Radiology Student RDH 2024
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Nucleus of an atom contains
protons and neutrons
= atomic mass
K shell has the highest
binding energy
most useful for medical imaging
to remove an electron from orbit, energy must be
equal to or stronger than binding energy keeping electron in orbit
Who discovered radiation?
Roentgen 1895
radiation travels through space as
waves (electromagnetic radiation) or particles (Particulate radiation)
ionization
the process of adding or removing electrons from an atom or molecule, which gives the atom or molecule a net charge (not neutral)
Ionizing radiation
high in energy
capable of producing ions
the type of xray we use is
electromagnetic radiation
travels in a wave like motion
travels at the speed of light
has no charge and no mass
the ___________ determines the penetrating power of an xray
wavelength
Power Supply of an xray machine
electricity= power source (DC=direct current or AC= alternating current)
circuit= route the electrical current takes (high voltage, 65,000-100,000 volts)
transformer= mechanism used in an electrical circuit to increase or decrease the voltage. (can be step down, step up or auto)
Control panel of xray machine
displays on/off, kvp, mA, time (exposure time)
ampere= number of electrons
volt= force that moves electrodes from cathode to anode
kvp= detemines speed of voltage away from cathode (to anode) and determines quality.
What does the lead glass housing of an X-ray tube head contain?
Cathode and anode
What is the function of the molybdenum in an X-ray tube head?
Focuses direction of electrodes towards the anode
How is the anode in an X-ray tube head controlled?
By kvp settings
Where do electrons hit to produce x-rays in an X-ray tube head?
Tungsten target
What is the focal spot in an X-ray tube head?
Small area on the tungsten target where electrons hit and x-rays originate
What components are contained in the tube head of an X-ray machine?
X-ray tube, high/low voltage transformers, and insulating oil
What is the function of the PID in an X-ray machine?
Reduces exposure and directs x-ray beams
How does the copper stem contribute to an X-ray tube head?
Dissipates excess heat
the tungsten target is not the same as the
tungsten filament
if you go from a C to an A+ thats even better!
Cathode (-) to anode (+)
primary radiation basics
at the cathode, when the power switch is activated, the tungsten filament produces electrons, causing an electron cloud to form (this process is called thermionic emission)
When the exposure button is pressed, the
electrons barrel at high speed to the tungsten target and transform kinetic energy into x-rays. heat that is formed is dissipated through the copper stem.
photons (bundle of energy) leaves the x-ray tube as primary radiation
Xrays are formed at the tube mainly by two mechanisms braking radiation, and characteristic radiation
Braking radiation (Bremsstrahlung)
major source of xrays produced in dentistry (70%)
results when high energy electrons move come close to the nucleus of the tungsten atoms. (at the tungsten target). they then slow down (braking) and energy is released
characteristic radiation
electrons from the cathode dislodge electrons from the inner orbit (K or L shell) and make little xrays
scatter radiation
A form of secondary radiation that occurs when an x-ray beam has been deflected from its path by interaction with matter
may cause fogging of an xray
compton scatter
MOST COMMON TYPE (60%)
ionization occurs
-x ray photon knocks electron from OUTER orbit
-it can interact with other atoms
photoelectric effect
photon interacts with inner shell electron (less common type of scatter radiation, 30% of scatter radiation)
ionization occurs
coherent scatter
photons interact with electron, in outer shell, but matter is not altered
no ionization
sievert
SI unit of equivalent dose and effective dose
1 sv =
100 rem
1 Gy =
100 rad
exposure measurements
roentgen(standard)
Coulomb (SI)
Absorbed dose vs dose equivalent.
absorbed dose= dose of radiation
dose equivalent = absorbed dose adjusted to the biological damage potential of the particular type
Radiation damage (indirect and direct)
direct= damage to cell's protein, lipid barrier and DNA accounts for 1/3 of biological damage
indirect= radiation interacts with cells water content, and produces free radicals = ACCOUNTS for 2/3 of biological damage
somatic effect
occurs when the biological change or damage occurs in the irradiated individual, but is not passed along to offspring
cataracts, cancer
stochastic effect
When a biological response is based on the probability of occurrence rather than the severity of the change
ie. all or none
non-stochastic effect
also called deterministic effect. severity of the damage is dependent on the dose
Highly sensitive cells
immature cells
quickly dividing cells
younger persons cells
Less sensitive cells
highly specialized cells, mature cells, slowly dividing cells
In order from most to least sensitive cells
bone marrow
reproductive
intestines
blood
skin
immature bone, thyroid, kidney liver, CT
most sensitive part of cell= DNA and chromosomes
Natural resources of radiation
Radon (gas released from decaying material in the ground)
background radiation
a FMS is equivalent to background radiation from
1-2 days of background (naturally occurring) radiation
Dental exposure is similar in radiation exposure to a
commerical flight
a CT scan emits
100 TIMES the radiation of a dental radiograph
Filtration of radiation is produced by
aluminum discs
collimation
The restriction of the size and shape of the x-ray beam in order to reduce patient exposure.
(rectangular collimation reduces tissue exposure by 60% then circular)
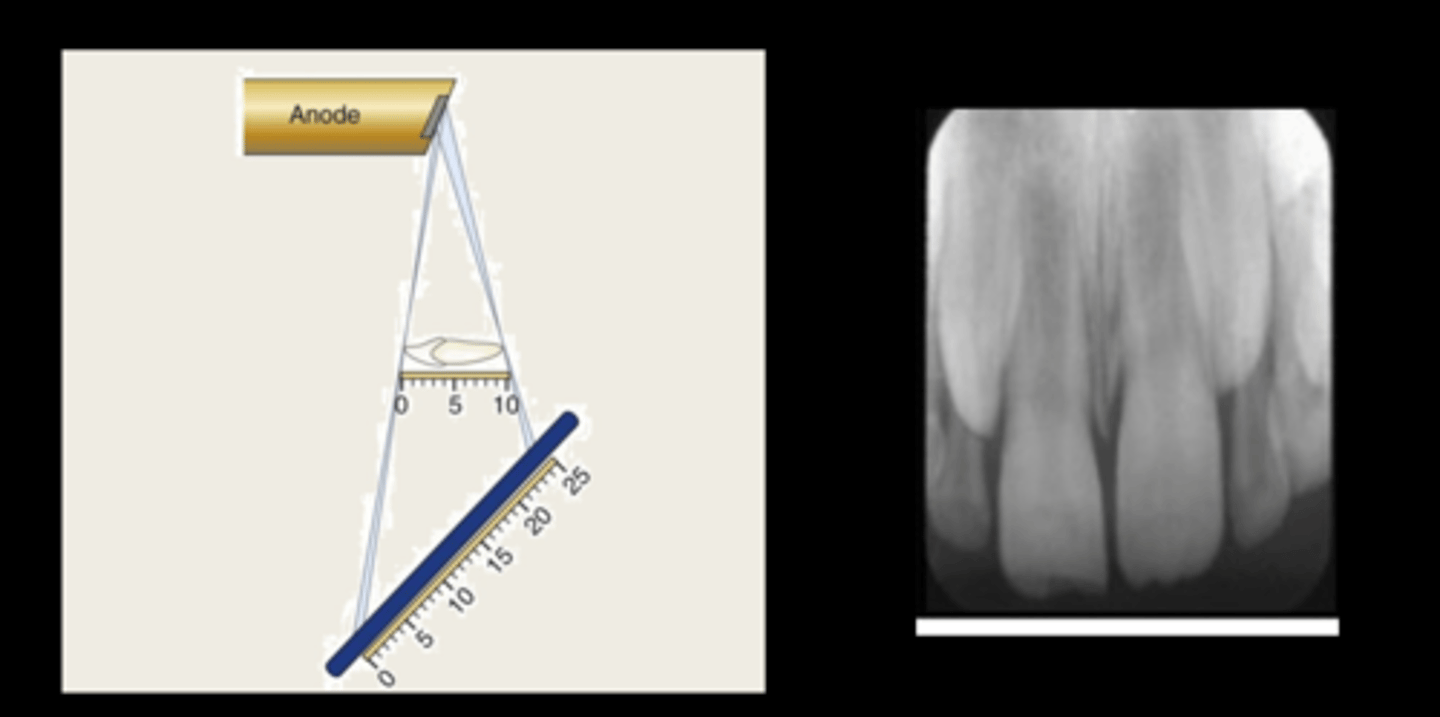
standard PID lengths
8-16 inches
16 inches produce more parallel rays and reduce radiation exposure
ALARA
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
dosimeter
a badge that records exposure to radiation that is worn when taking x-rays, worn on waist
MPD
maximum permissible dose
MPD for occupationally exposed persons is?
5 rem = 50 mSv= 0.05 Sv/year
20mSv/year averaged over 5 years, not exceeding 50 mSv in any 1 year
MPD for non-occupationally exposed persons
1 mSv/year (0.1 rem/year)
(0.1 rem per year)
pregnancy and MPD
0.5 mSv per year
Beam intensity
total energy contained in the beam affected by mA, kVp, distance, and exposure time
To increase beam intensity, you must
increase kvp, mA, and time
decrease distance
to decrease beam intensity you must
decrease kvp, ma, time
increase distance
inverse square law
the intensity of radiation is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of radiation
how to calculate inverse square law
how much longer? two times? then 2 squared = 4 then INVERT,
so beam is 1/4 as intense (if farther away)
**but if question is shortening distance, If closer, then 4 times MORE intense
Density
proportional to mA, kvp and time
To maintain similar density,
if time is increased, milliamperage must be ____
decreased, and vice versa
Contrast is dependent ONLY on?
