Astrophysics
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
What does a convex or converging lens do?
Focuses incident light
What does a convex or diverging lens do?
Spreads out incident light
What is the principle axis
The line passing through the centre of the lens at 90 to its surface
What is the principle focus In a converging lens? (F)
The point where Incident beams passing parallel to the principal axis will converge
What is the principle focus in a Diverging lens? (F)
The point from which the light rays appear to come from, this is the same distance either side of the lens
What is the focal length? (f)
The distance between the centre of the lens and the principal focus
What does a shorter focal length show
A stronger lens
When is the real image formed?
Phone when light raises cross after refraction
When is a virtual image formed?
Formed on the same side of the lens, the light rays do not cross so a virtual image cannot be formed on the screen
What is the lens formula?
Where u is the distance of the object from the centre of the lens, V is the distance of the image from the centre of the lens and f is the focal length of the lens
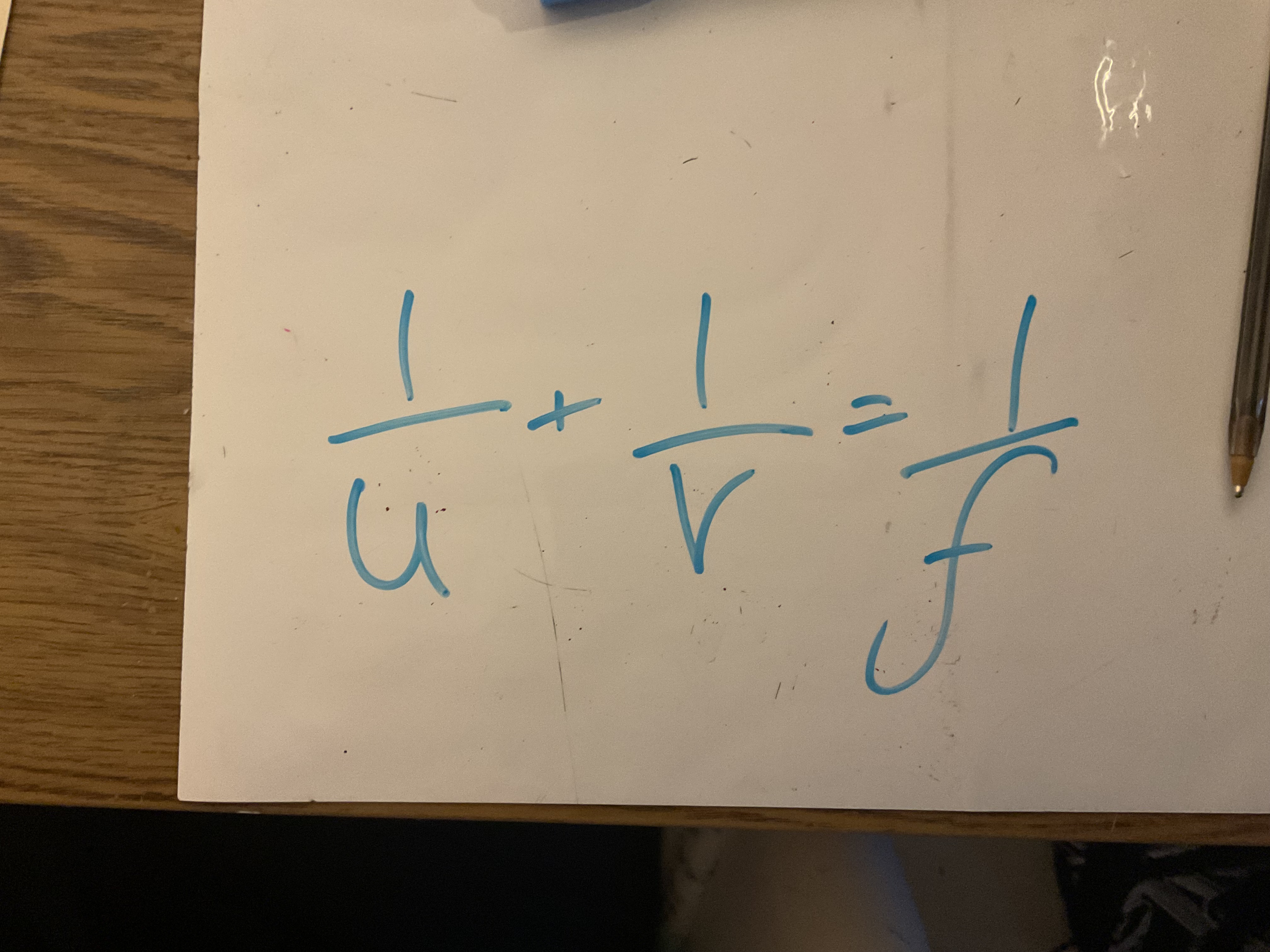
What is the power of a lens?
A measure of how closely a lens can focus a beam that is parallel to the principal axis (how short the focal length is)
What is power lens measured in?
Dioptres (D)
Power of a lens equation
P=1/u+1/v=1/f
What two lenses were refracting telescope made of?
Two converging lenses, the objective lens and eyepiece lens
What is the role of the objective lens in refracting telescopes?
To collect light and create a real image of a very distant object the lens should have a long vocal length and be large as to collect as much light as possible
What is the collecting power of a telescope directly proportional to?
The square radius of the objective lens
What is the role of the eyepiece lens in a refracting telescope?
Magnify the image produced by the objective lens so that the observer can see it. This lens produces a virtual image at Infinity since the light rays are parallel. This reduces eye strain for the observer as they do not have to refocus every time they look between the telescope image and object in the sky
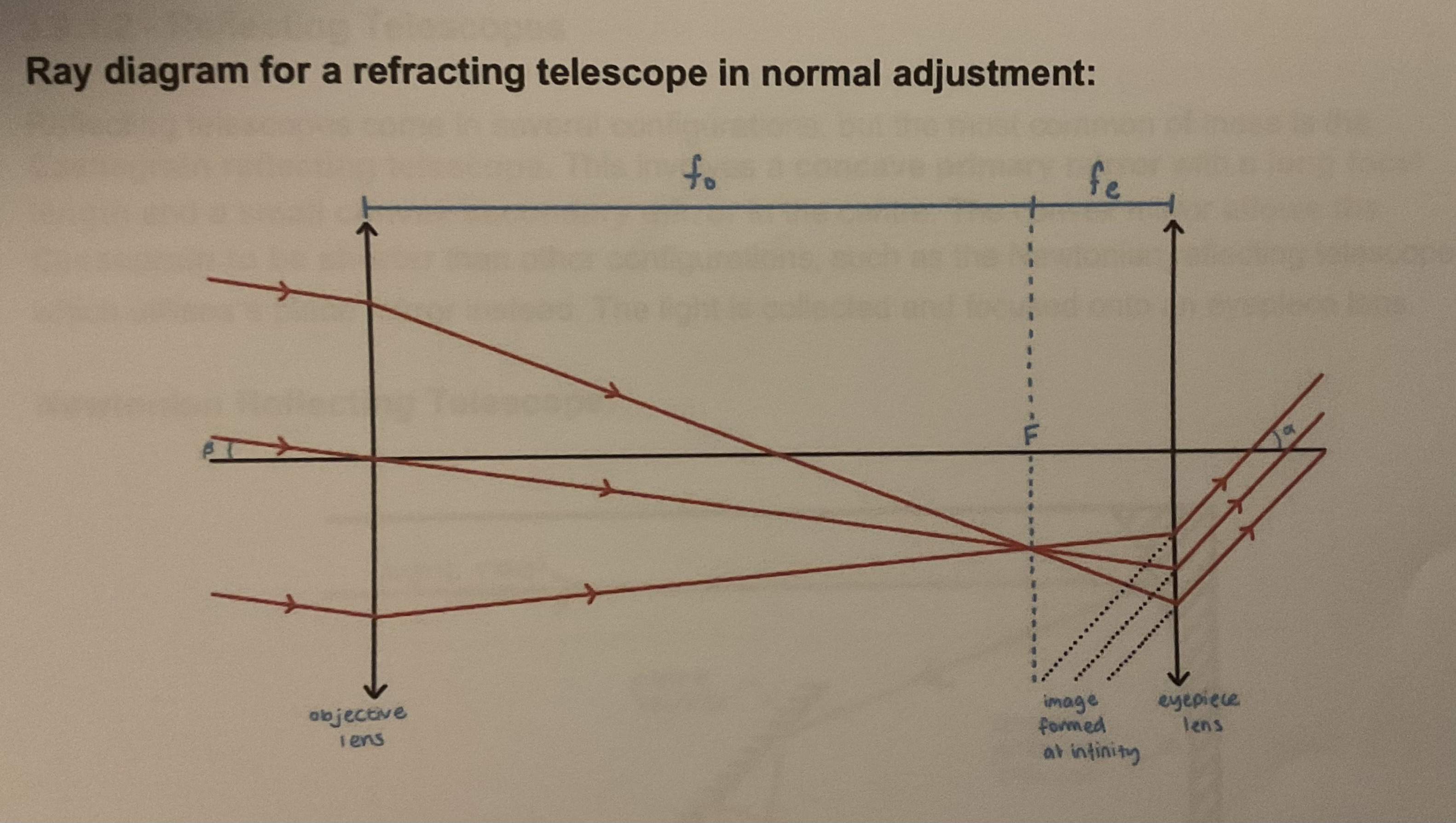
What is normal adjustment for refracting telescope?
