Midterms PO
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Visual Integrity
involves the different ocular structures and its adnexa, visual pathway and brain that must be properly functioning.
Visual Efficiency
includes the refractive condition of the eye, eye teaming, focusing and tracking.
Visual Processing
composed of visual memory, form constancy, spatial relations, sequential memory, figure ground, closure and visualization.
Adnexa
Accessory structures which are involve in protecting and/or supporting the function of an organ
Receptors
receiver of environmental stimulus
Receptors
Lacks Axons
Receptors
forms synapses with dendrites of other sensory neurons
Receptors
Effectors
Physiological Connectors
This is where the Adaptive Mechanism of Humans depend on
Effectors
End Receiver of this phenomenon
Effectors
refers to the responding organ
Physiological Connectors
the nerve fibers where the nerve impulse travel
Visual/Sight
Auditory/Sound
Olfactory/Smell
Gustatory/Taste
Touch
What are the Five Senses
Sensation
refers to physical stimulation of the sensory receptors
Perceptions
involves interpreting sensory information (decoded)
Sensation and Perception
These are the sensory information from the environment
True
Stimulus Response Phenomenon creates homeostasis to the body
Central and Peripheral Nervous System
It dictates the response of our body
Stimulus
Any change in an environment that causes a reaction
External and Internal Stimulus
Types of Stimulus
Response
Reaction to stimulus and a change in behavior
Instinctual/Reflex and Learned Response
Types of Response
Homeostasis
process that living things use to actively maintain fairly stable conditions necessary for survival. leading to dynamic equilibrium in the body
True
Successful self regulating process leads to continuity of life, if unsuccessful it can lead to disaster or death
Nervous System (brain)
Responsible for all stimulus response phenomenon
Nervous System (brain)
Responsible for body’s response whether it is learned or taught
Sensory Receptors
It causes reaction of the body by receiving stimulus. It is also known to be biological transducers that collect stimulus(energy) and convert them to impulses (electrical)
Dendrites of Sensory Neurons
Specialized for receiving specific kind of stimuli
Afferent Nerve
A sensory neuron that sends signals from sensory receptors to the brain
Efferent Nerve
A motor neuron that sends signal from the brain to the muscles
Reception
Transduction
Perception
What are the sensory processes
Reception
it is the receiving stimulus in the sensory perception
Transduction
it is the conversion of stimulus into impulse (energy → electrical)
Perception
It is how brain interacts or intercepts (process) the stimulus
Exteroceptors
Visceroceptors/Interoceptors
Proprioceptors
Types of Receptors in terms of location
Exteroceptors
Located on the body surface or specialized to detect external stimuli
Its Specific Response are pressure, pain, touch, temperature.
It Functions in reporting the external environment.
It is Found in Sense organs
Visceroceptors/Interoceptors
Located within internal organs detects internal stimuli
It is Found in internal organs
Its Specific Response are blood pressure, pain, fullness.
It Functions in sampling the internal environment.
Proprioceptors
It is found in the joints and muscles, also in vestibular structures and the semicircular canals of the ear and limbs.
Its Specific Response are body position, and movement.
It Functions in sensing the posture, movement of body, & position in space.
Mechanoceptive
Thermoceptive
Nociceptive
Photoreceptors
Chemoreceptive
Types of Receptor in terms of modality or sensitivity
Mechanoceptive
it detects stimuli which mechanically deform the receptor
Its Stimulus are pressure, vibration, touch, sound.
It can be found in the skin and cornea
Thermoceptive
It detects changes in temperature
Its Stimulus are hot or cold.
It can be found in the Skin
Nociceptive
It detects damage to the structure
Its Stimulus is pain.
It can be found in the Skin and viscera
Photoreceptors
It detects light
Its Stimulus is vision
It can be found in the Eye specifically in retina
Chemoreceptive
It detects chemical stimuli
Its Stimulus are carbon dioxide and oxygen in blood, glucose, smell, taste.
It can be found in the Olfactory and Gustatory Also known as Tongue and Nose
Simple
Complex
Types of Receptor in terms of complexity
Simple
It is usually a single modified dendrite
and used for General sense
Its Stimulus are touch in skin, pressure, pain, vibration, and temperature.
It has No physical specialization.
Complex
It is usually highly modified dendrites.
It is used for Specialized sensory senses
Its Stimulus are vision, hearing, smell and taste.
It has physical specialization.
400-700nm
range of energy level received by the eye
20-20000Hz
range of energy level received by the ear
True
Taste buds only accept specific chemicals
Johannes Muller
He wrote the Law of Specific Energies
Law of Specific Energies
It states that:
Sensory messages are carried on separate channels to different areas of the brain.