kvp
sharpness of image is increased when
focal point on tungsten target is small
object to receptor distance is short
tube to receptor distance is long
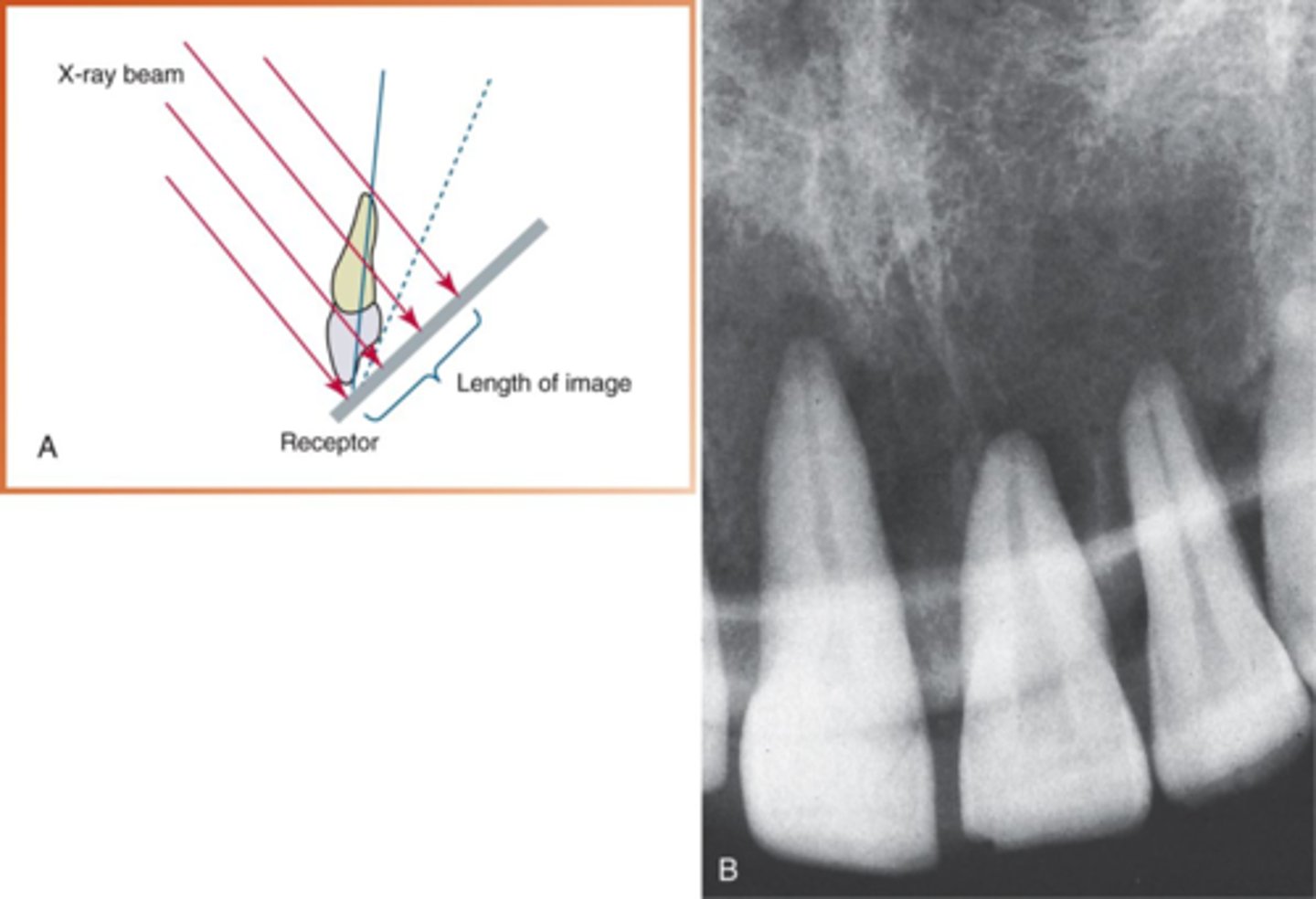
distortion: elongation is caused by
underangulation
foreshortening is caused by
overangulation
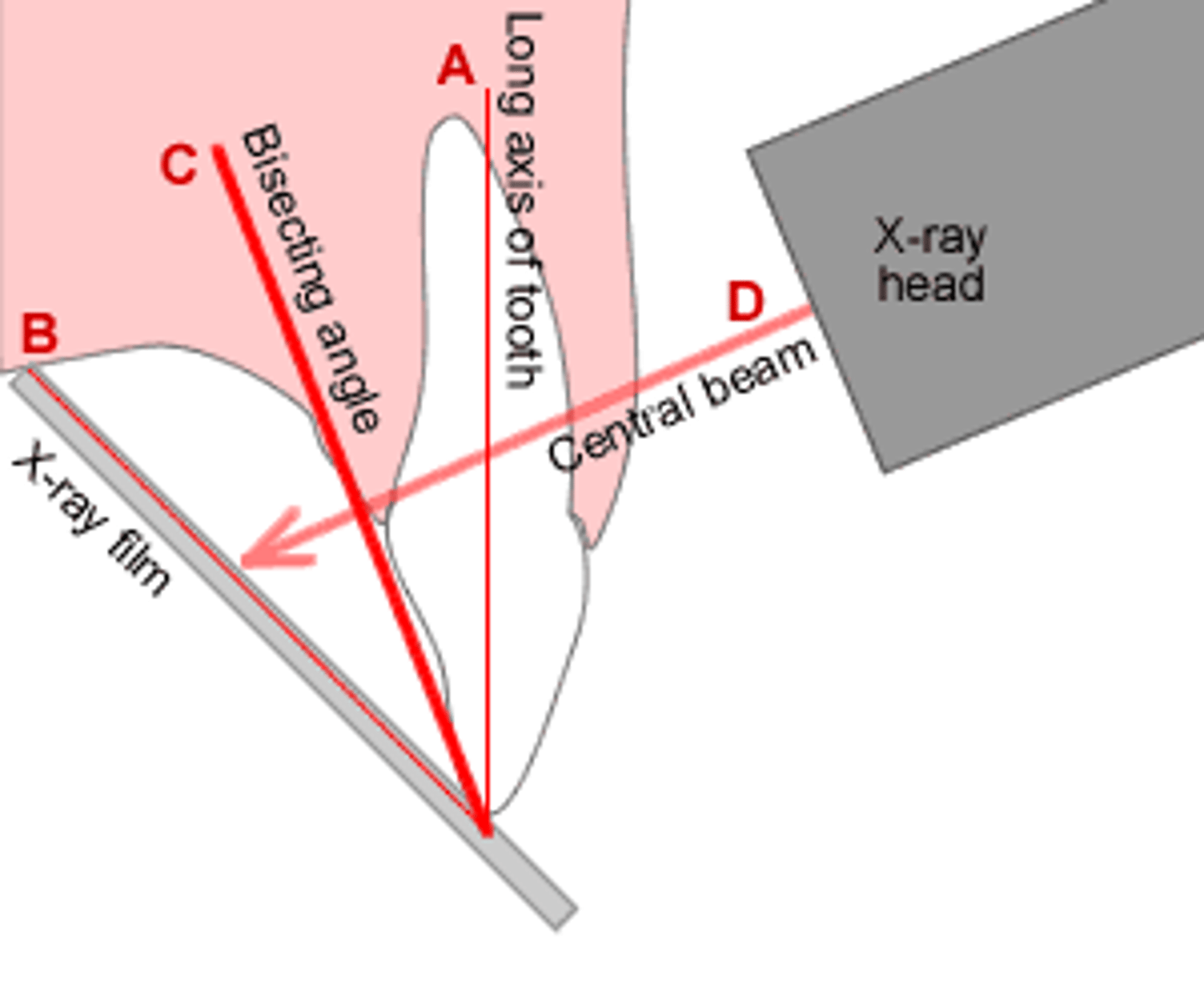
bisecting technique
Primary beam aligns with bisecting line of tooth and sensor
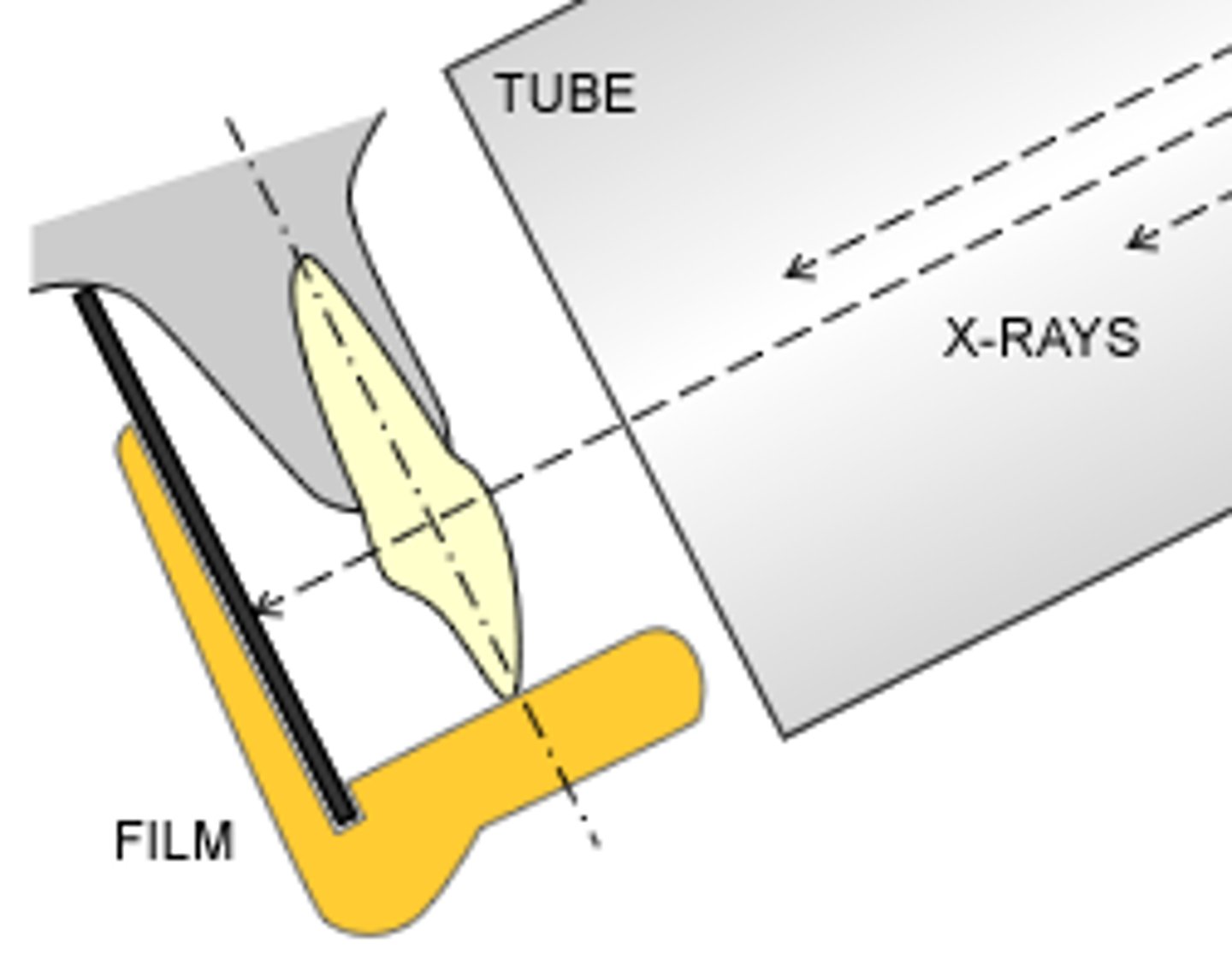
paralleling technique
Intraoral technique of exposing periapical and bitewing images
in PID angulation, a negative angle is
up
positive angle is pointing down
SLOB rule
1. Same Lingual
2. Opposite Buccal
3. Lingual objects move in same direction as the tube head
4. Buccal objects move in the opposite direction as the tube head
herringbone pattern
film put in backwards
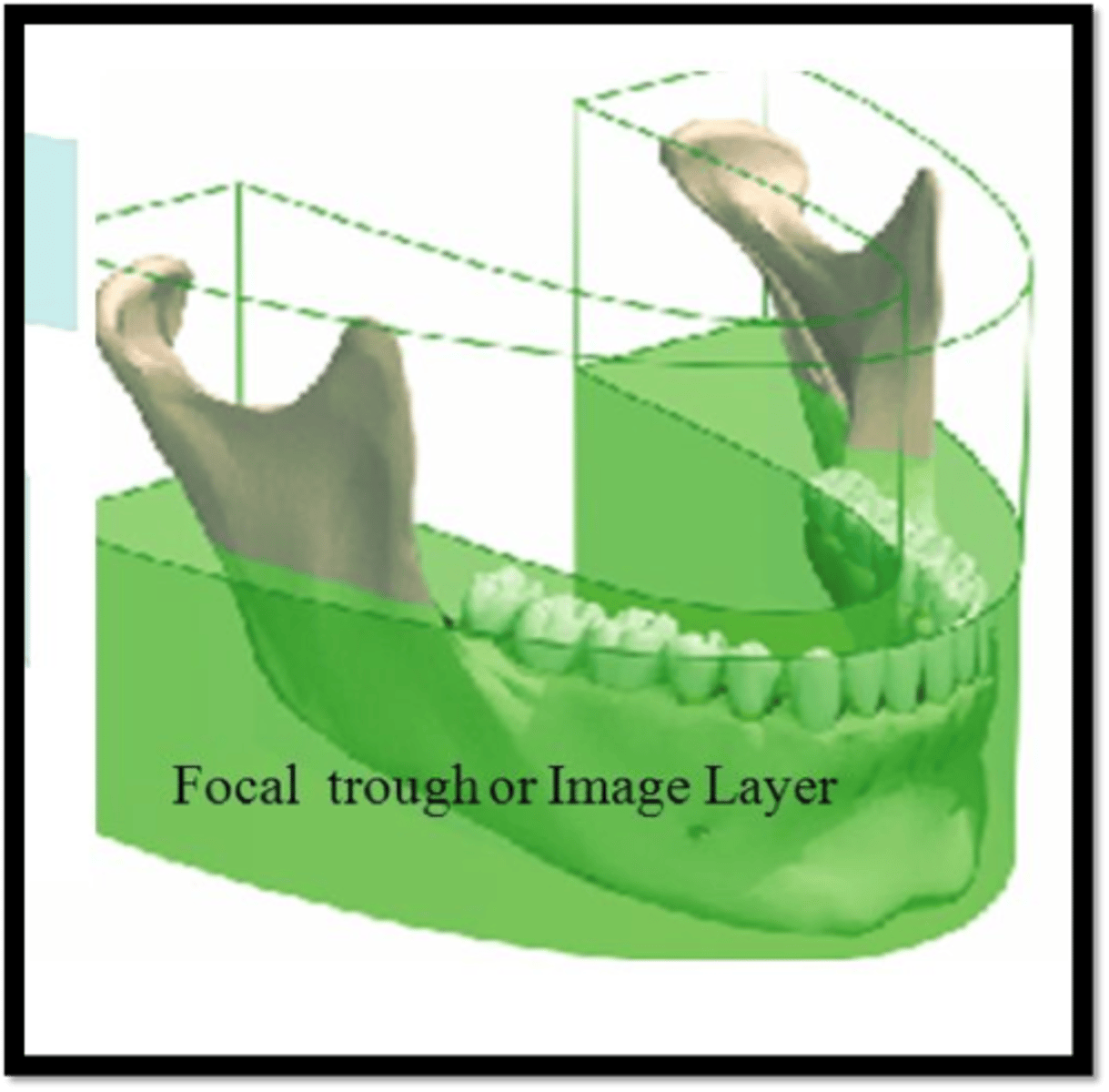
Focal trough (image layer)
A three-dimensional curved zone in which structures are clearly demonstrated on a panoramic image
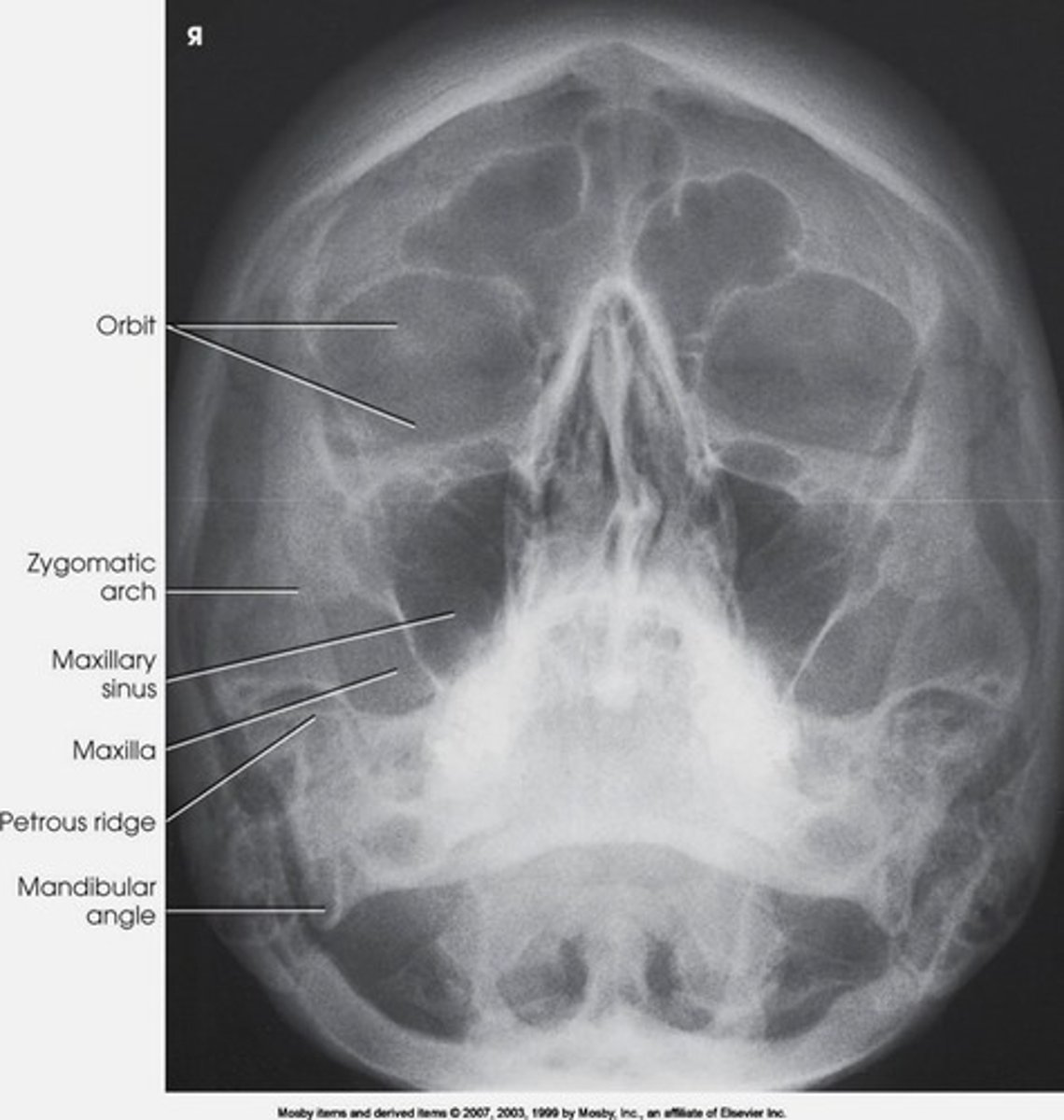
waters projection
to evaluate the maxillary sinus area
MRI
for soft tissue
Shark fin error
lead apron above collqr
flat line in pan (frown)
patients chin tipped forward
opacity in middle of pan
spine slumped
large dark shadow over apices of maxillary arch
tongue
pt did not touch tongue to the roof of the mouth
thin and blurry anterior teeth
patient is biting too far forward
wide and fat anterior teeth
patient is biting too far back (away bite is fat and blurry)
New Patient Guidelines
Primary dentition= selected periapical/occlusal views or posteior bitewings if proximal surfaces cannot be visualized or probed.
Patients without evidence of disease= may not need xrays
Mixed dentition= BWs, Pan and select PAs as needed
Adolescent= Same as mixed dentition (above)
Patients with evidence of disease may need FMS
In general, if no evidence of disease NEW PATIENT with, mixed dentition, adolescents, and adults (including partially edentulous adults) need posterior BWs, Pan, and select PAs. if they have evidence of disease, these patients need a FMS.
Recall Patients at INCREASED RISK FOR CARIES
Primary dentition, mixed dentition,, adolescent= BW at 6-12 intervals if proximal surface is unable to be probed.
