backwards testing effect
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
learning to learn
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Karpicke et al, 2009
surveyed students’ study strategies
84%: re-reading notes/ textbook
11%: self testing
Kornell and Bjork, 2007
asked “if you quiz yourself while you study, why do you do so”
68%: to figure out how well they have learnt the information
18%: I learn more that way than re-reading
9%: I don’t usually quiz myself
4%: I find it more enjoyable
what is the backwards testing effect?
actively retrieving previously studied information strengthens memory
taking a test on studied material improves later retrieval of the same material
retrieval practice and backwards testing effect?
retrieval practice produces superior memory to restudy
simple memory model used for experiments
encoding- initial learning phase where pps study information
storage- looks at how long the information is stored by manipulating the retention interval
retrieval- final test where ops are asked to retrace the information from the initial learning phase
common experimental design
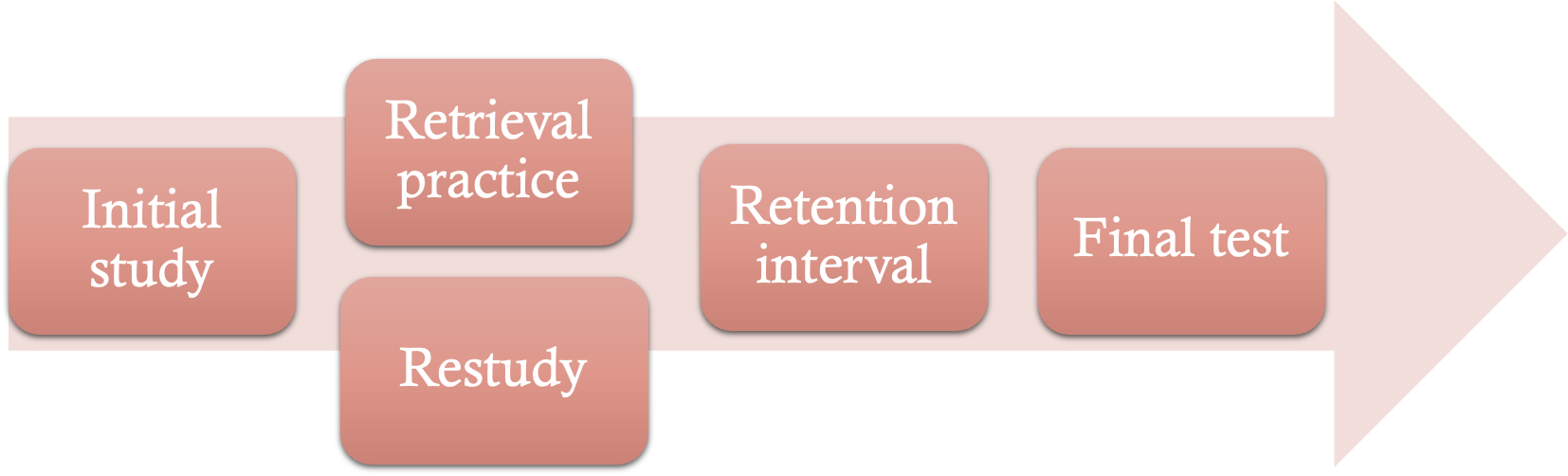
what is a retention interval?
the time between encoding and final test phase
Roediger and Karpicke, 2006- key example
pps studied two prose passages
they studied one passage twice, and the other once
then completed a free recall test (with no feedback)
pps completed final free recall tests for each passage either 5 minutes, 2 days or 1 week later
results: for short retention intervals, restudying was better (after 5 minutes). for longer retention intervals, testing was more effective
what is the theory of transfer appropriate processing?
final test performance should be better when cognitive processes required at encoding and retrieval are the same/similar
mismatch leads to poor performance
what is the theory of retrieval effort hypothesis?
retrieval is more difficult than passive study and serves as a desirable difficulty
the greater the retrieval effort, the greater the benefit of testing
what is the theory of mediator effectiveness hypothesis?
testing creates strong mental links (mediators) between cues and targets, making them easier to recall
semantic elaboration during initial test boots subsequent memory
testing in the real world?
the backwards testing effect is a reliable phenomenon in the lab and in the classroom
Mcdaniel et al, 2007
students took weekly quizzes or were given information to read only
quizzing but not restudying, enhanced final test performance
Agarwal et al, 2021
meta-analysis of 50 experiments of retrieval practice
94% of studies revealed positive effects
Kromann et al, 2009
medical students’ final test performance was significantly better in the intervention group (teaching/ training and 30 minutes of low stakes testing) than the control group (teaching/ training and 30 minutes of running through a scenario)
tests and mental health?
stress impairs memory
but tests reduce anxiety- 72% of pre-college students said retrieval practice made them less anxious
Smith et al, 2016
pps studied a list of words and images
restudy or free-recall retrieval practice x3
24 hours later: stress induction or non-stressful control task
retrial practice enhanced recall and for the study group, stress impaired recall
retrieval practice can protect against memory loss effects of stress