Nerve impulses have only one pathway going to the brain (converted to image or SAMPLING)
Mind has no access to objects in the world but only to our nerves
Contents of the mind have no qualities in command with environmental objects
Each type of sensory nerve has its own specific sensation
Sensory messages are carries on specific channels to specific areas i n the brain
Photoreceptors
special cells in the retinal responsible for converting light into signals that are sent to the brain
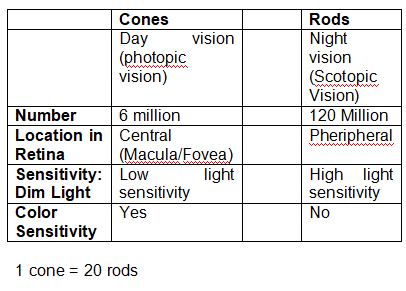
Rods and Cones
Reflex Action
An automatic neural activity wherein a stimulus leads to an immediate action
Reflex Action
An inborn central nervous system activity not involving consciousness
Pupillary Light Reflex
Lacrimal Reflex
Eyelash Reflex
Types of Reflex Action
Pupillary Light Reflex
When light is flashed near one eye, both pupils of the eye will constrict
Its Stimulus is Light stimulus creates impulses that reach the brain via the optic nerve
Its Response is that it is conveyed to the pupillary musculature by autonomic nerves.
Direct Pupillary Light Reflex
Dilation / constriction when light is dim/directed in one eye (same stimulated w/ light)
Indirect Pupillary Reflex
Dilation/constriction in the other eye when light is dim/directed in the other eye (eye not stimulated by light)
Lacrimal Reflex
Its stimulus is irritation on the conjunctiva or cornea of the eye
Its response in afferent is nerve impulses pass along the fifth cranial nerve or the trigeminal nerve and reach the midbrain then the efferent is autonomic and parasympathetic nerves causing the outpouring of tears by the lacrimal gland
Basal
Reflexive
Psychic
Types of Tears
Basal
normal tears for lubrication
Reflexive
tears caused by wind or foreign objects
Psychic
tears produced due to emotion
Eyelash Reflex
Its stimulus is peripheral stimulus in the mechanoreceptors in the epithelium of the cornea and its response in afferent is nerve impulse sent to the trigeminal and facial nerve and the efferent is impulse sent to cranial nerve 7 or facial nerve and will cause a contraction of the orbicularis oculi or eyelids
Dioptrics of the Eye
Includes curvature, thickness, refractive index, and axial length
Optical System of the Eye or Optical Function of the Eye
Other term for Dioptrics of the eye
Refraction
the bending of light a s it travels from one medium to another
Medium
any substance through which light can propagate and transfer energy.
Interface
the line or boundary between two mediums of difference indices
60D
total refractive power of the eye
Refraction of Light
where do the measurement of the refractive power of the eye base on
True
Refraction is dependent on the index of refraction
Cornea
Aqueous Humor/Anterior Chamber
Crystalline Lens
Vitreous Humor
Retina
These are the Dioptric Apparatus
Gauss Cardinal Points
It calculates the image position without concern for optical details
Gauss Cardinal Points
It is the simplification of refraction in the eye through compound homocentric system of six points
Optical Axis
where do the cardinal points based on
False
In Gauss Cardinal points, the refractive surfaces are not considered to have one refractive index and points are independent on the refractive index
True
In Gauss Cardinal points, all the refraction or bending o light in the eye are ignored
Anterior Focal Point
Posterior Focal Point
Anterior Principal Point
Posterior Principal Point
Anterior Nodal Point
Posterior Nodal Point
What are the Cardinal Points
Anterior Focal Point
It is the nearest or the most anterior point to the object and it is composed of Diverging Light Rays
Posterior Focal Point
It is the farthest and most posterior point to the object and it is composed of converging light rays
Focal Point
it is the focus of parallel rays on the retinal plane after refraction or reflection by a curved mirror or lens
Principal Point
point of intersection of the principal plane with the optical axis
Pupillary Plane
posterior cornea to the pupil
Nodal Point
points in the lens on the principal/optical axis from which objects and images appear under the same angle
Anterior Nodal Point
point in the anterior lens capsule
Posterior Nodal Point
point in the posterior lens capsule
False
Anterior and Posterior nodal points are not equal
True
Nodal points don’t intersect
Optical Center
point that intersects the visual axis with the optical axis
Optical Center
point where the undeviated ray crosses the optical axis
Optical Axis
the line joining the centers of all the refractive surfaces of the eye
False
points entering the posterior lens capsule and the light exiting the posterior lens capsule is unequal
7.7mm
Curvature of Cornea
0.5mm
Thickness of cornea
1.37
RI of Cornea
40D
Estimated Dioptric Power of Cornea
1.33
RI of Aqueous Humor
10-5.3mm
Curvature of Anterior Lens