When the distance between the objective lens and eyepiece lens is the sum of their focal lengths (fo + fe) this means the principal focus F for these two lenses is in the same place
Formula for magnifying power or angular magnification (M)of a telescope
M= angle subtended by the image at the eye/ angle subtended by the object at the unaided eye
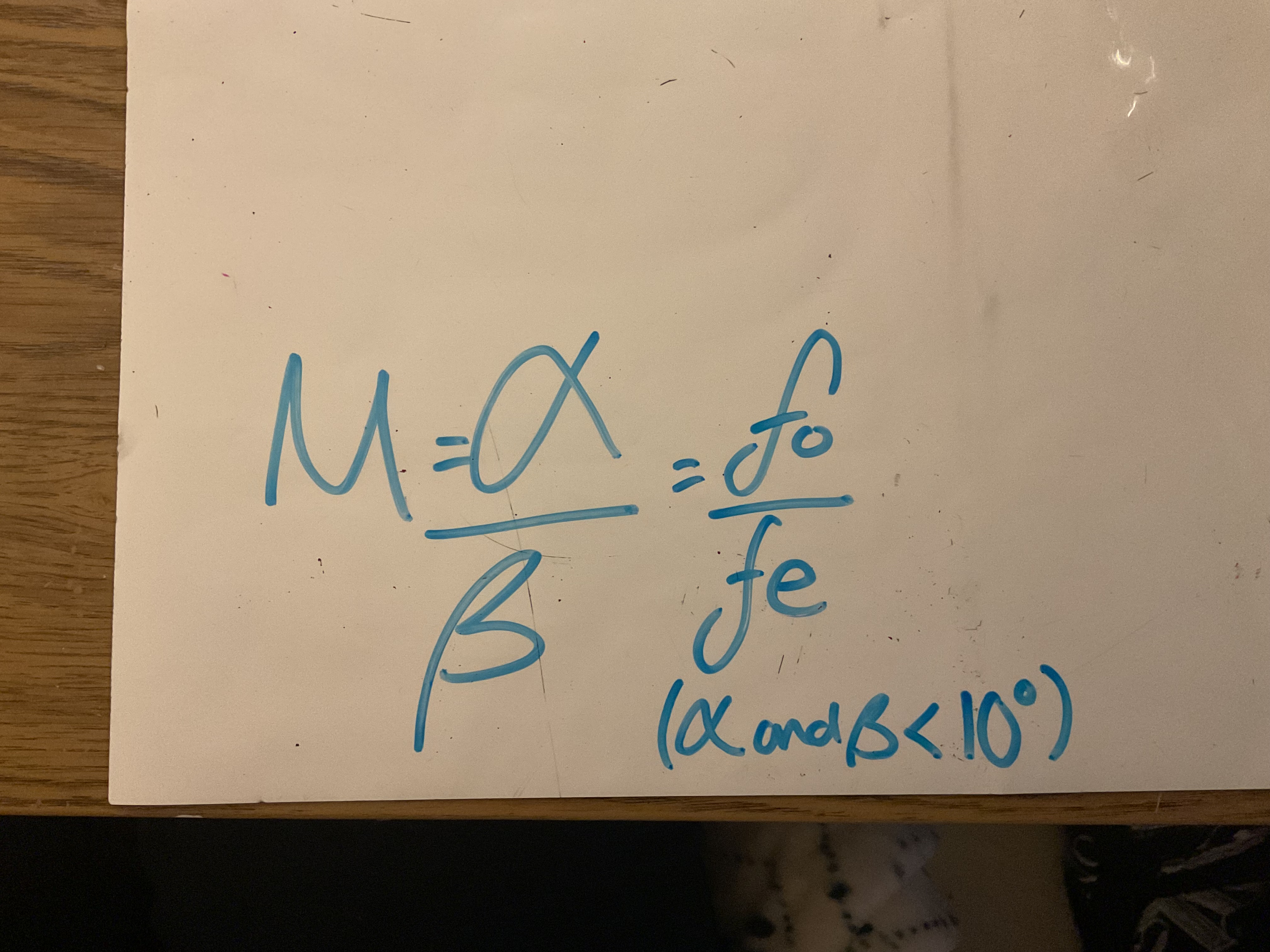
Ray diagram for refracting telescope in normal adjustment
Rays enter parallel, crossover after objective lens at F ,and leave the eyepiece lens parallel for me a virtual image at Infinity
What makes up a reflecting telescope?
Concave mirror with a long focal length and a small secondary mirror in the centre
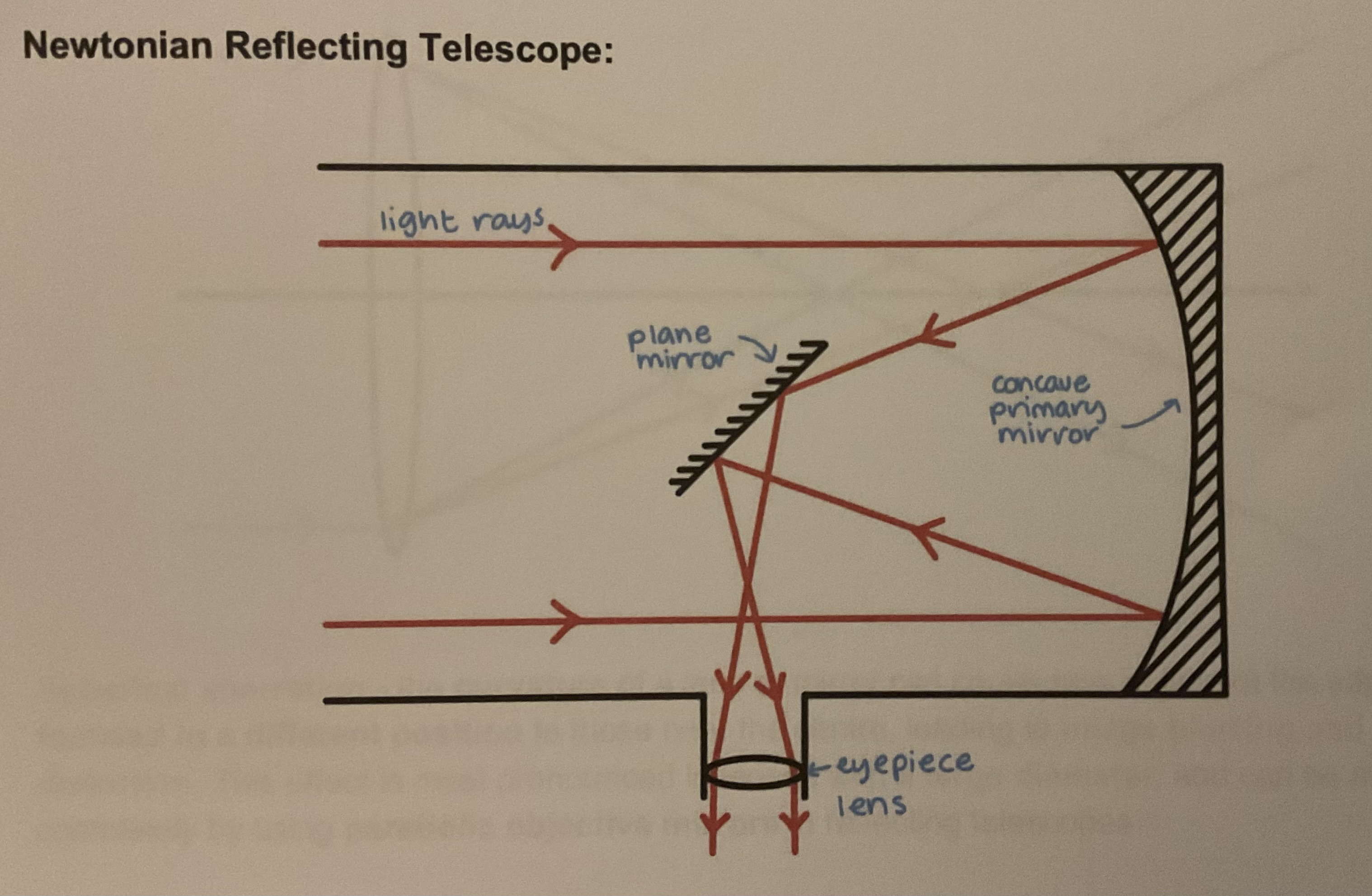
Newtonian reflecting telescope diagram
Light rays enter parallel, refracted by concave primary mirror, reflected by the plane mirror at angle into eyepiece lens
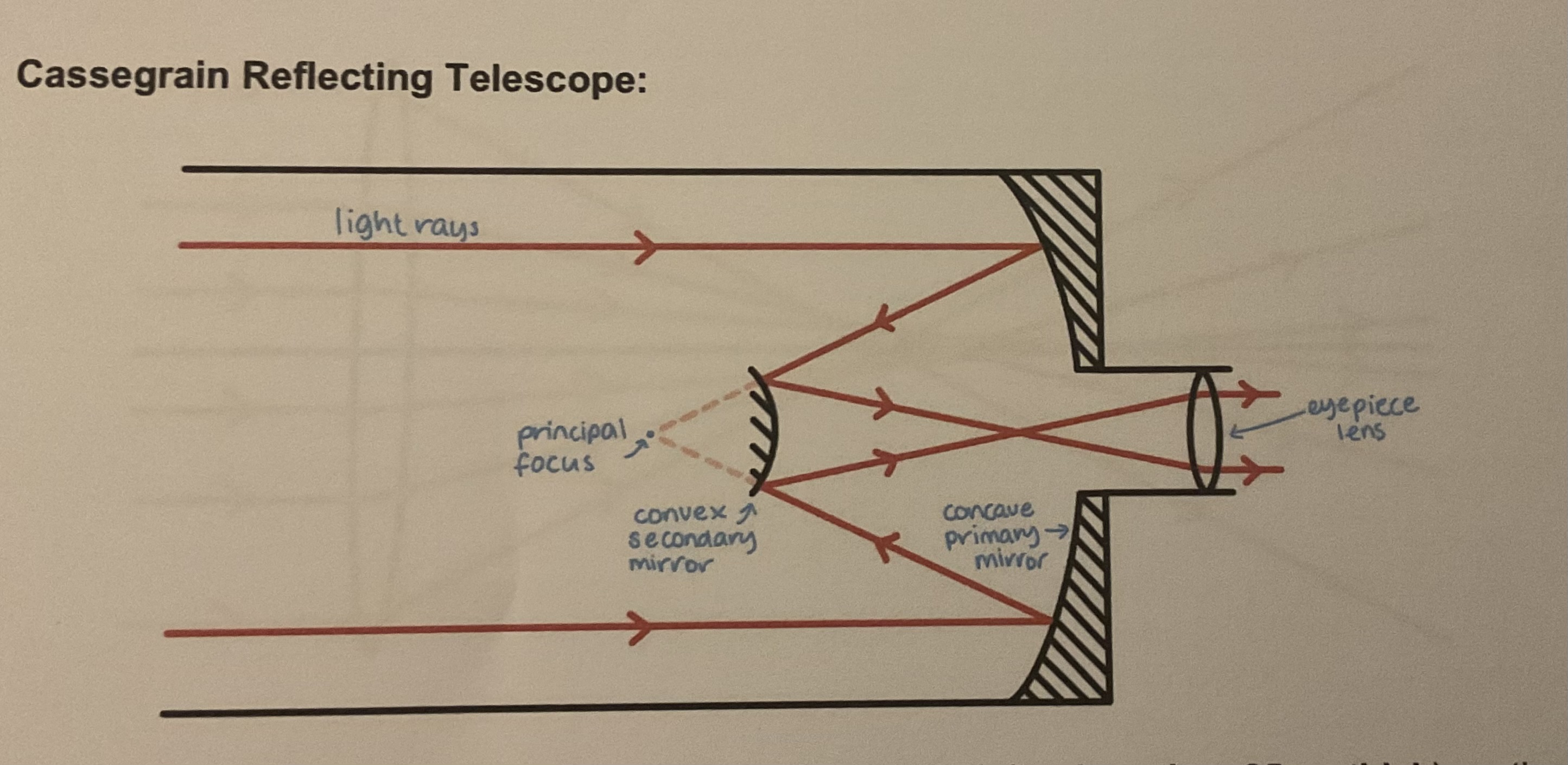
Cassegrain reflecting telescope diagram
Light rays enter parallel refracted by primary concave mirror refracted again by secondary convex mirror and then through eyepiece lens
Why are the mirrors in our reflecting telescope usually very thin? (Less than 25nm thick)
Allows mirrors to be as smooth as possible And minimise distortions of Images. Usually coating of aluminium or silver atoms that are deposited onto a backing material
What is the purpose of the convex mirror in the category reflecting telescope?
