AP Psychology - Unit 0 - Scientific Foundations of Psychology
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
experimental research
studies that seek clues to cause-effect relationships by manipulating one or more factors (independent variables) while controlling others (holding them constant)
dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
Confounding variable
a factor other than the independent variable that might produce an effect in an experiment
Random assignment
assigning participants to experimental and control conditions by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups
Population (experiment)
the entire set of individuals to which generalizations will be made based on an experimental sample
Sample (experiment)
participants in an experiment (usually people)
Random sampling
a sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
Representative sampling
a sample that accurately reflects the characteristics of the population as a whole
Non-experimental research
research that lacks the manipulation of an independent variable, random assignment of participants to conditions or orders of conditions, or both
Independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
Convenience sample
only members of the population who are easily accessible are selected
Sampling bias
a flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample
Generalizability
the extent to which we can claim our findings inform us about a group larger than the one we studied
Experimental group
In an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.
Control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
Placebo group
A control group of participants who believe they are receiving treatment, but who are only receiving a placebo.
Placebo effect
experimental results caused by expectations alone; any effect on behavior caused by the administration of an inert substance or condition, which the recipient assumes is an active agent.
Single-blind procedure
research design in which participants don't know whether they are in the experimental or control group
Double-blind procedure
an experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant (blind) about whether the research participants have received the treatment or a placebo. Commonly used in drug-evaluation studies.
Experimenter bias
a phenomenon that occurs when a researcher's expectations or preferences about the outcome of a study influence the results obtained
Case study
an observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
Positive correlation
a relationship between two variables in which both variables either increase or decrease together
Negative correlation
the relationship between two variables in which one variable increases as the other variable decreases
Directionality problem
the researchers find a relationship between two variables, but they cannot determine which variable may have caused changes in the other variable
Third variable problem
A problem that occurs when the researcher cannot directly manipulate variables; as a result, the researcher cannot be confident that another, unmeasured variable is not the actual cause of differences in the variables of interest.
Scatterplots
a graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables. The slope of the points suggests the direction of the relationship between the two variables. The amount of scatter suggests the strength of the correlation (little scatter indicates high correlation).
Correlation coefficient
a statistical measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other
Quantitive measures
units of measure expressed in numerical terms
Likert scale
measurement scales in which the respondent specifies a level of agreement or disagreement with statements expressing either a favorable or an unfavorable attitude toward the concept under study
Qualitative Measures
Data not recorded in numerical form
Structural interviews
Clinicians ask standardized questions in the same order each time.
Surveys
Questionnaires and interviews that ask people directly about their experiences, attitudes, or opinions.
