Econ terms and questions: micro
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
1
New cards
what does ceteris paribus mean
it means “assuming all other things stay the same”. You use it when analyzing an isolated shock to indicate that you are only assuming the specific shock is what caused the change
2
New cards
what are the 4 factors of production (FOPs)
land, labour, capital, and entrepreneurship
3
New cards
who can own FOPs and what are the reasons that each owner produce goods
they can be publicly (government) or privately (companies) owned, public sector produces goods that will better society eg. health care, the private sector produces to gain profits
4
New cards
what are the 3 types of capital
physical capital, human capital, financial capital
5
New cards
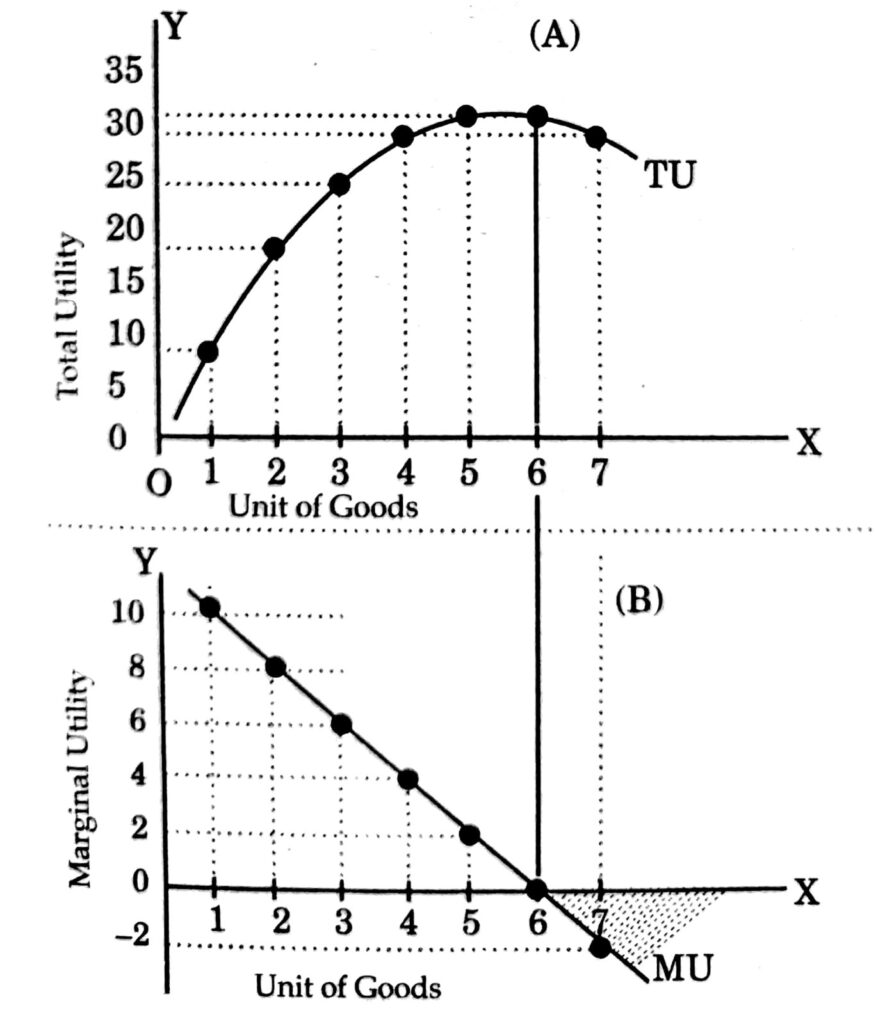
define marginal utility
the amount of additional satisfaction each extra unit of a good produces when consumed
6
New cards
explain the law of diminishing marginal utility
as more of a good is consumed each additional unit will provide less satisfaction than the last
7
New cards
define opportunity cost
it is the cost of making a decision on how to use scare resources; the cost of deciding. It is the cost of giving up the next best option
8
New cards
define free goods vs economic goods
there is an infinite access to the resources required to produce the good and they do not cause an opportunity cost eg. oxygen, sunlight, sunset
vs
they use scarce resources in their production and there is always an opportunity cost to make them
vs
they use scarce resources in their production and there is always an opportunity cost to make them
9
New cards
define capital goods
goods created to produce other goods eg. machinery
10
New cards
define consumption goods
goods used for final consumption to directly satisfy a need/want eg. food, clothing
11
New cards
what is the purpose of a ppf
to show us how much or what combination an economy can produce of 2 goods with a certain amount of FOPs
12
New cards
where is inefficient on a ppf, where is efficient, and where is unattainable
anywhere along the ppf curve FOPs are being used efficiently, below the ppf curve they are being used inefficiently, and producing an amount above the ppf curve is impossible because there is not enough FOPs available
13
New cards
define GDP - gross domestic product
a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold in a specific time period by a country or countries, usually measured each year
14
New cards
economic growth
the rate of change is the output (production of goods and services) of a given country from one year to the next measured in monetary terms. Change in GDP.
15
New cards
what is the result of investing in capital goods
investing in them will increase your FOPs and increase your capacity for production which will shift out the curve of the ppf and therefore increase GDP
16
New cards
what is industrialization
when a country starts to produce more capital goods than consumption goods to invest in the future of their economy
17
New cards
what is economic development
the process of improving the quality of human life by increasing income, reducing poverty, bettering education, improving health care, etc.
