Physics - 2.3 - Nuclear reactions - Decay processes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What does the atomic number tell you?
The number of protons.
What does the mass number tell you?
The number of protons plus neutrons.
What are words used to describe the radioactive forms of an element?
Radioisotope and radionuclide.
What are isotopes said to be if they are unstable?
Radioactive.
What do radioactive isotopes do?
They release particle or electromagnetic waves to become a stable form of the element or become a completely different element.
What is an alpha particle?
A helium nucleus, 42He
Why are alpha particles highly ionising?
They have a large positive charge and so can pull electrons from nearby atoms.
Why do alpha particles lose kinetic energy easily?
They are the largest of the three types of radiation and so collide with other nuclei more easily, causing them to lose kinetic energy.
What can alpha particles be absorbed by?
Thin materials, like a sheet of paper.
What do you do for alpha decay calculations?
Take away 4 from the mass number, take away 2 from the atomic number.
What are beta particles?
Fast-moving electrons.
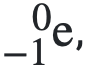
Are beta particles less ionising than alpha particles?
Yes, as they only have a singular negative charge.
Are beta particles more or less penetrating than alpha particles?
They are more penetrating than alpha particles as they are smaller.
What can beta particles be stopped by?
They can be stopped by a few millimetres of metal, such as aluminium.
Where does the electron (beta particle) come from?
It comes from the nucleus.
What happens to create a beta particle?
A neutron splits into a proton and an electron. The proton remains in the nucleus and the electron is ejected at a high speed.
What do you do for beta decay calculations?
Add 1 to the atomic number.
What happens to the nucleus during gamma decay?
Nothing, the nucleus does not change its structure, (unlike alpha and beta decay).
How does gamma decay differ from alpha and beta decay?
It takes the form of electromagnetic waves rather than particles.
When are gamma rays usually given out and why?
They are usually given out after alpha or beta decay in order to release excess energy.
Why are gamma rays the most penetrating?
They have zero mass and no charge.
Are they more or less ionising than beta decay?
They are less ionising.
What is the symbol for gamma decay?
0/0Y
What can reduce the level of gamma radiation?
Lead.
How can the radiation/s of a radioactive source be determined? (experiment)
By using 3 different absorbers and placing them in front of a detector.
What decay processes involve the release of a particle from the nucleus?
Alpha and beta decay.