Framing
the way an issue is posed
Self report bias
systematic errors that can occur in self-report data because participants are unable or unwilling to answer accurately
Social desirability bias
A tendency to give socially approved answers to questions about oneself.
Meta analysis
a procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies
Naturalistic observation
a descriptive technique of observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
Falsifiability
a feature of a scientific theory, in which it is possible to collect data that will prove the theory wrong
Operational definitions
a carefully worded statement of the exact procedures used in a research study
Replication
repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
Peer review
a review by people with similar professional qualification
Ethical guidelines
suggested rules for acting responsibly and morally when conducting research or in clinical practice
institutional review board
A committee at each institution where research is conducted to review every experiment for ethics and methodology.
Informed consent
an ethical principle that research participants be told enough to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
Informed asset
Participant's agreement to participate in the absence of full understanding
Commonly applies to individuals who have not attained legal majority and/or capacity
Protection from harm
During a research study, participants should not experience negative physical or psychological effects, such as physical injury, lowered self-esteem, or embarrassment
Confidentiality of participants
The legal and ethical obligation to protect privacy and identity of research participants
Minimal deception
Sometimes it is necessary to conduct research without participants knowing the true purpose of the study.
Confederates
a person who is secretly working with the researcher, pretending to be a regular participant in the study, but is actually instructed to behave in a specific way to manipulate the situation and observe how real participants react to it
Debriefing
the post-experimental explanation of a study, including its purpose and any deceptions, to its participants
Central tendency
Mean, median, mode
Mean
the arithmetic average of a distribution, obtained by adding the scores and then dividing by the number of scores
Median
the middle score in a distribution; half the scores are above it and half are below it
Mode
the most frequently occurring score(s) in a distribution
Measure of variation
A measure used to describe the distribution of data
Range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
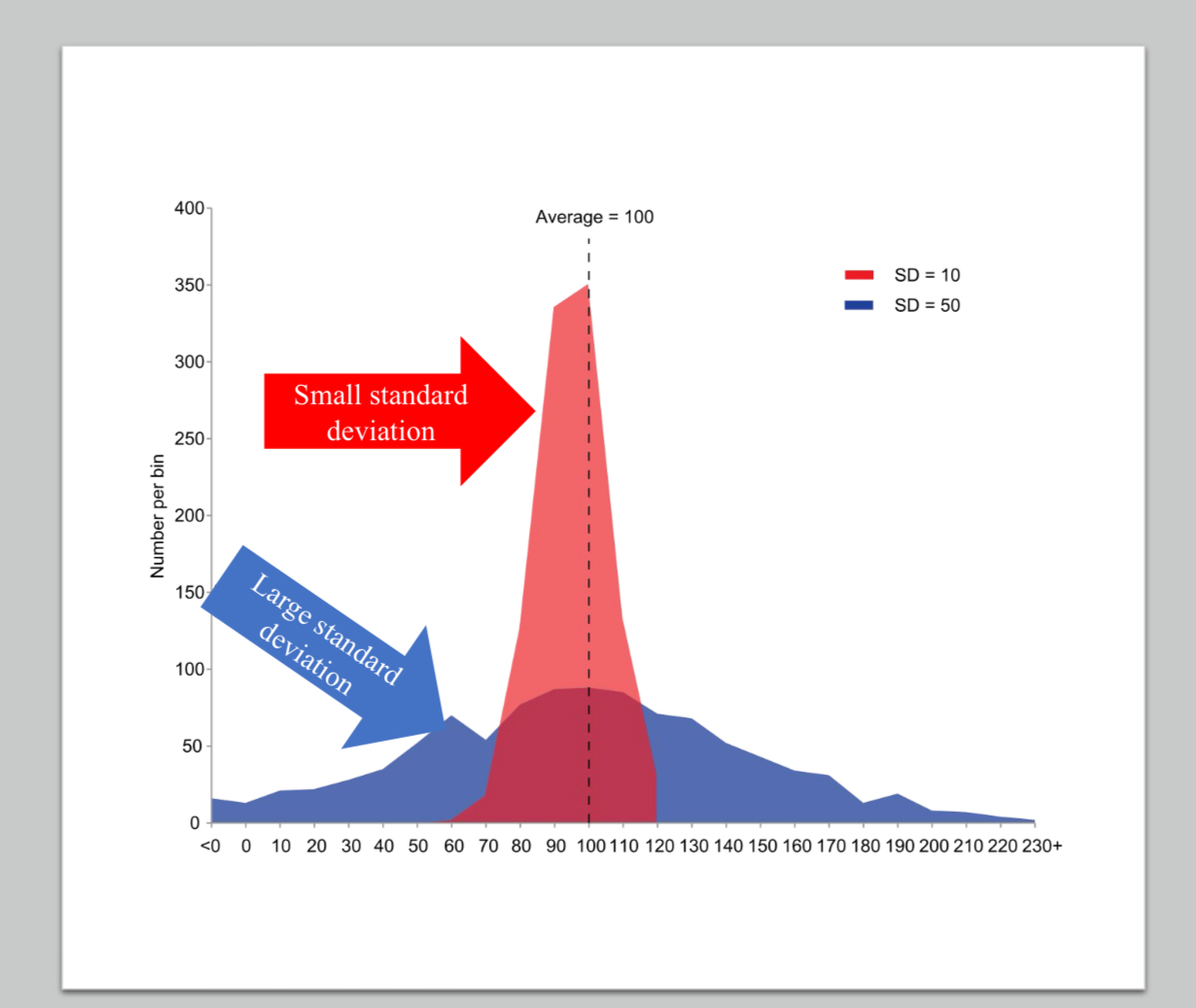
Standard deviation
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
Normal curve
A symmetrical, bell-shape that describes the distribution of many types of data; most scores fall near the mean and fewer and fewer near the extremes.
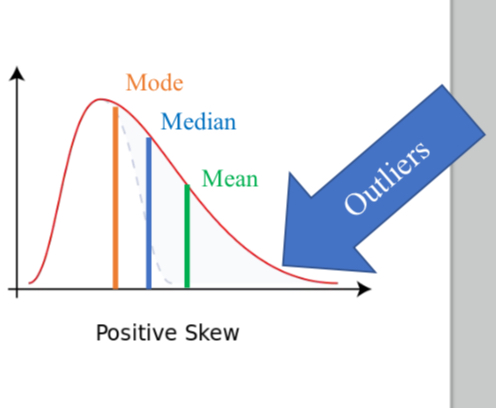
Positive skew
Higher outlier
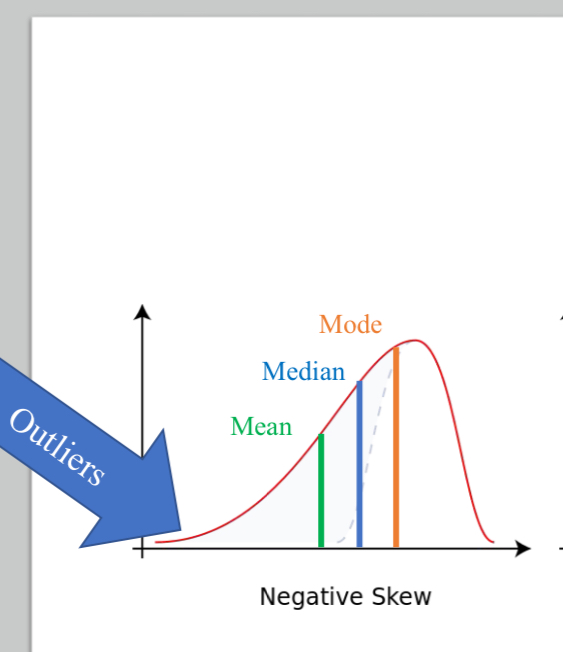
Negative skew
A curve or distribution of scores that has extreme scores below the mean that are atypical of the majority of scores.
Bimodal distributions
a set of scores with two peaks or modes around which values tend to cluster, such that the frequencies at first increase and then decrease around each peak (e.g., when graphing the heights of a sample of adolescents, one would obtain a bimodal distribution if most people were either 5'7" or 5'9" tall)
Regression towards the mean
the tendency for extreme or unusual scores to fall back (regress) toward their average.
Statistical significance
The condition that exists when the probability that the observed findings are due to chance is very low.
Effect sizes
Quantitative measure of the strength of a phenomenon.
Confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
Hindsight bias
the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it
Overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct—to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments.
Cognitive biases
Systematic patterns of deviation in judgment.