Allows the category to be shorter than other configurations such as Newtonian reflecting telescope. The light is collected and focused onto an eyepiece lens
What is chromatic aberration?
For a given lens, the focal length of red light is greater than that of blue light which means they are focused at different points. Since blue is refracted more than red, this can cause white objects to produce an image with coloured fringing with the effect being most noticeable for light passing through the edges of the lens
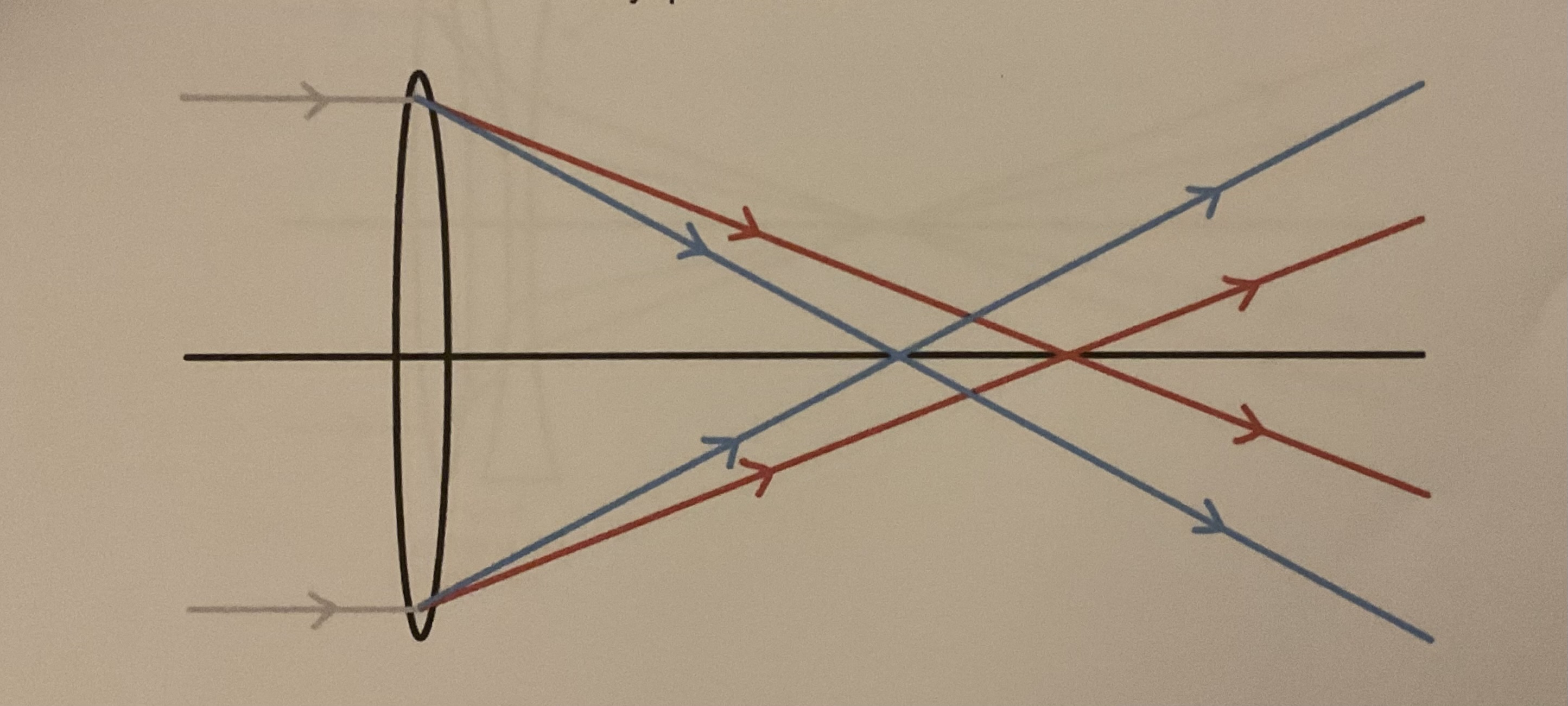
Which telescope has most issues with chromatic aberration?
Refracting telescope since chromatically aberration is caused by refraction. It has very little effect on reflecting telescope as only because It only occurs in the eyepiece lens
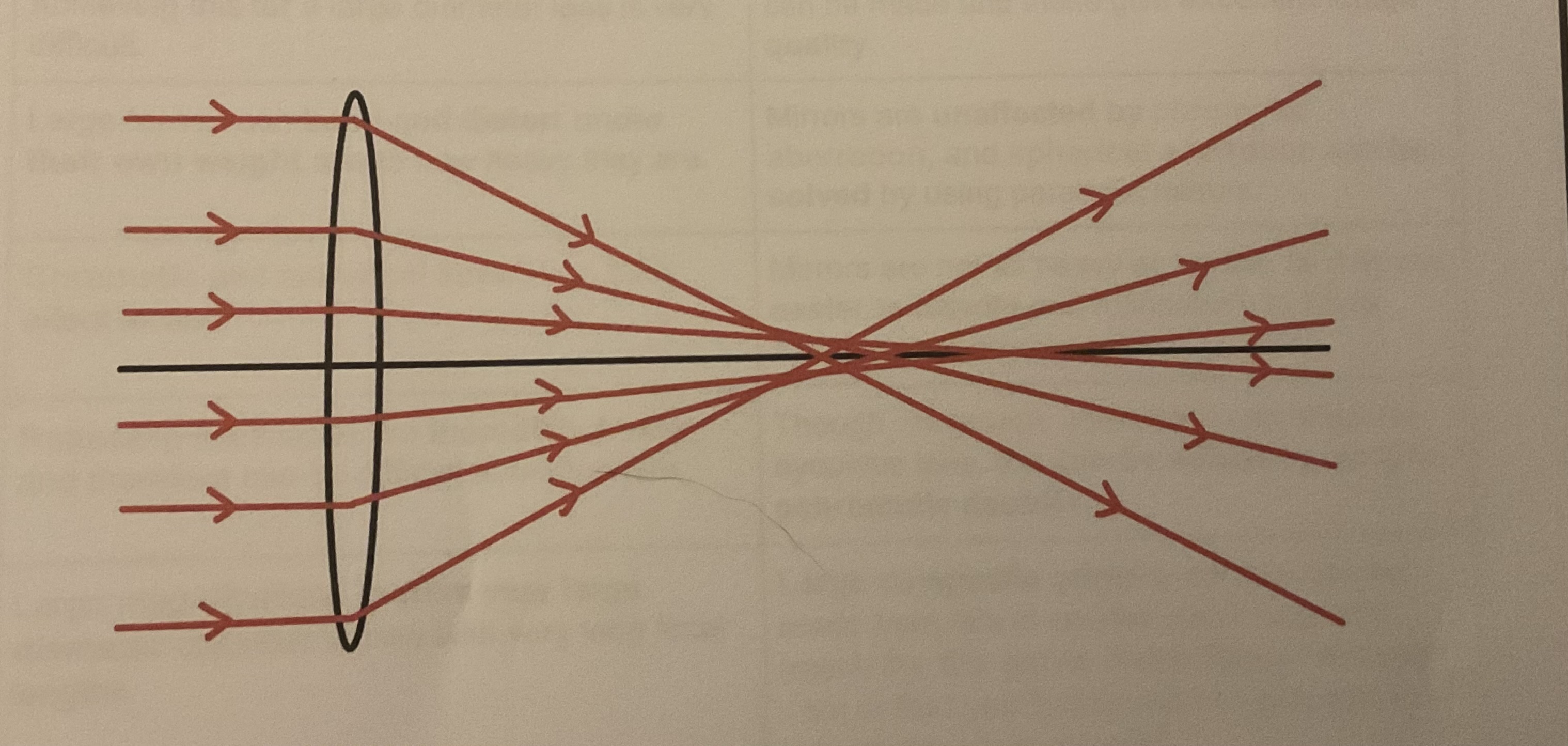
What is spherical aberration?