18
New cards
explain the difference between economic growth vs economic development
the rate of change is the output (production of goods and services) of a given country from one year to the next measured in monetary terms
vs
the process of improving the quality of human life by increasing income, reducing poverty, bettering education, improving health care, etc.
vs
the process of improving the quality of human life by increasing income, reducing poverty, bettering education, improving health care, etc.
19
New cards
explain the difference between increasing productivity vs increasing production
increasing productivity involves using FOPs more efficiently eg. use tech to produce faster
vs
increasing production involves utilizing unused FOPs or gaining more FOPs to increase the amount you are able to produce
vs
increasing production involves utilizing unused FOPs or gaining more FOPs to increase the amount you are able to produce
20
New cards
define public goods
goods or services not provided by private investment or the free market eg. national security, roads and bridges, etc. which means that the government must produce them
21
New cards
define merit goods, their production, and their main characteristics
goods that are beneficial to society but are underproduced by the free market considering what society needs. eg. health care, education, etc. they. are underproduced by the free market because consumers may not be able to afford or feel the need to buy them. merit goods have positive externalities in consumption that may be ignored by the consumers eg. libraries, museums, etc.
22
New cards
define sustainable development
development that is able to provide for and meet the needs of current generations without compromising the ability to meet those needs for future generations
23
New cards
define demand
