chapter 11: Introduction to organic chemisry
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
organic chemistry
chemistry of organic compounds
features of carbon
4 electrons in its outer shell
can form 4 covalent bonds only
C-C bonds are strong and non polar
can form rings
can form long chain hydrocarbons
formation of organic compounds from inorganic
isomerisation reaction

what did friedrich wohler disprove (1828)
organic compounds were produced by living things only
alkane
only has single bonds
e.g methane
alkene
1 double bond between the 2 carbon atoms
e.g ethene
alkyne
has a triple bond
e.g ethyne
empiricle formula definition
simplest ratio of atoms of each element present in a compound
how to calculate empiricle formula
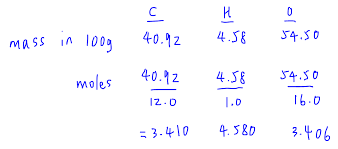
moles= mass/mr
molecular formula
actual number of atoms of each element used
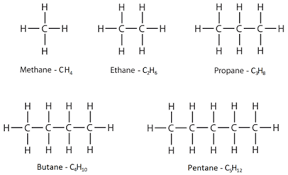
displayed formula
shows every atom and every bond
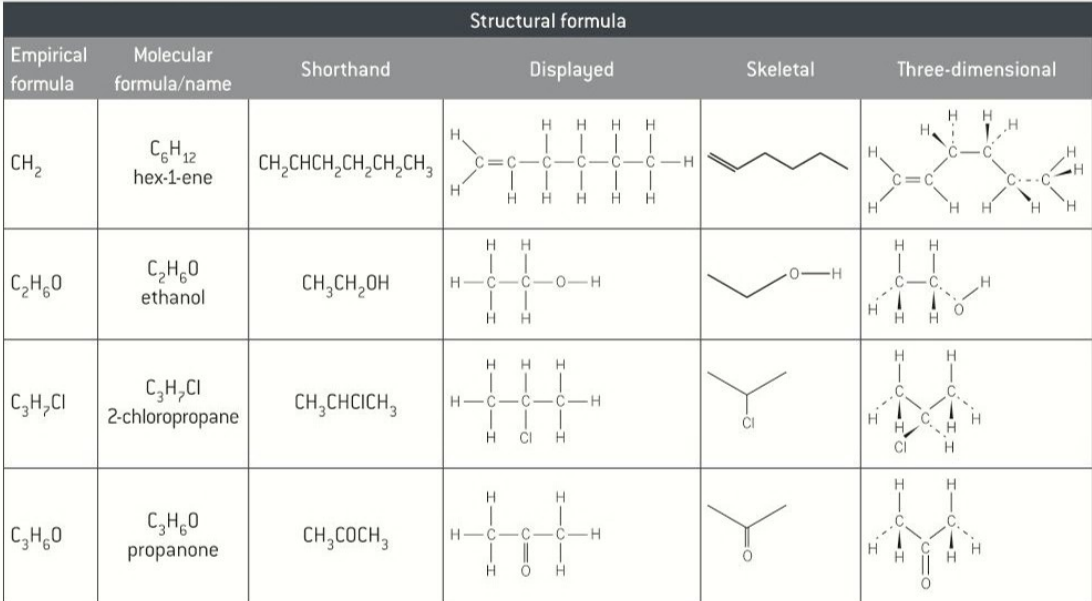
structural formula
unique arrangement of atoms in a molecule without showing all the bonds

skeletal formula
straight lines represent C-C bonds
uses of wedges
bonds coming out of paper
uses of dotted lines
bonds going into the paper
examples of different types of formula
each type tells you different things
curley arrows
show the movement of electrons
why are curley arrows used
because electrons move to areas of high electron density or slightly positive areas
how are free radicals formed
when a shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond break so each atom has an electron
what are free radicals
fragments of original molecules that have an unpaired electron
reacticityy of free radicals
extremely reactive
nomenclature
system used for naming compound
IUPAC
international union of pure and applied chemistry
root
longest unbranched hydrocarbon chain
syllables used after the root
ane, ene, yne, ol,
uses of prefixes
describe changes made to the root and are added to the beginning of the compound
e.g methyl or cyclo
suffixes
added to the end of the root
functional groups
an atom or group of atoms in an organic molecules responsible for the associated/characteristic reactions of that molecule
prefixes used for halogenoalkanes
fluoro, chloro, bromo and iodo
suffix for ketones
one
e.g propanone or pentanone or hexanone
suffix for aldehydes
al
e.g ethanal , propanal etc
suffix for carboxylic acids
oic acid e.g propanoic acid
naming longer chain hydrocarbons
states where the side chain is and its functional group
define locant
a number used to describe the position of any branching or functional group
history of naming organic compounds
common names were given originating from latin
disadvantages of IUPAC naming system
some systematic names are too long
common names are given e.g housane
1 or more hydrogen are substituted naming system
also use numbers to indicate where the halogen atom is
di= 2
tri = 3
tetra = 4
homologous series
a set of organic compounds with the same functional group where the chain length can vary
features of a homologous series
same general formula
same functional group
each member differs
length affect physical properties
chain branching decreases the melting point due to decreased packing
isomerism
a compound with the same molecular formula and different arrangement of atoms
structural isomer
same molecular formula and different structural formula
types of structural isomerism
positional
fucntional group
chain
positional group isomerism
same functional group but on different carbons e.g a bromine atom on third or first carbon
functional group isomerism
the functional group is attached to different carbons
chain isomerism
different arrangements of the hydrocarbon chain
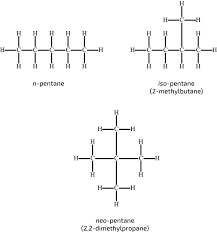
stereoisomerism
2 or more compounds that have the same structural formula with different arrangements
E isomerism
priority group is on the opposite side of the alkene
Z isomerism
priority groups are on the same side of the alkene