The curvature of a lens or mirror can cause rays of light at the Edge to be focused in a different position to those near the centre leading to image blurring and distortion. This effect is most pronounced in the lenses with a larger diameter and can be avoided completely by using a parabolic objective mirror in reflecting telescopes
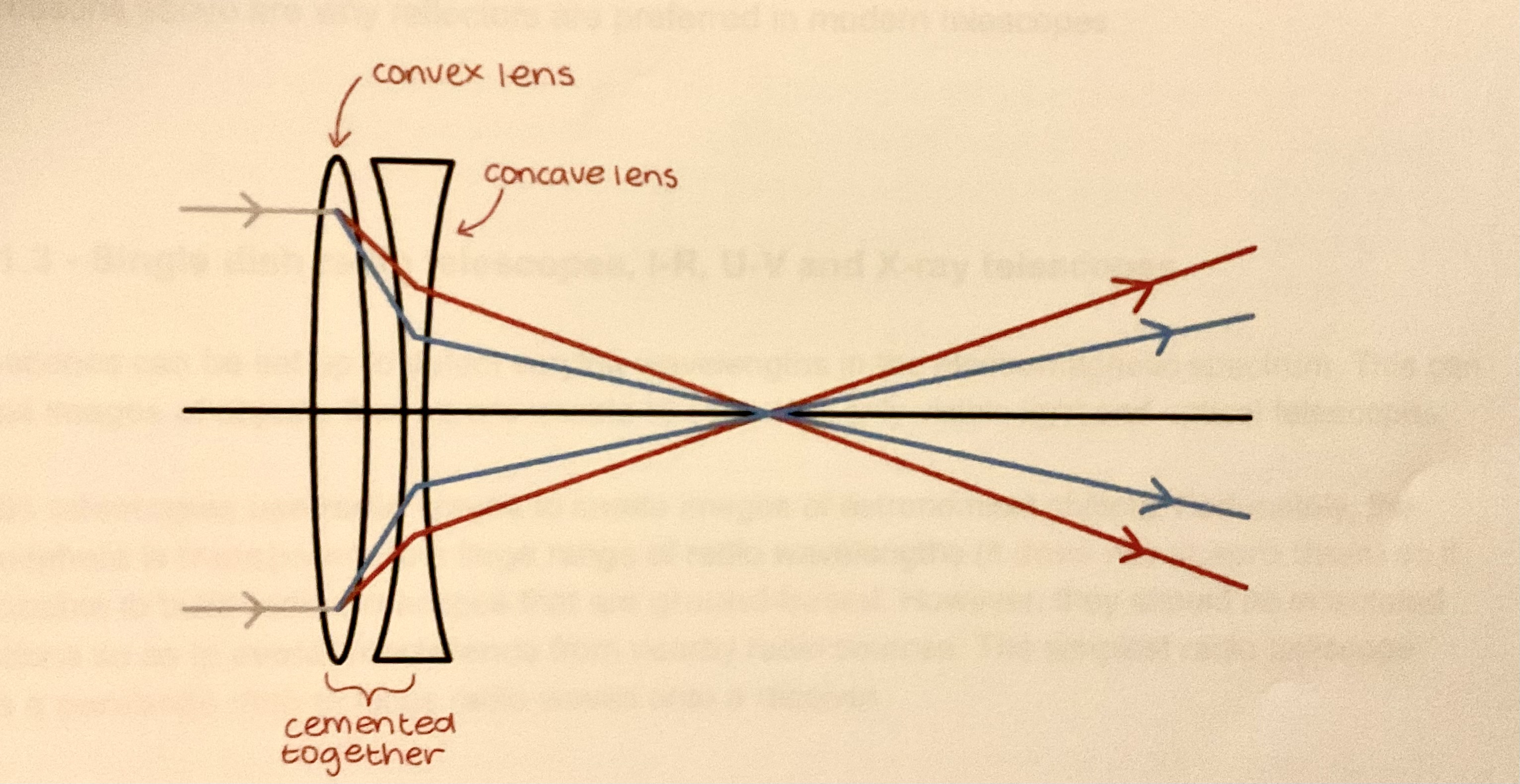
What is an Achromatic doublet?
One way of minimising spherical and chromatic aberration in lenses by using an achromatic doublet. This consists of a convex lens made of a crown glass and a convex lens made of flint cemented together in order to Bring all rays of light into a focus in the same position
Disadvantages of refracting telescopes
Class must be pure and free from defects achieving this for a large diameter lens is very difficult
Large lenses can bend and distort under their own weight Due to how heavy they are
Chromatic spherical aberration both affect lenses
Reflecting telescopes can be incredibly heavy and therefore can be difficult to manoeuvre
Large magnifications require very large diameter objective lens with very long focal lengths
Lenses can only be supported from the edges which can be an issued when they are larger and heavy
Advantages for reflecting telescope
Mirrors that are just a few nanometres that can be made and give excellent image quality
Mirrors are unaffected by chromatic aberration and spherical aberration can be solved using parabolic mirrors
Mirrors are not as heavy as lenses so they are easier to handle a manoeuvre to follow astronomical events
Although chromatic aberration can affect the IP lens this can be solved by using an achromatic doublet
Large composite primary mirrors can be made from lots of small segments much like James Webb space telescope
Large primary mirror is easy to support from behind since you do not need to be able to see through them
Where Should radio telescopes be placed?
On the ground as the atmosphere is transparent to a large range of radio waves so it’s possible to build them on the ground however they should be in isolated locations to avoid interference from nearby radio sources
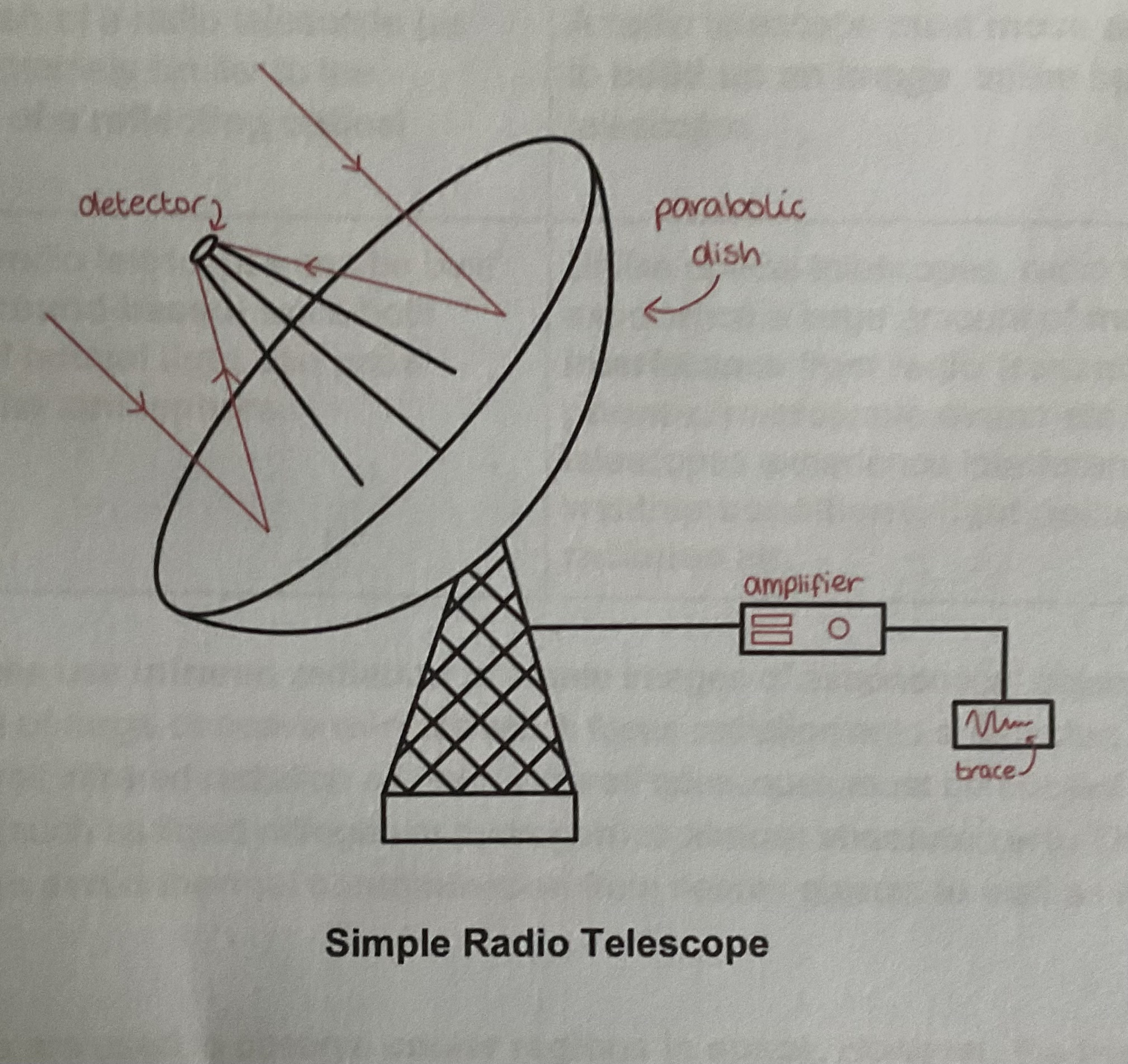
What are the similarities between radio telescopes and optical telescopes?
Both function in the same way by intercepting and focusing incoming radiation To detect its intensity
Both radio and optical telescopes can be moved to focus on a different source of radiation or to track a moving source
The parabolic dish of a radio telescope is extremely similar to the objective mirror of reflecting optical telescope
Both can be built on the ground since radio waves and optical waves can pass easily through the atmosphere
Differences between radiotelescopes and optical telescopes
Since radio wave lengths are much larger than visible wavelengths radio telescopes have to have much larger diameter than optical telescopes in order to achieve the same resolving power as radio waves have a larger objective diameter. They also have a larger collecting power.
Construction of radiotelescopes is cheaper and simpler because why mesh is used instead of a mirror as long as the mesh size is less Then the wavelength over 20 Radio waves will be reflected and not refracted
A radio telescope must move across an area to build up an image, unlike optical telescopes
Unlike optical telescopes radiotelescopes experience a large amount of man-made interference from radio transmissions, phones and microwave ovens et cetera optical telescopes experience inference from weather conditions, light pollution and stray radiation, et cetera
How did infrared telescopes work?
Use infrared radiation to create images of astronomical objects they consist of large concave mirrors which focus radiation onto a detector. However since all objects are infrared radiation as heat infrared telescopes must be called using cryogenic fluids such as liquid nitrogen to almost 0 they must be well she will need to avoid them contamination from nearby objects as well as their own infrared admissions.
Where are infrared telescopes used?
As the atmosphere absorbs most infrared radiation is telescopes must be launched into space and accessed remotely from the ground and are used to observe cooler regions in space
How do ultraviolet telescopes work?
Use ultraviolet radiation to create images of astronomical objects as the ozone layer blocks or ultraviolet rays that have a wavelength of less than 300 nm.
UV telescopes need to be positioned in space the telescopes utilise the cassagrain configuration to bring UV rays to a focus. The rays are then detected by solid state devices Which use the photoelectric effect convert UV photons into electrons which then pass around a circuit they can be used to observe interstellar medium and star formation regions.
How do x-ray telescopes work?
Use x-ray to create images of astronomical objects, since all x-rays are absorbed by the atmosphere the telescopes need to be in space to collect data.
The rays have such high energy that using mirrors would not work as they were just passed right through so the telescopes must be made from a combination of parabolic and hyperbolic mirrors All of which must be extremely smooth
the rays enter the telescope and skim off of the mirrors and are bought into focus on CCD which converts light into electrical pulses
since x-rays are high energy they can be used to observe high energy events and areas of space such as active galaxies is black holes and neutron stars
How do gamma telescopes work?