the relationship between price, and the quantity of what consumers are willing and able to pay for a good/service
24
New cards
state the law of demand
the law of demand states that price and quantity demanded of a good have a negative relationship because as the price of a good increases the QD decreases, and vice versa.
25
New cards
what are exogenous variables
a factor outside of the demand function that affects quantity demanded for example weather, income, population, etc. Anything other than price
26
New cards
what are endogenous variables
a factor within the demand function that effects quantity demanded. This can only be price.
27
New cards
what is a veblen good and what is its relationship with the law of demand
is is a good where quantity demanded increases as price increases. this can because consuming the good will show status/it is a popular good, or because the value of the good is expected to rise as you own it for longer eg. gold it is an exception to the law of demand because quantity demanded increases as price increases.
28
New cards
what is a giffen good and what is its relationship with the law of demand
it is a good with no substitute that people consume even as the price rises. for example potatoes that low income people buy regardless of price because everything else is still more expensive
29
New cards
define supply
the willingness and ability for producers to produce a good at a given price. The relationship between quantity supplied and it price
30
New cards
what are the determinants of supply
price of FOPs and resources
government intervention eg. taxes + subsidies
number of suppliers in the market
state of technology
\
\
government intervention eg. taxes + subsidies
number of suppliers in the market
state of technology
\
\
31
New cards
state the law of supply