Adult, partially edentulous= Post BWs at 6-18 month intervals
Recall patient with no caries risk
if patient has no caries risk, intervals are:
primary, mixed dentition= BW 12-24 months
adolescents= BW 18-36 months
Adults= 24-36 months
incisive foramen
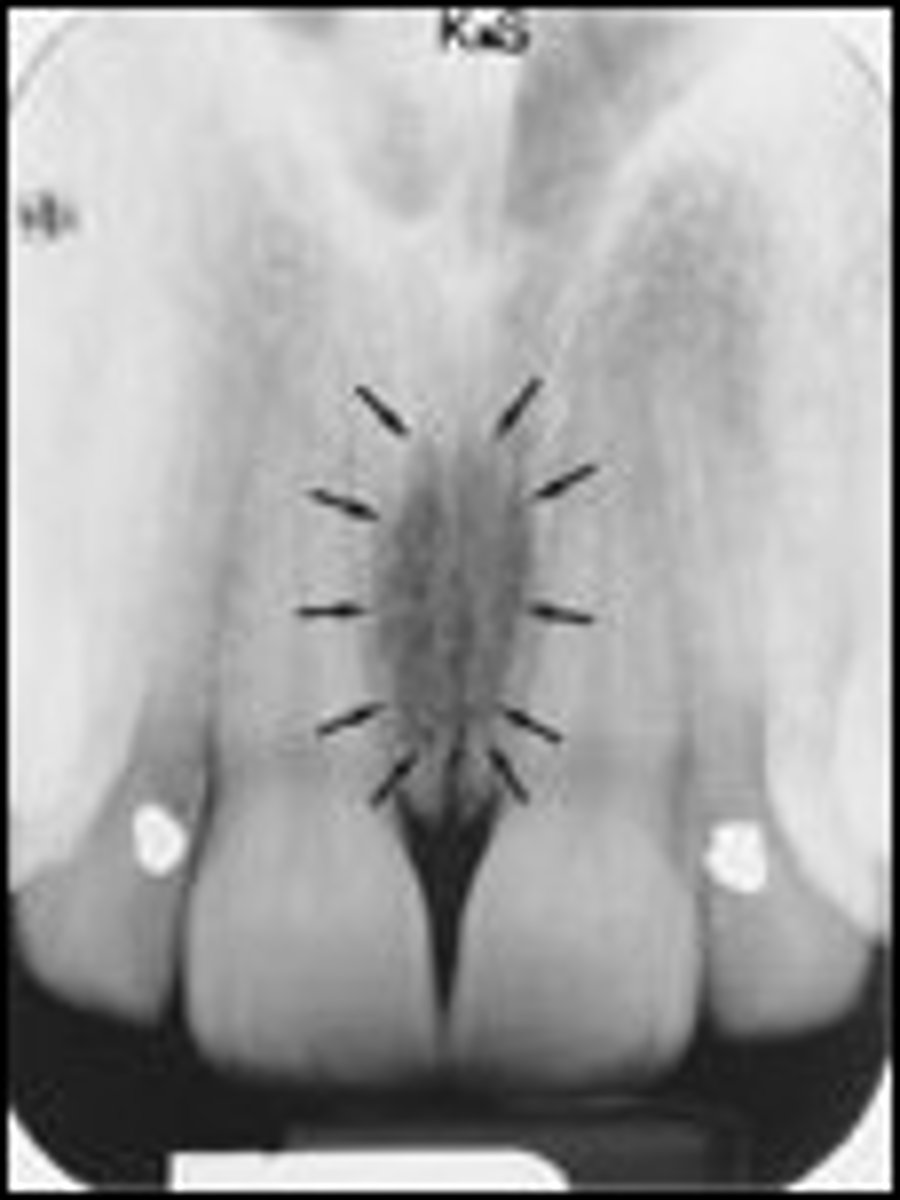
nasal septum
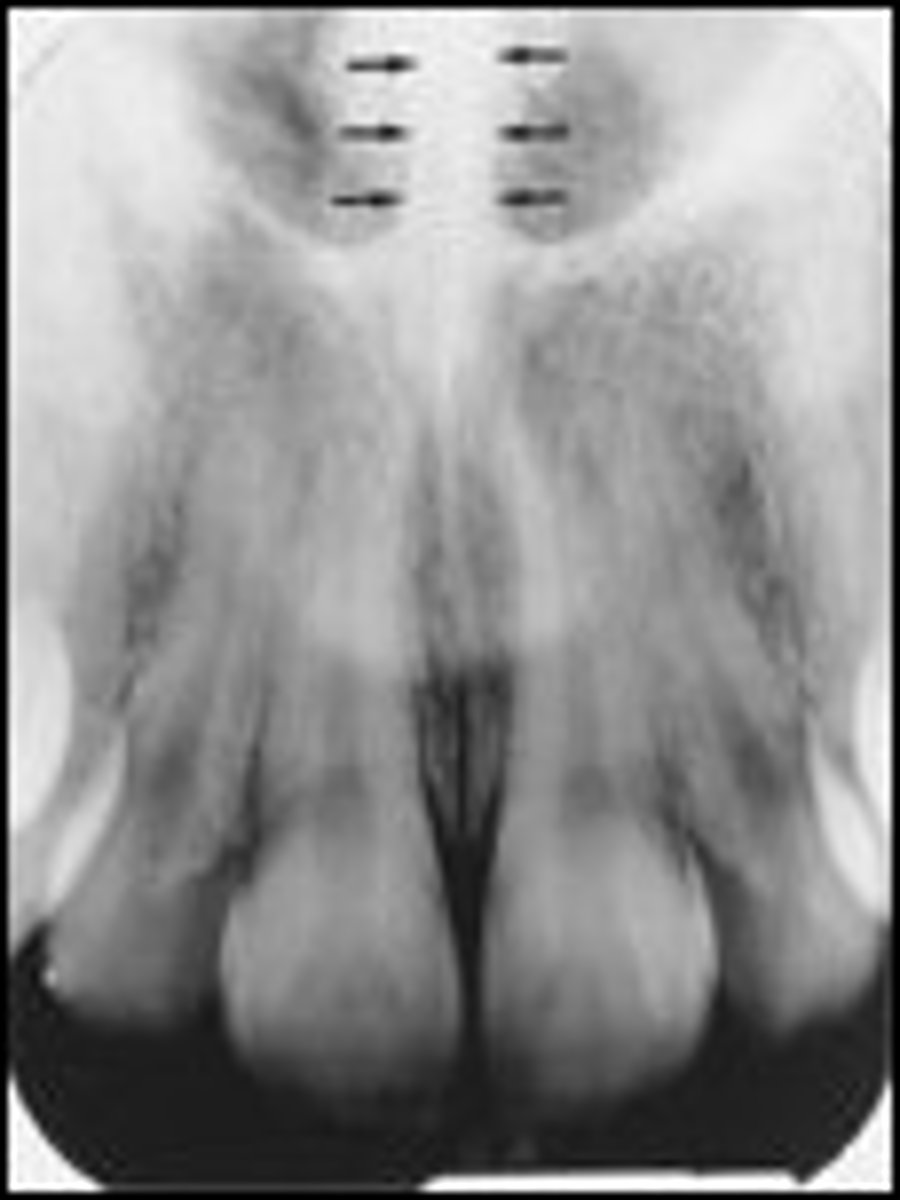
maxillary sinus