Use gamma radiation to create images of astronomical objects telescopes do not use mirrors as gamma rays have so much energy. They were just passed straight through and instead use a detect made of layers of pixels as Gamma futons pass through they cause a signal in each pixel they come into contact with these telescopes are used to observe things such as gamma ray bursts (GRBs), quasars, black holes and solar flares
What are the two types of GRB’s?
Short lived - which lasts between 0.01 to 1 second and are thought to be associated with merging neutron stars forming a black hole or a neutron star falling into a black hole
Long lived - which lasts between 10 and 1000 seconds and associated with a Type II supernova, the death of a massive star
What are the advantages of a large diameter telescope?
Collecting power, which is a measure of the ability of a lens or a mirror to collect Incident EM radiation. The collecting power increases with the size of the objective line/mirror it is directly proportional to the area of the lens and collecting power is proportional to the object diameter squared
Resolving power, which is the ability of a telescope to reduce separate images of close together objects. For an image to be resolved an angle between the straight lines from Earth to each object must be at least the minimum angular resolution where the angle is in radians.

What is The Rayleigh Criterion?
States that two objects will not be resolved if any part of the central maximum of either of the images falls within the first minimum diffraction ring over the other this is related to the fact that as light enters the telescope it is diffracted in a target like shape called an airy disk . The central maximum is the bright white circle in the centre and each the dark rings around it and the minimum rings.

What is a charge coupled device?
An array of light sensitive pixels which become charged when they’re exposed to light by the photoelectric effect
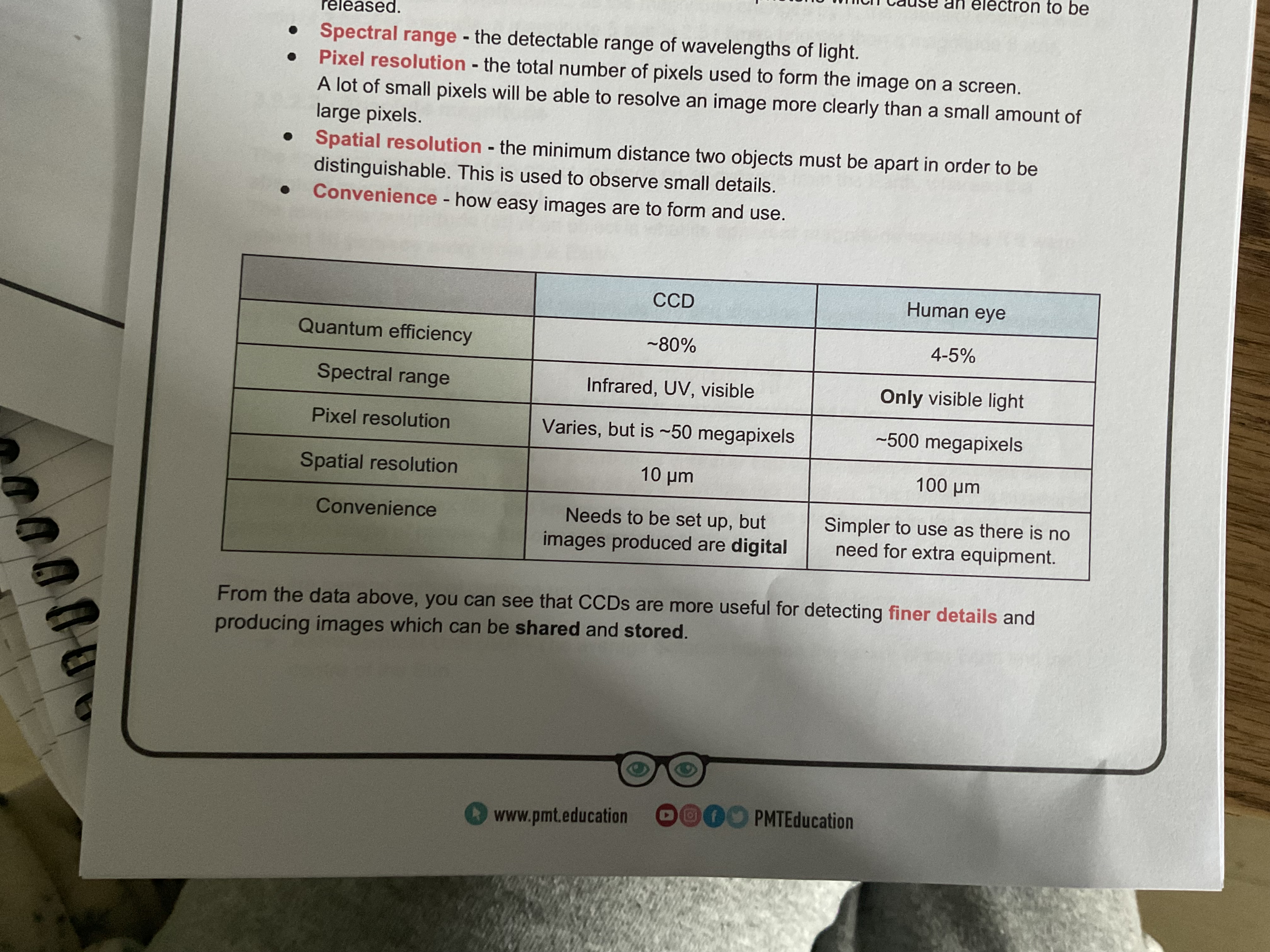
CCD is compared to human eye
Quantum efficiency - the percentage of incident photos which can cause an electron to be released
Spectral range - the detectable range of wavelength of light
Pixel resolution- the total number of pixels used to form the image on the screen. A lot of pixels will be able to resolve an image more clearly than a small amount of large pixels.
Spatial resolution- the minimum distance to objects must be apart in order to be distinguishable. This is used to observe small detail details.
Convenience- how easy images are to form and use
What is luminosity?
The rate of light energy released or power output of a star
What is intensity?
Power received from a star (it’s luminosity) per unit area unit Wm-2
Does the intensity star follow the inverse square law?
Yes
What is the apparent magnitude? (m)
How bright the object appears in the sky, therefore this will Depend on the stars luminosity and the distance from the Earth
How does The Hipparcos scale classify astronomical object objects
Classifies objects by their apparent magnitude with the brightest stars being given a magnitude of one and the faintest visible stars being Given An apparent magnitude of six The intensity of a magnitude one star is 100 times greater than a magnitude six Star
How much greater is the intensity of a magnitude one star compared to a magnitude six?
100
What sort of scale is the hipparcos scale?
Logarithmic as the Mac and cheese changes by one the intensity changes with the ratio of 2.51 for example a magnitude five star is 2.5 times Brighter than a magnitude six
What is absolute magnitude? (M)
The absolute magnitude of an object is what the apparent magnitude will be if it was placed 10 parsecs away from earth
Equation linking Apparent and absolute magnitude
m-M = 5log(d/10)
What day is distance in parsecs?
What is parallax?
The apparent change of position of the nearest star in comparison to distant stars in the background as a result of Earth orbit around the Sun the property is measured by the angle of parallax
What does A greater angle of parallax mean
The star is closer to Earth
What is an astronomical unit? (AU)
The average distance between the centre of Earth and the centre of the sun
1au =149,597,870.7 km = 1.50×10 11
What is a parsec? (pc)
The distance of which the angle of parallax is one arch second or the distance which one are you subtends an angle of one arch second
1pc=3.0857×10¹³ km = 3.26ly
What is an arc second?
1/3600th of a degree
What is a black body radiator?
A perfect meter and absorber of all possible wavelengths of radiation, stars can be approximated as black bodies
What is Stefan’s law?
The power output of a black body radiator is directly proportional to its surface area and it’s absolute temperature^4

What can Stefan’s law be used to do?
Compare the power output, temperature and size of stars
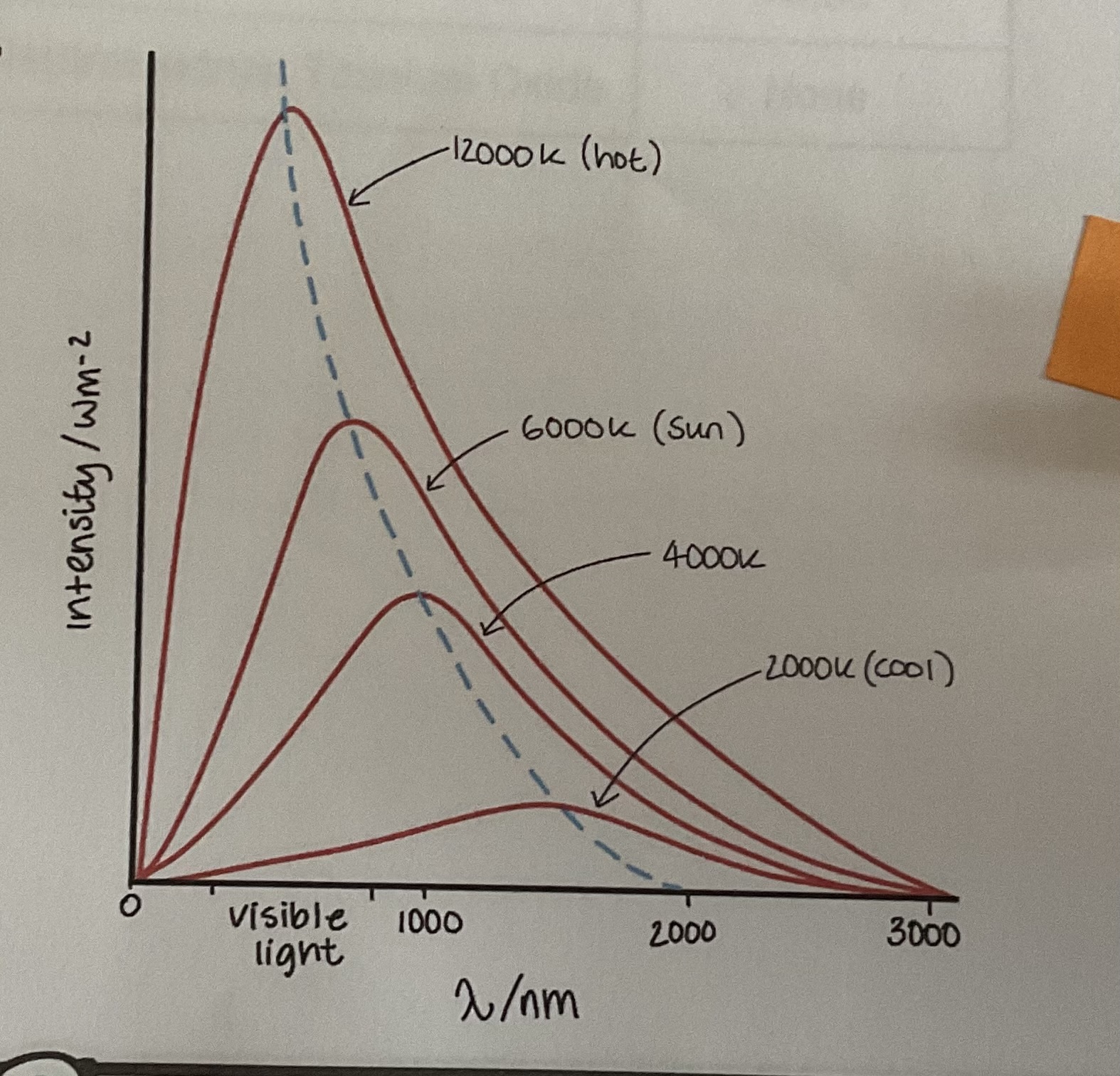
What Is Weins displacement law?
