Unit 1 & 2
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
flashcards from different types of psychologists to statistical experiments
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Psychology
the scientific study of the behavior/ mental processes of humans and animals
Structuralism
identifying the elements of thought and mind (structures) the way early chemists developed the periodic table to classify elements
Introspection
the process of looking inward to directly observe one’s own psychological processes
Behaviorism
believes psychology should be an objective science
Humanism
the belief that humans strive to reach their full potential. The study of potential and personal growth.
Contemporary psychology
influenced by biology and experience, culture and gender, and human flourishing
Cognitive psychology
study of mental processes
Evolutionary Psychology
study of how behaviors and mental processes present in the species today exist because they were naturally selected
Behavior Genetics
study of the relative influence and limits of genetic (nature) and environmental (nurture) influences on behaviors and mental processes
Culture
shared ideas, values, behaviors, and traditions, shared by a group of people and passed from one generation to the next
Gender
socially constructed roles and characteristics by which a culture defines male and female
Positive Psychology
the study of human flourishing
Behavioral Perspective
how learned and observable behaviors impact behavior/mental processes
Biological Perspective
how biological (genetics, neural, hormonal) and physiological processes impact behavior/mental processes
Cognitive Perspective
how interpretations of situations and mental processes (thoughts, memories, problem-solving) impact behavior/mental processes
Evolutionary Perspective
how the natural selection of traits has promoted the survival of genes
Humanistic Perspective
how the drive for personal growth and self-actualization impact behavior/mental processes
Psychodynamic Perspective
how unconscious drives and conflicts impact behavior/mental processes
Social-Cultural Perspective
how behavior and thinking vary across situations and cultures
Basic research
scientific inquiry that aims to increase psychology’s knowledge base
Applied research
scientific inquiry that aims to use psychology to solve practical problems
Counseling Psychologists
help individuals cope with or make difficult life changes
Clinical Psychologists
asses and treat mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders
Psychiatrist
prescribe drugs to treat the physiological causes of psychological disorders
Cognitive Psychologists
study human thinking
Developmental Psychologists
study how our behavior changes as we age
Educational Psychologists
study how we learn in different environments and in different ways
Experimental Psychologists
conduct experiments to understand our behaviors and mental processes
Psychometric Psychologists
use math and statistics to create, administer, score and interpret tests
Social Psychologists
study how we interact with others and how groups impact us individually
Forensic Psychologists
brings law and psychology together
Environmental Psychologists
study how we are influenced and affected by our natural or built (urban) surroundings
Health Psychologists
work to promote health and prevent disease
I/O Psychologists
study the relationship between people and our work environments
Human Factors Psychologists
study the interaction of people, machines, and physical environments
Neuropsychologists
study how our brain impacts our behavior and thoughts
Rehabilitation Psychologists
help individuals who have lost functioning after an accident or illness
School Psychologists
work with kids in school dealing with problems that may negatively impact learning in the classroom
Sports Psychologists
work with athletes to help them improve their performance
Community Psychologists
work with larger groups and communities and focusing on crisis management (i.e. recovering from a hurricane)
Hindsight bias
tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that we would have foreseen it
Overconfidence
tendency to think we know more than we do
Theory
an explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events
Hypothesis
testable prediction, often implied by a theory
Operational definition
carefully worded statement of the exact procedures (operations) used and meanings in a research study
Case studies
descriptive technique in which one individual or group is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
Naturalistic observations
descriptive technique of observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate or control the situation
Surveys and interviews
descriptive technique for obtaining the self-reported attitudes/behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of the group
Survey bias
when the people surveyed are not representative of the population
Representative samples
have the same distribution of demographic qualities in it as the population as a whole
Random sample
a sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
Cross-sectional research
studies compare people of different ages at the same point in time
Longitudinal studies
follow and retest the same people over time
Correlation
a measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and how well either factor predicts the other, simply put, how related two things are to each other
Positive Correlation
two sets of data tend to rise or fall together
Negative Correlation
one set of data rises while the other falls
Illusory correlations
perceiving a relationship where none exists, or perceiving a stronger-than-actual relationship
Scatterplots
are a graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables
Random Sampling
Choosing a representative sample of the population being studied
Random Assignment
assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between the different groups
Confounding variable
a factor other than the factor being studied (the IV) that might influence a study’s results
Single blind
the participants in the study are uninformed about the treatment, if any, they are receiving
Double blind
the participants AND the researcher are uninformed about which group receives the treatment and which does not
Placebo effect
inert treatment; like a pill without any medication inside
Experimental validity
the extent to which a test/experiment measures/predicts what it is supposed to
Consent
“are you willing to participate in this experiment?”
Informed consent
This experiment involves exposure to graphic images that may be disturbing and random bursts of light that have been known to induce seizures. Are you willing to participate in this experiment?
Deception
the true purpose isn’t revealed because it would influence the results
Debriefing
when temporary deception is necessary to the research, it must be fully explained at the conclusion of the experiment
Descriptive statistics
Numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups
Histogram
a bar graph that shows a frequency distribution
Mean
The average of a set of numbers
Median
The middle score in a distribution, arrange scores from highest to lowest with half of the data above and half below n
Mode
most frequently occurring data point in a distribution
Range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
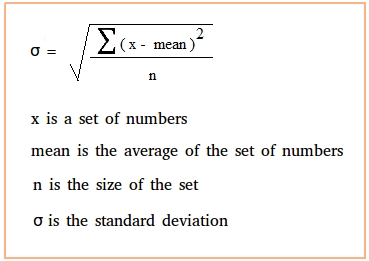
Standard Deviation
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
Skewed distribution
most of the scores or data fall on one side of the scale
Outlier
one data point is extremely different from the others
Normal distribution
symmetrical curve where most scores fall near the mean
Inferential statistics
Numerical data that allow one to generalize—to infer from sample data the probability of something being true of a population
Descriptive statistics
describe a population or data set
Inferential statistics
examine relationships between variables in sample
Statistical significance
statistical statement of how likely it is that a result occurred by chance