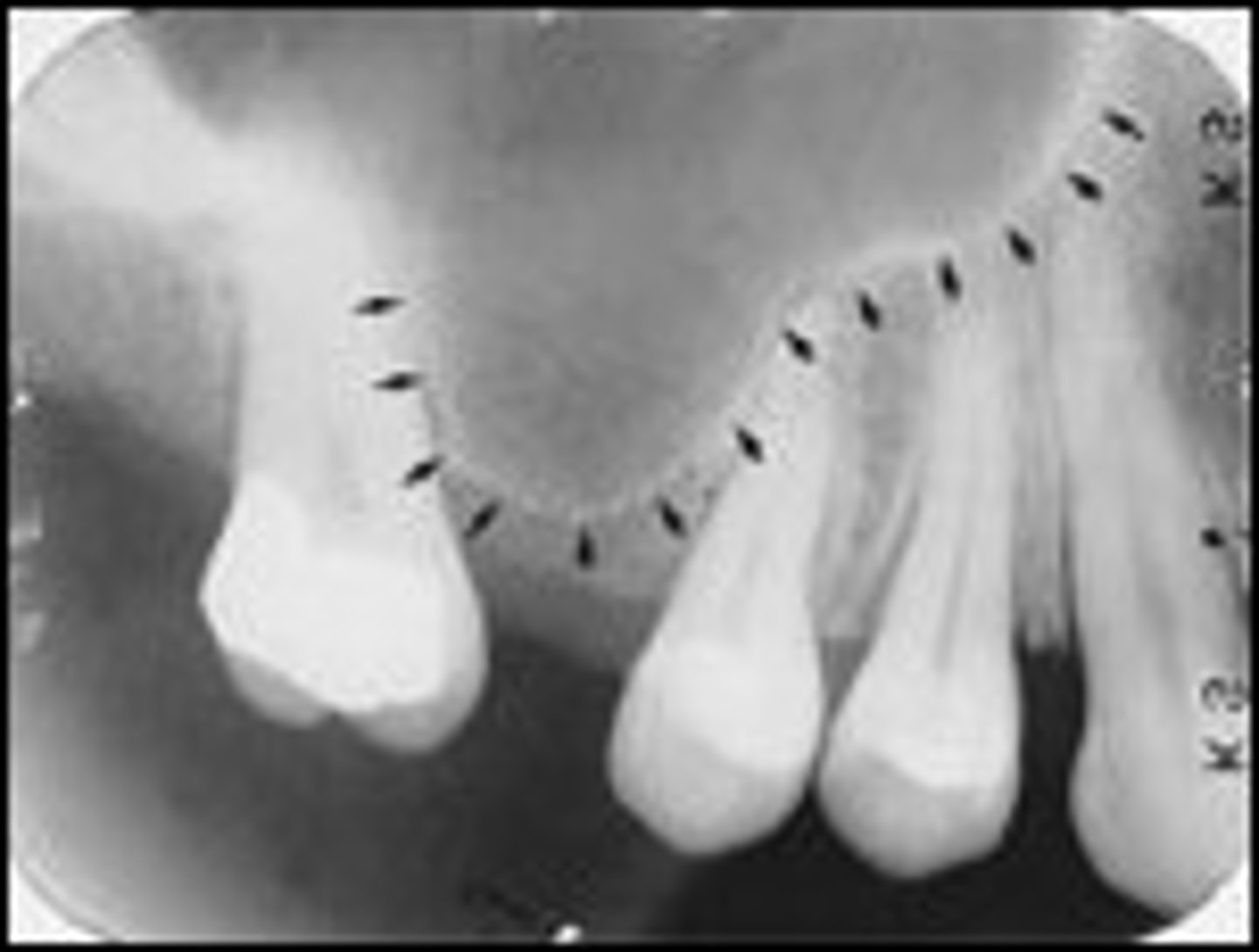
inverted Y
The intersection of the maxillary sinus and the nasal cavity
located above maxillary canines
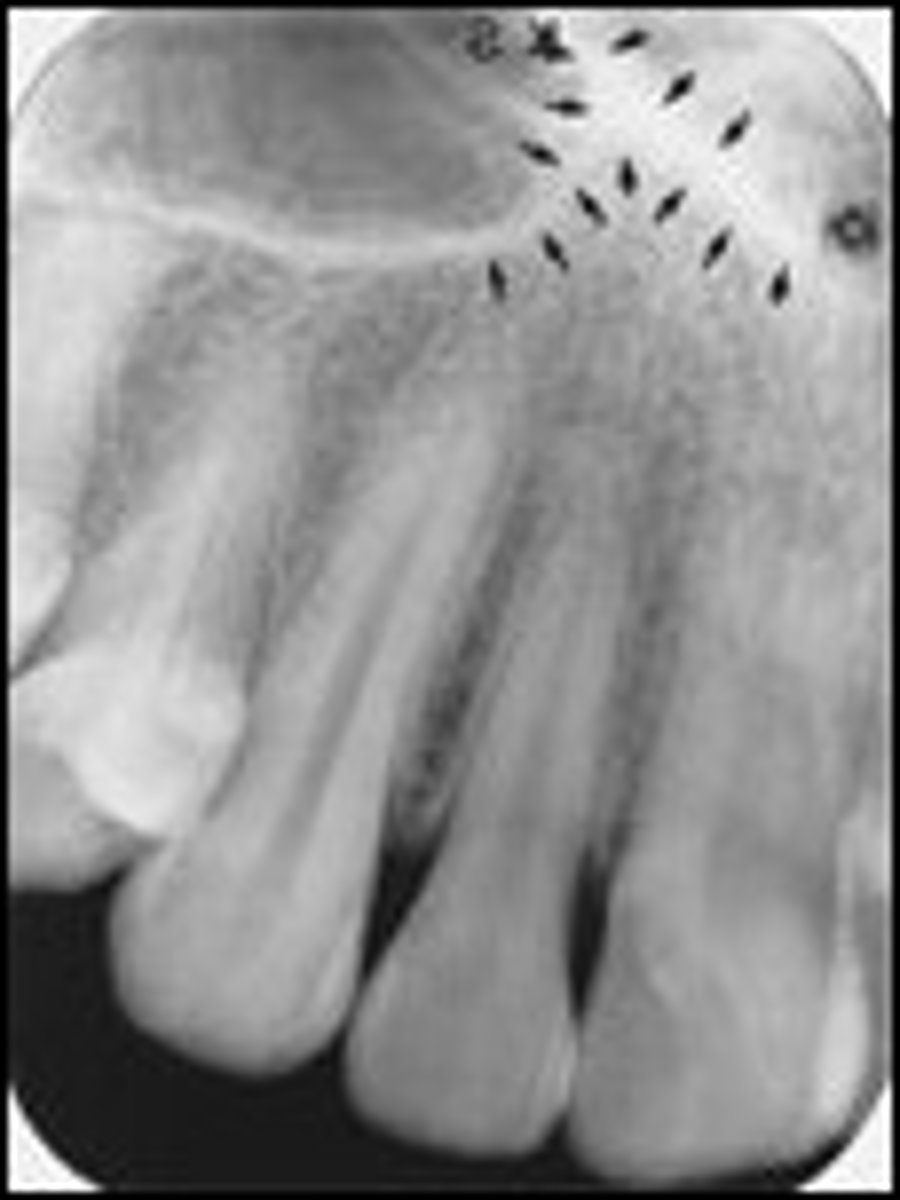
nutrient canal
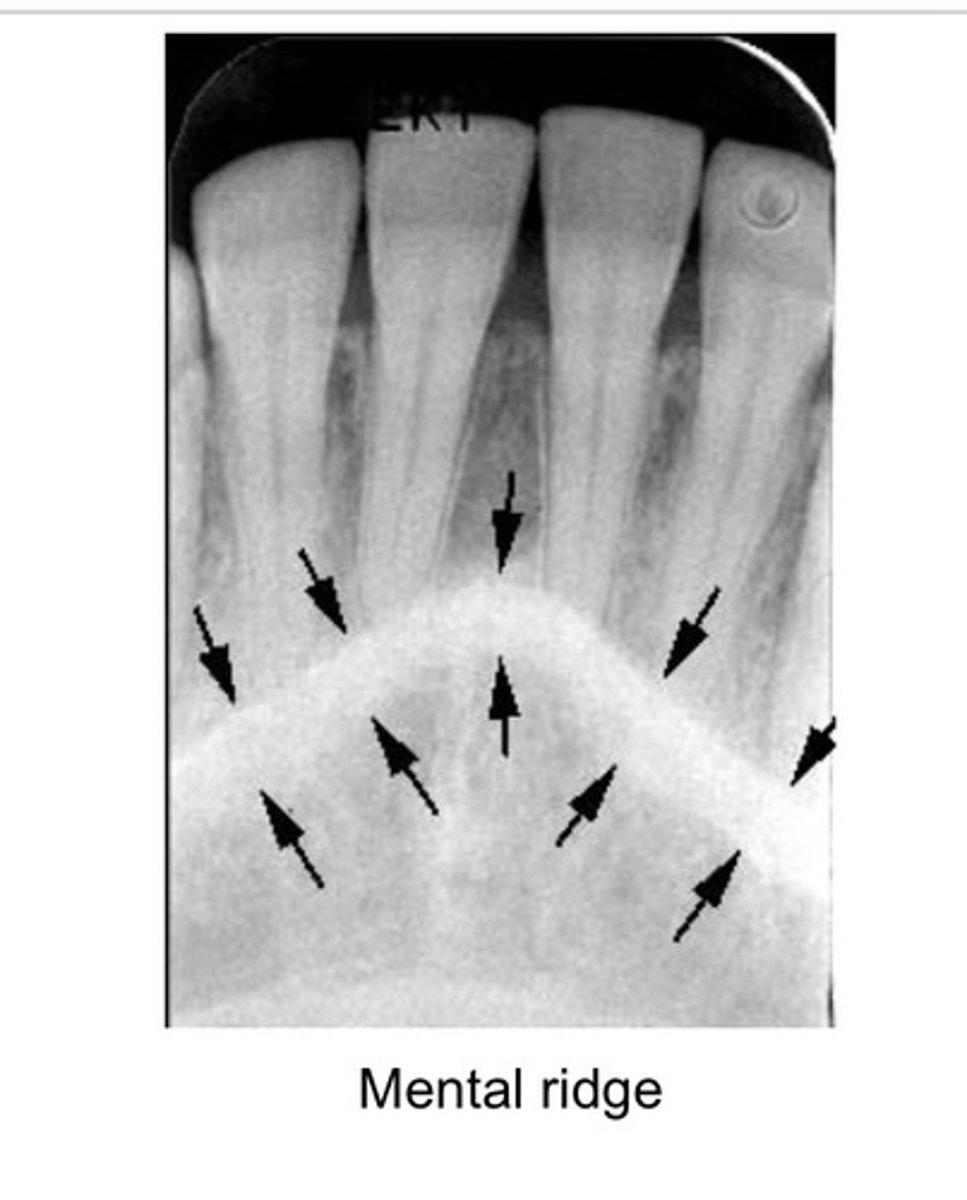
mental ridge
coronoid process
often seen in maxillary posterior PAs
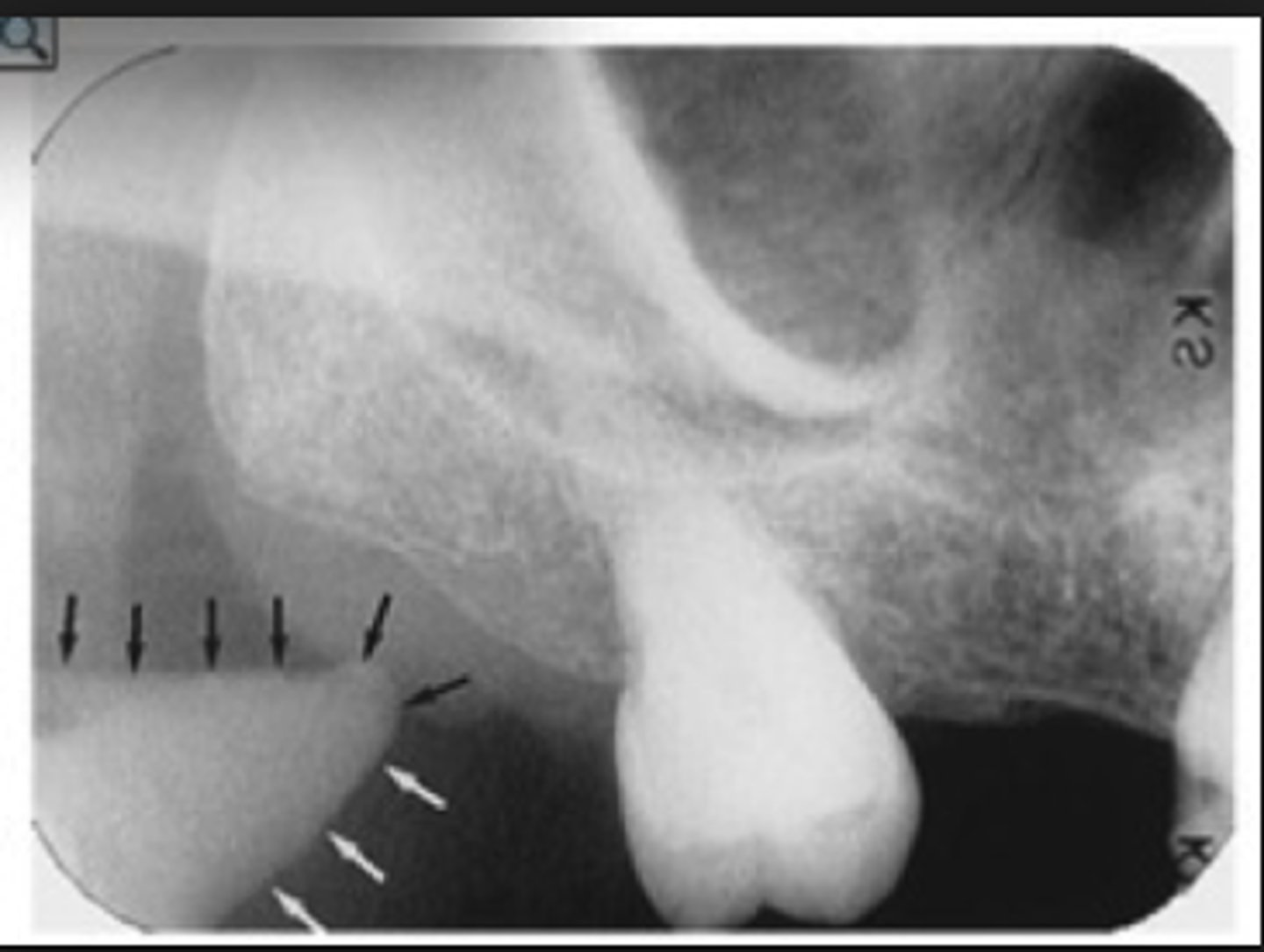