Peak wavelength of emitted radiation is inversely proportional to absolute temperature of the object. The peak wavelength is the wavelength of light released maximum intensity
units metre Kelvin mK
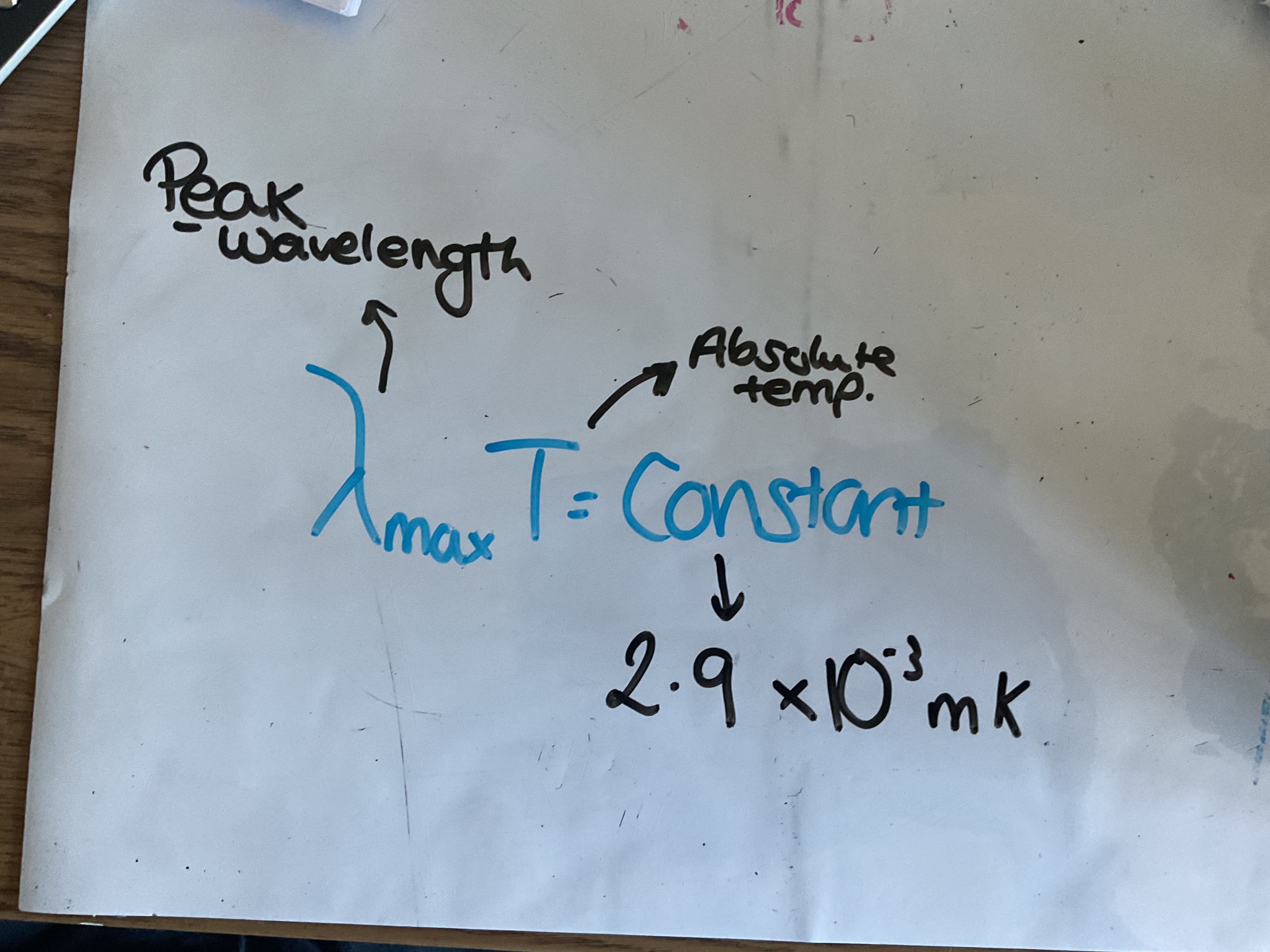
What does Weins law show?
The peak wavelength for the body decreases as it gets hotter meaning the frequency increases so the energy of the wave increases as expected. The localised estimate the temperature of black body sources.
What is the graph for black body curves?
Graph of Intensity against wavelength of radiation omitted for objects of various temperature as the temperature of the body increases peak wavelength decreases
What law does the intensity of light committed by a star follow?
The inverse square law meaning intensity is inversely proportional to the distance between the start and the observer it is assume that light Is admitted in all directions from a point so will spread out in the shape Of a sphere
Equation showing the inverse square law of intensity of a star
I = P/4pid2
Where P is the power output the star and D is distance from star
How are stars classified?
Classified into spectral classes based on the strength of absorption lines Which are dependent on the temperature of the star this is because the energy of particles which make up the start is dependent on the temperature
What are hydrogen balmer lines?
Absorption lines are found in inspector of OB and A type stars they are caused by excitation of hydrogen atoms from any equals 2 to higher or lower energy levels. If the temperature of the star is too high the majority of hydrogen atoms will become excited to a high level than any equals two or electrons might even become ionised so hydrogen bomber lines will not be present. If the temperature of the star is too low hydrogen atoms are unlikely to become excited or may not be present at all so hydrogen balmer lines will not be present
What is the intensity of hydrogen baalmer lines dependent on?
Temperature
Spectral Classification
OBAFGKM
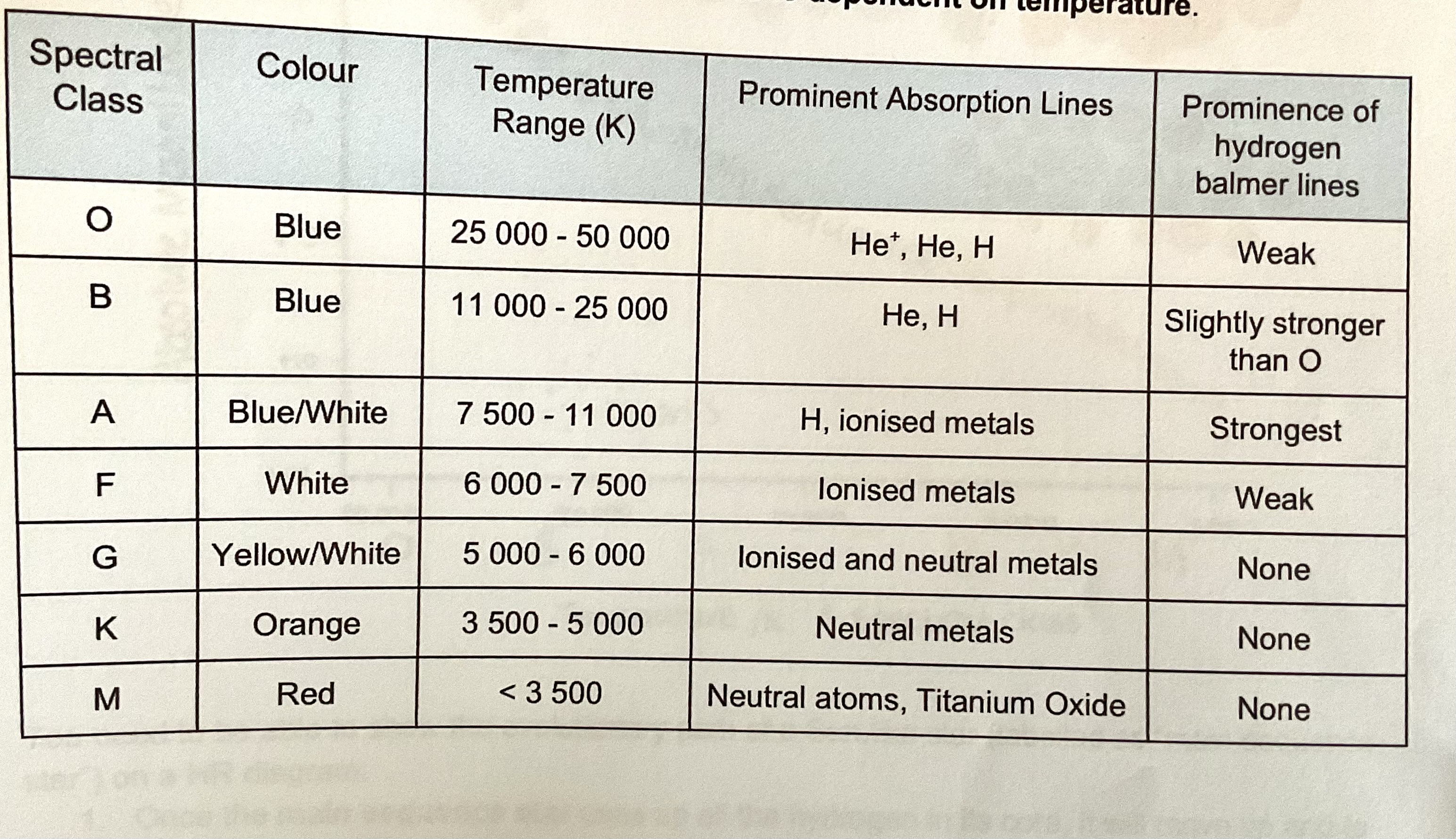
What colour is an O star?