the higher the price of a good in the market, the more incentive to increase the quantity supplied, ceteris paribus. Therefore the as price of a good increases, so does the quantity produced
32
New cards
what are 3 things needed for markets to reach equilibrium
there must be many buyers and sellers so one single firm cannot influence the price, there must be free competition and no barriers to enter the market, and it must be the same good and price is the only thing determining demand
33
New cards
market disequilibrium: what happens if the price is above the equilibrium
if price is above the equilibrium supply is increased however there aren't enough people willing and able to pay the price so there is an overproduction of the good which creates an excess of production
34
New cards
market disequilibrium: what happens if price is below the equilibrium
if market price is below the equilibrium there are many people willing and able to pay that price however there is not enough of an incentive to produce the good so this creates a shortage
35
New cards
how do markets achieve equilibrium on their own
when a price is too high one supplier will lower their price to entice consumers and other producers will compete with that price, lowering it until equilibrium is reached. if the price is too high, consumers will bid up the prices, producers will produce more at new higher prices until equilibrium is reached
36
New cards
what is allocative efficiency
an allocation of resources that allows production to align with a state where production aligns with consumer wants and, and for each good produced its marginal cost of production is equal to the selling price. this can also be defined as when P=MC
37
New cards
how will an an exogenous shock on supply affect demand
an exogenous shock on supply with create an endogenous shock on demand
38
New cards