coronoid process on the skull
anterior portion of the ramus
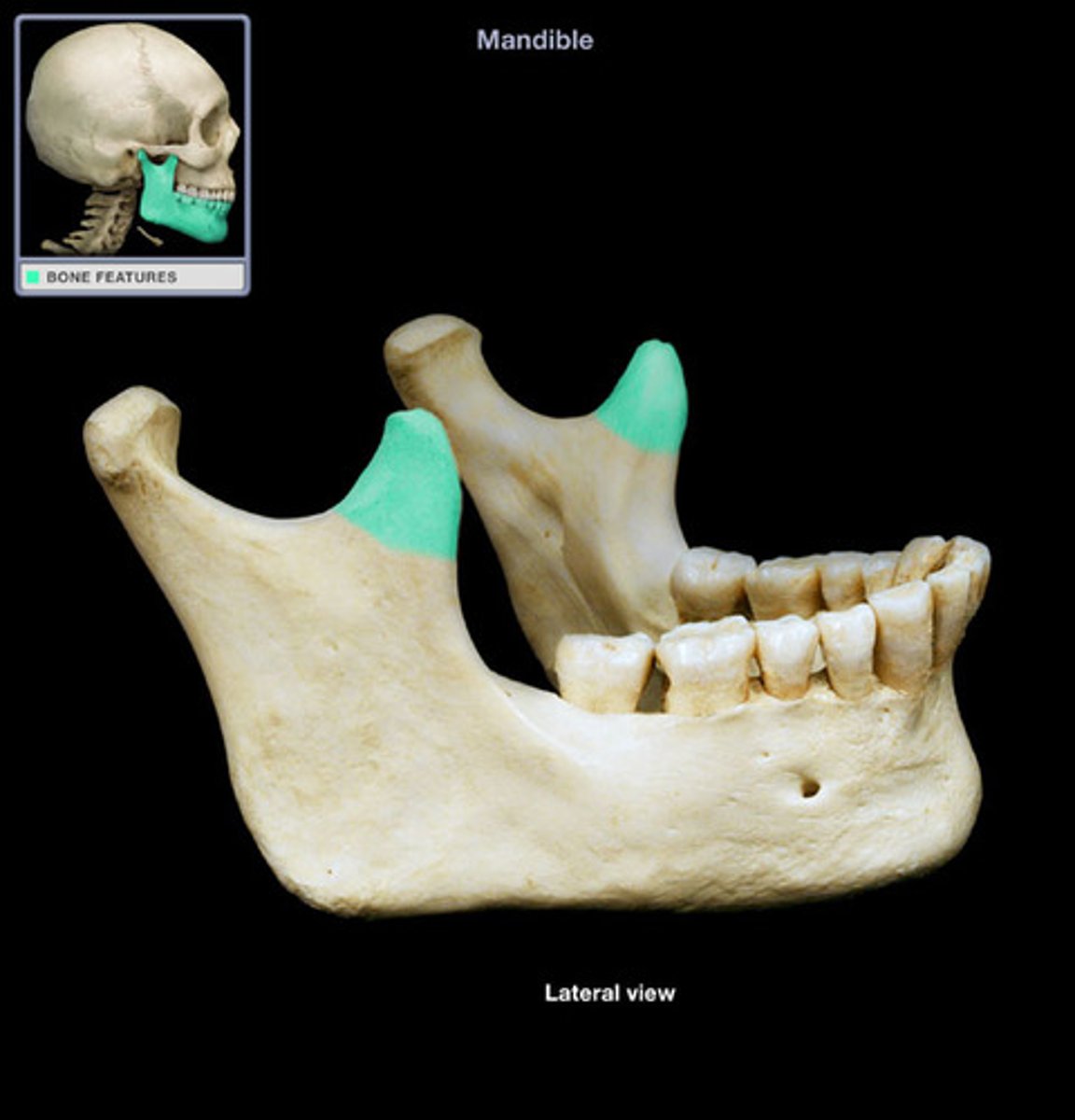
ramus of the mandible
vertical part of mandibleRa
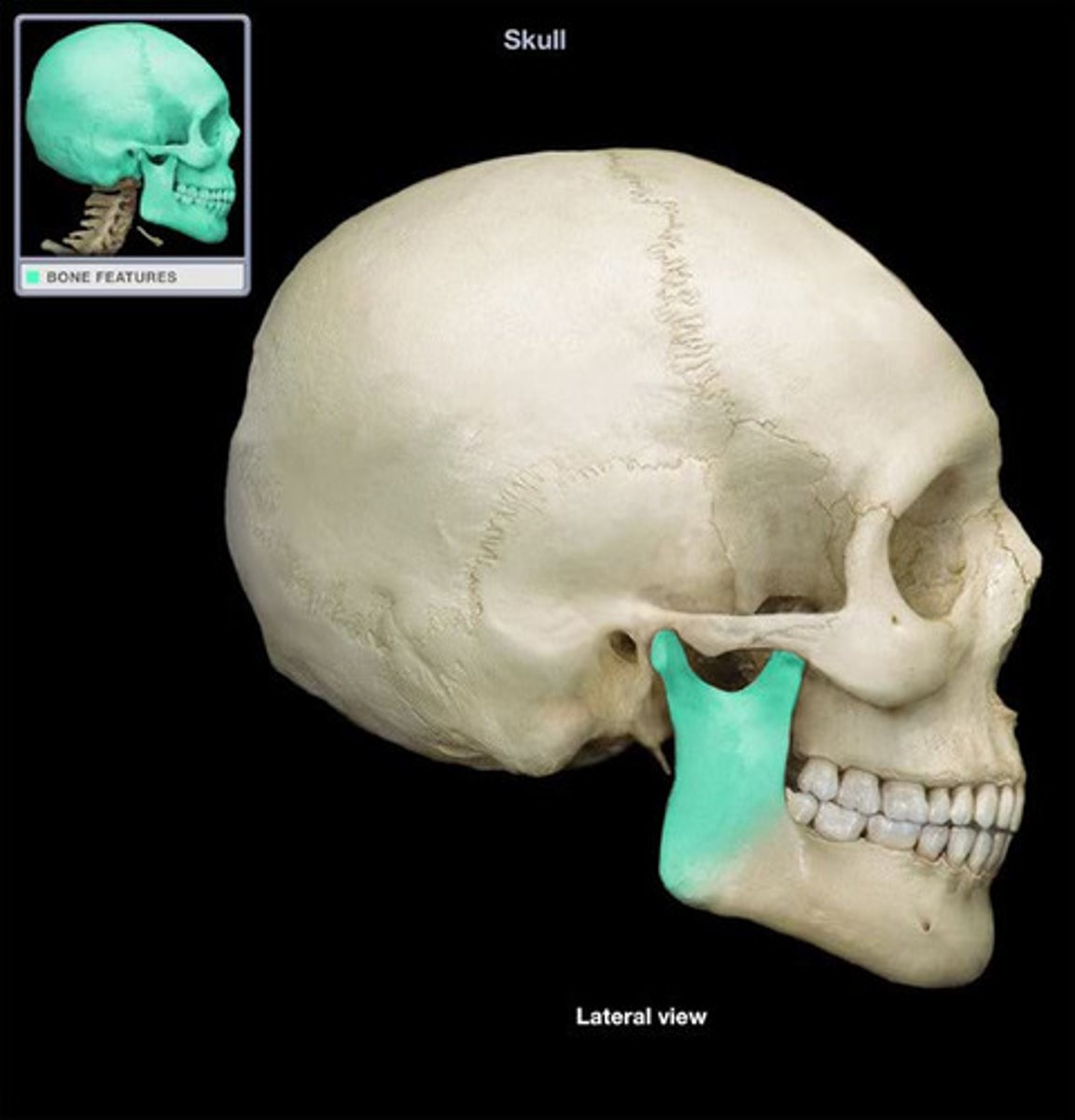
maxillary tuberosity
often seen in maxillary posterior PAs
coronoid process
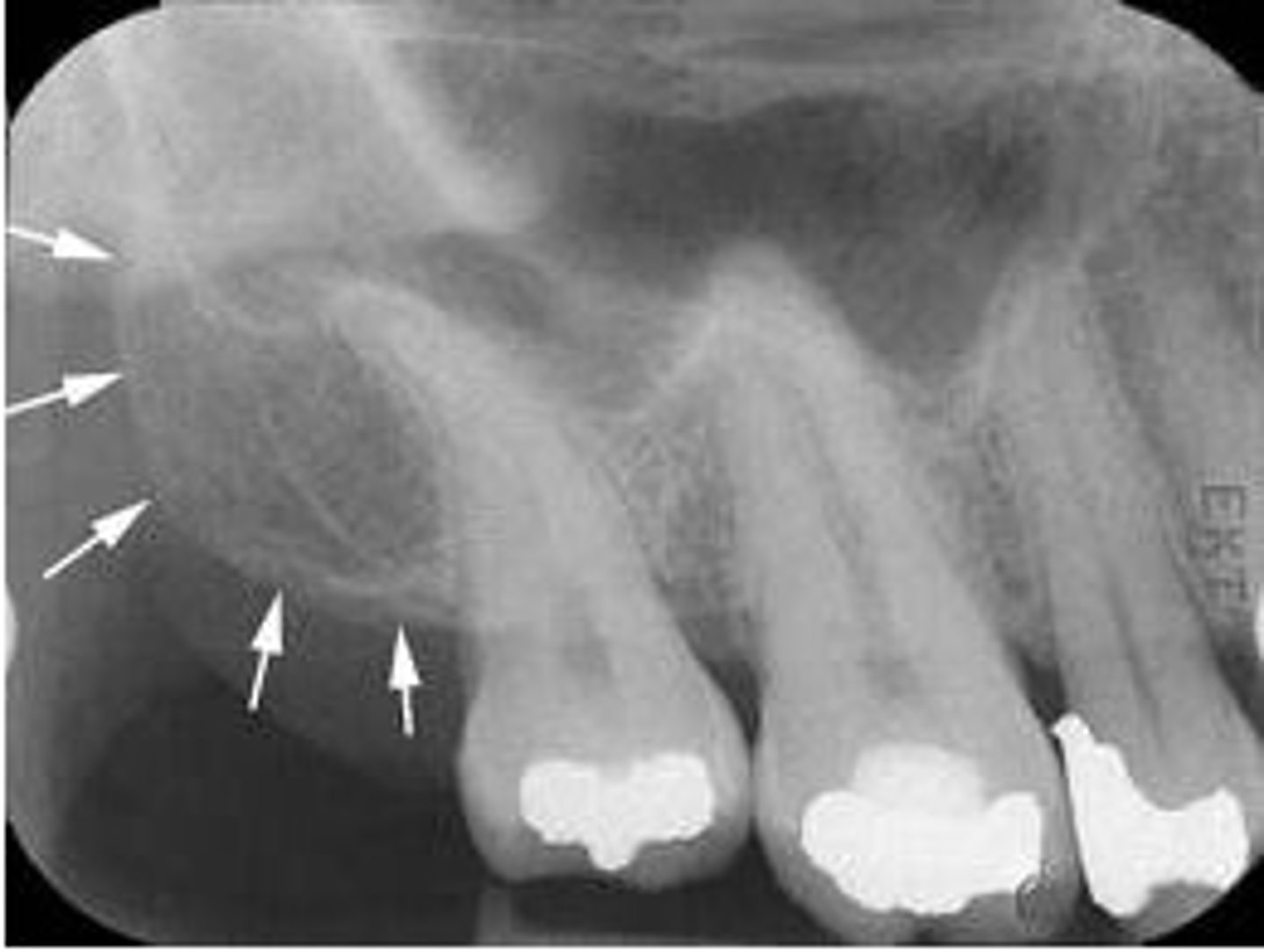
maxillary tuberosity
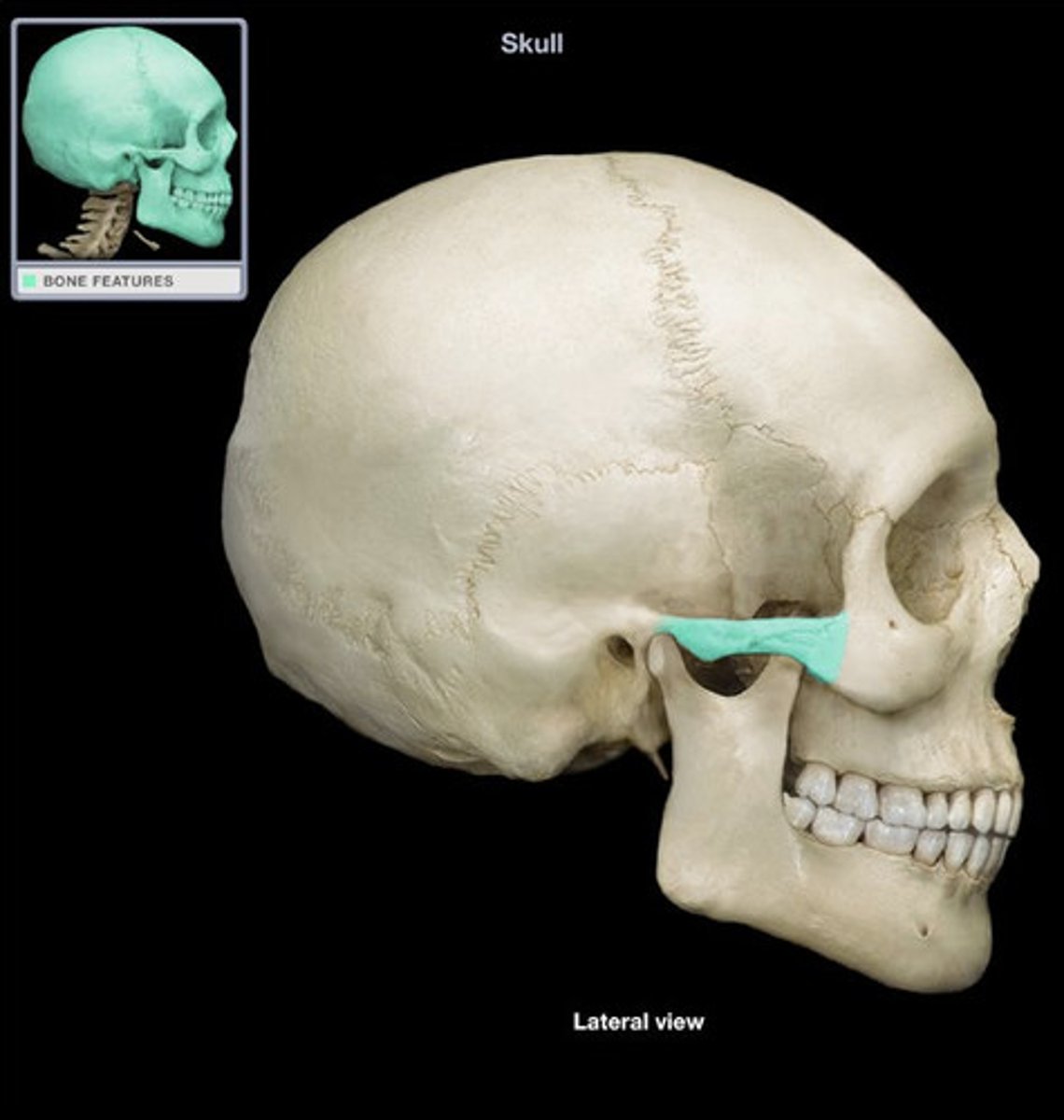
