and objects that are less threatening
* Involves letting out our feelings and moving it to another entity
* Involves letting out our feelings and moving it to another entity
22
New cards
Projection
Involves taking our own unacceptable qualities or feelings and ascribing the to other people
* Allowing the expression of the desire/impulse, but in the way the ego does not recognize, therefore reducing anxiety
* Allowing the expression of the desire/impulse, but in the way the ego does not recognize, therefore reducing anxiety
23
New cards
Regression
When confronted by stressful events, people sometimes abandon coping strategies and revert to patterns from childhood / earlier years
* Act out the behaviors of the stage they’re fixated in
* Act out the behaviors of the stage they’re fixated in
24
New cards
Denial
Functions to protect the ego from things with which the individual cannot cope
* Outright refusal to admit or recognize something
* Outright refusal to admit or recognize something
25
New cards
Rationalization
Involves explaining / justifying an unacceptable behavior or feeling in a rational manner, avoiding the true reasons for the behavior
* Protects anxiety, self-esteem, and self-concept
* Protects anxiety, self-esteem, and self-concept
26
New cards
Reaction-Formation
Reduces anxiety by taking up the opposite feeling, impulse, or behavior
* Hiding true feelings by overcompensating in the opposite direction
* Hiding true feelings by overcompensating in the opposite direction