how will an exogenous shock on demand affect supply
an exogenous shock on demand with create an endogenous shock on supply
39
New cards
define consumer surplus
the value of the difference between what consumers are willing and able to pay and what they actually pay
40
New cards
define producer surplus
the value of the difference between what producers are willing and able to sell at and what they actually sell at
41
New cards
define social welfare
consumer surplus and producer surplus together, the amount the society is benefitting from the price at the time
42
New cards
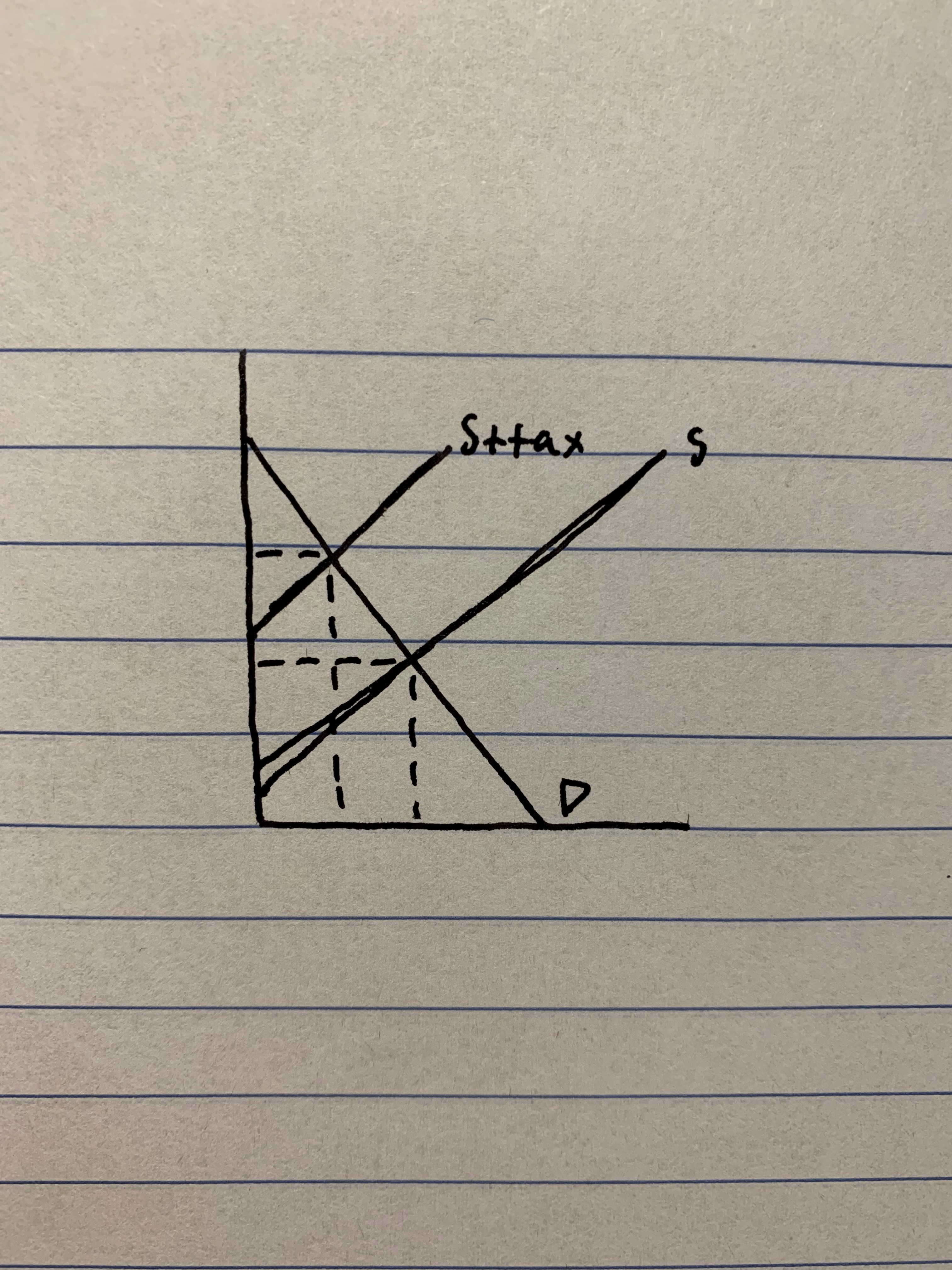
identify producer surplus after the tax
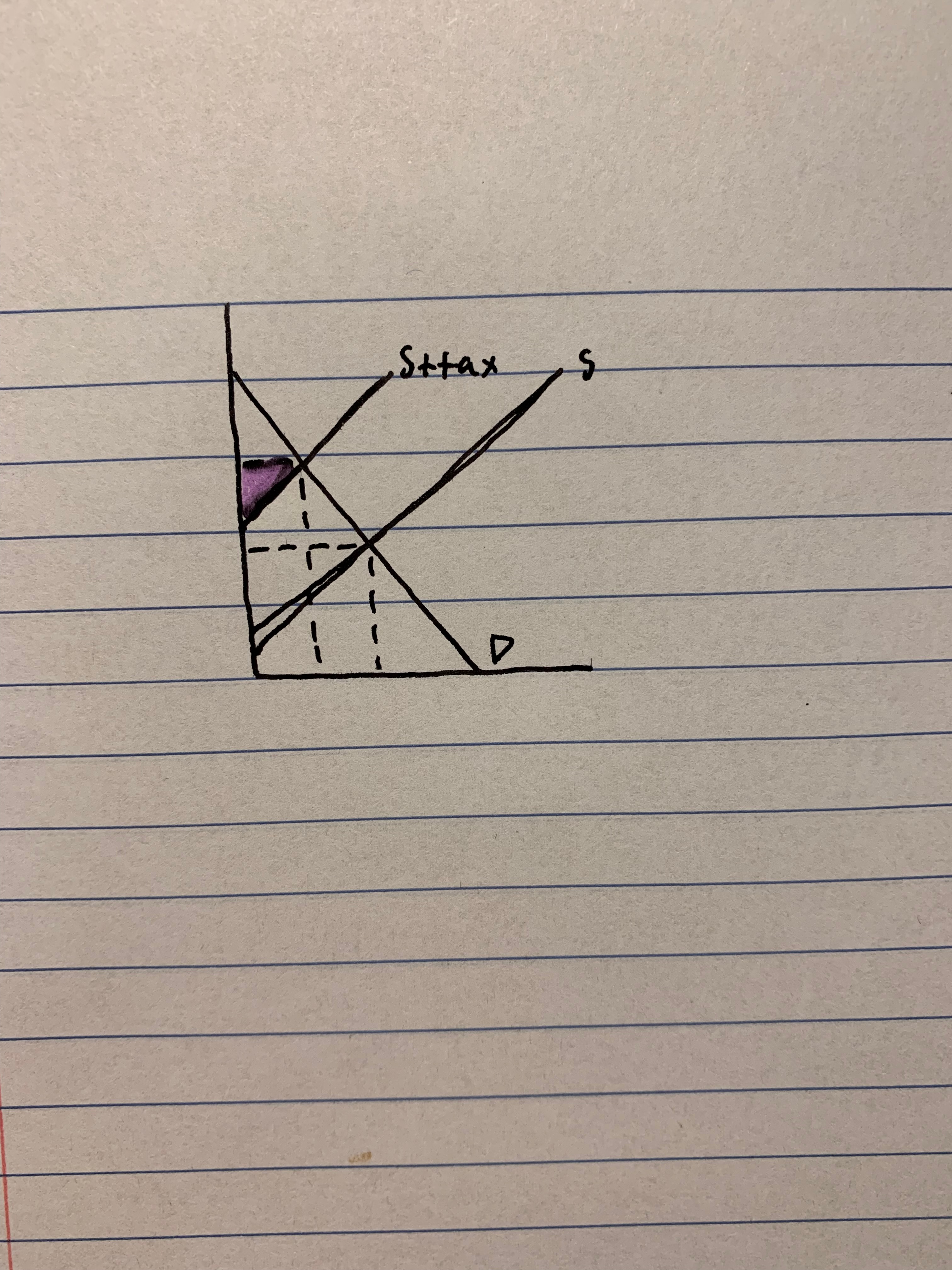
43
New cards
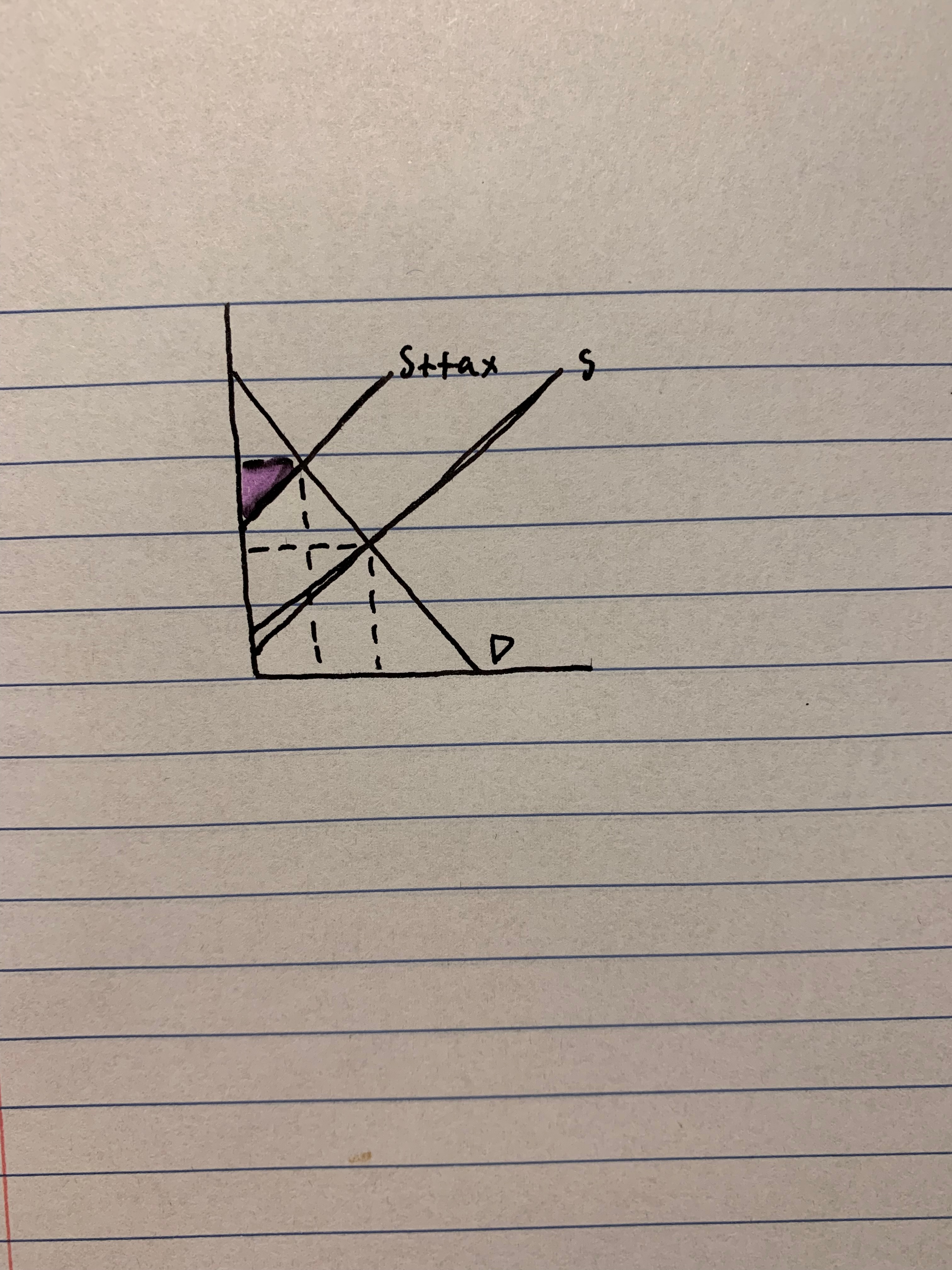
identify consumer surplus after the tax
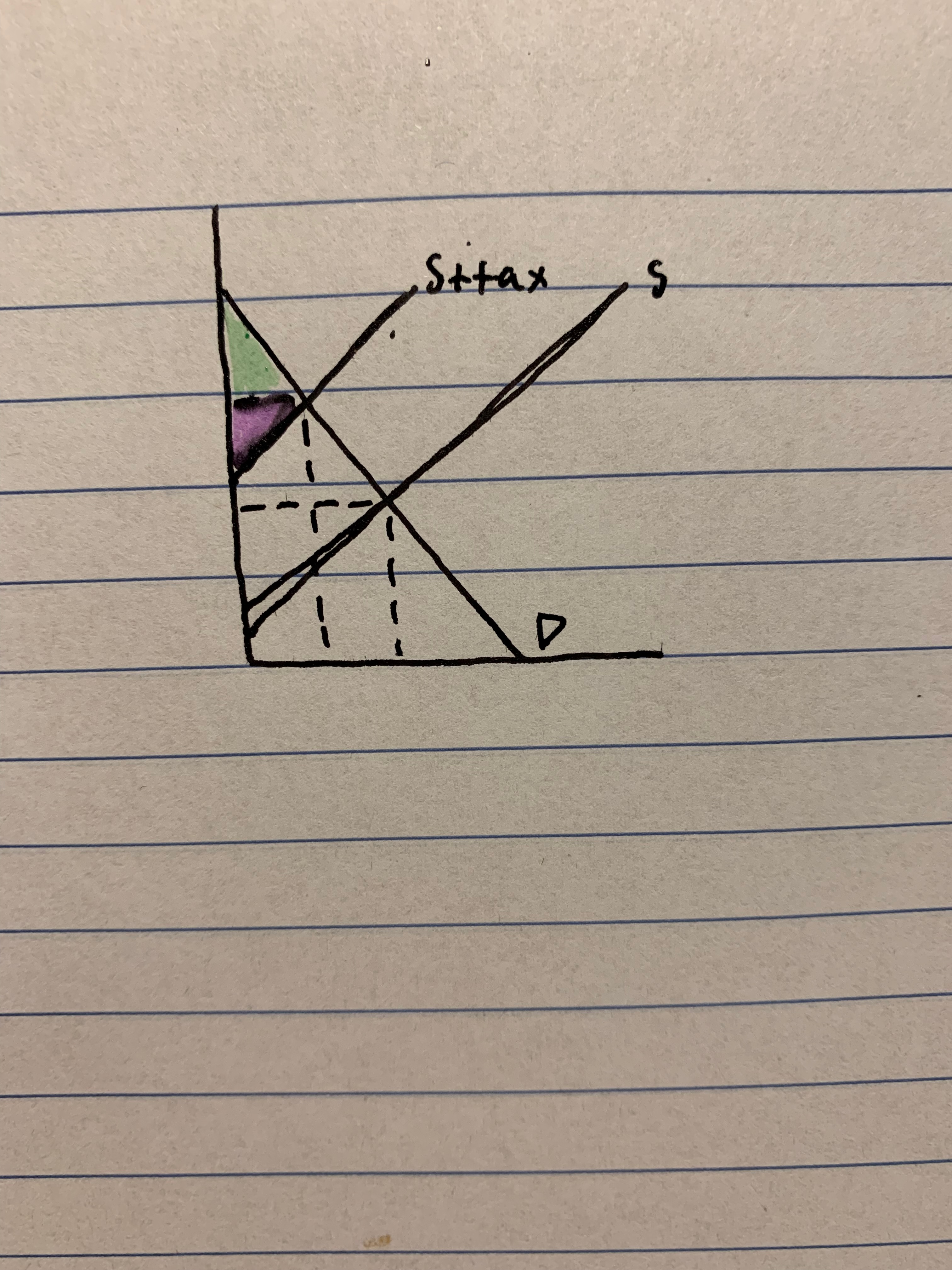
44
New cards
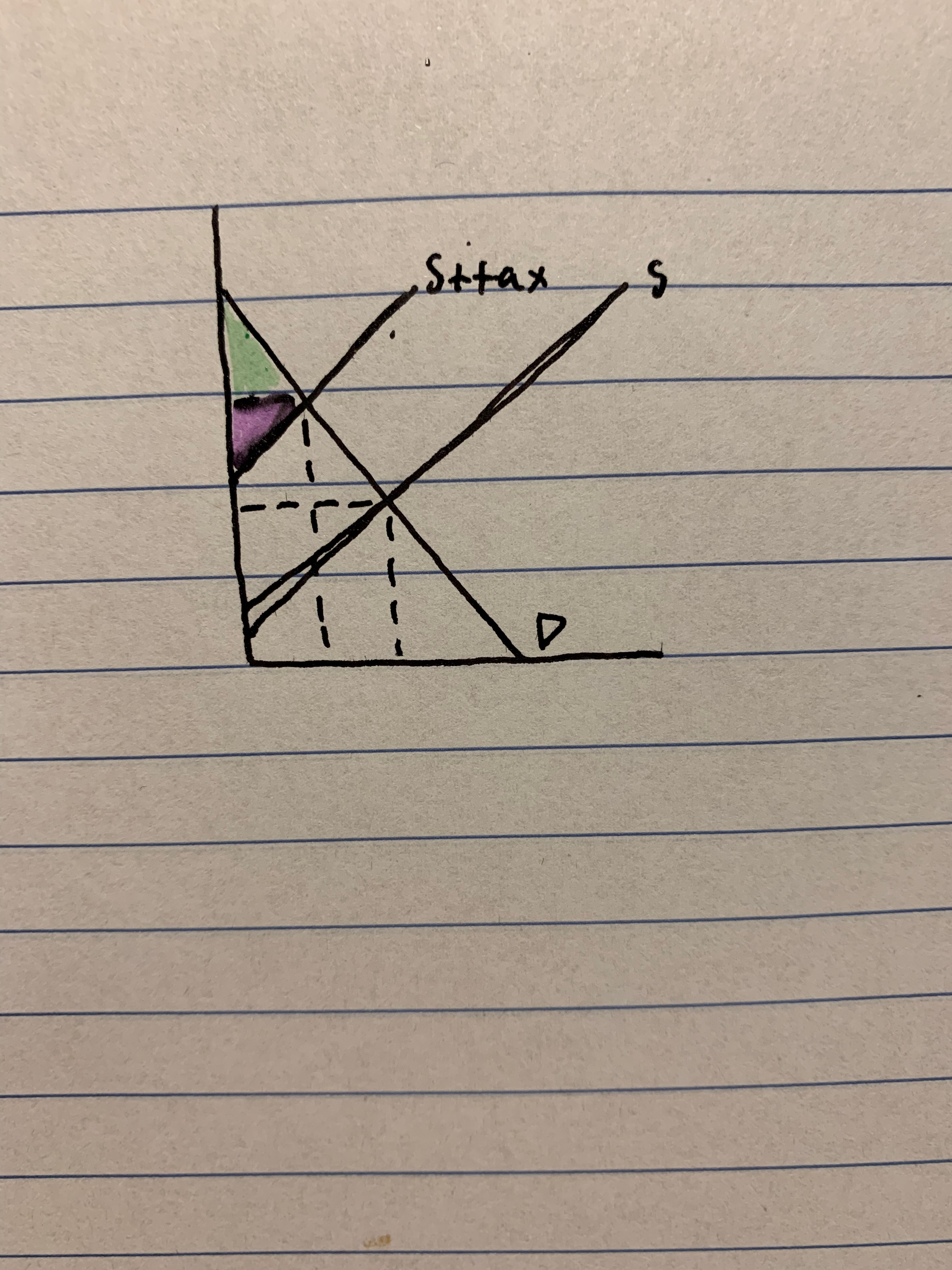
identify welfare loss after the tax
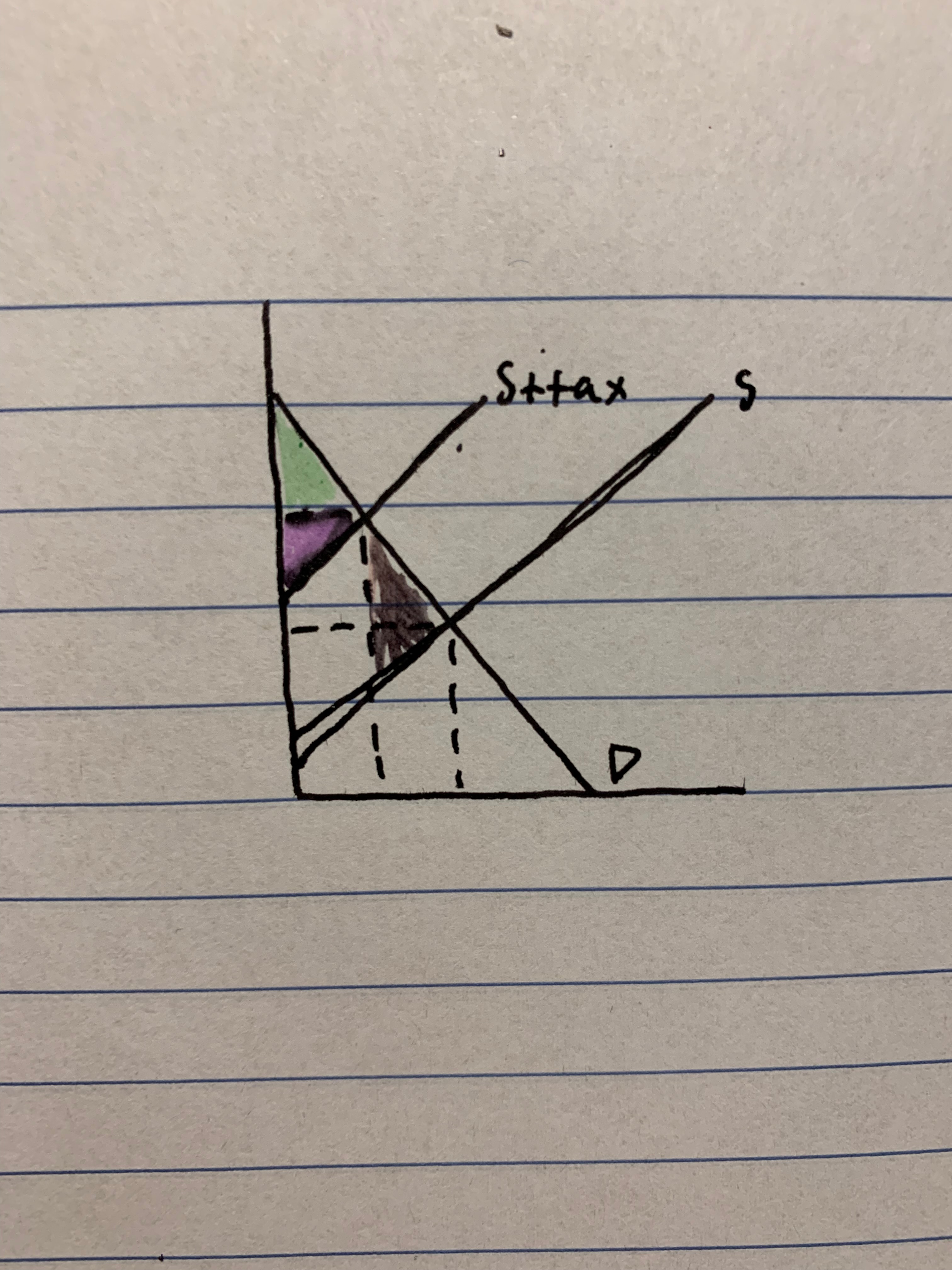
45
New cards
what is welfare loss
a cost to society created when the market is not operating at the equilibrium. It is the loss of a portion of the social welfare due to market failure and MSC not equalling MSB
46
New cards
what is economic efficiency
when equilibrium is met all goods and FOPs are distributed, allocated, and produced to their most valuable uses and waste is eliminated. when allocative and productive efficiency is reached. when MSB is equal to MPB or when MSC is equal to MPC. When the Pareto Optimum is reached and when social welfare is maximized. WHEN ALLOCATIVE EFFICIENCY IS REACHED
47
New cards
what type of diagram do you use to illustrate allocative efficiency?
supply and demand
48
New cards
what type of diagram do you use to illustrate productive efficiency
a PPF
49
New cards
what are the 2 types of taxes
direct and indirect
50
New cards
what is a direct tax