zygomatic process
maxillary sinus (found superior to maxillary molar/premolar area)
zygomatic process
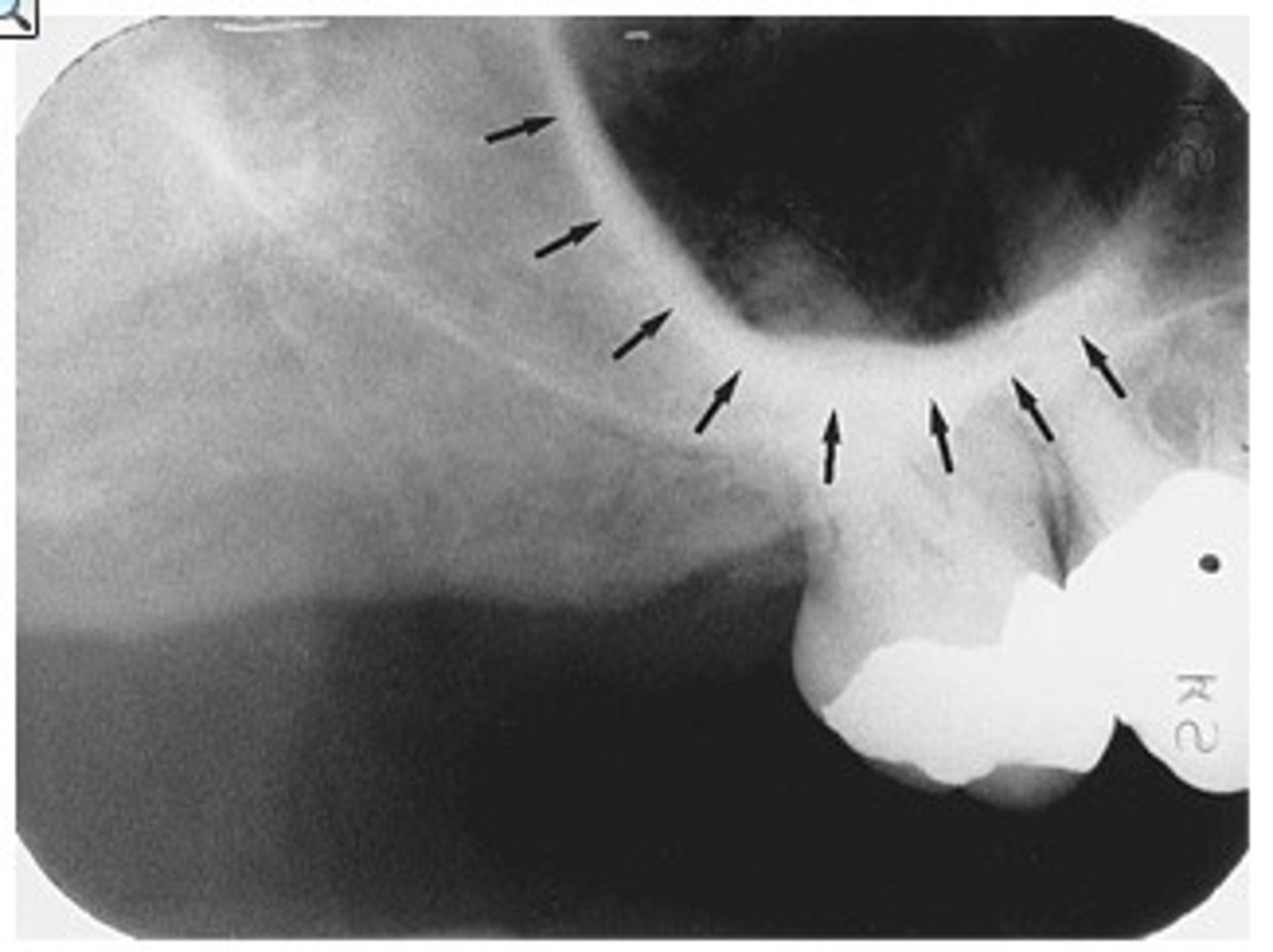
zygomatic process on skull
cheekbone
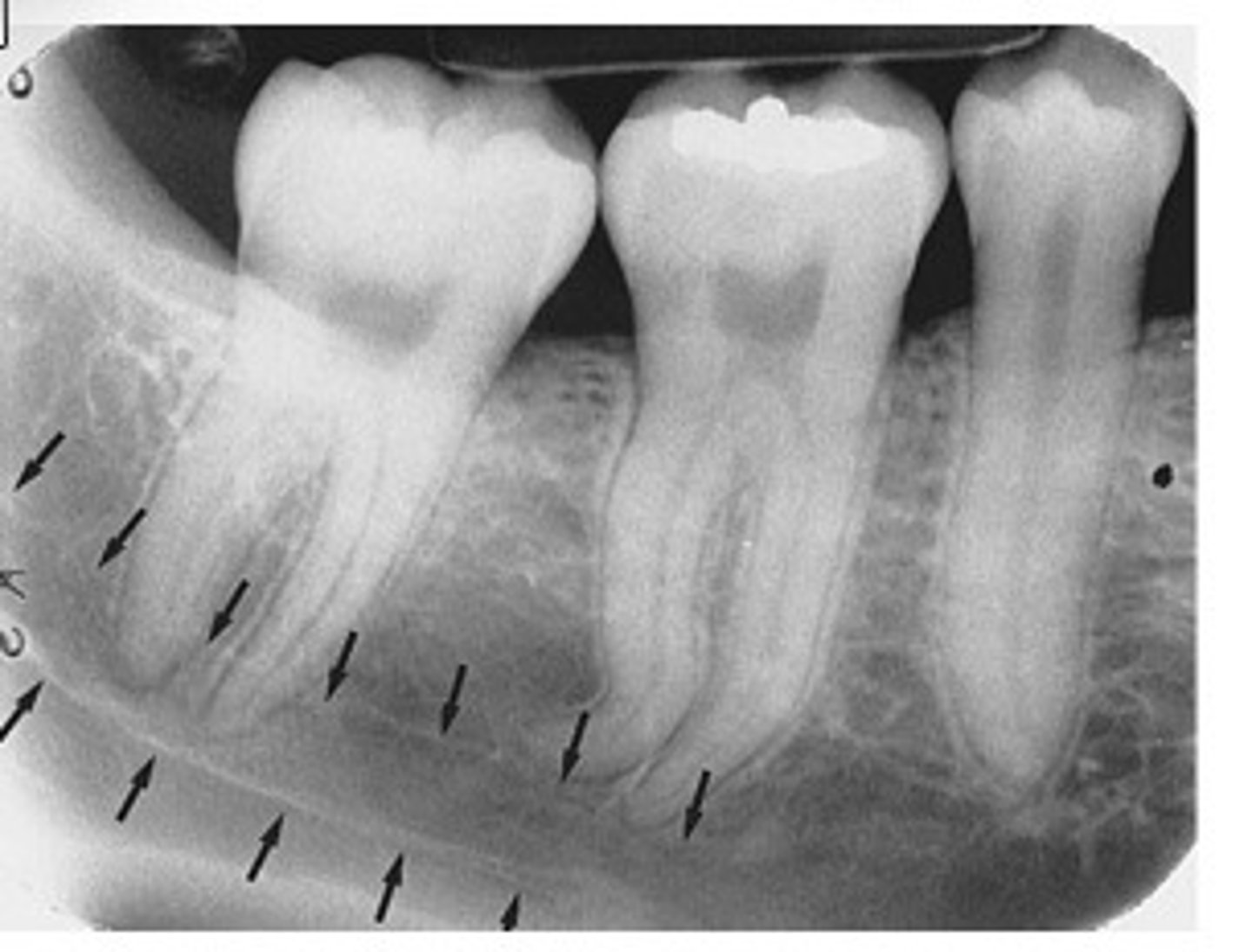
mandibular canal
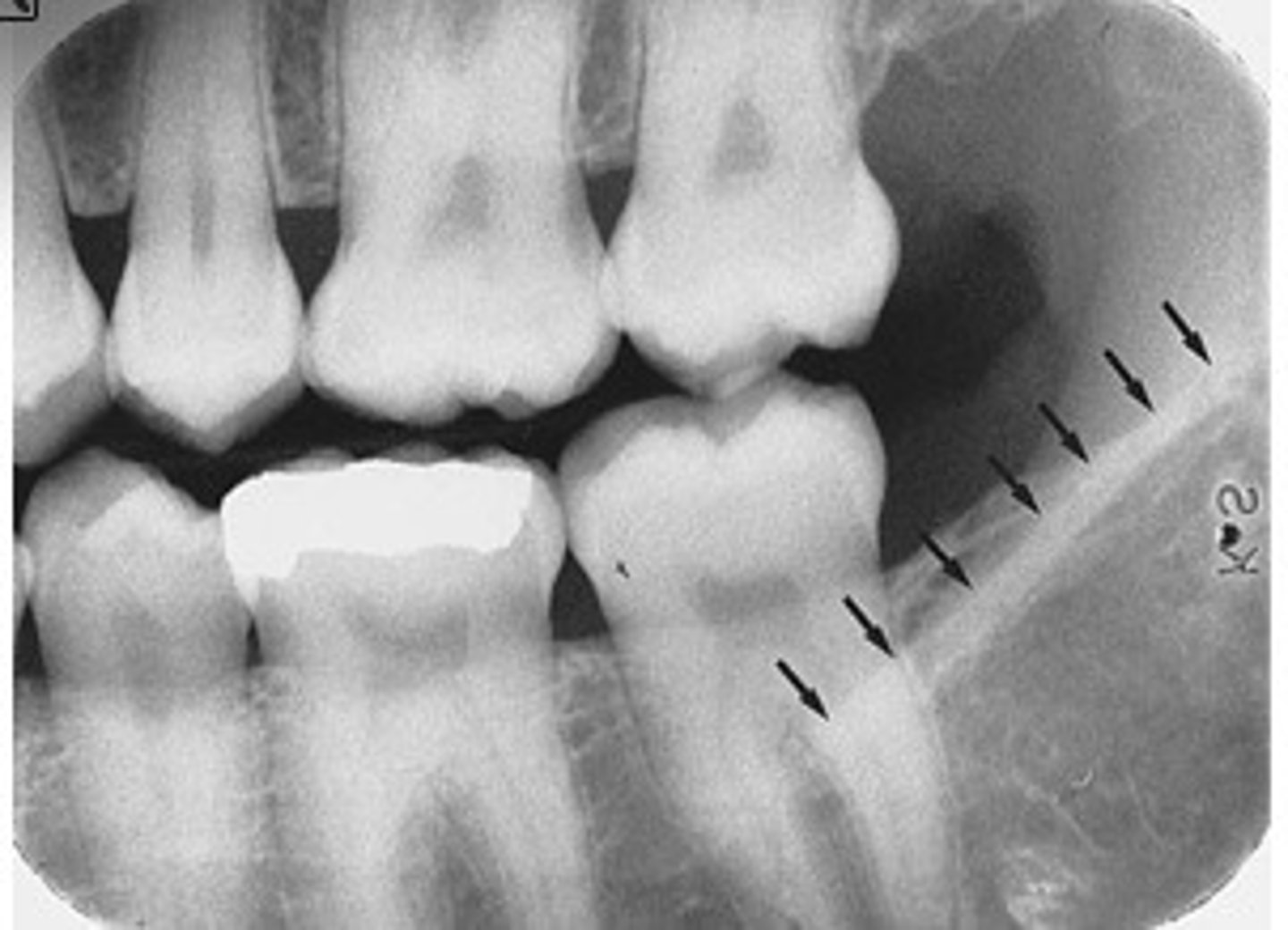
external oblique ridge