Blue
What colour is a B star?
Blue
What colour is an a star?
Blue/white
What colour is an F star?
White
What colour is a G star?
Yellow/white
What colour is a K star?
Orange
What colour is an M star?
Red
What is a Hertzsprung Russell diagram?
Diagram of temperature against absolute magnitude temperature scale is logarithmic and absolute magnitude goes From positive at the bottom to negative at the top
shows position of different types of stars
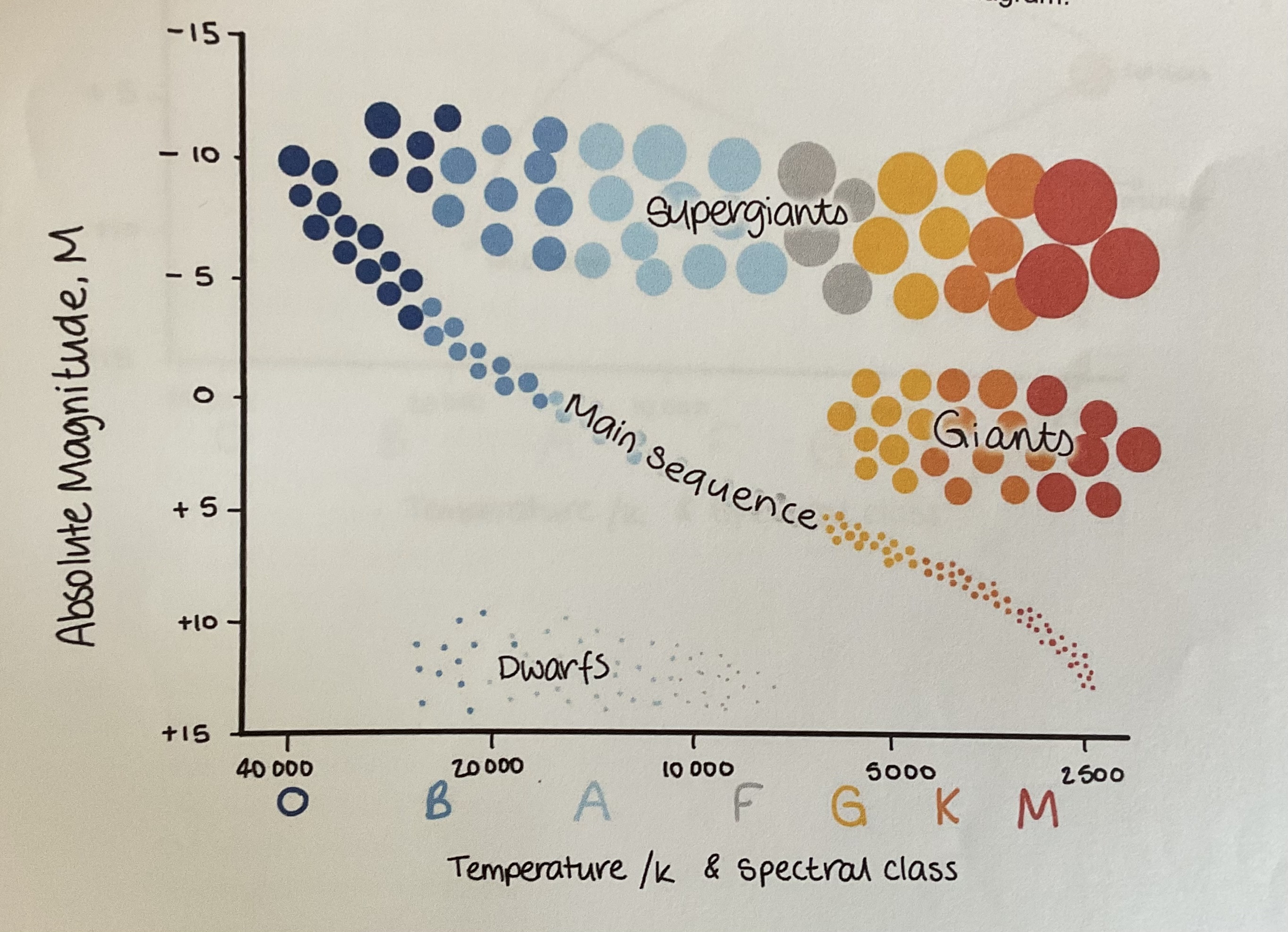
What is the evolutionary path of sun like star on a HR diagram?
Once the main sequence stars use up all the hydrogen in its coat, it will move up to the right on the HR diagram as it becomes a red giant. A red giant is brighter and cooler than main sequence star once the red giant use up all of its helium and it’s cold it will eject its outer layers and will move down on the left on the HR diagram as it becomes a white dwarf. A white dwarf is hotter and dimmer than a main sequence star.
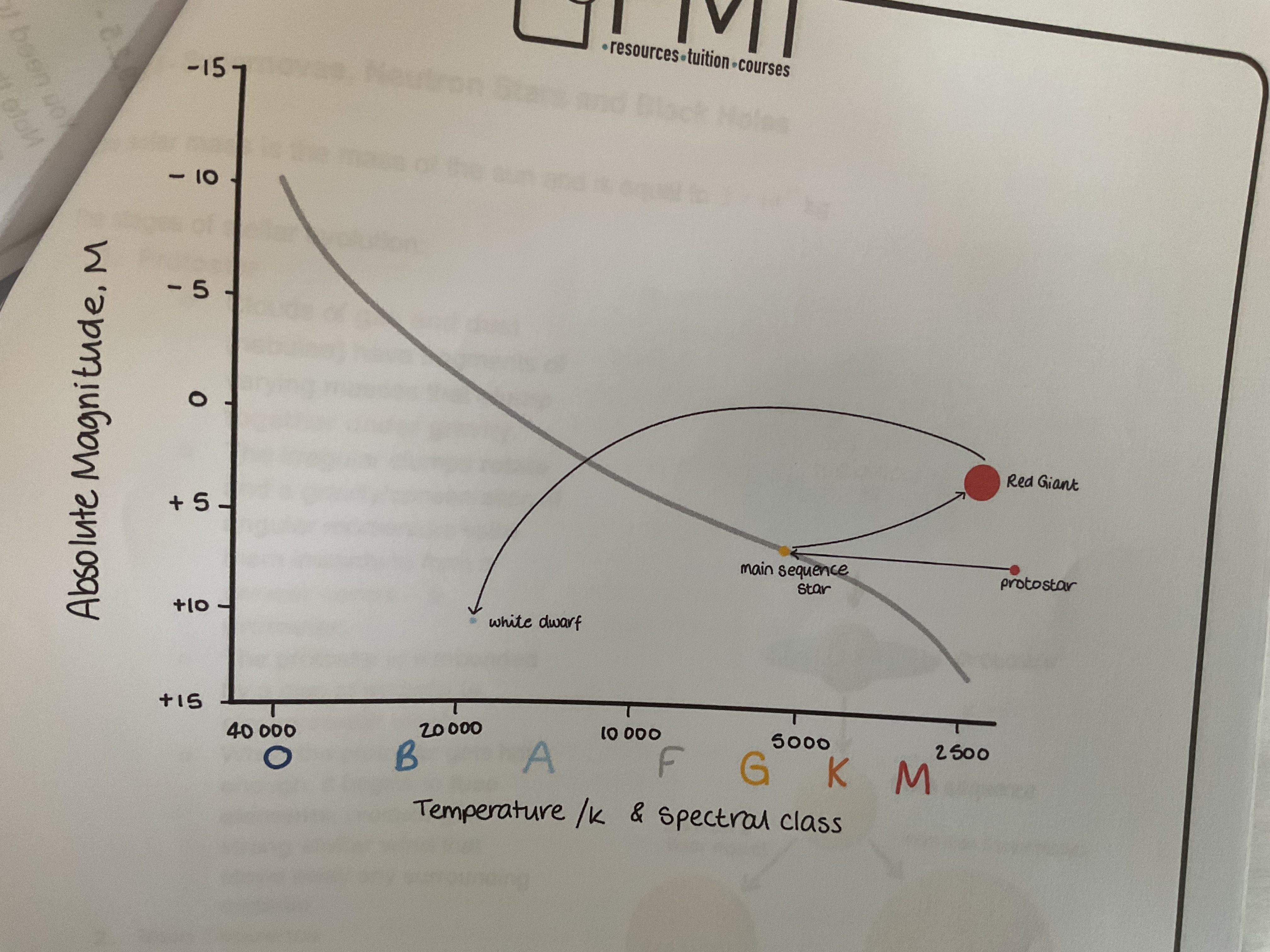
What is one solar mass?
The mass of the sun
Solar mass = 2×10³0 kg
What are the stages of stellar evolution?