a tax on income or profits of a person
51
New cards
what are the 2 types of indirect taxes
fixed tax and ad valorem tax
52
New cards
what is a fixed tax
when the tax is a the same amount no matter the price of the good
53
New cards
what is an ad valorem tax
when the tax is a percentage of the price of a good, so as the price increases, the tax also increases
54
New cards
what is a subsidy
it is money granted by the government to producers to assist the industry or business and decrease the cost of production so that the final price can be lower for consumers
55
New cards
using demand and supply, and quantity and price explain the effect of a tax on cigarettes
a tax will increase the cost of production which will shift the demand curve in causing the final sale price to be higher than before, therefore because of the law of demand less people will be willing and able to buy cigarettes
56
New cards
using demand and supply, and quantity and price explain the effect of a subsidy on electric cars
a subsidy will decrease the cost of production which will shift the demand curve out causing the final sale price to be lower than before, therefore because of the law of demand more people will be willing and able to buy electric cars
57
New cards
explain a price ceiling
opposite of what you think! it is set by the government BELOW the equilibrium price, it is the maximum price producers are allowed to sell at
58
New cards
explain a price floor
opposite of what you think! it is set by the government ABOVE the equilibrium and it is the lowest price producers are allowed to sell at
59
New cards
explain why a government would want to set a price ceiling
price ceilings are set when the price becomes too high compared to what the government thinks it should be. the price ceiling is set BELOW the equilibrium to try and lower the market prices