...A radiopaque band extending downward and forward from the anterior border of the ramus of the mandible
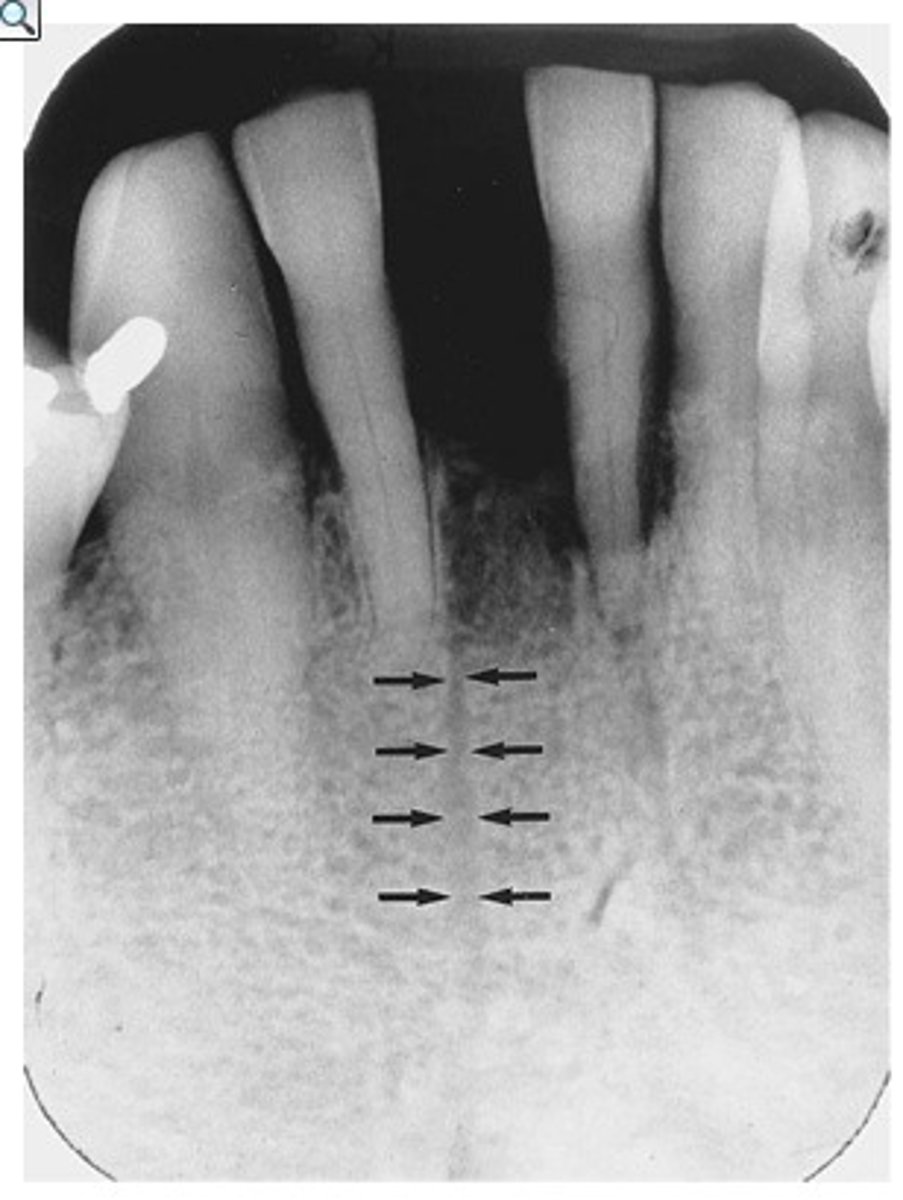
median palatine suture
NOT a fracture
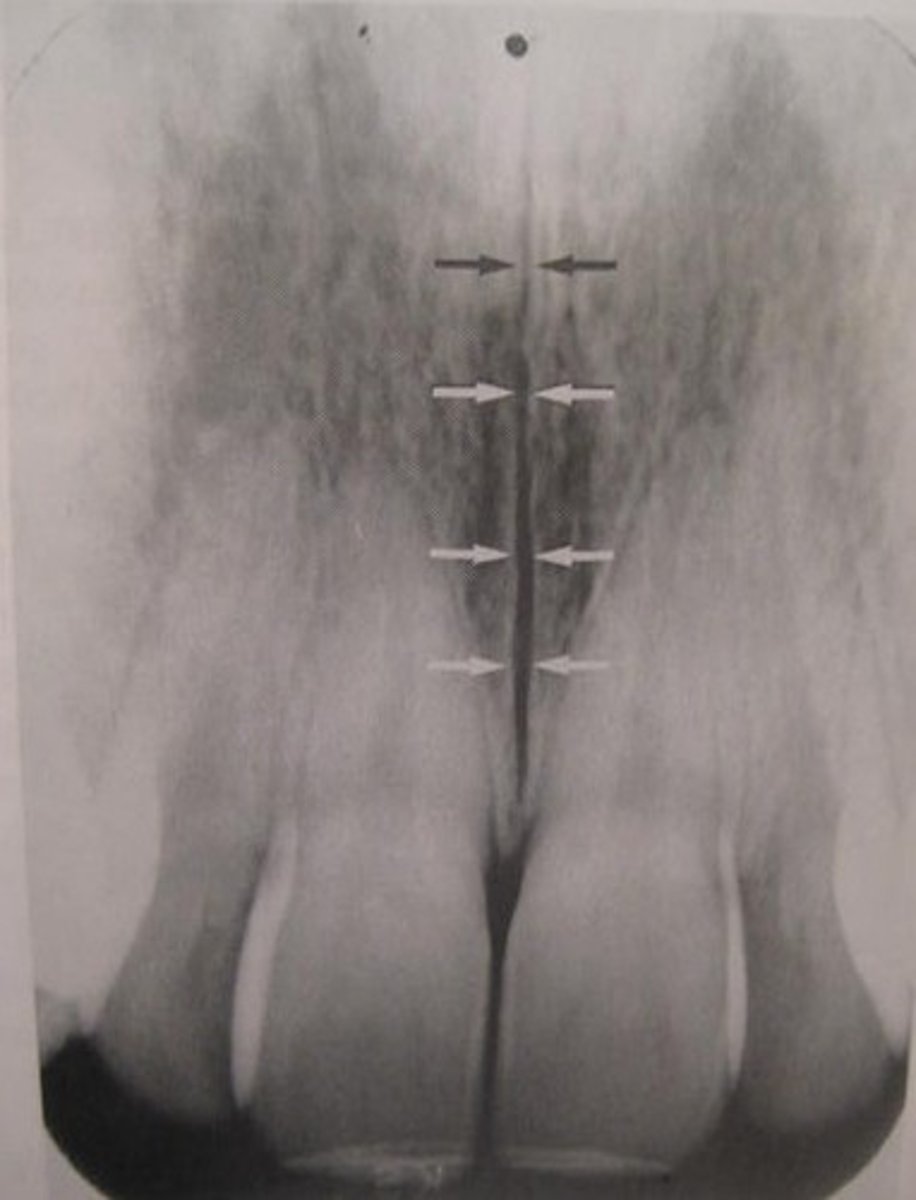
radiopaque restorations
gold
amalgam
composite (darker though)
silver point
ortho brackets
retention pins
implants
slightly radiopaque restos
base material
gutta percha
porcelain