Protostar ,main sequence, red giant, white dwarf, red super giant, supernova, neutron star, black hole
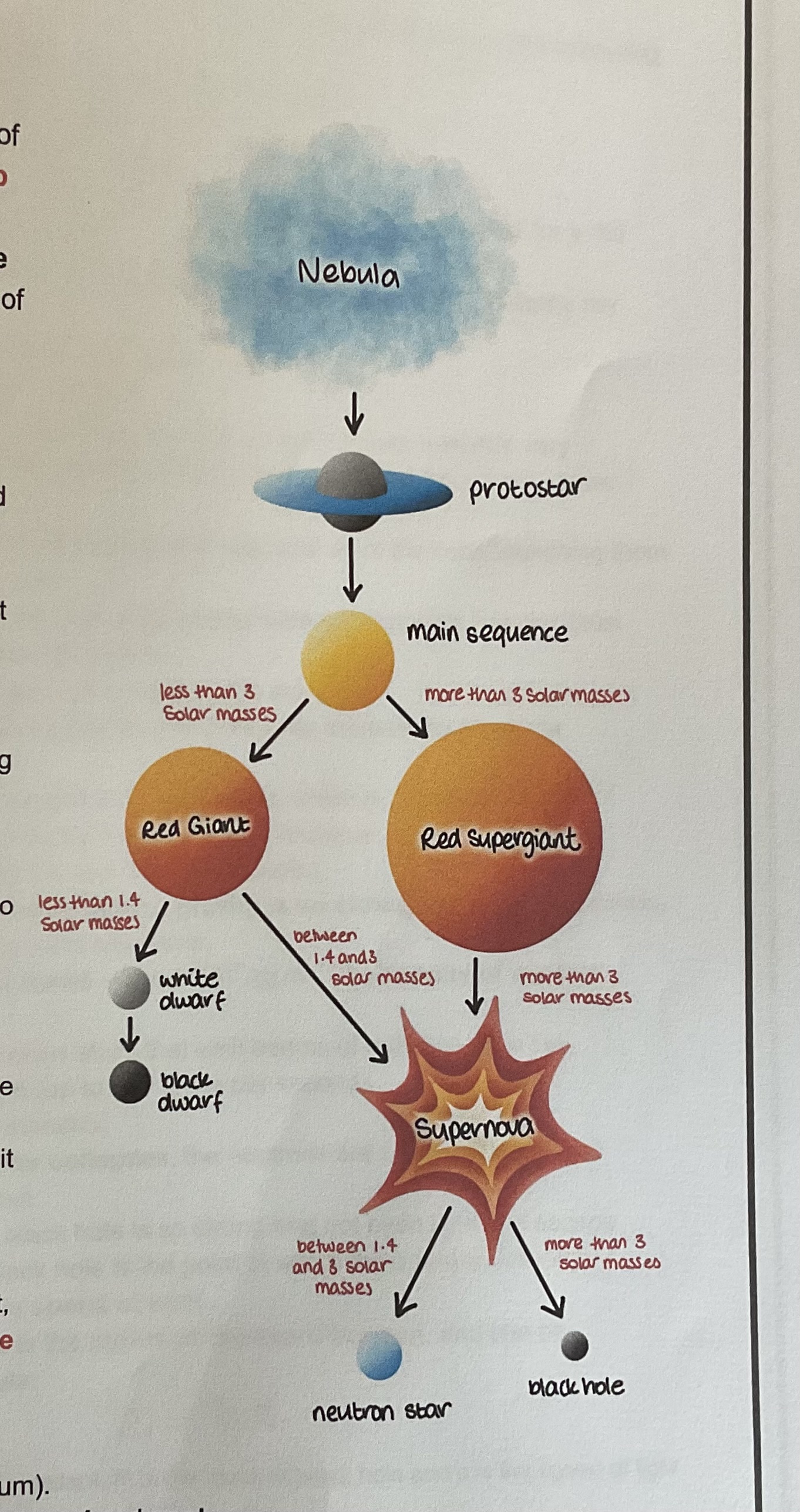
How is the protostar formed?
Clouds of gas and dust have fragments of bearing masses that come together under gravity the irregular clumps rotate and have a gravity/conservation of angular momentum. This spins them in was to form a denser Centre a protostar The protostar is surrounded by a disc of material a circumstellar disc when the pro star gets hot enough it begins to fuse elements producing a strong Stella wind that blows away any surrounding material
How is the main sequence Star formed?
The inward force of gravity in the outward force due to the fusion or an equilibrium a star is therefore stable hydrogen nuclei are used in helium and the greater the mass of the start of the Shorter, it means sequence period is because it uses fuel more quickly
How is the red giant formed? For a star Less than three solar masses
Once the hydrogen runs out the temperature of the core increases and begins fuel, fusing helium nuclei into heavier elements, e.g. carbon oxygen and beryllium the outer layers of the star expand and cool
How is a white dwarf formed for a star less than 1.4 solar masses?
When a red giant has used of all of its fuel fusion stops in the core contracts as gravity is now greater than the outward force. The outer layers are thrown off forming a planetary nebula around the remaining core. The core becomes very dense and a white dwarf eventually called to a black dwarf.
How is a red super giant formed for a star greater than three solar masses?
When a high mass runs out of hydrogen nuclei the same process for a red giant occurs but on a larger scale the collapse of a red super giant in the supernova causes Gammer Ray bursts red super Giants can fuse elements up to iron
How is a supernova formed for a star greater than 1.4 solar masses?
When all fuel runs out fusion stops in the core collapses inwards very suddenly and becomes rigid as somatic can no longer be forced any closer together the outer lay the star fall inward and rebound off the court launching them out in space as a shockwave as the shockwave passes through surrounding material elements heavy than iron refused and flung out into space. The remaining code depends on the mass of the star at finding characteristic of a supernova if it is It’s rapidly increasing absolute magnitude
Supernova release about 10 to the 44 J of energy which is the same amount of energy is the Sun outputs in 10 billion year lifetime.
How are neutron? Stars formed for stars between 1.4 and three stone masses?
When the core of a large star collapses gravity is so strong that forces protons and electrons together to form neutrons and neutron star is incredibly dense. Paul stars are spinning neutron stars that emit beams of radiation from the magnetic poles as they spin up to 600 times per second.
How are black holes formed stars greater than three solar masses?
When the court of a giant star collapses the neutrons are unable to withstand the gravity force in them together the gravitational pull a black hole so strong that not even like escape the event of a black hole is the point which the escape velocity becomes greater than the speed of light the Schwartz child radius is the radius of the event horizon and can be calculated

What Is the event Horizon of a black hole?
The point at which the escape velocity becomes greater than the speed of light
What is a binary system?
A system where two stars orbit a common mass
What are the two types of a supernova?
Type one which is when a star accumulates matter from its companion starting a binary system and explodes after reaching a critical mass
Type two is the death of a high mass star after it runs out of fuel
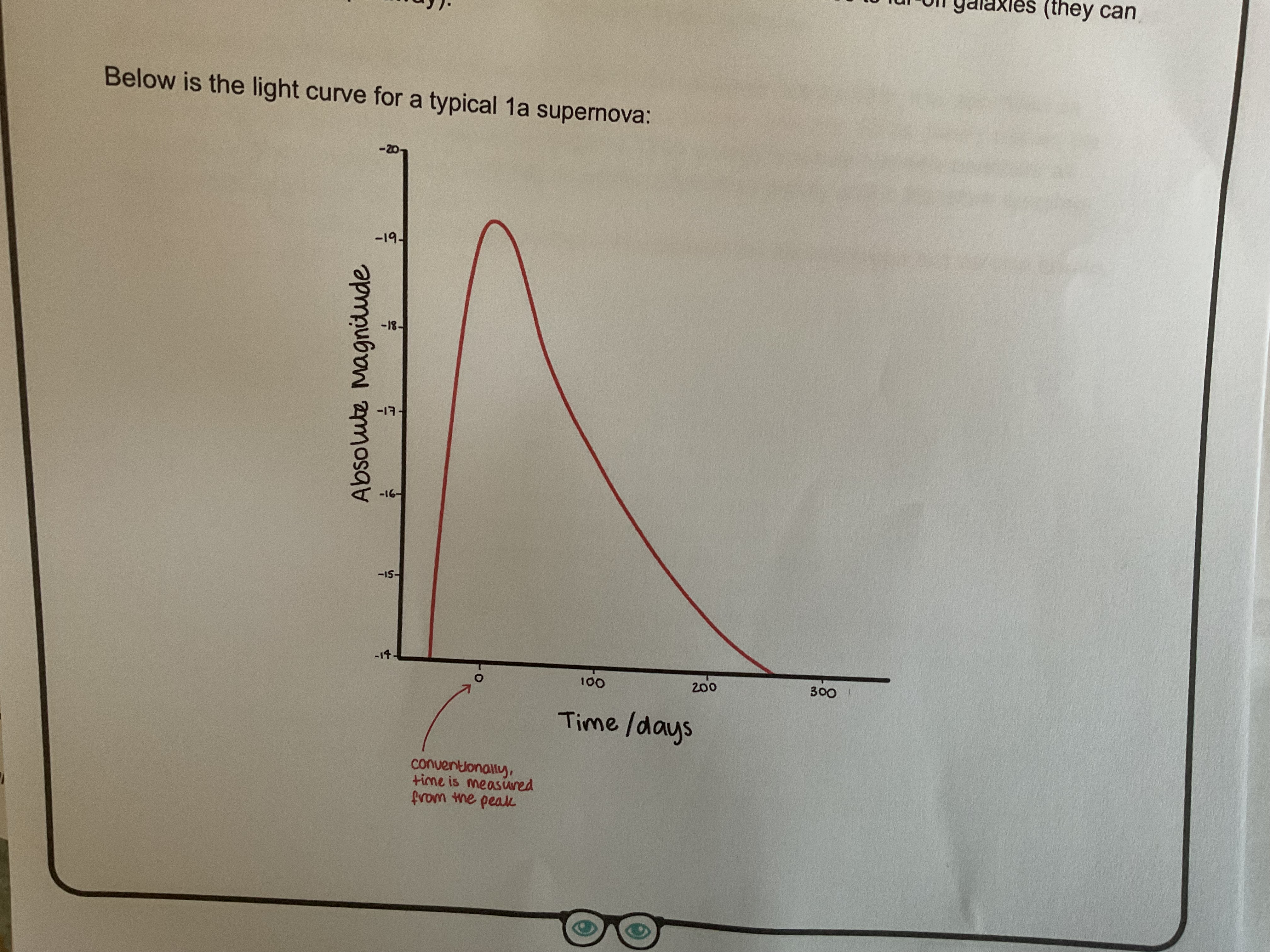
What is the type 1a supernova?
A type one supernova with a white dwarf when the companion start and the binary system runs out of hydrogen expands, allowing the white dwarf to begin accumulating some of its mass when the white dwarf star reached its critical mass fusion begins and becomes unstoppable as the mass continues to increase eventually causing the white dwarf to explode in a supernova
Why can supernovas be used as standard candles?
All types of supernova occur at the same critical mass so have very similar peak. Absolute magnitude and produce very consistent light curves
Can therefore be used to calculate distances of far off galaxies
Why do scientists believe that there are super massive black holes at the centre of every galaxy?
Stars and gas near the centre of galaxies appear to be operating very quickly therefore there must be a super massive object at the centre with a very strong gravitational field attracting them
What can super massive black holes form from?
The collapse of a massive gas cloud when the galaxy was forming
A normal black hole that accumulated huge amounts of matter over millions of years
Several normal black holes merging together
What does Hubble’s law show?
That the universe is expanding
What is the evidence that the universal expanding?
If the expansion of the universe was slowing down more distant objects would be observed to be receiving more quickly since expansion was faster in the past objects would also appear brighter than predicted as they would be closer than expected however type one a supernova have been seen to be dimmer than they’re expected to be meaning they are more distant than Hubble’s law predicted. This suggested the expansion of the universe is accelerating and is actually older than Hubble’s law estimate.
What is thought to be the reason behind the universe accelerating?
Dark energy As it is described as having an overall repulsive effect throughout the whole universe