60
New cards
explain why a government would want to set a price ceiling
price ceilings are set when the price becomes too low compared to what the government thinks it should be. the price ceiling is set ABOVE the equilibrium to try and raise market prices
61
New cards
what is the definition of a monopoly and describe the characteristics
a Monopoly is when there is one dominant seller of a good.
high barriers to enter
cannot be other close substitutes
no supply curve in a diagram because the 1 firm can just determine the price as they wish and consumers must pay that price if they want the good
high barriers to enter
cannot be other close substitutes
no supply curve in a diagram because the 1 firm can just determine the price as they wish and consumers must pay that price if they want the good
62
New cards
what is the definition of a oligopoly and describe the characteristics
the same as a monopoly (when there is one dominant seller of a good.
high barriers to enter
cannot be other close substitutes
no supply curve in a diagram because the 1 firm can just determine the price as they wish and consumers must pay that price if they want the good)
but with a few large firms dominating the market, can collude and act as a monopoly
high barriers to enter
cannot be other close substitutes
no supply curve in a diagram because the 1 firm can just determine the price as they wish and consumers must pay that price if they want the good)
but with a few large firms dominating the market, can collude and act as a monopoly
63
New cards
what is monopolistic competition
large amounts of firm producing similar goods that are differentiated, they can set the price and share the market by differentiating their products, and entry barriers are particularly low. almost every market we know eg. shoes, pens, cars, etc.
64
New cards
what is the difference between perfect competition and monopolistic competition
in perfect competition, firms produce exactly the same goods, the only difference is the prices, and in monopolistic competition, firms produce the same goods but with different characteristics
65
New cards
what is elasticity of demand
a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good in respect to a change in the price of a good. how much will QD change proportionally compared to the change in price. if price goes up how willing are people to still buy it?
66
New cards
what determines how elastic demand is (3 things)
1. how available perceived alternatives are
more substitutes available means more elastic
2. how much time you have to find an alternative
shorter time period to find an alternative makes a good more inelastic
3. the proportion of income spent on the good
the smaller the proportion of income spent on it the more elastic it is (the less people will respond to a price change)
67
New cards
on a linear demand curve where are the different areas of elasticity?
the top half is elastic
middle is unit elastic
bottom half is inelastic
middle is unit elastic
bottom half is inelastic
68
New cards
describe the characteristics of an inelastic good in regards to revenue vs price change
total revenue will decrease when price decreases and total revenue will increase when price increases, this is because a price change will result in a small change in amount of people buying it
69
New cards
describe the characteristics of an elastic good in regards to revenue vs price change
revenue will increase when price decreases and vice versa, this is because a price decrease will result in a high proportion of people buying it
70
New cards
what is a superior good
it is a good with an elasticity greater than 1, so a small percent change in income will result in a large percent change in quantity demanded
71
New cards
what is the relationship between superior goods and income
as income increases so will the quantity demanded of superior goods
72
New cards
what is an inferior good
they are necessities or goods that no matter your income you will need the same amount of it, they are unit elastic or inelastic goods
73
New cards
what is the relationship between income and inferior goods
as income increases you will buy less inferior goods and as income decreases you will buy more inferior goods because they may be substitutes for other superior goods
74
New cards
define price elasticity of supply
the ability and capacity for producers to provide more or less of a good in response to a change in price, how responsive is quantity supplied to a change in price
75
New cards
what are the 2. determinants of supply elasticity
1. time period, if the goods can be changed and produced quickly, the producers can respond quickly to a change in price which makes a shorter time period good more elastic
2. the availability of FOPs, the less available they are the more inelastic it will be.
76
New cards
define market failure
market failure occurs when the free market fails to achieve efficiency or when resources are not allocated properly. market failure occurs when the pareto optimum is not reached or when the equilibrium is not met. it can also be defined by the fact that social welfare is not maximized and when MSB does not equal MSC
77
New cards
define productive efficiency
when goods are produced at the lowest possible cost per unit and resources are used at their best capacity to produce
78
New cards
what are the reasons and root causes for market failure
markets fail because of
public and merit goods also known as missing markets
lack of competition
externalities in production and consumption, and common access resources
information failure
poverty and inequality in an economy
public and merit goods also known as missing markets
lack of competition
externalities in production and consumption, and common access resources
information failure
poverty and inequality in an economy
79
New cards
define the Pareto optimum, or Pareto efficiency
pareto optimum is said to be achieved when no economic changes can make one individual better off without making someone worse off. It is the point in the economy where society wants to produce
80
New cards
define externality
an externality is a benefit or cost to a third party that is the result of the production or consumption of a good
81
New cards
what is a positive externality in production
a positive externality in production happens when MSC is lower then MPC, so the production of a good gives more benefits to the society as a whole than it does to the producer
82
New cards
what is a negative externality in production
a negative externality in consumption is when MSC is larger then MPC, so the cost to society is larger than the cost it takes for someone to produce the good
83
New cards
what is a positive externality in consumption
a positive externality in consumption is when a third party receives a benefit that they do not pay for because of the consumption of a good, so MSB is larger than MPB and the benefit to society is greater than the benefit to the individual consuming the good
84
New cards
what is a negative externality in consumption
a negative externality in consumption means that the MSB is lower than the MPB, so the individual consuming the good is receiving more benefit than the society
85
New cards
what is a Pigouvian tax
it is a specific tax aimed to correct market failures and and offset negative externalities
86
New cards
define a merit good
good that is desirable for consumers but is under-provided by the free market. this could be because
there is a positive externality in consumption
consumers with low income cant afford it
or the benefits of the good are ignored
there is a positive externality in consumption
consumers with low income cant afford it
or the benefits of the good are ignored
87
New cards
define a demerit good
a good that is bad for consumers but is over-provided by the free market. they may be over-provided because there is a negative externality in consumption or the negative effects of them are ignored
88
New cards
what are the determinants of demand
income
price of substitute goods
price of complimentary goods
population
\
price of substitute goods
price of complimentary goods
population
\